Blue Mountains tap water not worth drinking
Thursday, August 1st, 2013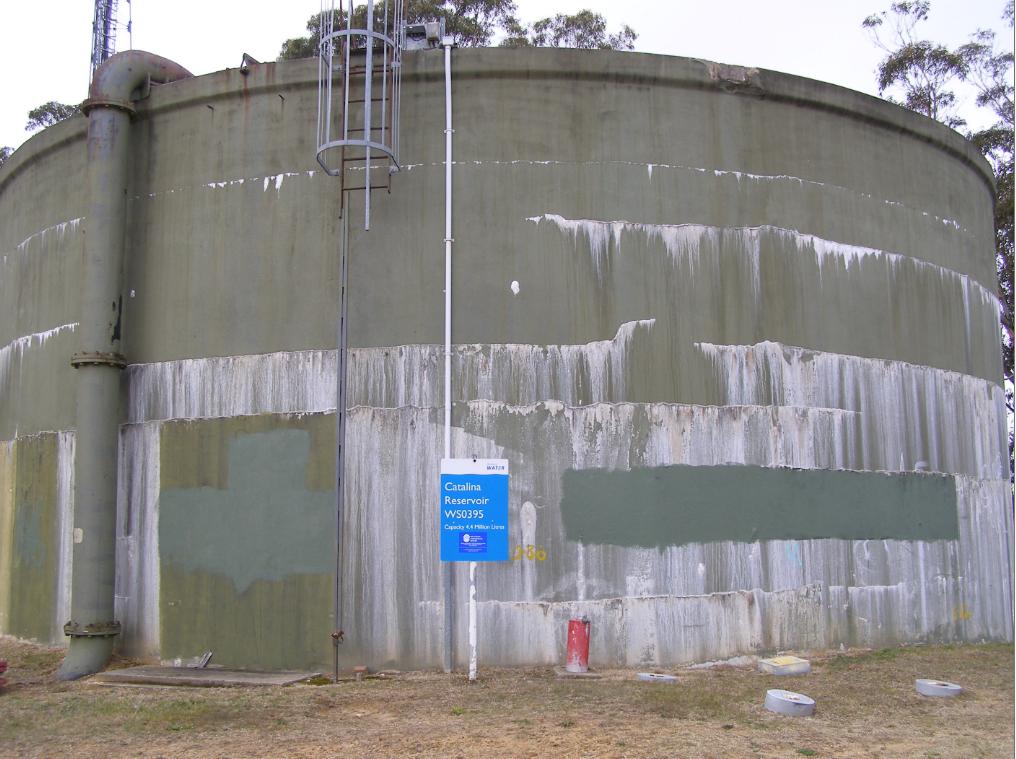 Blue Mountains drinking water tank with chlorine salt stains
Blue Mountains drinking water tank with chlorine salt stainsMineral salt efflorescence Narrow Neck Road, Katoomba [Photo by Editor, 20130507, Photo © under ^Creative Commons]
.
Rainwater, streams, surface water, ground water, aquifers and Australia’s Great Artesian Basin are all interconnected hydrology across Eastern Australia.
In the Blue Mountains plateau country, west of Sydney, sandstone-ironstone geology creates a subterrainean barrier to rainwater absorption and so the ground water slowly flows horizontally over longer periods. This sustains upland swamps and wetland ecosystems.
Human built settlement across the central Blue Mountains ridgeland since the 1820s introduced sewage contamination into the downstream watercourses, gullies and gorge country below. The raw sewage drainage piping into the valleys below the townships has recently been diverted expensively to contained closed system sewage infrastructure. But urban runoff and dodgy stormwater overflows into legacy sewage mains cause ongoing leakages into the water catchments of the Blue Mountains.
Savvy local bushwalkers know not to drink the water from watercourses downstream of Blackheath, Springwood, Katoomba and other such townships.
Prudent government authority, Sydney Water, disinfects its drinking water reservoirs in the Blue Mountains, to be safe.
But some of the Blue Mountains water that falls as rain in a largely wilderness region, is captured as drinking water in a few reservoirs, then pumped by larged pipes up to large water tanks above the Blue Mountains townships to enable gravity to deliver pressurised water to thousands of homes.
.
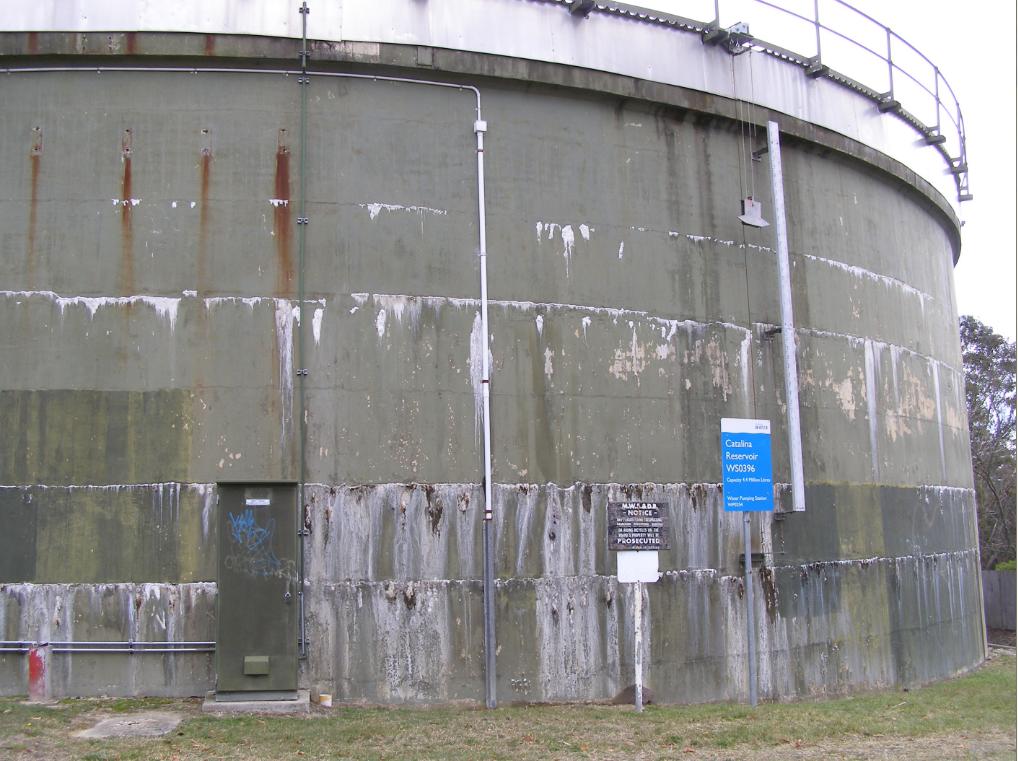 Second Blue Mountains drinking water tank with chlorine salt stains
Second Blue Mountains drinking water tank with chlorine salt stainsNarrow Neck Road, Katoomba [Photo by Editor, 20130507, Photo © under ^Creative Commons]
.
Ed: Are we to now expect fresh green paint over the chlorine salt efflorescent tanks to hide the problem?
.
.
Chloramine Tap Water
.
Across New South Wales, Sydney Water routinely disinfects drinking water in its reservoirs to control the risk of prevalent and toxic E. coli, Cryptosporidium and Giardia bacteria contamination.
Sydney Water applies a derivative of chlorine known as chloramine in its reservoirs – a disinfectant formed by mixing chlorine with ammonia. This is less toxic than the hypochlorous acid typically applied to swimming pools. Given the history in the Blue Mountains of sewage and runoff downstream from upstream townships, Sydney Water ups the dosage of chloramine, to be sure.
Chloramine is a less effective disinfectant than the hypochlorous acid, but it is longer lasting and stays in the water system as it moves through the pipes that transport it to consumers (a process that can take three or four days). For this reason, chloramine is often used alongside chlorine as a “secondary” disinfectant designed to remain in drinking water longer. But what are the long term impacts of drinking Chloramine contained in drinking water. What long term scientific studies have been done and publicly reported?
Chlorine by itself is a very dangerous material. Liquid chlorine burns the skin and gaseous chlorine irritates the mucus membranes. Concentrations of the gas as low as 3.5 parts per million can be detected by smell while concentrations of 1000 parts per million can be fatal after a few deep breaths.
In the Blue Mountains, the tap water is decidedly hardened in taste by the chlorine additive. So should tap water in the Blue Mountains be drunk safely?
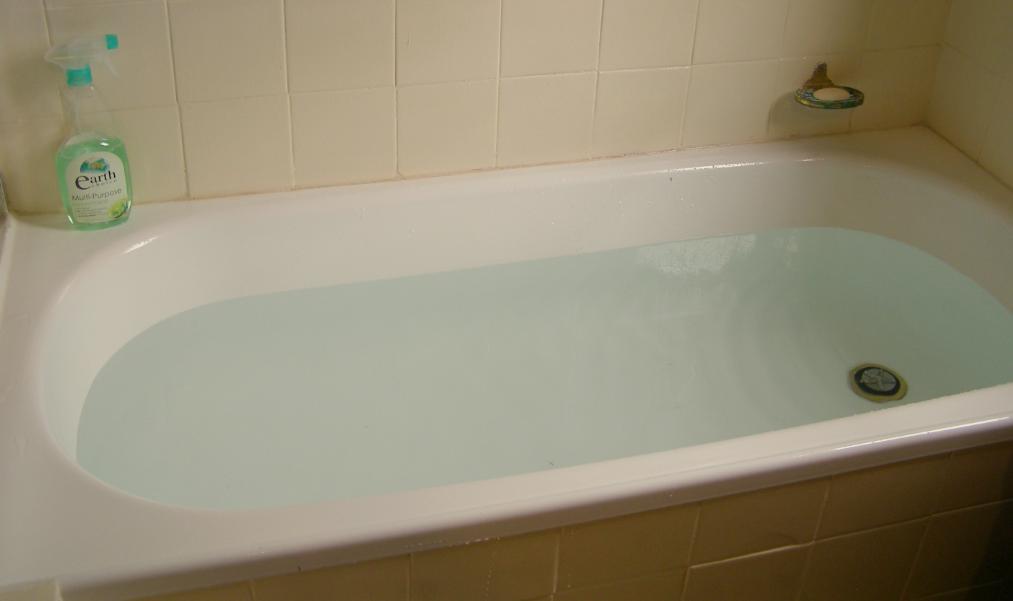 Blue Mountains bath with a distinctive chlorine aqua tinge
[Photo by Editor, 20130502, Photo © under ^Creative Commons]
Blue Mountains bath with a distinctive chlorine aqua tinge
[Photo by Editor, 20130502, Photo © under ^Creative Commons]
So is the Blue Mountains tap water safe to drink?