‘Prescribed Burning’ is a greenhouse gas
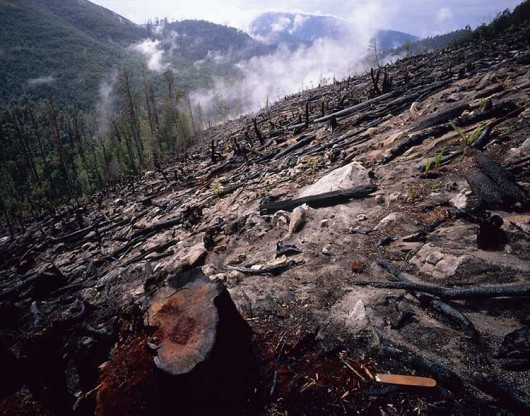 What’s left of Tombstone Creek old growth rainforest in Tasmania after a ‘Planned Burn’
This wet forest was dominated by sassafras, myrtle, tree-ferns and tall Eucalyptus after logging and subsequent regeneration burn, 2006. It is situated at the headwaters of the South Esk River catchment water supply for the town of Launceston.
(Photo by Rob Blakers, 2006)
What’s left of Tombstone Creek old growth rainforest in Tasmania after a ‘Planned Burn’
This wet forest was dominated by sassafras, myrtle, tree-ferns and tall Eucalyptus after logging and subsequent regeneration burn, 2006. It is situated at the headwaters of the South Esk River catchment water supply for the town of Launceston.
(Photo by Rob Blakers, 2006)
.
‘My name is Prue Barratt and I live in Maydena in the Derwent Valley (Tasmania). I’m writing this to highlight what small towns around this state have to deal with in Autumn and Winter.
Today (Wednesday) started off as a spectacular crisp winter’s day; one of a few really beautiful days we get through our colder months. So I was excited to get outside for the day to enjoy the sun. But by the time I organised myself to venture out it was too late … as I opened my front door I was confronted by smoke … it was literally blowing in my door.
I covered my nose and stepped out to see what was going on and realised there were fires right around our little town; not one fire but a two or maybe three, I couldn’t actually see how many because I couldn’t see and I could hardly breath, I stepped back inside, grabbed the camera, and took the pictures above; this was the view from my roof … 360 degrees surrounded by smoke.
It was one of the worst smoke-outs I had experienced whilst living here and by the time I got back inside I reeked of smoke.
This is just plain wrong. It is the 21st Century on a planet that is worried about carbon pollution! Our leaders need to put an end to these archaic practices now. There is no need to subject communities or the environment in general to this kind off filthy practice.
Tasmania already has one of the country’s highest rates of asthma allergies and lung problems. Why is this allowed to continue? Tassie is supposed to be the “Clean Green State”.
I’m pretty sure the tourist bus loaded with people which crawled through town didn’t think it was a clean green state. I’m pretty sure they were horrified that this happens in a supposed developed country every year.
When your eyes are stinging and you are too scared to open the doors of your home because your house will become unbearably flooded with smoke; when you are concerned for the wellbeing of old and frail family members because you just can’t get away from it unless you completely pack up and leave for the night …
You feel like a prisoner in your own home … in country in this day and age.. There is a serious problem!
Postscript: I just needed to add to my article that three Norske Skog (Boyer pulp mill) employees just turned up on my doorstep and apologised for all the smoke. They weren’t burning coupes but were asked by a couple of locals to burn piles close to their houses; most of the coupes were already burnt earlier in the season, so I need to acknowledge that … but the whole burning off thing needs to stop regardless. They said they were looking into alternatives but it needs to stop now; not later. They have had long enough to change the way they do things … at our expense.’
[end of article]
 .Smoke-filled atmosphere engulfing Maydena, South West Tasmania
(Photo by Prue Barratt, April 2012)
.Smoke-filled atmosphere engulfing Maydena, South West Tasmania
(Photo by Prue Barratt, April 2012)
.
 In 2009 paper maker, Norske Skog, with its pulp mill plant situated at Boyer on Tasmania’s Derwent River, axed 50 jobs as a combined consequence of its automation upgrade to its pulp mill plant and due to the structural downturn in paper sales by its newspaper clients.
In 2009 paper maker, Norske Skog, with its pulp mill plant situated at Boyer on Tasmania’s Derwent River, axed 50 jobs as a combined consequence of its automation upgrade to its pulp mill plant and due to the structural downturn in paper sales by its newspaper clients.
.
Ed: Newspapers are losing advertising revenue to Internet based businesses like Seek.com, CarSales.com.au, and HomeSales.com.au and so selling less newspapers and so buying less paper from the likes of Norske Skog.
Pile burning and forest (coupe) burning by Norske Skog is typical business-as-usual deforestation across Tasmania, not only by the forestry industry but by National Parks, the Tasmanian Fire Service and by rural landholders. It is all part of an inherited colonial cult of bush arson that is a key threatening process driving habitat extinctions across the island. Prescribed burning, aka ‘hazard reduction’, is a euphemism for State-sanctioned bush arson which is endemic practice not only across Tasmania’s remanining wild forests, but throughout Australia. It is a major contributor to Australia’s greenhouse gas emissions, which are what many scientists argue are Man’s cause of global warming and climate change.
The Gillard Labor Government is about to introduce a Carbon Tax on 1st July 2012, whereby Australia’s major industrial polluters must pay a Carbon Tax of $23 per tonne. Yet the many hundreds of thousands of tonnes of timber that are burnt by bushfires is somehow excluded – whether it be lightning ignitions allowed to get out of control, or deliberate State-sanctioned bush arson. This makes the Carbon Tax nothing but discriminating political greenwashing, with minimal climate impact. Meanwhile, and more critically, Australia’s ecology, regions by regions, is being driven closer to extinction by destructive bushfire management.
.
Comments to Prue’s article by Tigerquoll
.
‘CEO Bob Gordon and his Forestry Tasmania (FT) forest marauders along with his partners in eco-crime Tasmania Fire Service (TFS) Chief Officer Mike Brown need to be paying Julia’s Carbon Tax. But instead of $23 per tonne, it ought be $23 per cubic metre.
Send the two organisations broke. Do not donate to the TFS bastards. They light more fires than they put out. ‘Fuel’ Reduction is a euphemism for bush arson. It gives ‘em somthing to do in the off season. It reflects the helpless defeatism of Tasmania’s non urban fire emergency service denied proper and effective government resources to put out serious wildfires when they occur.’
.
TFS bastards setting fire to native forests is defeatism, knowing that unless native vegetation is converted to sterile parkland that in a real wildlife it is every man for himself.
They even have removed the ‘Low Fire Risk’ category and added a ‘Catastrophic Fire Risk’ category. They may as well add an ‘Armageddon’ category and be done with it! It is defeatism at its worst.
Local case in point – look recent Meadowbank Fire near Maydena in February this year east of Karanja. It started on Saturday, reportedly by “accident” at the Meadowbank Dam and burnt out 5000 hectares. Two days later was still officially ‘out of control’. The meaningless and flawed motto of ‘Stay or Go’ was supplanted by the false sense of security of ‘Prepare, Act, Survive’. In reality the pragmatic community message ought to be ‘You’re On Your Own’.
This Tassie Dad’s Army fire agency is more adept at starting bushfires than putting them out.
The under-resourced, raffle funded volunteer dependent model is abject Government neglect of emergency management. Every time someone criticises the non-urban fire fighting performance, the government bureaucracy and politicans hide behinds the nobleness of community volunteers.
Imagine if URBAN fire fighting was volunteer dependent on someone’s pager going off? Goodbye house.
I feel for the volunteers, but have no respect for the policy or organisation.’
 Tasmania’s Derwent Valley 20120401
..a Forestry Industry April fool’s joke
[Source: ^http://www.themercury.com.au/article/2012/04/02/314811_tasmania-news.html]
Tasmania’s Derwent Valley 20120401
..a Forestry Industry April fool’s joke
[Source: ^http://www.themercury.com.au/article/2012/04/02/314811_tasmania-news.html]
.
Here’s a question..what is the impact on Tasmanian fauna?
Here’s some research…
“It’s spring, and soon we’ll start to get sensationalist stories predicting a horrendous bushfire season ahead. They will carry attacks on agencies for not doing enough to reduce fuel loads in forests close to homes, for unless those living on the urban fringe see their skies filled with smoke in winter they panic about losing their homes in January.
Fighting fires with fear is a depressing annual event and easy sport on slow news days. Usually the debate fails to ask two crucial questions: does hazard reduction really do anything to save homes, and what’s the cost to native plants and animals caught in burn-offs?
…A new scientific paper published in the CSIRO journal Wildlife Research by Michael Clarke, an associate professor in the department of zoology at La Trobe University, suggests the answer to both questions is: we do not know.
Much hazard reduction is performed to create a false sense of security rather than to reduce fire risks, and the effect on wildlife is virtually unknown.’
.
[Read More: ‘The dangers of fighting fire with fire‘ by James Woodford, Sydney Morning Herald, 20080907, ^http://www.smh.com.au/news/opinion/the-dangers-of-fighting-fire-with-fire/2008/09/07/1220725850216.html].
~ Tigerquoll..
 State-sanctioned bush arson in Tasmania
[Source: http://www.forestrytasmania.com/fire/fire1.html]
State-sanctioned bush arson in Tasmania
[Source: http://www.forestrytasmania.com/fire/fire1.html]
.
Bushfires, their smoke and heat, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. So Bushfire Management has an obligation to reduce bushfires, not create them. Bushfire Management needs to pay a Carbon Tax just like any other industrial polluter.
.
.
‘Forestry tries to spin results of CSIRO Emissions Study’
..more smoke and mirrors from an out-of-touch agency.
‘The Tasmanian Greens today said that a CSIRO study comparing smoke emissions from wood-heaters with forestry burn-offs did nothing to justify Forestry Tasmania’s outdated and unsustainable management practices. The study, commissioned by Forestry Tasmania, found that the majority of smoke pollution in specific parts of the Huon Valley during 2009 and 2010 was caused by wood-heater emissions.
Greens Forestry spokesperson Kim Booth MP said that these results aren’t surprising, particularly in the more densely populated areas such as Geeveston and Grove where the study was conducted.
“This is not a case of one type of smoke pollution being better than another. All smoke emissions are an unwanted nuisance for the community, particularly for those with pre-existing respiratory problems such as asthma.”
“The commissioning and release of this study by Forestry Tasmania is another obvious attempt to justify their so-called regeneration burns. That’s despite the Environment Protection Authority identifying numerous breaches of guideline safety levels for particle emissions caused by burn-offs.”
“We need to be working as a community to reduce all smoke emissions and improve air quality. This means that we must work to educate people on the importance of installing heaters that burn efficiently, and comply with Australian standards.”
“Forestry can’t play down the negative impact of its burn-offs. The Greens receive many complaints from people suffering from respiratory problems, such as asthma, who have no option in some cases but to pack up and leave home during the forest burns season.”
“Proper systems need to be put in place, or its time these burns were stopped once and for all.”
[Source: ‘Forestry tries to spin results of CSIRO Emissions Study’ – more smoke and mirrors from an out-of-touch agency, by Kim Booth MP, Tasmanian Greens Forestry Spokesperson, 20110825, Tasmanian Times, ^http://tasmaniantimes.com/index.php/article/smoke-from-regeneration-burns-exceeded-healthy-limits-only-three-times].
[Source: Water S.O.S Tasmania, ^http://www.water-sos.org/forestry-tasmania/index.html].
.
2010: Escaped Controlled Burn at Ansons Bay in mid-Summer
.
‘The derived fire location..corresponds to a wildfire at Ansons Bay (north-east Tasmania, near Bay of Fires) , listed on the Tasmanian Fire Service (TFS) webpage on the 23rd of January.
This fire had burnt out 100 ha on 23rd January 2010, and had burnt a total of 200 hectares when reported as extinguished on the 26th.
The fire was reported as an escaped permit burn. The permit burn was ignited on the 22nd of January 2010. The local TFS brigade responded to the wildfire at 14:00 EDT on the 23rd. The wildfire burnt mainly in grassland.
Smoke from a bushfire at Ansons Bay on the 23rd of January 2010 moved westwards towards the Tamar River. The BLANkET air stations at Derby, Scottsdale and Lilydale each detected the smoke as it moved. Ti Tree Bend station(Launceston) and the Rowella station in the lower Tamar also detected the smoke. Derby is approximately 35 km from the fire location, while Ti Tree Bend and the Rowella stations are approximately 100 km from the burn. The peak 10–minute PM2.5 concentrations at these stations were of order 10 to 15 μg m−3.
At Rowella the hourly–averaged PM2.5 reached to near 20 μg m−3 near 21:00 AEST.
[Source: ‘Blanket Brief Report 7: ‘Smoke from a bushfire at Ansons Bay, north–east Tasmania moving into to the Tamar Valley 23rd January 2010’, Air Section, Environmental Protection Authority (EPA), Tasmanian Government, February 2011, ^http://epa.tas.gov.au/Documents/BLANkET_Brief_Report_07.pdf, Read Report].
.
Tasmanian Forest Industry – its case for burning native forests every year
.
‘The Tasmanian forest industry planned burning program, which includes both burning for forest regeneration, and burning for property protection generally commences in mid-March if conditions are suitable.
.. The Coordinated Smoke Management Strategy developed by the Forest Practices Authority is being used by the Tasmanian forest industry.
As of 2011, all smoke complaints are being received and investigated by the Environment Protection Authority, a Division of the Department of Primary Industries, Parks, Water and Environment. [Ed. But the EPA has no watchdog besides the community, so it can be as incompetent, as negligent, as complicit, as dismissive, as colluding with its sister Tasmanian Government agencies all it likes. The EPA does not have any law that requires it to be publicly transparent. The photos in this article evidence the Tasmanian EPA as an ineffectual and spurious organisation.]
.
Forest Regeneration
Fire is an important part of the life cycle of Eucalypts. In nature most eucalypt species require the disturbance provided by fire to regenerate. Eucalypt seeds and seedlings need a mineral soil seedbed, abundant sunlight and reduced competition from other plants to establish and grow. In nature this situation is provided by a major wildfire. Tasmanian forest managers mimic nature by using fire in a planned and controlled way to re-establish healthy fast growing trees after harvesting.
Planned burns are part of an industry-wide programme by :
- Forestry Tasmania (FT)
- The Forest Industries Asssociation of Tasmania (FIAT).
- Tasmania Fire Service
- Parks & Wildlife Service, Tasmania.
.
Forests & Timber
Forests managed for timber production take more carbon out of the atmosphere over time than unmanaged forests locked up in reserves. Tasmania currently has 47% of forests locked up and unmanaged.
Timber from managed forests is used to build an array of structures from houses to multi-level buildings, sports arenas to architecturally designed public spaces. Timber is light and easy to work with and allows for flexibility and efficiency in design. Timber is warm, aesthetically pleasing and most importantly, renewable. Environments rich in timber have a kinship with nature and make people living and working in them feel at one with the outdoors.
It is so important, in these tough economic times, to use local products. Tasmanian timber produced in the state comes from sustainably managed forests, administered under processes established by Government. In addition, all public and most private forests in Tasmania are third party certified as being sustainably managed by the Australian Forestry Standard. Tasmanian timber is a particularly environmentally friendly choice and we should be using more wood to help combat climate change.
Wood is stored greenhouse gas – held together with stored sunlight. If we are serious about trying to address greenhouse and climate change problems, we should be growing and using more forests, for sustainable energy-efficient products that store carbon and for sustainable biomass-based energy systems.
Harvesting a forest results in the release of some carbon dioxide back into the air from which it came however a considerable portion remains stored in resulting forest products such as furniture, timber for housing and a myriad of paper products.
Use more wood not less.’
[Source: Forestry Industry Association of Tasmania (FIAT), ^http://www.fiatas.com.au/]
Ed: Fire is unnatural in old growth wet Eucalypt forests. Many forest plant species are fire sensitive so will not recover in teh evnt of a fire. No fauna are fire tolerant – they either burn to death or die after fire from starvation, exposure or predation. Those who burn forests have no idea of the impacts upon fauna populations, nor the impacts of fire upon biodiversity. Their lay observation upon seeing regrowth of some species is that setting fire to forest habitat must be ok.
Those who perpetuate and extend this myth, fabruicate the notion that fire is healthy and indeed essential for forest regeneration and survival. All new recruits of the Tasmanian Forest Industry, Tasmania Fire Service and Parks & Wildlife Service are duly indoctrinated to this dogma. Of course it is unsubstantiated crap. Al one needs do is walk through an ancient Styx forest that has not been burnt for hundreds of years to disprove the myth.
Those vested interests who stand to profit from deforestation and exploitation of native forests, brandish all protected forest habitat as being ‘locked up’ and ‘unmanaged’. The ecological values of the forests are dismissed as worthless. It is no different to 17th Century traders denied access to Africans for the slave trade.
Timber that is from native old growth forests is not “renewable” unless the industrial logger is prepared to wait 500 plus years to harvest. Logging old growth is eco-theft and irreversibly ecologically destructive.
Tough economic times means that the smart investment is into sustainable industries where there is strong market demand and growth for products not vulnerable to buyer rejection on the basis of immoral sourcing or production.
Biomass-based energy is a technical euphemism for burning forests, which is unacceptable because is causes green house gas emissions. Buring natiuve forests also drive local habitat extinctions.
Use LESS wood NOT more!
 2010: Smoke rises into the sky above the Huon Valley in southern Tasmania
as the state’s Forestry Department (Forestry Tasmania) conducts fuel-reduction burns on April 18, 2010
[Source: ‘Anger over smoke haze prompts review’ , ABC Northern Tasmania, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2010/04/19/2877011.htm?site=northtas]
2010: Smoke rises into the sky above the Huon Valley in southern Tasmania
as the state’s Forestry Department (Forestry Tasmania) conducts fuel-reduction burns on April 18, 2010
[Source: ‘Anger over smoke haze prompts review’ , ABC Northern Tasmania, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2010/04/19/2877011.htm?site=northtas]
.
Parks & Wildlife Service – its case for burning native forests every year
.
‘Planned burning is an important part of fire management designed to maintain biodiversity and to reduce the risk posed by bushfires to people, houses, other property and the natural environment. Fire plays a major role in the ecology of the Tasmanian natural environment. Fire can be a vital force in maintaining healthy bush. But in the wrong place at the wrong time, it can also lead to the destruction of unique vegetation communities, human life and property.
Our diverse vegetation communities have differing responses to fire, from potentially devastating impacts in alpine areas and conifer forests, to ecologically sustainable effects in buttongrass moorlands and dry scelerophyll forest. Tasmania’s unique fauna has some interesting adaptations to fire. For some species, it is essential for their habitat requirements.
‘The Parks and Wildlife Service is responsible for the management of bushfires on all reserved land in Tasmania.
This management includes:
- control of unplanned bushfires
- planned burning to reduce fuel loads and make fire control easier and safer
- planned burning to help maintain biodiversity, promote regeneration of plants that depend on fire and to maintain suitable habitat for animals
- maintaining assets that assist with bushfire control, for example, fire trails, firebreaks and waterholes.
.
Planned Burning of Tasmania’s National Parks (to date) for 2012
| Burn Date | Location | Hectares |
|---|---|---|
| 16/05/2012 | Narawntapu | 796 |
| 10/05/2012 | Binalong Bay | 21 |
| 8/05/2012 | Peter_Murrell_(private_land?) | 15 |
| 7/05/2012 | Arthur River | 75 |
| 30/04/2012 | Lime Bay | 175 |
| 30/04/2012 | Fisheries, Coles Bay | 20 |
| 30/04/2012 | Wineglass Bay Walk Track | 4 |
| 26/04/2012 | Mt William | 710 |
| 18/04/2012 | Coles Bay | 43 |
| 17/04/2012 | Rifle Range | 251 |
| 4/04/2012 | Mt Field | 16.5 |
| 3/04/2012 | Dora Point | 20 |
| 2/04/2012 | Seaton Cove | 9.5 |
| 27/03/2012 | Arthur River | 532 |
| 27/03/2012 | Arthur River | 50 |
| 26/03/2012 | Stieglitz | 5 |
| 19/03/2012 | Peter_Murrell_(private_land?) | 3 |
| 14/03/2012 | Mt Field | 6 |
| 23/02/2012 | Trevallyn | 9 |
| 23/02/2012 | Trevallyn | 7 |
| 23/02/2012 | Trevallyn | 3 |
| 2,771 ha |
.
The first planned burn area in the table above labelled as ‘Narawntapu‘ applied to Narawntapu National Park, specifically at Cosy Corner, Bay of Fires Conservation Area, in north-east Tasmania. The ecology is renowned for its Wombats and Tasmanian Devils. Where do they go when Parks Service starts fires?
 Tasmania’s famous ‘Bay of Fires’
(Narawntapu National Park)
Tasmania’s famous ‘Bay of Fires’
(Narawntapu National Park)
.
The posted notice read:
‘Parks and Wildlife Service is today (Tuesday 8 May) conducting a fuel reduction burn in the Bay of Fires Conservation Area south of St Helens at the Cosy Corner North campground. The burn is about 20 hectares. The objective is to reduce fuel loads to provide protection for the campground in the event of a wildfire.’
[Source: Parks and Wildlife Service, Tasmania, 20120508, ^http://www.parks.tas.gov.au/index.aspx?sys=News%20Article&intID=2575].
So somehow the planned burn of 20 hectares extended to nearly 800 hectares inside the protected National Park! Was this yet another escaped burn? Where is the ecological report of damage to flora and fauna? So much for the National Parks motto ‘leave no trace’. How hypocritical!
.
“How can walkers help keep Tasmania wild and beautiful?
Leave No Trace is an internationally accepted way of minimising impacts on the places we visit.”
~ Parks and Wildlife Service, Tasmania
.
 The National Park before the burn
The National Park before the burn
.
 A wombat in Narawntapu National Park cannot run from fire
A wombat in Narawntapu National Park cannot run from fire
.
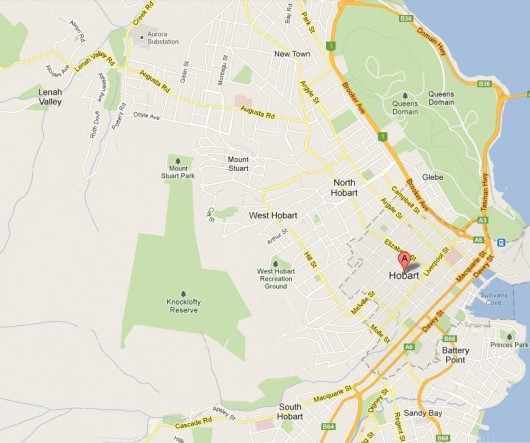 The Burn Area of nearly 2800 hectares of Tasmania’s National for 2012, translates to 28 square kilometres.
This is that aggregate area relative to Hobart – the entire map above!
It’s like Hobart’s 1967 Black Tuesday every year in Tasmania’s National Parks
The Burn Area of nearly 2800 hectares of Tasmania’s National for 2012, translates to 28 square kilometres.
This is that aggregate area relative to Hobart – the entire map above!
It’s like Hobart’s 1967 Black Tuesday every year in Tasmania’s National Parks.
 Forest Smoke across southern Tasmania, from planned burning, April 2008
Forest Smoke across southern Tasmania, from planned burning, April 2008
.
Tasmania Fire Service – its case for burning native forests every year
.
Ed: It doesn’t just have one programme, but two. One programme to burn native forests every year, the other to slash and bulldoze access to get good access to burn the native forests.
.
Fuel Reduction Programme
‘Each summer, bushfires in our forests pose a significant threat to communities in rural areas, and on the rural-urban interface. Large, uncontrollable bushfires can have serious consequences for Tasmanians. The Tasmanian Government has committed funds towards a program of planned fuel reduction burns to help protect Tasmanians from the threat of wildfires. The program will see the State’s three firefighting agencies, Forestry Tasmania, the Tasmania Fire Service and the Parks and Wildlife Service combine their expertise in a concerted program aimed at reducing fuel loads around the state.
The objective of the inter-agency Fuel Reduction Burning Program is to create corridors of low fuel loads to help prevent large wildfires. The program complements but does not replace fuel reduction burning and other means of fuel reduction close to houses and other assets.’
.
Bushfire Mitigation Programme
‘The Bushfire Mitigation Programme provides funds for construction and maintenance of fire trails and associated access measures that contribute to safer sustainable communities better able to prepare, respond to and withstand the effects of bushfires.
The program is administered by Australian Emergency Management (AEM) within the Australian Government Attorney-General’s Department. Tasmania Fire Service is the lead agency in Tasmania for the Bushfire Mitigation Program.
In the 2009 Budget the Australian Government announced funding of $79.3m over four years for a new Disaster Resilience Program (DRP).
The DRP will consolidate the existing Bushfire Mitigation Program (BMP), the Natural Disaster Mitigation Program (NDMP) and the National Emergency Volunteer Support Fund (NEVSF) in an effort to increase flexibility for the jurisdictions and streamline the associated administration for both the Commonwealth and the States and Territories.
The Commonwealth Attorney-General’s Department is currently working with representatives from each jurisdiction to ensure that the transition to the new DRP is as smooth as possible.
The DRP will commence in 2009-10 and details of the funding arrangements, program guidelines and implementation plans will be announced by the Commonwealth Attorney-General’s department and disseminated to the relevant agencies and stakeholders in each jurisdiction in due course.’
[Source: Tasmania Fire Service, ^http://www.fire.tas.gov.au].
.
.
‘Burnoffs’ Chemical Cocktail’
.
Smoke haze from burnoffs pushed Tasmania close to breaching air safety standards last week.
In one 24-hour period, emission levels from the forestry regeneration and fuel-reduction burns “were approaching the standard”, state environmental management director Warren Jones told the Sunday Tasmanian.
Elevated particle levels had been detected in Launceston and Hobart on several days during the week.
A Sunday Tasmanian investigation into the smoke haze has revealed:
- Between 5000ha and 7000ha is earmarked for forestry regeneration burns this season.
- About 70,000ha of the state’s forest was razed by wildfire in the past summer.
- The smoke contains a mix of carbon monoxide, tar, ash, ammonia and known carcinogens such as formaldehyde and benzene.’
.
.
‘Forestry burn offs continue to threaten…’
.
The Tasmanian Greens today said that the Parliament needs to commission an independent study into the total social, environmental and economic costs of forestry burns, as they continue to emit pollutants into the air causing distress to the many Tasmanians suffering from respiratory complaints, and also impacting on Tasmania’s clean, green and clever brand.
Greens Health spokesperson Paul ‘Basil’ O’Halloran MP burn-off practice as outdated, old-school and not in line with appropriate practice today, especially when it continues to put thousands of Tasmanians with respiratory complaints in distressing situations. These airborne emissions impact disproportionately on children.
“Once again Tasmania’s beautiful autumn days are blighted by the dense smoke plumes blocking out the sun and choking our air,” Mr O’Halloran said.
Tasmanian forests – planned burn http://www.discover-tasmania.com/smoke-fire/
.
“This is an unacceptable situation. It compromises Tasmanians’ health, our environment, and is an insult to common-sense.”
“The Greens are calling for the Minister to commission independent social, environmental and economic impact study of these burns.”
“Tasmania’s tourism industry also has reason for concern over this due to the plumes of smoke that choke up the air sheds and appear as a horrible blight on the Tasmanian Landscape.”
“We also want to see an end to these burns, and are calling on the Minister to consult with the community to establish a date by which this polluting practice will end once and for all.”
“It is also concerning at the impact these burns have on Tasmania’s biodiversity and threatened species such as the Tasmanian Devil, burrowing and freshwater crayfish, and a myriad of other plant and animal species.”
“The annual so-called forest regeneration burns have just commenced with Forestry Tasmania alone intends to conduct 300 coupe burns over five districts, and this will emit copious amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change, not to mention the risk this poses for the many Tasmanians who suffer from respiratory complaints such as Asthma,” Mr O’Halloran said.
[Source: ‘Forestry burn offs continue to threaten…’, 20110315, Paul ‘Basil’ O’Halloran MP, Health spokesperson, Tasmanian Greens, ^http://mps.tas.greens.org.au/2011/03/forestry-burn-offs-continue-to-threaten-health-and-well-being-communities-animals-and-plant-life-being-threatened-by-forestry-burn-offs/].
.
The Killing of Wild Tasmania – Extinction by a Thousand Fires
.
These photographs provide an illustration of current Tasmanian forestry practices. The photos are from Coupe RS142E, in the upper valley of Tombstone Creek, one kilometer upstream from the Tombstone Creek Forest Reserve in the northeast highlands of Tasmania. Tombstone Creek is a tributary of the upper South Esk River, the headwaters of the water supply for Launceston.
 Majestic ancient Rainforest in Tombstone Creek (c.1000 AD to 2006)
BEFORE the Tasmanian Government’s State-sanctioned arson
(Photo taken in 2003)
Majestic ancient Rainforest in Tombstone Creek (c.1000 AD to 2006)
BEFORE the Tasmanian Government’s State-sanctioned arson
(Photo taken in 2003)
.
 AFTER
(Photo taken in October 2006)
AFTER
(Photo taken in October 2006)
‘I first came upon this forest in May 2003, and was so struck by it’s beauty that I made several return visits during the following 12 months. This steep valley-side supported a wet and mossy forest characterized by myrtles, blackwood, tall eucalypt emergents, groves of tree-ferns up to eight meters high and some of the largest sassafras that I have seen anywhere in Tasmania. Many of the sassafras trees had trunk diameters of one meter or more at chest height.
This forest was clear-felled by cable-logging in the summer of 2005 and burnt in an exceedingly hot fire in April 2006. All of the rainforest trees were killed outright. The site is steep and soils are sandy and the valley side was left in a condition which was highly vulnerable to severe soil erosion. This coupe is bordered by some areas that were logged within the last 10 years or so, and the regrowth in these adjacent coupes is a mix of wattle and eucalypt. A narrow strip of rainforest remains at the new coupe’s lowest edge, along Tombstone Creek, but recolonization by the rainforest trees cannot occur, due to the competitive advantage of the eucalyptus and wattles in a full sunlight situation. This is especially so in the context of a drying climate. Simply put, the process enacted here is conversion, in this case from a mature mixed rainforest dominated by myrtle and sassafras, with eucalypt emergents, to an uncultivated crop of wattle and, presumably, the aerially sown eucalypt species.
In this process of conversion, which is far from being confined to this particular coupe, two options are precluded. Firstly, the option for the natural forest to continue to exist for it’s own sake and to develop towards rainforest, a point from which, given the age of the eucalypts, it was not far removed. The second opportunity forgone is for the possibility of alternative uses of species other than wattle and eucalypt, including wood uses, for future generations of people.
Other negative and significant ecological impacts have occurred here, including devastating effects on wildlife, altered hydrology, atmospheric pollution, weed invasion and not least, the release of massive amounts of carbon, previously sequestered within the soil and the living vegetation, into the atmosphere.
The scenes depicted here are all within 100 meters of each other. The forest scenes were photographed in 2003, the other scenes in October 2006.
[Source: ^http://www.water-sos.org/before-after/index.html].
.
[Source: The Observer Tree, Styx Valley South West Tasmania^http://observertree.org/].
.
Further Reading
.
[1] Bush Arson excuse by Forestry Tasmania ^http://www.forestrytas.com.au/uploads/File/pdf/pdf2012/regen_burn_program_insert_2012.pdf [Read Document (PDF, 1.4 mb)]
.
[2] Fuel Reduction Programme, March 2008, Tasmania Fire Service, ^http://www.fire.tas.gov.au/Show?pageId=tfsFuelReductionProgramme, [Read Document (PDF, 1.7 mb)]
.
[3] ‘The burning of Tasmania’, 20080425, various contriubutors Vica Bayley, Dave Groves, Tim Morris, Matthew Newton, Tasmanian Times, ^http://tasmaniantimes.com/index.php?/weblog/article/tassie-burns/
.
[4] ‘The dangers of fighting fire with fire’, by James Woodford, 20080908, Sydney Morning Herald, ^http://www.smh.com.au/news/opinion/the-dangers-of-fighting-fire-with-fire/2008/09/07/1220725850216.html] Text extract below:
.
‘It’s spring, and soon we’ll start to get sensationalist stories predicting a horrendous bushfire season ahead. They will carry attacks on agencies for not doing enough to reduce fuel loads in forests close to homes, for unless those living on the urban fringe see their skies filled with smoke in winter they panic about losing their homes in January.
Fighting fires with fear is a depressing annual event and easy sport on slow news days. Usually the debate fails to ask two crucial questions: does hazard reduction really do anything to save homes, and what’s the cost to native plants and animals caught in burn-offs?
A new scientific paper published in the CSIRO journal Wildlife Research by Michael Clarke, an associate professor in the department of zoology at La Trobe University, suggests the answer to both questions is: we do not know.
What we do know is a lot of precious wild places are set on fire, in large part to keep happy those householders whose kitchen windows look out on gum trees.
Clarke says it is reasonable for land management agencies to try to limit the negative effects of large fires, but we need to be confident our fire prevention methods work. And just as importantly, we need to be sure they do not lead to irreversible damage to native wildlife and habitat.
He argues we need to show some humility, and writes: “The capacity of management agencies to control widespread wildfires ignited by multiple lightning strikes in drought conditions on days of extreme fire danger is going to be similar to their capacity to control cyclones.” In other words, sometimes we can do zip.
Much hazard reduction is performed to create a false sense of security rather than to reduce fire risks, and the effect on wildlife is virtually unknown.
The sooner we acknowledge this the sooner we can get on with the job of working out whether there is anything we can do to manage fires better. We need to know whether hazard reduction can be done without sending our wildlife down a path of firestick extinctions.
An annual burn conducted each year on Montague Island, near Narooma on the NSW far South Coast, highlights the absurdity of the current public policy free-for-all, much of which is extraordinarily primitive. In 2001 park rangers burnt a patch of the devastating weed kikuyu on the island. The following night a southerly blew up, the fire reignited and a few penguins were incinerated. It was a stuff-up that caused a media outcry: because cute penguins were burnt, the National Parks and Wildlife Service was also charcoaled.
Every year since there has been a deliberate burn on Montague, part of a program to return the island to native vegetation. Each one has been a circus – with teams of staff, vets, the RSPCA, ambulances, boats and helicopters – all because no one wants any more dead penguins.
Meanwhile every year on the mainland, park rangers and state forests staff fly in helicopters tossing out incendiary devices over wilderness forests, the way the UN tosses out food packages. Thousands of hectares are burnt, perhaps unnecessarily, too often, and worse, thousands of animals that are not penguins (so do not matter) are roasted. All to make people feel safe. Does the burning protect nearby towns? On even a moderately bad day, probably not. Does it make people feel better? Yes.
Clarke’s paper calls for the massive burn-offs to be scrutinised much more closely. “In this age of global warming, governments and the public need to be engaged in a more sophisticated discussion about the complexities of coping with fire in Australian landscapes,” he writes.
He wants ecological data about burns collected as routinely as rainfall data is gathered by the agricultural industry. Without it, hazard reduction burning is flying scientifically blind and poses a dangerous threat to wildlife.
“To attempt to operate without … [proper data on the effect of bushfires] should be as unthinkable as a farmer planting a crop without reference to the rain gauge,” he writes.
In the coming decades, native plants and animals will face enough problems – most significantly from human-induced climate chaos – without having to dodge armies of public servants armed with lighters. Guesswork and winter smoke are not enough to protect our towns and assets now, and the risk of bushfires increases with the rise in carbon dioxide.
James Woodford is the editor of www.realdirt.com.au.
.
Tags: Ansons Bay, Armageddon, Bay of Fires Conservation Area, Black Tuesday, burning native forests, bush arson, bushfire management, Bushfire Mitigation Programme, Carbon Tax, Catastrophic Fire Risk, Coordinated Smoke Management Strategy, Derwent Valley, Escaped Controlled Burn, Forest Practices Authority, Forestry Tasmania, Fuel Reduction Programme, global warming, hazard reduction, Huon Valley, industrial polluter, Leave No Trace, Low Fire Risk, Meadowbank Fire, Narawntapu National Park, Newspapers are losing advertising revenue, Norske Skog, Parks and Wildlife Service, planned burn, prescribed burning, Tasmania, Tasmania Fire Service, Tasmanian Forest Industry, Tombstone Creek, wombat
















A well-researched paper exposing the devastating impact of the Tasmanian Forest Industry’s, Parks and Wildlife Services’ and Tasmania Fire Service’s fire management on the ecology of Tasmanian forest. I do fully agree with the editor’s comments. He is very right, such inappropriate fire management is an “endemic practice not only across Tasmania’s remaining wild forests, but throughout Australia” with Victoria carrying the extra brunt of the newly introduced minimum yearly quota of burns irrespective of their impact on the forest ecology.