Fairy Penguins v FV Margiris in Bass Strait
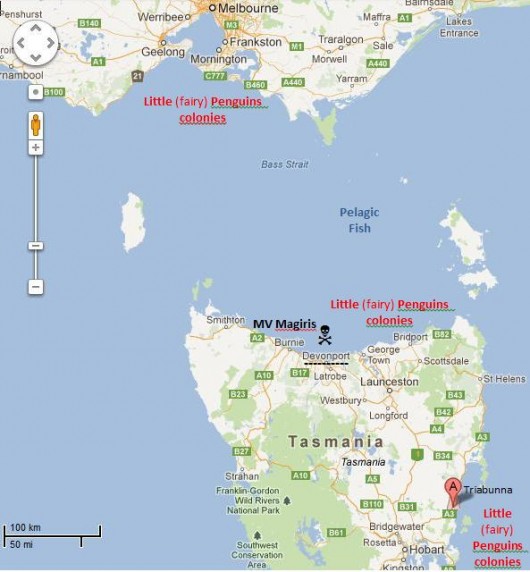
Friday, June 29th, 2012 Little Penguins (Eudyptula minor)
commonly called ‘fairy penguins‘ due to their small fairy-like size
Arrive ashore after feeding on ‘pelagic’ fish in Bass Strait in southern Australia
Little Penguins (Eudyptula minor)
commonly called ‘fairy penguins‘ due to their small fairy-like size
Arrive ashore after feeding on ‘pelagic’ fish in Bass Strait in southern Australia‘Little Penguins‘, marine birds native to Australia and New Zealand, every day consume about their body weight (~1.2kg). Their prime food sources are small marine pelagic fish (76%) and squid (24%). [Source: ^http://www.graniteisland.com.au/pdf/parks_pdfs_little_penguins.pdf]
Given that the Australian breeding population across coastal southern Australia is estimated to be up to 500,000 individuals (Ross et al.1995), the Australian Little Penguin’s annual dependency on marine pelagic fish would amass over 450,000 kgs. (Calculation: 500,000 penguins * 1.2kg each * 76% = 456,000 kg of pelagic fish).
Their numbers are healthy but how vulnerable are they to pelagic overfishing?
.
Australia’s industrial exploitation of Nature
.
“Australia has the worst mammal extinction rate in the world. The destruction and fragmentation of habitat, particularly as a result of clearance of vegetation for agriculture, and the impact of feral animals and invasive weeds has had a substantial impact on our biodiversity.
Altogether, 18 mammal species have become extinct since the arrival of European settlers a little more than 200 years ago. Twenty percent of our remaining mammal species are threatened with extinction.”
[Australian Wildlife Conservancy,^http://www.australianwildlife.org/wildlife-and-ecosystems/australias-biodiversity-crisis.aspx].
Australia’s states of Tasmania and Queensland, with their renowned parochial politics, hold Australia’s unenviable reputation for the worst industrial exploitation of Nature and ecological destruction.
In Queensland the extent of recent land clearing is more than 425 000 hectares per year. Between September 2001 and August 2003, approximately 1 051 000 hectares of
woody vegetation was cleared (Government of Queensland, 2005). If Queensland were a country, it would rank 9th worst in the world in terms of land clearing. [^CSIRO]
In Tasmania, less than 20% of the original rainforest is left, and the ancient Styx Valley is being clearfelled and incinerated by Forestry Tasmania for loss-making woodchips at the rate of 300 to 600 hectares a year. [^The Wilderness Society] Many wild river valleys have been flooded by damned hydro, and vast landscapes scarred by mining and the groundwater toxins and tannins they leave behind. Industrial scale ecological destruction on an industrial scale still continues with parochial government’s short term profit myopia.
Tasmanian politics has a prejudiced record of giving industrialists free reign to plunder the environment, branded ‘primary industry‘:
.
Tasmania’s ‘Primary Industry’ legacy
.
- Since 1803 when the whaling ship Albion took three whales at Great Oyster Bay, colonists started a whaling and fur seal industry based on the Derwent River as well as on Bruny Island and up the east coast of Tasmania to Spring Bay (Triabunna) and Bicheno
- Convict slave labour from 1803 on the Derwent River was put to work deforesting the surrounding countryside
- Convict ‘Piners’ from 1819 who ransacked the extremely rare (endemic) Huon Pine from forests near Macquarie Harbour
- Since 1895, damming of rivers for hydro power and the flooding of many rivers and notably Lake Pedder in 1972 under the Great Lake Scheme, when the Hydro-Electric Commission became an industrial power unto its own from 1929 through to 1998
- Mining since 1820 for coal, tin, copper, gold, lead, zinc, silver and nickel – leaving scarred moonscapes around Mount Lyell, Zeehan, Savage River, Mount Bischoff, along the Ringarooma Valley, Fingal Valley, Beaconsfield and elsewhere.
- Since 1916, the construction of industrial and polluting smelters such as Amalgamated Zinc Company, then in 1921 the Nyrstar Hobart Smelter on the Derwent River, and since 1955 the Bell Bay aluminium smelter on the Tamar River
- The industrial deforestation of Tasmanian forests since convict times, accelerating with the advent of steam and rail from the 1850s. By 1996, 43% of Tasmania’s original wet
Eucalyptus forest had been logged and still 64.5% remain open for logging including Eucalyptus regnans —the world’s tallest hardwood trees, many of which are over 400 years old. [Rainforest Action Network, p.8] - The recent establishment of industrial pulp and timber producer Ta Ann south of Hobart and the current proposed Gunns’ pulp mill which collectively threaten to woodchip most of Tasmania’s remaining unprotected native forests. The approval process has been plagued by political abuse of due process and special deals for Gunns, lacking independent scrutiny or community support.
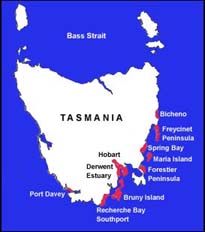 Map of 19th Century whaling bases on Tasmania’s coastline
Spring Bay was part of that exploitative legacy
Map of 19th Century whaling bases on Tasmania’s coastline
Spring Bay was part of that exploitative legacy
.
So what has this disgraceful legacy got to do with Little Penguins arriving ashore after feeding on pelagic fish in Bass Strait?
.
.
Greedy ‘Seafish Tasmania’ wants Bass Strait ecology
.
Tasmanian-based industrial fishing corporation, SeaFish Tasmania, is set to double its annual fishing catch of pelagic marine fish in Bass Strait from August 2012 from 5,000 tonnes to 10,600 tonnes. The problem is that such a massive quota risks jeopardising the sustainability of the fish populations and the dependent marine species that depend upon them.
Pelagic marine fish live near the surface of the water and range in size from small coastal forage fish like small herrings and sardines to large apex predator oceanic fishes like Southern Bluefin Tuna and oceanic sharks. Also feeding on pelagic fish are Little Penguins and Australia Fur Seals. Pelagic fish habitat stretches from inshore waters to offshore over the Australian Continental Shelf and variable continental slope waters at depths from the surface down to about 500 metres.
 Pelagic Pacific Jack Mackerel swim in schools near the sea surface
Pelagic Pacific Jack Mackerel swim in schools near the sea surface
.
Since 2000 Seafish Tasmania, based on Tasmania’s east coast at Spring Bay (Triabunna), has been the dominant Tasmanian fishing corporation targeting the Small Pelagics Fishery in southern Australian waters.
To date, Seafish Tasmania has relied upon its own purse seine trawler, the 800 tonne ‘Ellidi’ as well as two smaller contract vessels, to trawl for pelagic fish on the Continental Shelf off Tasmania. At its Triabunna factory, Seafish Tasmania converts its pelagic fish catches into a range of frozen seafood products for human consumption.both for domestic and export markets.
Seafish Tasmania also produces frozen Redbait specifically for the commercial Long-Line Fishing industry in Indonesia, the Pacific and Indian oceans.
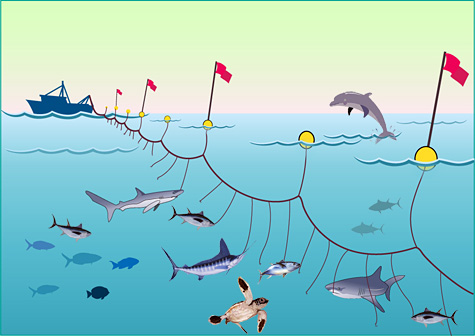 Long Line Fishing is indiscriminate
Long Line Fishing is indiscriminate
.
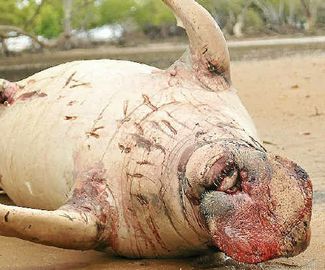
But Long line Fishing is cruel and indiscriminate. It is criticized worldwide for the merciless death of species such as sharks, turtles and seabirds, all caught unwanted as by-catch.
 Trapped Humpback whale
Caught in a Long Line Fishing net off Tonga in the Pacific in 2009
Trapped Humpback whale
Caught in a Long Line Fishing net off Tonga in the Pacific in 2009
This heart-breaking image shows the desperate plight of a whale trapped by equipment used in a controversial form of commercial fishing. The southern-hemisphere humpback became entangled in a long line and was spotted by a snorkeller last week fighting for her life.
Long lines, sometimes covering several miles, are left floating out in deep waters and have baited hooks placed on them every few metres. The fishing method has drawn criticism from conservation groups because they indiscriminately hook unwanted catches such as passing turtles, sharks and whales. Sadly for this female, she got snared near the Tongan island of Vava’u. Despite breaking free, she was left wrapped up in the line with several of the hooks imbedded in her flesh.
 Sea Turtles are no match for Longline Fishing.
Sea Turtles are no match for Longline Fishing.
.
The Marine Stewardship Council (has) allowed two eco-certifications for the use of longlines for swordfish fishing that will effect sea turtles and sharks drastically. For every swordfish caught, two sharks are killed. Every year 1,200 endangered sea turtles are hooked by longlines, resulting in drowning.
[Source: Sea Turtles And Sharks Are No Match For Longlines’, by Candice Chandler, Global Animal, 20120219, ^http://www.globalanimal.org/2012/02/19/sea-turtles-and-sharks-are-no-match-for-longlines/66846/http://www.globalanimal.org/2012/02/19/sea-turtles-and-sharks-are-no-match-for-longlines/66846/].
Seafish Tasmania’s supply of commercial bait to the Long Line Fishing industry raises concerns about the ecological ethics of Seafish Tasmania.
Seafish Tasmania also supplies fish meal and fish oil products for aquaculture feed and pharmaceutical fish oil products.  The research and development into these products supports ‘genetically modified‘ agriculture by AusBioech, headquartered at 322 Glenferrie Road, Malvern in eastern Melbourne. [Sources: ^http://www.ausbiotech.org/UserFiles/File/Code-of-Conduct.pdf, ^http://www.ausbiotech.org/directory/details.asp?companyid={FA8C42D7-EC6C-46BD-B065-BAA46BEE1963}&returntourl=%2Fdirectory%2Fsearch.asp%3Fpg%3D41]
The research and development into these products supports ‘genetically modified‘ agriculture by AusBioech, headquartered at 322 Glenferrie Road, Malvern in eastern Melbourne. [Sources: ^http://www.ausbiotech.org/UserFiles/File/Code-of-Conduct.pdf, ^http://www.ausbiotech.org/directory/details.asp?companyid={FA8C42D7-EC6C-46BD-B065-BAA46BEE1963}&returntourl=%2Fdirectory%2Fsearch.asp%3Fpg%3D41]
Seafish Tasmania’s involvement in GM aquaculture raises similar concerns about its ecological ethics.
.
Australia’s southern ‘Small Pelagic Fishery‘
.
Seafish Tasmania targets the following pelagic marine fish species in Australia’s southern Small Pelagic Fishery – Eastern sub-area for its chosen seafood markets:
- Jack Mackerel
- Blue Mackerel
- Redbait
.
However, this Small Pelagic Fishery (including eastern Bass Strait) provides a marine habitat to many diverse species of pelagic fish, which raises the question of the impact of non-targeted fish being caught as unwanted ‘bycatch‘?
Bass Strait lies between the Victorian coastline and the island of Tasmania, and the targeted Small Pelagics Fishery stretches eastward into the Tasman Sea. Its pelagic marine fish typically comprise Pilchards, Barracuda, Common Jack Mackerel (Trachurus declivis), Blue Mackerel (Scomber australasicus), Redbait (Emmelichthys nitidus), and Yellowtail Scad (Trachurus novaezelandiae). These attracts larger predators such as shark species preferring shallower depths such as Mako Sharks (Isurus oxyrinchus), Blue Sharks (Prionace glauca) and the Great White Shark (Carcharodon carcharias) which is listed by CITES as a protected species and similarly classified by the IUCN has having a ‘Vulnerable‘ status’.
But back in 1995, the marine health of Bass Strait was put into question when a 20-nautical-mile slick of dead pilchards was discovered off Devonport. The slick was thought to be caused by a mysterious deadly virus or toxin.
Tens of millions of pilchards were found floating dead in waters from Western Australia to Victoria. A merchant seaman had said that his cargo ship had sailed through 20 nautical miles of dead pilchards in Bass Strait. Mr Hamish Macadie, first mate on the Searoad Mersey, said he saw the fish about six nautical miles from the Devonport coast..
“They were floating on the water and were really thick in some areas. We sailed through about 20 miles of dead pilcards“, Mr Macadie said.
[Source: ‘Mystery Pilchard Deaths Cause Bass Strait `slick”, by Caroline Milburn, The Age, 19950509, ^http://www.toxin.com.au/toxin-articles/1995/5/9/mystery-pilchard-deaths-cause-bass-strait-slick/].
Australia’s coastal small pelagic fishes, which are often surface-schooling, includes several families which are often each represented by several species (see Allen 1997, Randall et al. 1997, Gomon et al. 2008), including the Clupeidae (sardines, herrings and sprats), Engraulidae (anchovies), Carangidae (scads, jack mackerel), Scombridae (short mackerels), Atherinidae (hardyheads, silversides), Arripidae (Australian herring) and Emelichthidae (redbait). [‘Pelagic Fishes and Sharks‘ by Hobday, Griffiths,Ward 2009 : 4]. Other fish species of Bass Strait include Majo Sharks, Gummy Sharks, Threshers, Yellowtail Kingfish and Snapper.
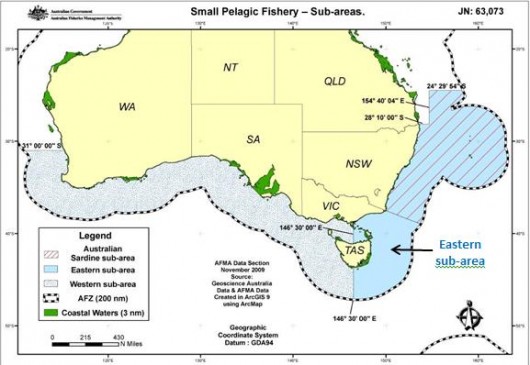 The Small Pelagic Fishery of the Eastern sub-area…’is just the beginning’
The Small Pelagic Fishery of the Eastern sub-area…’is just the beginning’But Seafish Australia’s utilisation of a factory trawler won’t be limited to just 10,600 tonnes of pelagic fish p.a.
It has in its sights the entire Small Pelagic Fishery across to Perth. This will deplete the fish stocks of the protected Great White Shark, so lookout surfers at Ceduna!! [Source: ^http://www.afma.gov.au/managing-our-fisheries/fisheries-a-to-z-index/small-pelagic-fishery/maps/]
.
Commonwealth Marine Reserves – Flinders and Freycinet Sanctuary Zones
.
The Small Pelagic Fishery set by the Australian Fisheries Management Authority ignores the marine ecologiccal values of the two delineated Sanctuary Zones of Australia’s South-east Commonwealth Marine Reserve Network. This includes the Flinders Commonwealth Marine Reserve and the Freycinet Commonwealth Marine Reserve (See green-shaded areas below).
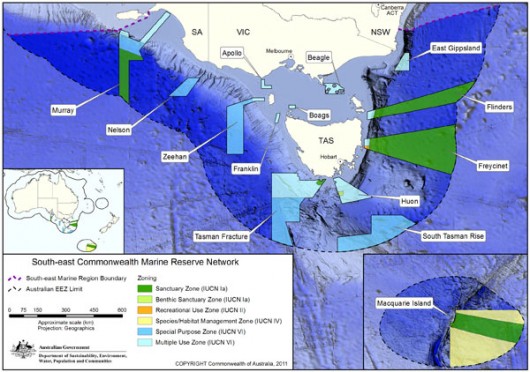 Yet the Australian Fisheries Management Authority’s (AFMA) map invades two IUCN Sanctuary Zones
i.e. the top two green shaded areas ‘Flinders’ and ‘Freycinet’
Yet the Australian Fisheries Management Authority’s (AFMA) map invades two IUCN Sanctuary Zones
i.e. the top two green shaded areas ‘Flinders’ and ‘Freycinet’.
This South-east Commonwealth Marine Reserve Network has been designed to contribute to the National Representative System of Marine Protected Areas (NRSMPA). The aim of NRSMPA continues to be to protect and conserve important habitats which represent all of Australia’s major ecological regions and the communities of marine plants and animals they contain.
Both the Flinders and Freycinet Commonwealth Marine Reserves were nationally proclaimed in 2007
March 2012: Tasmania’s parochialism again?
.
In Tasmania, when it comes to industrial exploitation, the old parochial adage still prevails – ‘it’s not what you know, but who you know‘.
Director of Seafish Tasmania, Gerry Geen, is:
“Advisor to Australia and international governments on fisheries management and fisheries economics.”
[Source: Seafish Tasmania website, ^http://www.seafish.com.au/_content/board.htm].
The fishing quota limits (Total Allowable Catch) for this Small Pelagic Fishery are periodically assessed and determined by the committee of Australian Fisheries Management Authority (AFMA), which takes advice specifically from the South East Management Advisory Committee (MAC). The fishing quota for this Small Pelagic Fishery for 2012-13 was agreed at a recent teleconference by the South East MAC on 26 March 2012, based upon the advise from the Small Pelagic Fishery (SPF) Resource Assessment Group (RAG).
Of note, two out of the ten members of the SPF RAG have pecuniary interests specifically in this Small Pelagic Fishery. Denis Brown has commercial fishing permits including in SPF zones A, B, C, and D and controls a Pelagic Fish Processors plant at Eden on the New South Wales south coast. While director of Seafish Tasmania, Gerry Geen, holds a Zone A purse-seine SPF Permit, four Tasmanian purse-seine Jack Mackerel Permits, a Southern and Eastern Scalefish and Shark Trawl Boat SFR permits.
The reported minutes of the South East MAC on 26 March 2012 teleconference included Total Allocable Catch Declarations as follows:
.
Recommended Total Allowable Catches for Blue Mackerel, Redbait and Yellowtail Scad for 2012/13 in the Eastern Zone
~ by the Small Pelagic Fishery (SPF) Resource Assessment Group (RAG)
Total Allowable Catch Recommendation #1:
- “Blue Mackerel 2,600 (Tier 2)
- Redbait 6,900 (Tier 1)
- Australian Sardine 200 (Tier 2)”
.
Total Allowable Catch Recommendation #3:
- “Increase the Jack Mackerel (east) Recommended Biological Catches (RBC) from 5,000 tonnes to 10,600 tonnes, subject to conditional support from the RAG’s conservation member and the RAG’s recreational member.”
.
[Source: ‘South East MAC Chair’s Summary from 26 March 2012 Teleconference – Small Pelagic Fishery Total Allowable Catch (TAC) Recommendations for 2012/13’, AFMA, ^http://www.afma.gov.au/managing-our-fisheries/consultation/management-advisory-committees/south-east-mac/south-east-mac-chairs-summary-from-26-march-2012-teleconference/].
Strangely enough, this teleconference dealt with the relevance of a ‘Factory Freezer Vessel‘ on the total allowable catch (TAC).
[Sources: ^http://www.theadvocate.com.au/news/local/news/general/company-partner-declared-conflict-in-catch-discussion/2586769.aspx, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/2012-06-01/fishing-authority-denies-conflict-of-interest/4046334].
June 2012: Factory Freezer Vessel (FV Magiris) chartered by Seafish Tasmania
 10,000 tonne Lithuanian-owned Factory Fishing Vessel ‘FV Margiris’
Recently contracted by Seafish Tasmania to trawl the Small Pelagic Fishery off Tasmania’s north east coast
Its draft of 5.5 metres is too deep for Spring Bay, so it must be operated out of Devonport
[Source: ^http://www.shipspotting.com/gallery/photo.php?lid=1220863]
10,000 tonne Lithuanian-owned Factory Fishing Vessel ‘FV Margiris’
Recently contracted by Seafish Tasmania to trawl the Small Pelagic Fishery off Tasmania’s north east coast
Its draft of 5.5 metres is too deep for Spring Bay, so it must be operated out of Devonport
[Source: ^http://www.shipspotting.com/gallery/photo.php?lid=1220863]
.
‘Super trawler operator Seafish Tasmania yesterday indicated it had begun the process of having the Lithuanian vessel Margiris registered as Australian.
Director Gerry Geen said the company aimed to start fishing in Australian waters (the Small Pelagic Fishery) by August 2012…
[Source: ‘Trawler approval begins’, 20120627, The Mercury (Hobart), ^http://www.themercury.com.au/article/2012/06/27/340551_tasmania-news.html].
The company has been granted an 18,000 tonne annual quota. Greens Leader Nick McKim told parliament the increase had been allowed because of the super trawler, Margiris.
“The Commonwealth quota for jack mackeral will be doubled” he said. “Now this makes a mockery of claims that it is science underpinning these decisions because, of course, the doubling has only occurred because this super trawler has applied to come down and work in Australian Commonwealth waters.”
[Source: ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/2012-06-21/greens-step-up-pressure-over-super-trawler/4084658?section=tas].
‘Supertrawler brings global problem to Australian waters’
[Source: ‘Supertrawler brings global problem to Australian waters‘, by Andrew Darby, Hobart correspondent for Fairfax Media, 20120611, ^http://www.smh.com.au/opinion/political-news/supertrawler-brings-global-problem-to-australian-waters-20120611-205b7.html].
 Vast swathe … the Margiris supertrawler. Photo: Greenpeace
Vast swathe … the Margiris supertrawler. Photo: Greenpeace
.
‘Say hello to our fishing future. It’s called Margiris. If ever Australians needed convincing that the global appetite for fish is our problem too, this supertrawler is it. Twice the size of the previous largest vessel ever to fish our Commonwealth waters, it measures 142 metres in length and weighs 9,600 tonnes. Its Dutch owners are changing its flag of registration from Lithuanian to Australian.
By August, it is scheduled to be roaming between the Tasman Sea and Western Australia in pursuit of 17,500 tonnes a year of small pelagic fish.
 Tagged … Greenpeace activists write on the side of the Margiris in the Atlantic off Mauritania in 2011
(Photo by Greenpeace, March 2011)
Tagged … Greenpeace activists write on the side of the Margiris in the Atlantic off Mauritania in 2011
(Photo by Greenpeace, March 2011)
.
But it’s not simply the size of FV Margiris that brings home the issue of rising industrial pressure on fish stocks. It’s the stark story of seafood market forces. Last March, in the Atlantic off Mauritania, Greenpeace activists wrote “plunder” on the side of the Margiris. They are campaigning against European operators who are taking West Africa’s fish, leaving locals catchless.
In Australia, the Margiris is set to catch the same sort of fish – jack mackerel, blue mackerel and redbait – and freeze them into blocks for export.
The destination of the catch? “The large majority will go to West Africa for human consumption, as frozen whole fish,” said Seafish Tasmania director Gerry Geen.
Australian fishers have long sought to exploit the country’s so-called “small pelagics”, which are prey for bigger fish such as tuna and marlin. Seafish Tasmania is partnering with ship owners Parlevliet & Van der Plas to do this on a scale previously unseen.
Alarms have been raised in other global fisheries about these mainly Europe-based small-pelagic hunters.
.
According to The New York Times, stocks of Jack Mackerel have dropped from an estimated 30 million metric tons to less than a tenth of that amount in just two decades.
.
The minutes of an Australian Fisheries Management Authority advisory committee show serious debate about the introduction of the Margiris. They reveal that Mr Geen, who was on the committee, gave “background” input. But because of his conflict of interest, he did not contribute to a recommendation to double the Australian eastern jack mackerel catch to 10,000 tonnes.
This has given the single greatest fillip to the Margiris venture. Mr Geen told the National Times the Margiris would take less than 5% of the total stock of small pelagics, as measured by surveys of egg production by the target species.
“I think people are worried about the size of the vessel, but that is really irrelevant,” he said. “It’s the size of the total allowable catch that counts.”
Other advisory committee members pointed to the ecological impact on existing fishers of taking so much of the small pelagics, even though these catches are outside state waters.
A coalition of global, national and state environment groups has written to Fisheries Minister Joe Ludwig, calling for the Margiris to be banned.
Right now it’s moored in the Netherlands, and Greenpeace is keeping an eye on its movements. Watch this space.’
.
..didn’t have to wait long..
 Greenpeace in The Netherlands: ‘Stop Exporting Overcapacity’
Greenpeace in The Netherlands: ‘Stop Exporting Overcapacity’
.
On 28th June 2012, Greenpeace activists in the Netherlands attached themselves to the mooring ropes and chained the ship’s propellers of the super trawler FV Margiris, to delay its journey to Australia to serve Seafish Tasmania’s plans to overfish 18,000 toinnes of pelagic fish.
Greenpeace spokesman Nathanial Pelle said:
“Really this is to demonstrate that the European Commission, which has committed to reducing its capacity, shouldn’t be allowed to ship its oversized fleet off to other fisheries around the world and that goes for Australia as well.”
[Source: ‘Greenpeace protest delays super trawler’, 20120628, ABC, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/2012-06-28/greenpeace-protest-delays-super-trawler/4098672].
“The MAC noted some concerns raised in relation to the proposed TAC for jack mackerel (east) suggested that a super trawler might also have differential impacts on the stock and ecosystem.”
~ South East Management Advisory Committee (MAC) Chairman Steve McCormack noted.
.
Of Course the Maritime Union of Australia (MUA) celebrated Seafish Australia’s strategy as “A Shot In The Arm For Tassie Economy” , given that the MUA is only narrowly self-interested in its members. MUA Assistant National Secretary, Ian Bray, said the news of new jobs was welcome.
“This initiative is welcome news for Tasmania’s seafarers and maritime workers”, Mr Bray said. “This is just the kind of development the Tasmanian economy needs. We’re pleased that there will be new jobs for Tasmanians”, Mr Hill said.
[Source: ‘ “A Shot In The Arm For Tassie Economy”, MUA Media Release, 20120605, The Maritime Union of Australia (MUA), ^http://mua.org.au/news/seafish-tasmania-announcement-a-shot-in-the-arm-fo/].
Footnote
Super Trawler: AFMA did not follow the law
[Source: ‘Super Trawler: AFMA did not follow the law’ , by Andrew Wilkie MP,Independent Member for Denison MR, 20130115, Tasmanian Times,
^http://tasmaniantimes.com/index.php?/weblog/article/super-trawler/]
The Commonwealth Ombudsman has written to me outlining his findings in response to my complaint that the Australian Fisheries Management Authority (AFMA) erred when setting the quota relevant to the super trawler Margiris.
The Ombudsman found that AFMA did not follow the law when the South East Management Advisory Committee finalised its recommendation for the quota relevant to the super trawler.
In particular the Ombudsman found that one of the members of that committee had a financial conflict of interest but was allowed to remain in, and contribute to, discussions about the quota.
As a direct result of the Ombudsman’s investigation AFMA has undertaken remedial and corrective steps to address the substantive issues arising from my complaint.
The Ombudsman has also forwarded material to the Federal Government’s review of fisheries legislation.
Seafish Tasmania has responded by attacking the Ombudsman which is clearly a case of attacking the messenger who found very serious problems with fisheries management in Australia.
Seafish claims the Ombudsman “had completed the investigation and found nothing to report’’. In fact the Ombudsman’s letter to me of 18 December 2012 outlining the results of the inquiry runs to four pages and includes the findings “processes relating to a scheduled meeting of the South East Management Advisory Committee (SEMAC) on 26 March 2012 were not in accordance with legislative requirement’’ and that the “conflicted SPFRAG [Small Pelagic Fishery Resource Assessment Group] members did not seek approval to remain at, and participate in, group deliberations after declaring the conflict [of interest]’’.
In other words my complaint to the Ombudsman that AFMA did not follow proper process when it set the quota relevant to the Margiris has been upheld.
Seafish claims I didn’t release the letter because it didn’t suit my “agenda’’. In fact I decided not to release the letter during the Christmas/New Year holiday period because it was simply too important a document to bury during the holiday period and subsequent bushfire emergency. Moreover I did hand the letter to the Mercury newspaper this morning, well before Seafish issued its media release.
Seafish notes the Ombudsman’s report (which it claims to have not seen) offers no comment on Director Gerry Geen or Seafish itself. But in fact Mr Geen is well known as being the relevant member of SEMAC and SPFRAG.
Seafish claims my comments last year about the Ombudsman investigating “other matters’’ was some kind of beat up. But in fact it was the Ombudsman who
referred to other matters being under investigation and the Ombudsman’s letter to me does in fact address other issues, and in particular the conflict of interest and communications difficulties associated with the SPFRAG.
Seafish Tasmania claims there is now no question mark over the quota relevant to the Margiris. But in fact all the Ombudsman says is that “it does not necessarily follow that errors in the SEMAC process operate to invalidate the TAC [Total Allowable Catch]’’ and goes on to note the review of fisheries legislation which is still ongoing.
That there were at least very serious problems within AFMA is beyond question for all, it seems, other than Seafish Tasmania. The Federal Government has already identified the need for a roots and branch review of fisheries legislation and the Ombudsman’s letter to me lists 11 AFMA actions as a result of my complaint.
.