Ironbark Firewood: receiving stolen forests?
Friday, May 18th, 2012 The classic image of the ‘Camp Fire’
The classic image of the ‘Camp Fire’
.
Australia’s tradition of the ‘Wood Fire’ is ecologically destructive
.
During Australia’s winter months, many in older homes habitually yearn for the warmth and glow of a traditional Wood Fire, and so utilise their open fire places and wood heaters. So habitually, upon the onset of winter people stock up on Firewood. It is a cultural yearning for the nostalgia of the Wood Fire – warm, earthy, dancing flames, flickering, spark spitting, the woodsmoke – we’ve all been there, it is tantalising and it feels right because it is natural – the ancient campfire tradition across humanity. In doing the Wood Fire ritual, we seek to rekindle our connection to Nature.
 The warmth and glow of a traditional Open Fire
…but the demand is driving deforestation of Ironbark Forests
The warmth and glow of a traditional Open Fire
…but the demand is driving deforestation of Ironbark Forests
.
In earlier times when a few hundred of us settled in a given forest region, few forest resources were taken and so the forests replenished and seemed to cope. The forests were naturally resilient.
But as subsequent human hoards have invaded the land, and have bred and sprawled across the countryside in the hundreds of thousands, we have deforested entire forests in the process. These forests haven’t coped with the devastation. No forest could cope.
Australia’s native forests have been hacked, logged, burned and bulldozed into agrarian pasture to the horizon. Australia’s original blanket vegetation cover has been reduced to sad islands barely able to support wildlife habitat and in many cases causing extinctions – locally, regionally and nationally. All one needs do is a Google Earth search to appreciate the devastation on the natural landscape.
 A legacy of forestry
A legacy of forestry
.
Humanity’s sheer numbers and the encouraged consumption rate of Australians risk exacerbating the deforestation. Contemporary Australia is simply extending and perpetuating the old colonial exploitive mindset and a lifestyle reminiscent of 19th Century invading colonists.
The cultural heritage of the Wood Fire is necessarily contributing to this deforestation, particularly to Australia’s native Box-Ironbark Forests.
For Australians to continue to yearn for the glow, warmth and woodsmoke of the traditional Wood Fire now that we number in the hundreds of thousands, if not millions, and so the aggregate consumption of timber for firewood has simply become unsustainable. Our native forests have become too small and disparate to sustain wildlife breeding.
The few shrinking native forests that our forebears and their frenzied clearing have left us, simply are disappearing. Australia’s remnant native forests continue to be destroyed by us just to serve this selfish cultural yearning for earthy nostalgia of the Wood Fire. The same applies to all woodheaters.
 A classic wood fire in an old style open fireplace
A classic wood fire in an old style open fireplace
.
The Australian Wood Fire cultural imperative through winter has become a driver of forest extinctions. There have become too many of us wanting tonnes of the forest to burn in our open fires and wood heaters, and too few forests left.
Australia’s firewood demand is driving deforestation. There is estimated to be around 800,000 wood heaters and 700,000 open fire places in Australia (ANZECC, 2001). There combined use is unsustainable and has got to stop! We need to question this inherited and habitual Open Fire/Woodheater culture and the devastating impact it is causing to our native forests.
.
“One of the hidden environmental issues affecting Australia’s woodlands, the collection of firewood, is starting to be revealed. CSIRO has prepared a report, Impact and Use of Firewood in Australia, pointing out alarming environmental problems. For example, up to 6 million tonnes of fuelwood is consumed in Australia each year – double the amount of annual exports of eucalypt woodchips!”[Source: ‘Firewood Conference’ in Armidale, NSW, May 2001, ^http://dazed.org/npa/npj/200102/FebYourNPA.htm]
.
Commercial Firewood is Forest ‘Eco-theft‘
.
Firewood taken from a native forest for personal use is one thing. The scale and severity of adverse impact upon forest ecology will vary according to the amount taken and the ecological sensitivity of the place it is taken from. Few domestic takers of firewood will be qualified ecologists and so will have no or little comprehension or respect for such impacts.
 A private firewood stack
A private firewood stack
.
According to the CSIRO, up to 5.5 million tonnes of timber is harvested annually for Australian domestic firewood use. When industrial firewood use is included, the total amount rises 20% to between 6-7 million tonnes. This weight is roughly double the amount of eucalypt currently exported annually from Australia as woodchips. About half of all domestic firewood is collected by the consumer and 84% of domestic firewood is collected on private property. [CSIRO, 2000]
Across Australia, access to State Forests is unfettered and the collecting of firewood for personal (domestic) consumption is an uncontrolled free-for-all, little improved from the exploitative mindset of Australia’s early and more ignorant colonists.
 Australian colonial ‘progress’
Australian colonial ‘progress’
.
Deforestation by firewood taking is perhaps not as broadscale and well known as the Conservation Movement’s exposure of state-sanctioned Industrial Logging by the likes of Australian state government departments:
- ‘VicForests‘ (Victoria)
- ‘Forests NSW‘ (New South Wales)
- ‘Forestry SA‘ (South Australia)
- ‘Forestry Tasmania‘ (Tasmania)
- ‘Forests and Wood‘ (Queensland)
- ‘Forests Products Commission‘ (West Australia)
.
Or is it?
It is Australia’s Commercial Firewood Industry that contributes to the demise of Australia’s remnant native forests by its ‘death by a thousand cuts‘. Commercial Firewood entails the direct taking of wood from Australia’s native forests for commercial sale and profit. It is of a scale far greater than domestic forewood collecting, but where are the statistics kept and publicised by the Australian Government?
Just as demand for firewood drive supply, the artificial low economic cost of firewood encourages demand volume. Since firewood is sold a low cost, it competes favourably with jalternatiuve sources of fuel, such as gas and electricity, for domestic heating. Commercial firewood suppliers also deliberately appeal to the Wood Fire cultural image to encourage their firewood sales. Suppliers and consusmers thus feed off each other at low cost and high volumes, and so more native forests lose out.
 A commercial firewood stack
A commercial firewood stack
.
The low or no cost availability of timber from State Forests Native timber means that the industry operates on an industrial scale taking vast quantities of timber, particularly from the preferred hardwood Box-Ironbark Forests and the like. The Commerical Firewood Industry is encouraged by the Australian Government and by all state governments, which ignore the practice as if Australia’s natuve forests are unlimited, as if it had no adverse ecological impact upon the forest ecologies, as if it didn’t matter, as if there were no tomorrow.
 Commercial Firewood Production
Norwegian Hakki-Pilke industrial machinery enables an industrial scale operation
[Source: Mascus Australia, ^http://www.mascus.com.au/]
Commercial Firewood Production
Norwegian Hakki-Pilke industrial machinery enables an industrial scale operation
[Source: Mascus Australia, ^http://www.mascus.com.au/]
.
Across Australia, each state government issues cheap permits for collecting firewood from State Forests.
This reflects:
- A cultural disregard for the values of Australia’s disappearing forest ecologies up to Prime Ministerial and Cabinet level
- The inadequacies of State laws to protect forest ecology
- An antiquainted colonist mindset persisting throughout the dominating Liberal and Labor parties.
.
The ecological impacts and the plethora of ecological advice and warnings about the destructive impacts of logging on forest ecology are being ignored. Australia’s Commercial Firewood Industry fuels demand for cheap firewood and in the process exacerbates Australia’s deforestation.
Australia’s Firewood Industry is unsustainable and has got to be nationally controlled. We need to challenge this exploitative industry and correct ignorant government policies. We need to find alternatives to the Wood Fire to stem the devastation of Australia’s remaining native forests and to help prevent more wildlife extinctions.
.
‘Forest Eco-theft’ involves the immoral taking of timber from a native forest, especially in large industrial quantities, for commercial gain and incurring no or little economic cost to the taker. The intended or actual use of the timber is irrelevent, but may include logs, firewood, craft timber, or woodchips. The greater the timber volume taken, the greater impact upon a forest and so the more serious the Eco-theft.
.
‘Eco-theft’ is only different to criminal theft because of the colonist exploitative mindset of current governments rejecting native forest having ecological value worthy of protection under the Crimes Act.
.
 An industrial scale Hakki-Pilke firewood processor from Norway
An industrial scale Hakki-Pilke firewood processor from Norway.
Forest Eco-theft in an environment of dwindling forest habitat has become a key threatening process. At the current rate of Forest Eco-theft, Australia’s native forests fueling our pleasure for earthy glows and hearth warmth, will be gone.
Firewood Logging simply destroys forest habitat and contributes to the demise and local extinctions of threatened and endangered wildlife. Australia’s flora and fauna deaths and ultimate extinctions has become infamy – Australia currently has the worst record of mammalian extinctions on the planet, and the Firewood culture is contributing to it.
Many consumers of firewood either actively couldn’t care, or else passively turn an insular blind eye to the adverse ecological impacts of firewood harvesting. Our Australian Government ignores the firewood deforestation problem, avoiding it for party political convenience – immorally, irresponsibly and unrepresentingly.
Just as Poaching Wildlife is immoral, so too is Forest Eco-theft. Both these exploitative practices hark to colonial times and need to be banned.
 Firewood Logging of State Forest near Taralga NSW in 2006.
(along the Goulbourn-Oberon Road, just west of the Blue Mountains)
“This is in the habitat of Diuris aequalis. Had a fair result after two visits to this site and three submissions to local Council. Department of Environment and Conservation have imposed rigid conditions on this business.”
Firewood Logging of State Forest near Taralga NSW in 2006.
(along the Goulbourn-Oberon Road, just west of the Blue Mountains)
“This is in the habitat of Diuris aequalis. Had a fair result after two visits to this site and three submissions to local Council. Department of Environment and Conservation have imposed rigid conditions on this business.”[Source: ‘Habitat – Protection or Destruction‘, 2006, by Alan W Stephenson, Conservation Director, Australian Orchid Council Inc.
^http://www.orchidsaustralia.com/article_%20conservation_no3.htm]
.
.
Why choose ‘Ironbark Firewood’ ?
.
Why choose Ironbark Firewood ? Why not choose an alternative sources of fuel for home heating? Never thought to question the legitimacy of your fuel?
Here’s the justification by one firewood supplier as to why one should choose Ironbark Firewood:
- ‘Long Burning. Harder to start but will burn 6 – 8 hours. These timbers are the slowest growing and the hardest of all hardwoods.’
- ‘Very little ash. Clean out fire only once per season approximately.’
- ‘Strong Burning. Cannot be put out even if the vent closed, unless water is used.’
 A classic Ironbark ‘Open Fire’
A classic Ironbark ‘Open Fire’
.
The most common type of firewood commerically sold and promoted in the eastern Australian states is Ironbark Firewood. This is typically sourced from Box-Ironbark Forests (native grassy woodlands).
According to the Firewood Association of Australia (FAA), Ironbark and Box are the preferred firewood in Queensland, while in Victoria, southern NSW and South Australia, River Red Gum is preferred. Jarrah and Wandoo hardwood timbers are preferred in Western Australia, while in Tasmania, Brown Peppermint is considered the best firewood.
[Source: ^http://www.firewood.asn.au/faq.html].
 What the hell?
Old Growth cut up for cheap firewood?
What the hell?
Old Growth cut up for cheap firewood?
[Source: “Environmental vandals” cut down 100-year-old trees on land at East Maitland, 20180905, by Donna Sharpe, ^https://www.beaudeserttimes.com.au/story/5629093/chainsaw-massacre-environmental-vandals-cut-down-100-year-old-trees/]
.
Sydney’s Firewood has been linked to ongoing Queensland land clearing, and in Queensland successive backward state governments have an ignoble reputation for land clearing like there’s no tomorrow.
Landclearing in Queensland has become the major supplier of Sydney’s quality firewood. Most of Sydney’s big firewood companies now rely on the Sunshine State for a significant proportion of ironbark and box logs – highly sought-after timbers because of their density. The National Parks Association says firewood from endangered Queensland woodlands is being used in homes across New South Wales.
Back in 2001, the National Parks Association of NSW called on the NSW Government to limit the State’s use of firewood following revelations that most of the wood sold by Sydney’s big firewood companies comes from clearing of Queenslands threatened Ironbark and Box woodlands.
 Ironbark Woodland of Central Queensland
[Australia Natural Resource Atlas]
Ironbark Woodland of Central Queensland
[Australia Natural Resource Atlas]
.
At the time, Mr Charlie Spiteri, the owner of Betta Burn Firewood, one of the biggest suppliers in Sydney, refused to reveal how much firewood he supplies each year but estimates that the Sydney region, including Katoomba, consumes about 100,000 tonnes.
 Commercial Firewood stockpile
(click photo to enlarge)
Commercial Firewood stockpile
(click photo to enlarge)
.
Spiteri said about a third of his supply was sourced from Queensland, where the wood is worth between $40 and $50 a cubic metre. By the time the freight reaches Sydney, it is worth up to $125 and is being snapped up. “People are choosing ironbark and box and we have to go where the timber is,” Mr Spiteri said.
Other major sources of hardwoods for Betta Burn include the Pilliga State Forest in north-west NSW and private properties in the Nyngan area.
Executive officer at the National Parks Association (NSW), Mr Andrew Cox, said:
“Firewood collecting is the second largest threat to Australia’s temperate woodlands after land clearing. Now its being linked to landclearing!” “We know little about the impacts of firewood collecting and governments have been slow to take an interest. Most firewood consumers are unaware of where their wood comes from or the huge impact it has on threatened animals, birds and reptiles.”
“The firewood industry is large, but mostly unknown”, said Andrew Cox, NPA Executive Officer. “About 1,500,000 tonnes of firewood are used by New South Wales each year, exceeding the State’s yearly combined production of sawlogs and woodchips.”
“Firewood collecting targets slow-growing ecosystems and some of their most important components. Eucalypt species such as ironbark, box and red gum are the most favoured firewood sources.”
“We need to move away from the need to ‘clean-up’ a forest or woodland and instead look at dead wood as an important ecological component – just as important as the living trees.”
“Its because we’re not properly managing the woodlands that a wave of bird extinctions is underway in central NSW. More than 20 woodland dependent birds are declining from their former range and may become extinct in NSW. “It’s not ecologically sound, it’s not sustainable and there are serious impacts on birds, on animals that depend on the hollows.”
But no-one knows for sure how much timber salvaged from the bulldozed woodlands of Queensland is making its way south of the border in convoys of semi-trailers. Firewood collection operates in a legal vacuum – especially on private land – and virtually no figures are kept for where wood is sourced or how it is collected.
[Source: ‘Sydney’s Firewood Linked to Queensland Land Clearing‘, by Andrew Cox, Executive Officer, National Parks Association of NSW, 20010428, ^http://dazed.org/npa/press/20010428firewood.htm] A typical commercial firewood truck – 2 tonne?
A typical commercial firewood truck – 2 tonne?
.
Since then, over a decade ago, what has changed? Anything? Nothing? Has the problem gotten worse?
.
83% of the original Box-Ironbark Forests have gone
 Box Ironbark forest in central Victoria dominated by Red Ironbark (Eucalyptus tricarpa)
Box Ironbark forest in central Victoria dominated by Red Ironbark (Eucalyptus tricarpa)[Source: Ian Lunt’s Ecological Research Site, ^http://ianluntresearch.wordpress.com/2012/01/20/fire-and-rain-2-water-for-ironbarks/]
In Victoria, few forest and woodland ecosystems are as poorly represented in parks and reserves as the distinctive Box-Ironbark ecosystems of northern Victoria.
Since European settlement these forests and woodlands have been extensively cleared and fragmented for agriculture, urban development and gold mining, and cut for a variety of wood products. They once covered three million hectares of northern Victoria, but 83% of the original Box-Ironbark vegetation has now been cleared.
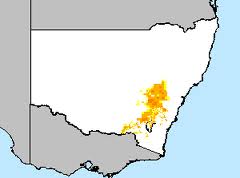 Original distribution of grassy woodlands across New South Wales
Original distribution of grassy woodlands across New South Wales(Dominated by Box-Ironbark Forests)
.
Not only have the forests and woodlands been mostly cleared, but what is left is highly modified from its original structure and is also very fragmented. These remaining forests and woodlands are mostly on public land and these areas are ecologically important for a rich diversity of flora and fauna, many of which are rare or threatened.
Box-Ironbark forests and woodlands are highly accessible and the visitor is rewarded by a vibrant array of bird species, carpets of wildflowers in Spring, the rich aroma of eucalypt nectar, and many sites of historical and cultural interest. Despite their apparent uniformity, these forests actually have great diversity with around 1 500 species of higher plants and over 250 vertebrate species recorded in the region; many are largely restricted to Box-Ironbark forests and woodlands.
Some 297 Box-Ironbark plant species and 53 animal species are now classified as extinct, threatened or near-threatened. In addition, at least ten plant and animal species are known to have disappeared from the study area since the 1840s, and numerous others have become locally extinct. It is also clear and of great concern that many species, particularly birds, are known to be still declining.
Accordingly, a key feature of Box-Ironbark nature conservation is the promotion of ‘recovery’ for many species, rather than simply maintaining the status quo. Many Australian animals are dependent upon large, old eucalypt trees which contain the hollows required for shelter and breeding. At least six of the threatened Box-Ironbark fauna species are strongly dependent upon these trees. The massive loss of large old trees over the last 150 years is strongly implicated in the decline of these species and perhaps many others. It is therefore recommended that as well as protecting existing large old trees, additional measures be taken to ensure that there will, over time, be more large old trees in the forests.
[Source: ‘Box-Ironbark Forests & Woodlands Investigation‘, (Environment Conservation Council, 2001), Executive Summary, by The Victorian Environmental Assessment Council, 2001, ^http://www.veac.vic.gov.au/documents/385-Executive-Summary.pdf]
 .
.
‘Why is Firewood so cheap?
.
Ironbark is a preferred firewood in eastern Australia because it burns longer and hotter, so Australia’s native Ironbark forests continue to be logged for firewood.
 Ironbark firewood stack, commercially cut and split ready for domestic delivery
Ironbark firewood stack, commercially cut and split ready for domestic delivery
.
The Australian hardwood timber industry now mainly relies upon plantation timbers and sustainable forestry management practices. Australian Ironbark Flooring retails at a premium price at typically over $80/m2 at 19mm thick. If that square meter of flooring was stacked one metre high to achieve a cubic metre, the calculated retail price for a cubic metre would be (1000m/19mm = 50 layers of flooring roughly, making the retail price for a cubic metre of Ironbark flooring around $80 x 50 = $5600/m3!
 Expensive Ironbark Flooring
Sourced from sustainable plantation timber, unaffordable to the Commercial Firewood Industry,
so firewood suppliers take the Ironbark out of State Forests instead.
[Source: Northern Rivers Timber, ^http://www.northernriverstimber.com.au/gallery.php]
Expensive Ironbark Flooring
Sourced from sustainable plantation timber, unaffordable to the Commercial Firewood Industry,
so firewood suppliers take the Ironbark out of State Forests instead.
[Source: Northern Rivers Timber, ^http://www.northernriverstimber.com.au/gallery.php]
.
But commercial suppliers of firewood do not own plantation timber, nor do they buy their firewood from plantation timber growers. They certainly do not pay $5,600/m3 for firewood.
Commercial firewood is generally sold at considerable profit at under $160/m3, reducing in price according to volume purchased. Why would an commercial grower of plantation Ironbark hardwood sell the timber for firewood at $160/m3, when as flooring the typical market price is a factor of some 35 times greater at $5600/m3?
.
Commercial Firewood taken from native forests means that the $160 selling price is nearly all profit!
.
Australia’s commercial firewood instead is simply taken from Australia’s native hardwood forests. It is simply taken from State Forests at no cost to the commercial operator, except for a pultry token permit fee. That is why it is sold so cheaply.
This is why firewood remains a cheap affordable source for domestic household heating. But the cost is artifically economic and excludes the ecological cost.
How is this not Forest Eco-Theft? If the suppliers of Ironbark Firewood had to pay hardwood plantation owners a fair wholesale price for firewood, at such a high price their business model would be unviable. Firewood suppliers only exist because their business model relies upon firewood theft from dwindling State Forests, which continues to go unpoliced and ignored by the Australian Government.
 Industrial Firewood Industry
Industrial Firewood Industry
.
Where do YOU get your FIREWOOD from?
.
- Where do you get your firewood from?
- Is it legal or eco-stolen?
- Is it accredited?
- What is Australia’s Firewood Industry doing to protect Australia’s long exploited and dwindling Ironbark Forests from firewood theft by firewood suppliers?
- What is the Australian Government doing to prevent firewood theft from State Forests?
- What is the Australian Government doing to monitor and control Australia’s firewood industry?
- Who in the Australian Government monitors the integrity and ecological protection of State Forests across New South Wales and indeed across Australia?
- Where is the ongoing review and analysis into the ecological health of Box-Ironbark Forests (Grassy Woodlands) across New South Wales and Victoria?
- Why are the statistics on firewood theft from State Forests not collected and publicised?
- Who polices and penalises deforestation of State Forests?
- How many people are caught and fined/gaoled for deforestation of State Forests
- Isn’t it illegal to steal firewood from State Forests – living trees or deadwood?
.
At the time of publication of this article, the New South Wales Government’s official website on Environment and specifically on Threatened Species reads:
“There has been a serious system failure on the threatened species website (www.threatenedspecies.nsw.gov.au) and it is no longer available”
[Source: ^http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/threatenedspecies/].
 Pile of Ironbark Firewood cut and split ready for domestic delivery
Pile of Ironbark Firewood cut and split ready for domestic delivery
.
In the Blue Mountains of New South Wales, the local newspaper advertises numerous suppliers of firewood, particularly at the onset of winter, and particularly promoting Ironbark Firewood as the premium product as follows:
Firewood suppliers advertising in the Blue Mountains Gazette, 20120516.
But from where do these firewood suppliers source their firewood?
Not one of the above advertisements provides any proud statement about sourcing their wood ecologically responsibly, nor about being ecologically accredited. The default presumption thus is that none of these suppliers is environmentally responsible, nor accredited. So don’t buy from any of them!
Is the advertised firewood sourced illegally from Australia’s disappearing Box-Ironbark Forests, and so exacerbating the deforestation problem? How do we know it isn’t?
How simple is it for any common thief to buy a chainsaw, drive out to a patch of State Forest in a ute or in a truck or with a trailer in tow, then chainsaw several trees in a Box-Ironbark Forest, paying nothing for them, then flog the wood for personal profit? Too easy! Anyone can buy a chainsaw from a local garden tool supplier, even a kid. There are no chainsaw laws in Australia. It is treated like buying secateurs. Bunnings sells cheap chainsaws brand-new for just $200!
So armed with a trailer and chainsaw, a common thief has a lucrative business, one ignored by the Australian Government. With firewood retailing from $160/cubic metre, it is a nice little earner. This exploitative immoral trade in Ironbark Forest ecology is negligently condoned by the Australian Government and state governments.
 A native tree cut for firewood
A native tree cut for firewood(Blackheath Fire Brigade, Rural Fire Service, Blue Mountains, November 2011)
.
‘Forest Eco-theft’ wiping out Ironbark Habitat
.
Logs have life inside
.
‘Collecting firewood is one of humankind’s oldest activities. Australians enjoy the beauty and warmth of a wood fire, and in many regional areas wood fires are the only practical source of heating.
Dead trees, often with hollows, make popular firewood as they are seasoned and burn well. But firewood collection comes at a cost to the environment, the consequences of which may not be entirely understood for years. Many firewood users are unaware of the ecological price of collecting dead trees and fallen logs. Often they mistakenly think they are just keeping the forest or farm tidy.
Firewood harvesting has an effect on our native woodlands, and a variety of threatened species. Dead standing and fallen timber provides crucial habitat for numerous species of animals and birds. It is now recognised that the removal of this wood for firewood is contributing to a significant loss of wildlife, particularly in the woodlands of south-eastern Australia. It is not just native animals that benefit from old wood left lying on the ground. This debris is valuable shelter for stock too. How many times have you found a newborn calf or lamb against an old log safe from the weather?
 Habitat Tree of critical value to wildlife
…destroyed by Forestry NSW
Habitat Tree of critical value to wildlife
…destroyed by Forestry NSW
.
Not only does standing and fallen dead wood provide important habitat for animals and birds, it also plays an essential role in maintaining forest and woodland nutrient cycles. Scientists from the CSIRO believe that dead wood is at least as important as living trees, fallen leaves and soil for the maintenance oif ecological processes sustaining biodiversity.’
[Source: ‘Are you burning their homes to warm yours?‘, a brochure questioning the dependency on firewood), by The National Heritage Trust. The Natural Heritage Trust (the Trust) was set up by the Australian Government under the Natural Heritage Trust Act 1997 to help restore and conserve Australia’s environment and natural resources. The Trust had three overarching objectives: (1) Biodiversity Conservation, (2) Sustainable Use of Natural Resources, and (3) Community Capacity Building and Institutional Change. The Natural Heritage Trust ceased on 30 June 2008. It has been replaced by Caring for our Country, but taking supplanting a natural heritage conservation philosophy with a more anthropocentric utilitarian ‘resource management’ philosopy, ^http://www.nrm.gov.au/].
 Cleaning up some messy dead timber – through whose eyes?
Nature is naturally ‘messy’
Cleaning up some messy dead timber – through whose eyes?
Nature is naturally ‘messy’
.
The Regent Honeyeater has become a ‘flagship species’ for conservation issues in the box-ironbark forest region of Victoria and New South Wales.
 Regent Honeyeater (Anthochaera-phrygia)
Nationally listed as ‘Endangered‘.
Listed as endangered in Queensland and New South Wales, while in Victoria it is listed as threatened.
[Source: ^http://www.birdsinbackyards.net/species/Anthochaera-phrygia]
Regent Honeyeater (Anthochaera-phrygia)
Nationally listed as ‘Endangered‘.
Listed as endangered in Queensland and New South Wales, while in Victoria it is listed as threatened.
[Source: ^http://www.birdsinbackyards.net/species/Anthochaera-phrygia]
.
Australia’s native Regent Honeyeater, was formerly more widely distributed in south-eastern mainland Australia from Rockhampton, Queensland to Adelaide, South Australia, but is now confined to Victoria and New South Wales, and is strongly associated with the western slopes of the Great Dividing Range. Its natural habitat is eucalypt forests and woodlands, including Box-Ironbark Forests.
The Regent Honeyeater has been badly affected by land-clearing, with the clearance of the most fertile stands of nectar-producing trees and the poor health of many remnants, as well as competition for nectar from other honeyeaters, being the major problems. Birds Australia is helping to conserve Regent Honeyeaters as part of its Woodland Birds for Biodiversity project.
[Source: Birds Australia, ^http://www.birdsinbackyards.net/species/Anthochaera-phrygia, and further references: ‘Field guide to the birds of Australia, 6th Edition’, ‘The Honeyeaters and their Allies of Australia’].
 Leard State Forest Leadership
(New South Wales)
[Source: ^http://www.kateausburn.com/2012/04/10/leard-state-forest-next-frontier-of-the-coal-industry/]
Leard State Forest Leadership
(New South Wales)
[Source: ^http://www.kateausburn.com/2012/04/10/leard-state-forest-next-frontier-of-the-coal-industry/]
.
Further Reading:
.
[1] ‘Box-Ironbark Forests & Woodlands Investigation‘, by The Environment Conservation Council, 2001) by The Victorian Environmental Assessment Council, Australia,^http://www.veac.vic.gov.au/investigation/box-ironbark-forests-woodlands-investigation-ecc-
‘This report contains the ECC’s recommendations for public land use in the Box-Ironbark area of northern Victoria, extending from Stawell to Wodonga. The recommendations incorporate those for parts of the LCC’s North Central, Murray Valley and adjoining areas.’ (>Read Report, PDF 6.6MB – large file may be slow to load)
.
[2] ‘National Approach to Firewood Collection and Use in Australia‘ , June 2001, Australian and New Zealand Environment Conservation Council (ANZECC), Australia,^http://www.environment.gov.au/land/publications/pubs/firewood-approach.pdf (>Read Report , PDF 990kb).
[3] ‘Impact and Use of Firewood in Australia‘, by Don Driscoll, George Milkovits, David Freudenberger, CSIRO Sustainable Ecosystems, Australia,^http://www.environment.gov.au/land/publications/pubs/firewood-impacts.pdf, (>Read Report, PDF 400kb)