June 26th, 2011 .
Australia’s marine wildlife habitat continues to be decimated by commercial and recreational fishing, urban sewage and runoff, and pollution-caused global warming driving up sea temperatures.
Compounding these threats, new threats have emerged from two recent human sources:
.
-
The ‘Native Pet Trade’
-
‘Upmarket Restaurants’
.
.
.
.
.
Threats from the ‘Native Pet Trade’
.
The Native Pet Trade in Australia is on the rise.
The more discerning pet owner, not content with a garden variety dog or cat, are seeking more ‘exotic’ pets. Reptiles andf unusual marine life have become fashionable.
Then there is the increasing number of apartment dwellers without room for a dog or cat, who are now seeking ‘pocket pets’. Pocket pets are smaller and include animals such as rats, mice and guinea pigs and native and exotic wildlife species: birds, reptiles, fish, crabs, amphibians and invertebrates. Sydney in particular has an increasingly dense urban population and with the increasing housing density and apartment living, the popularity of smaller animals as pets is on the rise. The misconception by many seeking small wildlife species as pets is that these species are less needy and easier to care for than dogs and cats.
But the issue is not the interests of the ‘pet’ owner; the issue is the problem of wildlife poaching and inadequate government enforcement. Irrespective of the motivation, poaching is poaching; albeit for commercial gain, for deviant gratification from killing animals, or perverted ‘pet’ ownership.
Not content with the ordinary garden variety gold fish, discerning private aquarium owners seeking to keep up with the latest trends are seeking out rarer and more unusual marine species to make their showcase fish tank just that little more special and different. It’s a kind a fish tank fashion, it f that’s your thing. Perceived better that exotic fish, what better way to impress guests that having a real seahorse in your tank? No thought is given to the fact that these are generally poached from the wild. No thought is given to about their dwindling numbers or impacts on the ecosystems from which they are poached.
One of the latest aquarium fashion statements particular to Sydney seems to be Weedy Sea Dragons, an Australian native reptile, along with other Australian marine fauna. People are simply poaching marine life for their own personal gain.
To the casual observer, what may pass for innocuous weekend pastime of recreational beachcombing, has become wildlife poaching. Recent years have seen a trend of groups of people scouring coastal rock platforms not for chance inanimate objects washed ashore, but specifically taking Australian marine life. This is poaching is not beach-combing.
Yet governments around Australia are reneging on their custodial duty to protect Australia’s precious marine life.
.
Case in Point: ‘Long Reef Aquatic Reserve’
.

Long Reef Aquatic Reserve is a large rock platform situated on Sydney’s northern beaches area at Collaroy and extends from Collaroy rock baths south to the Long Reef Surf Life Saving Club. It contains a rich diversity and abundance of marine invertebrates rarely seen anywhere and for this reason and due to risks of wildlife poaching, in 1980 it was declared a protected aquatic reserve under the Fisheries Management Act 1994, primarily to protect marine invertebrates found on the rock platforms, and to protect subtidal marine plants and animals.
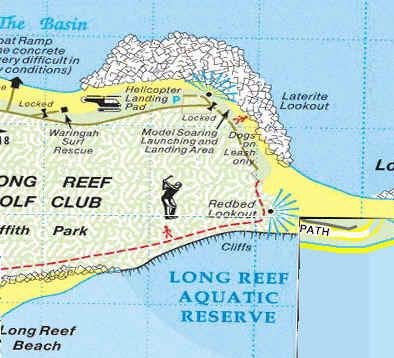
Long Reef is one of twelve aquatic reserves across New South Wales (Australia) established to protect biodiversity and provide representative samples of our wonderfully varied marine life and habitats. Only fin fishing is permitted. No marine plants or animals can be harmed. This includes the collection of empty shells and dead plants or animals because they provide important habitat or food for living invertebrates. The penalties for breaking the rules are quite severe. NSW Fisheries legislation provides for fines up to $110,000 and on-the-spot fines also apply. All fishing or diving gear may also be forfeited.
[Source: NSW Fisheries Sydney North, http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/nationalparks/parkHome.aspx?id=a0004]
.
.
.
Weedy Sea Dragon
One of the protected species of Long Reef is the ‘Weedy Seadragon‘ (Phyllopteryx taeniolatus), a marine fish related to the seahorse that grows up to 45cm in length. It is found only found in shallow coastal waters of southern Australian from Geraldton WA, to Port Stephens NSW and down around Tasmania. It is the only member of the genus Phyllopteryx. Weedy Seadragons are named for the weed-like projections on their bodies that camouflage them as they move among the seaweed beds where they are usually found.
Due to their unusual appearance, they have become the target marine poaching by private aquarium owners and those in the native pet trade seeking to profiteer.
 Weedy Seadragon‘ (Phyllopteryx taeniolatus)
Weedy Seadragon‘ (Phyllopteryx taeniolatus)
.
There is much concern for the future of the Weedy Seadragon and others in their family. They are threatened by habitat destruction, and potentially by the aquarium trade. Currently seadragons are protected under fisheries legislation federally and in most states where they occur, it is illegal to take or export them without a permit. [Source: http://www.abyss.com.au/scuba/pc/Weedy-Seadragon-p4291.htm]
Continual wildlife pillaging on Long Reef is causing reduction in the numbers and diversity of marine life including the weedy sea dragon. Despite the prospect of a $3300 fine or six months’ imprisonment, few offenders have been caught by authorities, because government monitoring by fisheries inspectors is woefully inadequate. The last arrest was in September 2009, when Manly police caught two teenagers with water dragons stuffed into their backpacks. The teenagers, who were from the western suburbs, told police they wanted to take the lizards home as pets. The poaching is also driven by the black market for native pets.
 Water Dragon (Physignathus lesueurii)
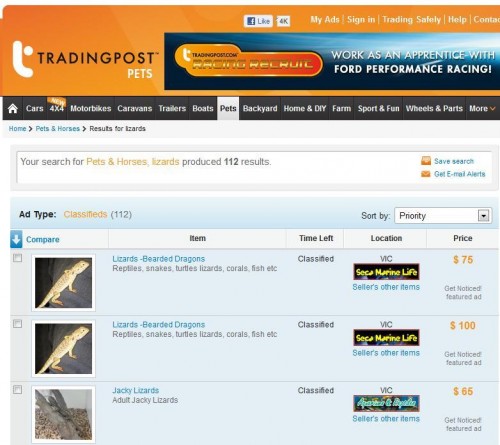
One doesn’t have to look far to find Water Dragons for sale on the Internet. They seem to go for $65 – $100.
Water Dragon (Physignathus lesueurii)
One doesn’t have to look far to find Water Dragons for sale on the Internet. They seem to go for $65 – $100.
.
‘Lizards For Sale’
www.tradingpost.com.au/Pets
.
‘Red Phase Bearded Dragons’
www.ultimatereptiles.com.au/…/dragons/dragongallery.html
.
‘Reptiles For Sale – petpages.com.au’
www.exotic-pets.co.uk/lizards-for-sale.html
.
‘Australia Reptiles / Amphibians for Sale, Adoption, Buy, Sell …’
www.adpost.com
.
‘Chinese Water Dragons Classifieds’
Water Dragons For Sale, $24.99 Each Plus $39.95 Overnight Shipping! … 60 Gallon Lizard Tank. 60 gallon 50inchesx13inchesx23inches including stand,screen …
www.hoobly.com/0/2619/0/
.
‘The Pet Directory: World’s largest online pet directory of …’
Specialising in Lizards – Over 80 species of Geckos, Dragons, ….. pythons pythons for sale snake breeders lizards for sale lizard breeders water dragons …
www.petdirectory.com.au/?Reptile_Breeders…1…

.
‘Buy Water Dragons Online. For Sale with Same Day Shipping’
Water Dragon. Manufacturer: ABOUT OUR LIZARDS; Average Size Shipped – Varies… Please add to cart to see current sizes available; We have beginner reptiles …
www.bigappleherp.com/Water-Dragon
‘Gippsland Water Dragons – Aquarium and reptile online shop in …’
The Gippsland Water Dragon(Physignathus lesueurii howittii) is a large lizar. It is grey-green and brown with black banding on back and a row of spines …
www.amazingamazon.com.au/…sale/lizards-for-sale/lizards-for-sale/gippsland-water-dragons-for-sale.html
.
.
Threats from Upmarket Restaurants
.
Also along Long Reef locals have reported witnessing groups poaching marine life on the protected rock platforms.
“Groups and whole families that start at Palm Beach in a bus and go down the peninsula, combing all the rock shelves for marine life, looking for anything they can sell in a restaurant or eat themselves – sea urchins, shellfish, cunjevoi, sea snails, the lot.”
.
[Source: Shannon Leckie, ‘Under cover of darkness a lone stance against wildlife poachers‘, by Tim Elliott, 20110430, ^http://www.smh.com.au/environment/under-cover-of-darkness-a-lone-stance-against-wildlife-poachers-20110429-1e0sj.html]
.
The Exclusive Restaurant Trade in Australia is also on the rise.
Not content with the garden variety fish and chips, exclusive seafood restaurants across Sydney are luring the more discerning diner try more novel offerings, including Australian native red sea urchins, which can be found at Long Reef.
 Red Sea Urchin
(Photo from Long Reef)
Red Sea Urchin
(Photo from Long Reef)
.
While it is not known which Sydney restaurants may be serving up sea urchins poached from the Long Reef Aquatic Reserve, the following article reveals recent trends by exclusive seafood restaurants across Sydney to include unusual marine animals on their menus.
.
.
.
‘Deep Sea Dining’
…by Olivia Riordan and Lissa Christopher,Sydney Morning Herald’s ‘Good Living’ magazine on 15th December 2009.
.
‘A few courageous chefs, the discovery of great local product and diners’ willingness to try novel foods have combined to bring a strange-looking creature off the sea floor and into Sydney’s fine dining venues. Sea urchin has a host of new fans.
”I’ve sold more sea urchin in the past 12 months than I have in the past four years,” says Wayne Hulme from Christie’s Seafood.
Christie’s Asian clientele have enjoyed the spiny creatures for years but, Hulme says, Neil Perry was among the first chefs to put it on a modern Australian menu. ”He’s 10 years ahead of everyone else,” Hulme says.
At Rockpool, Perry serves snapper with a sea urchin roe butter.
The roe inside sea urchins is the real prize. It has a rich, sharp taste Perry describes as “a spoonful of icing sugar, salt straight from the sea and an egg” and Hulme describes as “sweet, salty and weighty”.

Live sea urchin dish at Hugos Manly by chef Massimo Mele.
© Photo: Marco del Grande
Red sea urchins are prized over black sea urchins because they carry roe year round, says Ralph Lavender, a diver and fisher who works with his son on the coast near Kiama and provides Christie’s with up to 100 kilograms of sea urchins each week. Black urchins are more common, he says, but they’re barren for six months of the year. They’re just starting to carry roe again now.
Lavender attributes the rising popularity of sea urchins to chefs realising good local product is available and Australian diners’ growing willingness to try new things.
”People have changed their culinary delights, if you like,” he says. ‘‘They’ll try witchetty grub, a bit of kangaroo tail, a bit of camel meat.”
Now they’re trying sea urchin and Lavender couldn’t be happier. Demand for his catch outstrips his capacity to supply, he says. NSW Department of Primary Industries licensing restrictions place limits on how many sea urchins he can bring in.
Hulme says that, until recently, a lot of the sea urchin roe sold at Christie’s was imported from Chile, arriving fresh but pre-extracted and packaged. Lavender’s sea urchins arrive in Sydney alive with their spikes still wiggling.
Rockpool isn’t the only Sydney restaurant serving sea urchin. Martin Benn from Sepia serves a sea urchin roe butter with mulloway and at Kables Restaurant, chef Carl Middleton makes a sea urchin soup with shark fin and lemon grass, presented in a sea urchin shell.
The head chef with the Hugos Group, Massimo Mele, uses sea urchins in a range of dishes and has been known to dive for them himself. Mele grew up eating the “beautiful and simple” urchins on the Italian coast and doesn’t complicate them on his own menu.’
[Source: ^http://www.smh.com.au/articles/2009/12/14/1260639163722.html]
.
.
So where do Sydney restaurants serving ‘Sea Urchin Sauce’ get their sea urchins from?
.
At Rockpool restaurant in The Rocks, “Perry serves snapper with a sea urchin roe butter“.
[Source: ^http://www.smh.com.au/articles/2009/12/14/1260639163722.html]
.
Jonah’s of nearby Whale Beach offers as a main course: “Crepinette of Kingfish and Ocean Trout, prawn and scallop mousse, Kipfler potatoes, spinach and Sea Urchin sauce | $48.00“
Source: ^http://www.bestrestaurants.com.au/restaurants/NSW-Greater-Sydney-jonahs.aspx]
.
Rise in Darlinghurst back in 2005 served up Amuse-bouche which included “semi-poached egg, sea-urchin sauce, salmon roe and shiso“.
[Source: ^http://grabyourfork.blogspot.com/2005/02/rise-darlinghurst.html]
.
Quadrant Restaurant at Circular Quay on its lunch menu includes for main, “pan roasted blue eye cod, braised fennel, sea urchin butter sauce“
[Source: ^http://mirvac-hotels.assets0.blockshome.com/assets/quay-grand-suites-sydney/7uqAftquXhxhatm/full-quadrant-menu-updated-250510.pdf]
.
Kabuki Shoroku Seafood Japanese Restaurant in St Martin Tower Clkarence Street Sydney, serves up ‘Kaisen Funamori’, which is described on the menu as:
“Chef’s best selection of fresh sashimi assortment ( live lobster, live abalone, oyster, tuna, salmon, sea urchin and white fish)”
[Source: ^http://www.kabukishoroku.com.au/menu.htm]
.
So where do these restaurants get their sea urchins from?
Are the sea urchins poached from wildlife sanctuaries?
Are the sea urchins endangered?
.
How would diners know?
Do diners care?
.
.
.K
.
Concerned locals frustrated at government inaction are taking matters into their own hands
.
‘SOS..Save-Our-Snails’
‘Pressure is mounting on authorities to do more to stop the illegal collecting of marine life from Long Reef Aquatic Reserve. Locals have flooded The Manly Daily with complaints about people illegally gathering large sea snails and shellfish from the unique reserve.
Both Warringah Council and the National Parks and Wildlife Service claim to be regularly patrolling the rock platforms, but residents claim it is ineffective.
Beacon Hill resident Joe Van Ewyk took this photo at the reserve late last year.

Illegal poaching of marine life from Long Reef Aquatic Reserve
© Photo Joe Van Ewyk
“There was a group who were very efficient and methodical at removing shells, etc, using metal bars and placing them into a bucket,” he said. “They were there for a considerable length of time – no one confronted them, rangers or otherwise.”
Mr Van Ewyk said not enough was being done to protect the unique platform.
“Go up to Port Stephens and stick your nose into a marine park and you’ll have three rubber duckies onto you straight away, checking your boat for fishing equipment,” he said.
“They’re very keen up there but down here there is nothing.”
Lucette Rutherford said she and her husband regularly swam at Collaroy Basin near the rock platform and on numerous occasions had seen groups of people collecting buckets of shellfish from the rock platforms.
“My husband has called NSW Fisheries and Warringah Council numerous times and only ever reached an answering machine,” he said. “It is distressing to see this damage to the marine life in our protected areas and the open disregard these people show.”
Marine expert Phil Colman said the illegal activity was a regular occurrence and could have a detrimental impact on the broader environment.
“When you target somewhere like Long Reef Aquatic Reserve you are affecting an important link in the food chain,” he said.
A Warringah Council spokeswoman said rangers conducted daily patrols and worked closely with Fisheries, the Surf Club and the Friends of Long Reef to protect the area.
Anyone who sees any illegal activity should contact Warringah Council on 9942 2111 or Fishers Watch Phoneline 1800 043 536.
Mr Colman will lead a guided tour of Long Reef Aquatic Reserve on February 20 from 4pm to 6pm. Details: 0411 124 200.
[Source: ^http://manly-daily.whereilive.com.au/news/story/sos-save-our-snails/]
.
.
‘Come and join my marine corps urges reef saviour’
Wildlife warrior Shannon Leckie has extended his covert surveillance operation to Long Reef and is looking for volunteers to join the cause.

Concerned nearby resident to Long Reef, Shannon Leckie, is trying to catch the poachers in the act.
.
Mr Leckie, who uses night-vision goggles, camouflage equipment and video recorders to record illegal poachers, wants to create a group of wardens to help protect marine life at the protected reserve. Poaching has been an ongoing issue with people ignoring signs and taking large sea snails and shellfish from the rock platform at low tide.
The former navy medic said he needed volunteers to help record the details of illegal poachers.
“I will film them and then relay the information up to someone in the carpark who can record their licence plates,” he said. “We will then pass that information on to the authorities.”
Only last week Mr Leckie filmed a group of people poaching from the platform in plain sight. “I got them as they walked off the rock shelf and they just looked straight at me,” he said.
One person who has already enlisted is Warringah Greens councillor, Christina Kirsch, who said she would to hand out flyers educating people about the protected reserve.
AQUATIC RESERVE
- Extends from Collaroy rockpools to Long Reef Surf Life Saving Club.
- The reserve was declared in 1980 to protect marine invertebrates on rock platforms and sub-tidal marine plants and animals.
- Except for fin fishing, collecting or harming marine plants or animals in the reserve is banned.
HOW YOU CAN HELP
- To become a volunteer warden at Long Reef email ckirsch@optusnet.com.au
.
[Source:
‘Come and join my marine corps urges reef saviour’, by Brenton Cherry in Manly Daily newspaper, 20110513,
^http://manly-daily.whereilive.com.au/news/story/come-and-join-my-marine-corps-urges-reef-saviour/]
.
.
Under cover of darkness a lone stance against wildlife poachers
by Tim Elliott, Sydney Morning Herald, 20110430.
.
 ‘Eco Warrior … fed up with wildlife pillaging on the northern beaches, Shannon Leckie is donning camouflage gear and trying to catch people in the act.
© Photo: Edwina Pickles
‘Eco Warrior … fed up with wildlife pillaging on the northern beaches, Shannon Leckie is donning camouflage gear and trying to catch people in the act.
© Photo: Edwina Pickles
.
‘If you spot a man hiding in the bushes with a video camera around the northern beaches do not be alarmed. It’s just Shannon Leckie, former Royal Australian Navy medic and eco-vigilante extraordinaire. Fed up with the systematic pillaging of native wildlife from his local area, Mr Leckie is going undercover, dressed in combat fatigues and equipped with night-vision goggles and a video camera.
“It’s going to be hit and miss,” the 40-year-old father of two admits. “I plan to get a lie-out position and then just film whatever illegal activity I see. If I catch anyone I’ll call the police and then hand the footage over.”
Mr Leckie will not be carrying any weapons.
“I don’t want to scare anyone. It’s just that the government isn’t putting enough money into this. In Africa and America they have teams dedicated to stop poaching, but here it seems to be pretty much a free for all, especially with the water dragons at Manly and the sea life at Long Reef.”
The eastern water dragon, a lizard protected under the National Parks and Wildlife Act, was once a common sight along the walkway from Manly to Shelly Beach. But a recent spate of “lizard napping” has halved their numbers, with offenders plucking the animals from the cliffs and bundling them into pillowcases and beach towels.
“It’s a huge problem for us,” said Henry Wong, the general manager of Manly Council, which installed anti-poaching signs in December. “They tend to take the breeding males, because they’re the biggest, which is devastating the colonies.”
Stealing a water dragon attracts a $3300 fine or six months’ imprisonment, but catching offenders has proven difficult. The last arrest was in September 2009, when Manly police caught two teenagers with water dragons stuffed into their backpacks. The teenagers, who were from the western suburbs, told police they wanted to take the lizards home as pets. But Mr Wong believes it is possible the animals are being traded on the black market.
Mr Leckie agrees. “I assume they are selling them overseas, because native Australian flora and fauna fetches quite bit of money.”
Mr Leckie also plans to monitor the northern beaches’ rock platforms. “There are groups and whole families that start at Palm Beach in a bus and go down the peninsula, combing all the rock shelves for marine life, looking for anything they can sell in a restaurant or eat themselves – sea urchins, shellfish, cunjevoi, sea snails, the lot.”
Phil Colman, a marine expert with the Collaroy group Fishcare Volunteers, said the Long Reef Aquatic Reserve was particularly vulnerable, because of its size, diversity and various points of entry. “I have seen people using penknives and crowbars, even bits of wood, to forage on the reef. Usually they target turban shells, and sometimes limpets. They can collect 200 or 300 limpets in a session. You call the fisheries inspectors but by the time they arrive the people are long gone.”
Recognised as the most diverse intertidal marine environment in NSW (“and one of the best in Australia,” according to Mr Colman), the aquatic reserve is used as a teaching platform by university students and schools as far away as Broken Hill.
“And yet poaching there is a constant problem. The issue is that when you target somewhere like Long Reef, you effect the entire food chain.”
Warringah Council recently allocated $40,000 to look into establishing an education centre and “wet lab” at the reef for international and local students. However, in the meantime Mr Leckie will be watching. “I just feel I have to act now, because it’s been going on for so long.”
[Source: http://www.smh.com.au/environment/under-cover-of-darkness-a-lone-stance-against-wildlife-poachers-20110429-1e0sj.html]

Long Reef
© Photo by Brent Pearson 20090412.
.
.
References:
.
[1]
^http://www.awrc.org.au/uploads/5/8/6/6/5866843/gamble_pets.pdf
[2] ^
http://members.ozemail.com.au/~surfcity/Pages/Beach.html
[3] ^
http://www.redbubble.com/people/salieri1627/art/5500094-rock-pool-long-reef-aquatic-park-sydney-30-exposure-hdr-panorama-the-hdr-experience
Philip Johnson
[4] http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/nationalparks/parkHome.aspx?id=a0004
[5] http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/nationalparks/parktypes.aspx?type=aquaticreserve
[6] Weedy Seadragon,
^http://www.abyss.com.au/scuba/pc/Weedy-Seadragon-p4291.htm
[7] ^
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phyllopteryx
[8] Olivia Riordan and Lissa Christopher, 20091215,
^http://www.smh.com.au/articles/2009/12/14/1260639163722.html
[9] Under cover of darkness a lone stance against wildlife poachers, Tim Elliott, 201104309,
^http://www.smh.com.au/environment/under-cover-of-darkness-a-lone-stance-against-wildlife-poachers-20110429-1e0sj.html
[10] ‘Come and join my marine corps, urges reef saviour’, by Brenton Cherry, 20110513, ^
http://manly-daily.whereilive.com.au/news/story/come-and-join-my-marine-corps-urges-reef-saviour/
[11] ^
http://www.flickr.com/photos/lsydney/5626257447/
[12]
^http://www.aquariumslife.com/saltwater-fish/seahorse/weedy-sea-dragon-phyllopteryx-taeniolatus/
[13]
^http://www.riverwonders.com/p-97-weedy-sea-dragon-show-specimen-5-6.aspx
[14] ^
http://manly-daily.whereilive.com.au/news/story/sos-save-our-snails/
[15] Wobbegong sharks released at Long Reef Aquatic Reserve,
^http://mosman-daily.whereilive.com.au/photos/gallery/wobbegong-sharks-released-at-long-reef-aquatic-reserve-photos-by-simon-cocksedge/
[16] Wobbegongs return to the wild but stay close to home, Aaron Cook, March 9, 2011
http://www.theage.com.au/environment/animals/wobbegongs-return-to-the-wild-but-stay-close-to-home-20110308-1bmod.html
[17] A world in a rock pool, By Rachel Sullivan,
^http://www.abc.net.au/science/articles/2011/01/18/3114813.htm
[18]
^http://travel.aol.com/travel-guide/australia-and-south-pacific/australia/sydney/long-reef-aquatic-reserve-thingstodo-detail-387857/
[19] http://www.warringah.nsw.gov.au/news_events/documents/WMatters13Autumn09.pdf (page 5)
[20] ‘$40,000 kick start for plan to stop poaching’, by Brenton Cherry, 20110304
^http://manly-daily.whereilive.com.au/news/story/40-000-kick-start-for-plan-to-stop-poaching/
[21] http://www.warringah.nsw.gov.au/council_then/documents/20110208m.pdf (pages 9-10)
[22] ^
http://www.lachlanhunter.deadsetfreestuff.com/JB/geo-sitesK-L.htm
[23]
^http://www.reefcarelongreef.org.au/
[24] Save Long Reef Coalition.
.
[The above Internet references were accessed 20110626]
.
– end of article –
RSPCA Qld provides for pocket pets like rats, mice and guinea pigs but the category
“Pocket Pets” also includes native and exotic wildlife species: birds, reptiles, fish,
crabs, amphibians and invertebrates.
As the human population increases in Australia so does housing density, especially on
the East Coast. The popularity of smaller animals as pets is on the rise. It is
generally considered, and most often incorrectly, by the broader community that these
species are less needy and easier to care for than dogs and cats. I offer the following
for consideration in the wildlife as pets debate and argue that having wildlife as pets is
generally not a good idea.
http://www.awrc.org.au/uploads/5/8/6/6/5866843/gamble_pets.pdf
Long Reef Aquatic Reserve was declared in 1980 It extends from Collaroy rock baths south to Long Reef SLSC, and from mean high water out 100m from mean low water (Approx 60 ha.). The reserve was declared primarily to protect marine invertebrates found on the rock platforms, and to protect subtidal marine plants and animals. It is also important for marine education. Long Reef Aquatic Reserve includes two main rocky shores. The northern rocky reef area is protected from southerly swells by the prominent eastern headland, whilst the eastern large platform is more exposed. Different organisms occur in these different areas. Sydney’s northern beaches feature many diverse rock platforms. Long Reef Aquatic Reserve is unique due to its exposure to all four points of the compass. Species dwelling here have managed to adapt well to a huge range of severe conditions. Long Reef Aquatic Reserve has a wide variety of habitats, including sheltered boulder fields and surf-exposed ledges. The diversity and abundance of marine invertebrates here is rarely seen anywhere.
http://members.ozemail.com.au/~surfcity/Pages/Beach.html
The Long Reef Aquatic Reserve was declared primarily to protect the marine invertebrates and sub-tidal marine plants and animals. Isobel Bennett AO (1908-2007, at right) was a marine conservation pioneer whose work on Sydney’s rock platforms led to the establishment of the Aquatic Reserve in 1980 by the state government. The reserve covers an area of approx. 60ha from the high water mark out to 100m from low water, extending from the Collaroy rock pool south to Long Reef Surf Club on Long Reef beach.
Long Reef Aquatic Reserve was declared in 1980 It extends from Collaroy rock baths south to Long Reef SLSC, and from mean high water out 100m from mean low water (Approx 60 ha.). The reserve was declared primarily to protect marine invertebrates found on the rock platforms, and to protect subtidal marine plants and animals. It is also important for marine education. Long Reef Aquatic Reserve includes two main rocky shores. The northern rocky reef area is protected from southerly swells by the prominent eastern headland, whilst the eastern large platform is more exposed. Different organisms occur in these different areas. Sydney’s northern beaches feature many diverse rock platforms. Long Reef Aquatic Reserve is unique due to its exposure to all four points of the compass. Species dwelling here have managed to adapt well to a huge range of severe conditions. Long Reef Aquatic Reserve has a wide variety of habitats, including sheltered boulder fields and surf-exposed ledges. The diversity and abundance of marine invertebrates here is rarely seen anywhere.
http://www.redbubble.com/people/salieri1627/art/5500094-rock-pool-long-reef-aquatic-park-sydney-30-exposure-hdr-panorama-the-hdr-experience
Philip Johnson
Long Reef Aquatic Reserve on Sydney’s northern beaches is approximately 20 kilometres north of the city. It extends from Collaroy rock baths south to Long Reef Surf Lifesaving Club, and from mean high water to 100 metres out from mean low water.
The reserve includes two main rocky shores. The northern rocky reef area is protected from southerly swells by the prominent eastern headland, while the larger eastern platform is more exposed. Different organisms occur in these two areas.
Long Reef Aquatic Reserve protects the marine invertebrates on the rock platforms as well as subtidal marine plants and animals. It is also an important site for marine education.
What you can do in the reserve
Long Reef Aquatic Reserve has been set aside for the protection of marine plants and invertebrates. When lifting rocks, be careful of attached animals and about exposing animals underneath to direct sunlight. Also be sure that the rocks are put back in the same place.
Fin-fish can be taken by line or spear only but bring your own bait. Strict bag limits apply to both the numbers and sizes of fish caught. If unsure of what these are, ask the local Fisheries Officer.
With the exception of fin-fish, no marine plants or animals can be harmed. This includes the collection of empty shells and dead plants or animals because they provide important habitat or food for living invertebrates.
The penalties for breaking the rules are quite severe. NSW Fisheries legislation provides for fines up to $110,000 and on-the-spot fines also apply. All fishing or diving gear may also be forfeited.
For further information
Contact NSW Fisheries Sydney North on 8437 4901
or the Port Stephens Fisheries Centre, Protected Areas Unit on 4982 1232
Report any illegal activity to Fishers Watch Phoneline 1800 043 536
(free call 24 hrs State wide)
http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/nationalparks/parkHome.aspx?id=a0004
Reserve types in NSW – Aquatic reserve
Aquatic reserves have been established to protect biodiversity and provide representative samples of our wonderfully varied marine life and habitats. New South Wales currently has 12 aquatic reserves declared under the Fisheries Management Act 1994.
Although aquatic reserves are generally small compared with marine parks, they play a significant role in the NSW marine protected area system. Apart from protecting important habitat, nursery areas and vulnerable and threatened species, aquatic reserves also have valuable research and educational roles.
Community involvement is critical in the management of aquatic reserves. Through public involvement in management planning processes, the government seeks to achieve community partnership in these important places, providing on going protection for the future.
http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/nationalparks/parktypes.aspx?type=aquaticreserve
Weedy Seadragon
Weedy Seadragons are only found in southern Australian waters, usually ranging from Geraldton WA, to Port Stephens NSW and down around Tasmania. They are weird and mystical looking, not quite seahorse, not quite fish. The Weedy Seadragon is closely related to the seahorse, being a member of the Syngnathidae family. Their habitat is listed as moderately to sub maximally exposed reefs between 1-50m. In Sydney have a number of dive sites where seadragons are spotted on almost every dive. More details…
Previous Item Next Item
Details
video
Reviews
enriched air course
Weedy Seadragons can grow to about 46cm in length. They are orange/red in colour with numerous whitish spots on a lot of their body and along their tube shaped snout. The seadragon also have bluish purple stripes and some yellow markings along their bodies as well. They have leaf like appendages and a few short spines occurring along their body. The seadragon camouflage is quite good and they do resemble seaweed floating on the bottom of the sea floor. Unless you know what you are looking for seadragons can be easily overlooked. Once you have found a few of these creatures it becomes easier to spot them.
Weedy Seadragons usually have a single brood of eggs per season, but if conditions are favourable they have been known to have two broods in one season. They usually breed in spring, however several males weedy seadragon have been spotted in Sydney recently with eggs. Prior to mating the male prepares the area of his tail where he will keep the eggs. This area becomes slightly swollen, soft and spongy. The female actually pushes the eggs onto the males tail. Once on his tail they are fertilised. The male carries anything from 120 to 300 eggs on his tail. He carries the eggs for about 2 months and then the eggs hatch over a period of 6 days. The seadragon hatchlings are quite large when born ranging fm 2.5cm-3.5cm in length and still have a yolk sac attached to them, which supports them for two days while their snout grows. Once their snout is grown they can begin to feed. Juveniles can double in length in one week and can reach 15cm by the end of 14 weeks. Some baby weedy seadragons (about 7cms) have been spotted recently on some of our dives at Kurnell. January this year a lot of juveniles were seen out at Kurnell.
The seadragons diet mainly consists of sea lice and other small crustaceans. They seem to suck their prey straight into the snout! There is much concern for the future of the Weedy Seadragon and others in their family. They are threatened by habitat destruction, and potentially by the aquarium trade. Currently seadragons are protected under fisheries legislation federally and in most states where they occur, it is illegal to take or export them without a permit.
When diving with these beautiful creatures remember not to touch them, be happy to look and photograph the seadragon without harassing them.
http://www.abyss.com.au/scuba/pc/Weedy-Seadragon-p4291.htm
Phyllopteryx taeniolatus, the Weedy Seadragon or Common Seadragon, is a marine fish related to the seahorse. It is the only member of the genus Phyllopteryx. It is found in water 3 to 50 m deep around the southern coastline of Australia, approximately between Port Stephens, New South Wales and Geraldton, Western Australia, as well as around Tasmania. Weedy Seadragons are named for the weed-like projections on their bodies that camouflage them as they move among the seaweed beds where they are usually found.
Weedy Seadragon, Phyllopteryx taeniolatus, from the Sketchbook of fishes by William Buelow Gould, 1832
Weedy Seadragons can reach 45 cm in length. They feed on tiny crustaceans and other zooplankton, from places such as crevices in reef, which are sucked into the end of their long tube-like snout. They lack a prehensile tail that enables similar species to clasp and anchor themselves. Phyllopteryx taeniolatus swim in shallow reefs and weed beds, and resemble drifting weed when moving over bare sand.[1]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phyllopteryx
=======================
Olivia Riordan and Lissa Christopher
December 15, 2009
Page 1 of 2 | Single page
Afew courageous chefs, the discovery of great local product and diners’ willingness to try novel foods have combined to bring a strange-looking creature off the sea floor and into Sydney’s fine dining venues. Sea urchin has a host of new fans.
”I’ve sold more sea urchin in the past 12 months than I have in the past four years,” says Wayne Hulme from Christie’s Seafood.
Christie’s Asian clientele have enjoyed the spiny creatures for years but, Hulme says, Neil Perry was among the first chefs to put it on a modern Australian menu. ”He’s 10 years ahead of everyone else,” Hulme says.
At Rockpool, Perry serves snapper with a sea urchin roe butter.
The roe inside sea urchins is the real prize. It has a rich, sharp taste Perry describes as “a spoonful of icing sugar, salt straight from the sea and an egg” and Hulme describes as “sweet, salty and weighty”.
Red sea urchins are prized over black sea urchins because they carry roe year round, says Ralph Lavender, a diver and fisher who works with his son on the coast near Kiama and provides Christie’s with up to 100 kilograms of sea urchins each week. Black urchins are more common, he says, but they’re barren for six months of the year. They’re just starting to carry roe again now.
Lavender attributes the rising popularity of sea urchins to chefs realising good local product is available and Australian diners’ growing willingness to try new things.
”People have changed their culinary delights, if you like,” he says. ”They’ll try witchetty grub, a bit of kangaroo tail, a bit of camel meat.”
Now they’re trying sea urchin and Lavender couldn’t be happier. Demand for his catch outstrips his capacity to supply, he says. NSW Department of Primary Industries licensing restrictions place limits on how many sea urchins he can bring in.
Hulme says that, until recently, a lot of the sea urchin roe sold at Christie’s was imported from Chile, arriving fresh but pre-extracted and packaged. Lavender’s sea urchins arrive in Sydney alive with their spikes still wiggling.
Rockpool isn’t the only Sydney restaurant serving sea urchin. Martin Benn from Sepia serves a sea urchin roe butter with mulloway and at Kables Restaurant, chef Carl Middleton makes a sea urchin soup with shark fin and lemon grass, presented in a sea urchin shell.
The head chef with the Hugos Group, Massimo Mele, uses sea urchins in a range of dishes and has been known to dive for them himself. Mele grew up eating the “beautiful and simple” urchins on the Italian coast and doesn’t complicate them on his own menu.
http://www.smh.com.au/articles/2009/12/14/1260639163722.html
Live sea urchin dish at Hugos Manly by chef Massimo Mele.
Photo: Marco del Grande
=======================
Under cover of darkness a lone stance against wildlife poachers
Tim Elliott
April 30, 2011
Eco Warrior … fed up with wildlife pillaging on the northern beaches, Shannon Leckie is donning camouflage gear and trying to catch people in the act. Photo: Edwina Pickles
IF YOU spot a man hiding in the bushes with a video camera around the northern beaches do not be alarmed. It’s just Shannon Leckie, former Royal Australian Navy medic and eco-vigilante extraordinaire. Fed up with the systematic pillaging of native wildlife from his local area, Mr Leckie is going undercover, dressed in combat fatigues and equipped with night-vision goggles and a video camera.
“It’s going to be hit and miss,” the 40-year-old father of two admits. “I plan to get a lie-out position and then just film whatever illegal activity I see. If I catch anyone I’ll call the police and then hand the footage over.”
Mr Leckie will not be carrying any weapons.
“I don’t want to scare anyone. It’s just that the government isn’t putting enough money into this. In Africa and America they have teams dedicated to stop poaching, but here it seems to be pretty much a free for all, especially with the water dragons at Manly and the sea life at Long Reef.”
The eastern water dragon, a lizard protected under the National Parks and Wildlife Act, was once a common sight along the walkway from Manly to Shelly Beach. But a recent spate of “lizard napping” has halved their numbers, with offenders plucking the animals from the cliffs and bundling them into pillowcases and beach towels.
“It’s a huge problem for us,” said Henry Wong, the general manager of Manly Council, which installed anti-poaching signs in December. “They tend to take the breeding males, because they’re the biggest, which is devastating the colonies.”
Stealing a water dragon attracts a $3300 fine or six months’ imprisonment, but catching offenders has proven difficult. The last arrest was in September 2009, when Manly police caught two teenagers with water dragons stuffed into their backpacks. The teenagers, who were from the western suburbs, told police they wanted to take the lizards home as pets. But Mr Wong believes it is possible the animals are being traded on the black market.
Mr Leckie agrees. “I assume they are selling them overseas, because native Australian flora and fauna fetches quite bit of money.”
Mr Leckie also plans to monitor the northern beaches’ rock platforms. “There are groups and whole families that start at Palm Beach in a bus and go down the peninsula, combing all the rock shelves for marine life, looking for anything they can sell in a restaurant or eat themselves – sea urchins, shellfish, cunjevoi, sea snails, the lot.”
Phil Colman, a marine expert with the Collaroy group Fishcare Volunteers, said the Long Reef Aquatic Reserve was particularly vulnerable, because of its size, diversity and various points of entry. “I have seen people using penknives and crowbars, even bits of wood, to forage on the reef. Usually they target turban shells, and sometimes limpets. They can collect 200 or 300 limpets in a session. You call the fisheries inspectors but by the time they arrive the people are long gone.”
Recognised as the most diverse intertidal marine environment in NSW (“and one of the best in Australia,” according to Mr Colman), the aquatic reserve is used as a teaching platform by university students and schools as far away as Broken Hill.
“And yet poaching there is a constant problem. The issue is that when you target somewhere like Long Reef, you effect the entire food chain.”
Warringah Council recently allocated $40,000 to look into establishing an education centre and “wet lab” at the reef for international and local students. However, in the meantime Mr Leckie will be watching. “I just feel I have to act now, because it’s been going on for so long.”
Read more: http://www.smh.com.au/environment/under-cover-of-darkness-a-lone-stance-against-wildlife-poachers-20110429-1e0sj.html#ixzz1PuLdhur9
http://www.smh.com.au/environment/under-cover-of-darkness-a-lone-stance-against-wildlife-poachers-20110429-1e0sj.html
=====
WILDLIFE warrior Shannon Leckie has extended his covert surveillance operation to Long Reef and is looking for volunteers to join the cause.
Mr Leckie, who uses night-vision goggles, camouflage equipment and video recorders to record illegal poachers, wants to create a group of wardens to help protect marine life at the protected reserve.
RELATED NEWS: Guardians of the night gear up to catch poachers
Poaching has been an ongoing issue with people ignoring signs and taking large sea snails and shellfish from the rock platform at low tide.
The former navy medic said he needed volunteers to help record the details of illegal poachers.
“I will film them and then relay the information up to someone in the carpark who can record their licence plates,” he said. “We will then pass that information on to the authorities.”
Only last week Mr Leckie filmed a group of people poaching from the platform in plain sight. “I got them as they walked off the rock shelf and they just looked straight at me,” he said.
One person who has already enlisted is Warringah Greens councillor, Christina Kirsch, who said she would to hand out flyers educating people about the protected reserve.
AQUATIC RESERVE
*Extends from Collaroy rockpools to Long Reef Surf Life Saving Club.
*The reserve was declared in 1980 to protect marine invertebrates on rock platforms and sub-tidal marine plants and animals.
*Except for fin fishing, collecting or harming marine plants or animals in the reserve is banned.
HOW YOU CAN HELP
*To become a volunteer warden at Long Reef email ckirsch@optusnet.com.au
Come and join my marine corps, urges reef saviour
Environment
13 May 11 @ 03:45pm by Brenton Cherry
http://manly-daily.whereilive.com.au/news/story/come-and-join-my-marine-corps-urges-reef-saviour/
====
Aplysia dactylomela
PHOTO: Long Reef, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, December 1995, 12cm long alive.
======

=====
Species name: Phyllopteryx taeniolatus
Common names: Common seadragon, Weedy Sea Dragon
Family: Syngnathidae (Pipefishes and seahorses)
Subfamily: Syngnathinae
Order: Syngnathiformes
Class: Actinopterygii
Maximum length: 18.11 in
Minimum tank size: unknown
Hardiness: Difficult. Not many aquariums have weedy sea dragons because they do not survive well in captivity. In fact, only slightly more than half do survive.
Aggressiveness: Peaceful
Reef Compatibility: Excellent
Distribution: Eastern Indian Ocean: southern Australia, from southern Western Australia to New South Wales and Tasmania
Diet: They use their tube shaped snout to such up zooplankton and any other tiny crustaceans they can find including mysids. Feeding is what makes them difficult to keep Weedies in an aquarium. They refuse to feed on anything other than their native food or live mysiid shrimps
Additional information:
Phyllopteryx taeniolatus, also known as the Weedy Sea Dragon is native to the Eastern Indian Ocean where it is found among seaweeds and coral reefs at depths of 0-160 feet. Unfortunately, not many aquariums have weedy sea dragons because they do not survive well in captivity. According to Marine Depot Blog, only about 50 aquariums worldwide have sea dragons. This might explain why it was so difficult to find information about this species.
Phyllopteryx taeniolatus is a close relative of the seahorse. It looks similar to the seahorse, except it has long weed-like structures that stick out from their bodies which makes them really difficult to distinguish in their natural environment. They have a long pipe-like snout with a small terminal mouth. The body is usually brown or reddish with their weed-like structures being greener. They also have yellow spots. The body is long and covered in rings of bone.
It is interesting that the Weedy Sea Dragon is so well camouflaged because scientists are still unsure if these animals actually have predators or not.
Sea dragons, sea horses and pipe fish are the only species where the male carries the eggs but seadragons do not have a pouch for rearing the young. Instead, the male carries the eggs fixed to the underside of his tail from where they eventually hatch.
I have found close to nothing about how to keep the Weedy Sea Dragon in aquarium.
http://www.aquariumslife.com/saltwater-fish/seahorse/weedy-sea-dragon-phyllopteryx-taeniolatus/
http://www.riverwonders.com/p-97-weedy-sea-dragon-show-specimen-5-6.aspx
=====
PRESSURE is mounting on authorities to do more to stop the illegal collecting of marine life from Long Reef Aquatic Reserve.
Locals have flooded The Manly Daily with complaints about people illegally gathering large sea snails and shellfish from the unique reserve.
Both Warringah Council and the National Parks and Wildlife Service claim to be regularly patrolling the rock platforms, but residents claim it is ineffective.
Beacon Hill resident Joe Van Ewyk took this photo at the reserve late last year.
“There was a group who were very efficient and methodical at removing shells, etc, using metal bars and placing them into a bucket,” he said. “They were there for a considerable length of time – no one confronted them, rangers or otherwise.”
Mr Van Ewyk said not enough was being done to protect the unique platform.
“Go up to Port Stephens and stick your nose into a marine park and you’ll have three rubber duckies onto you straight away, checking your boat for fishing equipment,” he said.
“They’re very keen up there but down here there is nothing.”
Lucette Rutherford said she and her husband regularly swam at Collaroy Basin near the rock platform and on numerous occasions had seen groups of people collecting buckets of shellfish from the rock platforms.
“My husband has called NSW Fisheries and Warringah Council numerous times and only ever reached an answering machine,” he said. “It is distressing to see this damage to the marine life in our protected areas and the open disregard these people show.”
Marine expert Phil Colman said the illegal activity was a regular occurrence and could have a detrimental impact on the broader environment.
“When you target somewhere like Long Reef Aquatic Reserve you are affecting an important link in the food chain,” he said.
A Warringah Council spokeswoman said rangers conducted daily patrols and worked closely with Fisheries, the Surf Club and the Friends of Long Reef to protect the area.
Anyone who sees any illegal activity should contact Warringah Council on 9942 2111 or Fishers Watch Phoneline 1800 043 536.
Mr Colman will lead a guided tour of Long Reef Aquatic Reserve on February 20 from 4pm to 6pm. Details: 0411 124 200.
http://manly-daily.whereilive.com.au/news/story/sos-save-our-snails/
===
Wobbegong sharks released at Long Reef Aquatic Reserve
http://mosman-daily.whereilive.com.au/photos/gallery/wobbegong-sharks-released-at-long-reef-aquatic-reserve-photos-by-simon-cocksedge/
Wobbegongs return to the wild but stay close to home
Aaron Cook
March 9, 2011
Ads by Google
Free Practice Account
www.GFT.com.au
Want to learn more about cfds? We can help. Learn More
Nearly gone … a wobbegong is released.
Nearly gone … a wobbegong is released. Photo: Nick Moir
IT IS hard to take a shark seriously when it appears to be wearing brown pyjamas and sporting a beard, but the four wobbegongs released near Collaroy yesterday are worthy of some respect.
Raised in the Sydney Aquarium, the two-year-olds are now fending for themselves in the wilds of Long Reef Aquatic Reserve.
The sharks were carried across the beach in a big red bucket before entering their new home with barely a splash, as a crowd of more than 100 well-wishers scrambled to catch a glimpse.
Advertisement: Story continues below
Chelsea Kilgour, 5, from Glenorie, took a day off school to see a real shark, and described the 60-centimetre-long wobbegongs as friendly and not at all scary.
With shark populations collapsing worldwide and local wobbegong numbers in decline, the juveniles are part of a research program investigating whether sharks bred in captivity can thrive in the wild.
The joint venture between Sydney Aquarium and Macquarie University, called Project Wobbegong, is already a success, with 12 out of 17 individuals released setting up home in the area or returning on a regular basis.
The results raise hopes the aquarium’s shark breeding program can boost numbers in waters around Sydney.
”It gives Sydney Aquarium the chance to restock depleted wild populations knowing that they are going to have a chance of survival,” a Sydney Aquarium Conservation Fund spokeswoman, Claudette Rechtorik, said.
Now in its third year, the project tracks the sharks it releases with a mixture of electronic and visual tagging.
Researchers were surprised that most of the wobbegongs had remained near Cabbage Tree Bay Aquatic Reserve where they were released.
”We thought they would just take off and that would be the end of it,” Ms Rechtorik said.
Wobbegongs are one of six species of shark bred by the aquarium and are said to take their name from an Aboriginal word meaning ”shaggy beard”.
They can live for 30 years and pose no threat to humans, Ms Rechtorik said.
”The only way someone would be hurt by a wobbegong is if they step on one or provoke it.”
Read more: http://www.theage.com.au/environment/animals/wobbegongs-return-to-the-wild-but-stay-close-to-home-20110308-1bmod.html#ixzz1QJvS52XT
http://www.theage.com.au/environment/animals/wobbegongs-return-to-the-wild-but-stay-close-to-home-20110308-1bmod.html
=====
A world in a rock pool
Scoured out of the rock by millennia of wave action, rock pools are rich and fascinating places to explore. In the second part of our two-part beachcombing guide discover the plant and animal life you’ll find among the rocks.
By Rachel Sullivan
Slideshow: Photo 1 of 11
Rock pools
No two rock pools are the same. (Source: dazza17 – DJ/Flickr)
Related Stories
On the beach, Science Online, 12 Jan 2011
Stowaways found hitching ride on seaweed, Science Online, 15 Sep 2010
Sea urchins ‘bulldozing’ Tasmanian reef, Science Online, 08 Dec 2009
At first glance, they might appear to be home to only a few limpets and some seaweed, but peering into the depths of even the smallest rock pool reveals incredible diversity. And no two are ever the same.
Species vary widely between pools and between areas, says Dr Neville Barrett, a marine biodiversity expert from the University of Tasmania.
“You can never predict what you’ll find because every pool is a different shape, size and depth. Even experts don’t know every species,” he says.
“Generally speaking, though, the deeper the pool the more stable it is and the greater the diversity of species found within,” Barrett says.
Crabs and other crustaceans are easily spotted throughout pools, while small fish like blennies and gobies dart around the bottom feeding on tiny crustaceans.
Meanwhile, sea stars stick around the edges. Larger species like the eleven-armed sea star and the velvet sea star may be easily spotted, but smaller species like the little sea star which is less than 15 millimetres across, or the southern biscuit star which comes in a variety of patterns and colours are often only found under boulders.
Large red anemones are also fairly conspicuous, trapping amphipods and isopods in their sticky tentacles, but living under boulders are also lots of smaller species, says Barrett.
When: Summer provides great conditions for exploring the shoreline
When: The intertidal zone. Scientists divide the Australian coastline into tropical and temperate zones. On the east coast the two zones meet around Fraser Island, Queensland, and the west coast they meet around Shark Bay, Western Australia.
Shells and snails
Seaweeds, corals, worms, sponges, barnacles, limpets and other molluscs like mussels, snails, whelks, nudibranchs and oysters may be found in the depths of rock pools.
In temperate waters, beachcombers can often see the turban snail, known for its distinctive green-striped shell. Growing up to four centimetres in size, they feed on algae growing on rock platforms.
Limpets, with their distinctive, oval shaped shell, are another frequent sight along rocky shorelines. During high tide they move about and graze on algae, returning to the same place when the tide falls and sealing themselves tightly against the rock to conserve moisture.
“Rock pools are teeming with life and there’s a lot happening that we don’t see,” says Barrett.
However, you should avoid putting your hands in the water and exploring rock crevices, as not all creatures are harmless.
One creature that hides under boulders and in pools that have a sandy floor, is the blue-ringed octopus, which is very common in New South Wales and Victoria.
“They are able to burrow down and hide in the sand which makes them hard to see,” says Barrett.
Normally blending into its surroundings, this small brown octopus develops brilliant blue ring-shaped markings when it is threatened.
Despite its attractive markings, the blue-ringed octopus is extremely poisonous and should not be approached or handled.
Tropical pools
Rock pools are generally regarded as a temperate phenomenon, but they can also be found in the tropics, despite the higher proportion of sandy beaches to rocky headlands in the region.
However, with the extreme temperature variations that can occur in a small pool that is isolated from the sea for many hours at a time, tropical rock pools generally contain much less diversity than temperate ones, according to Barrett.
“To put it in perspective, coral bleaching occurs when the sea level temperature increases by one degree. In a rock pool the temperature can vary by up to 10 degrees,” he says.
“Life in tropical rock pools tends to be less colourful, and is restricted to the few species that are able to tolerate prolonged high temperatures like barnacles and limpets, which are able to seal tightly to the rocks to stop moisture loss.”
Even in temperate regions, the inhabitants of smaller pools face the same challenges, so small pools tend to be home to only the most robust species like sea lettuce, Neptune’s necklace and crabs.
http://www.abc.net.au/science/articles/2011/01/18/3114813.htm
=====
This impressive marine reserve covers the large rocky peninsula and the surrounding rock platforms between Long Reef and Collaroy beaches on Sydney’s North Shores. It features a range of coastal habitats from crumbling sea cliffs, blowzy dunes, surf-pounded rock platforms and sheltered rock pools. Long Reef’s rock platforms are unique as they are exposed on all points of the compass. The reserve was established in 1980 to protect the enormously diverse marine life that makes the most of these varied habitats. It is best explored at low tide, and snorkeling is possible on the south side on calm days. But remember: this is a protected area, so don’t take anything! Also check local press for details of free guided walks provided by Fishcare Volunteers where you might spot elephant snails, octopus, pelicans, penguins, fairy wrens, blue periwinkles or even the odd whale.
http://travel.aol.com/travel-guide/australia-and-south-pacific/australia/sydney/long-reef-aquatic-reserve-thingstodo-detail-387857/
====
Council Rangers now have the
authorisation to protect the diverse
marine life in the Long Reef Aquatic
Reserve.
The aquatic wonderland was declared
a reserve in 1980 to protect the
subtidal marine plants and animals and
marine invertebrates found on the
rock platforms.
Long Reef Aquatic Reserve covers
almost 60 hectares and extends from
Collaroy rockpool to Long Reef Surf
Life Saving Club and from the high
tide line to 100 metres out to sea.
Long Reef Aquatic Reserve has a
wide variety of habitats and the
diversity and abundance of marine
invertebrates is rarely seen anywhere
else. We are fortunate to have a truly
unique environment on our doorstep.
Until now only NSW Fisheries staff
had the authority to issue fines to
people taking marine life from the
platform or intertidal area.
Warringah Council Rangers have
recently undertaken training with
NSW Fisheries to investigate and
prosecute people illegally removing
marine fish and vegetation. Fines of up
to $500 can apply.
http://www.warringah.nsw.gov.au/news_events/documents/WMatters13Autumn09.pdf (page 5)
$40,000 kick start for plan to stop poaching
Environment
4 Mar 11 @ 05:32pm by Brenton Cherry
An environmental education centre is proposed for Fishermans Beach, Collaroy, in the Warringah Surf Rescue building
An environmental education centre is proposed for Fishermans Beach, Collaroy, in the Warringah Surf Rescue building
AN environmental education centre, with a full-time caretaker, is being touted as a way to stop illegal poaching at Long Reef Aquatic Reserve.
This week Warringah Council allocated $40,000 towards design concepts for the centre, which would be in the Warringah Surf Rescue building at Fishermans Beach.
It would attract international and northern beaches students, who would stay on site while studying the reef’s ecosystem.
The announcement of funding follows criticism that Warringah Council has not done enough to stop illegal poaching of marine life from the rock platform.
But Warringah Mayor Michael Regan said the centre could be an ideal solution.
“It’s an area we want to protect and preserve,” he said. “And having an environmental centre would be great for educational and scientific purposes.
“To have students, residents and many other community organisations using the facility will increase the understanding and awareness about the importance of the area, as well as be a deterrent to illegal poaching.
“I believe we could make it cost-neutral and we could have this very active natural site.”
Marine expert Phil Colman, who leads tours of the reef, said he had been pushing for a year for more to be made of the ecologically significant site.
“Long Reef is a fantastic biological teaching platform,” he said.
“This centre would allow university students coming from Sydney and overseas to use the room as a base (and) get material from the reef and study it on site.”
EDUCATION
CENTRE
-At the Warringah Surf Rescue building, Fishermans Beach
-Could include a laboratory with scientific research equipment as well as a “wet bench’‘, with a continuous supply of salt water
-Possibility for bunk-style accommodation to allow students to stay on site
-Existing surf rescue radio base would be incorporated in the design
http://manly-daily.whereilive.com.au/news/story/40-000-kick-start-for-plan-to-stop-poaching/
‘This article is factually incorrect. The mayoral casting vote killed a plan to stop poaching at Long Reef. I had asked for a report and recommendations to council on various options to tackle the ongoing poaching at Long Reef – including improved signage and patrols, volunteer guardians of the Reef and a potential zero tolerance zone for the Eastern platform. Unfortunately it got voted down – the voting pattern is in the council minutes of the last February meeting.’ – Christina Kirsch comment (Posted on 5 Mar 11).
4.2 Mr Paul Jaffe made a statement regarding the Long Reef rock platform and asked the
following question:
What can Council do to have Rangers patrolling the Long Reef rock platform?
Answer: The Mayor advised that Council needs to look at better ways of patrolling areas
such as this. The Director of Strategic and Development Services further advised that the
area is patrolled daily. The Director advised that there are eight Rangers on duty and that
Minutes of Council Meeting on 8 February 2011
Page 10 of 41
this area is already treated as a priority area. National Parks and Wildlife can be contacted
however Council can only pursue this if offenders can be identified. It was also advised that
the Rangers priorities do shift during the day to patrol other areas including school zones.
http://www.warringah.nsw.gov.au/council_then/documents/20110208m.pdf (pages 9-10)
References:
http://www.lachlanhunter.deadsetfreestuff.com/JB/geo-sitesK-L.htm
http://www.reefcarelongreef.org.au/
Save Long Reef Coalition
 How is this mass killing different to April 1994 when the Hutu militia hacked thousands of Tutsis to death in Rwanda, or July 1995 in Srebrenica when Serb General Ratko Mladic systematically selected and then massacred 8,372 men and boys ‘of fighting age’ (between the ages of twelve and sixty), or in May 2000 when the Sri Lanka Army used banned cluster bombs from China, multi barrel rocket Launchers killing 2,000 Tamil civilians in the island’s north?
How is this mass killing different to April 1994 when the Hutu militia hacked thousands of Tutsis to death in Rwanda, or July 1995 in Srebrenica when Serb General Ratko Mladic systematically selected and then massacred 8,372 men and boys ‘of fighting age’ (between the ages of twelve and sixty), or in May 2000 when the Sri Lanka Army used banned cluster bombs from China, multi barrel rocket Launchers killing 2,000 Tamil civilians in the island’s north? How is he any different to Sri Lankan Defence Secretary Gotabhaya Rajapaksa?
How is he any different to Sri Lankan Defence Secretary Gotabhaya Rajapaksa?