Tarkine Wilderness values sanctified by court
Thursday, July 18th, 2013Tarkine Wilderness Values
.
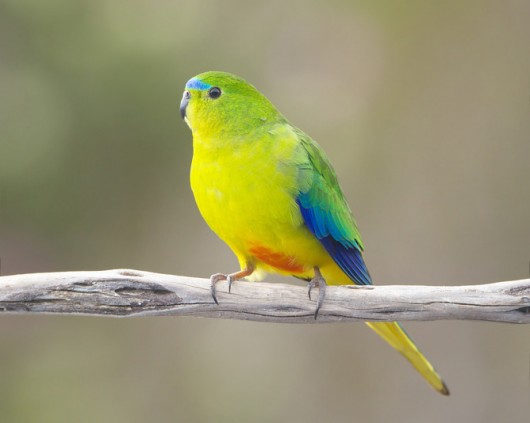
Tasmania’s Tarkine is a vast wilderness region of north west Tasmania covering nearly half a million hectares (the size of Kangaroo Island); a remnant of Gondwanaland and home to the last disease-free stronghold of the Tasmanian Devil.
The Tarkine covers 1,800 km² of beautiful ancient cool temperate rainforest, as well as around 400 km² of eucalypt forest and a mosaic of other vegetation communities, including dry sclerophyll forest, woodland, buttongrass moorland, sandy littoral communities, wetlands, grassland and Sphagnum communities. The Tarkine contains a diverse array of landscapes, from giant forests to huge sand-dunes, sweeping beaches, rugged mountains and pristine river systems. It retains a rare high diversity including:
- 28 terrestrial mammals
- 111 land and freshwater birds
- 11 reptiles
- 8 frogs
- 13 freshwater fish
- 151 species of liverworts
- 92 species of mosses.
.
The Tarkine provides habitat for over 60 rare, threatened and endangered species of flora and fauna. Tthe Tarkine is rich in frog species, with eight of Tasmania’s eleven frog species occurring in diverse parts of the Tarkine, including in the Tarkine’s rainforests, in Melaleuca swamps and scrub, and in the coastal lagoons and dune systems. Two threatened frog species, the Green and Golden Frog, and the Striped Marsh Frog, both occur in coastal lagoons, marshes and swamps of the Arthur-Pieman plains.
The Tarkine is particularly important for freshwater crustaceans – which are of global significance (PWS, 2001). One of the largest freshwater crustaceans in the world, the Tayatea, or Giant Freshwater Crayfish, inhabits the north of Tasmania and the Arthur River catchment – with the Tarkine a stronghold. This extraordinary creature, which can live for up to 40 years of age, and grow up to a metre in length, has been adversely affected by clearing of vegetation and recreational fishing, and is now listed as vulnerable.
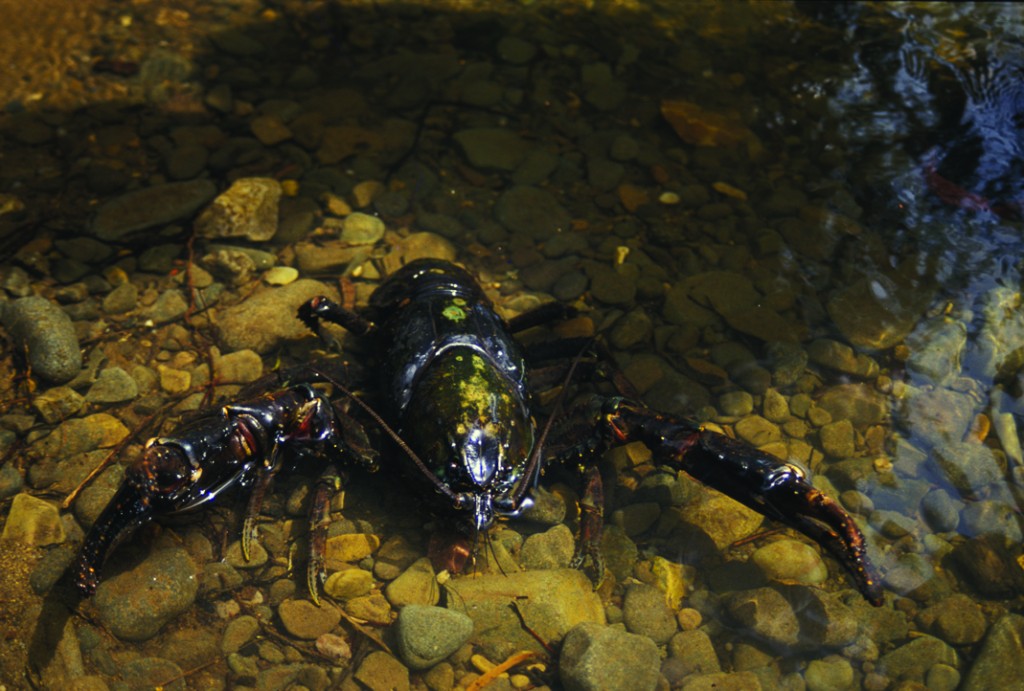 The Tarkine’s Tayatea, or Giant Freshwater Crayfish
The Tarkine’s Tayatea, or Giant Freshwater Crayfish
.
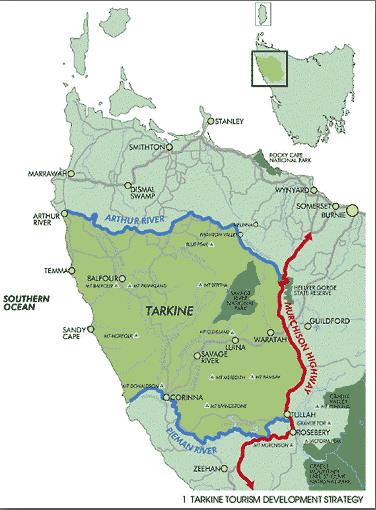 The Tarkine, showing the Tasmanian Government’s 2012 plans for a $34M upgrade of the Murchison Highway,
marketed as ‘tourism development’ but surreptitiously to subsidise increased mining access between the Tarkine and Port Latta.
[Source: Tasmanian Government, Department of Infrastructure, Energy and Resources
^http://www.dier.tas.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0020/81461/01_Murchison_Highway_Upgrades.pdf]
The Tarkine, showing the Tasmanian Government’s 2012 plans for a $34M upgrade of the Murchison Highway,
marketed as ‘tourism development’ but surreptitiously to subsidise increased mining access between the Tarkine and Port Latta.
[Source: Tasmanian Government, Department of Infrastructure, Energy and Resources
^http://www.dier.tas.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0020/81461/01_Murchison_Highway_Upgrades.pdf]
.
Read More: ^https://www.et.org.au/tarkine-wilderness
.
Tarkine threatened by exploitative greed
.
The backward Tasmanian Government continues to ignore the place, dismissing it as an “unbounded locality” in the Waratah-Wynyard council area, and repeatedly trying to mine it, log it and bulldoze roads through it. So the name ‘Tarkine’ does not appear in maps, in order that it may be exploited section by section. Former Environment Minister Tony Burke was hoodwincked by this tactic as he was guided by miners to the denuded sections, and so diluted his pure vision of the Tarkine’s being worthy of protection for the pristine sections.
Such has perpetuated the 19th Century/early 20th Century ^Robber Baron mentality that has long followed American industrialisation over the past two centuries. On the back of the Robber Barons, the post-war Baby Boomer – “the most self-righteous, self-important, incredibly arrogant generation of all time” [^Source], has bulldozed into oblivion 75% of Tasmanian Nature, 80% of Australian Nature and exterminated Tasmania’s endemic Thylacine.
Still in Tasmania, inherited Taswegian attitudes and addictive exploitation die hard.
.
 Industrial Robber Barons
Industrial Robber Barons
.
However, many of the Tarkine’s unique values are threatened by destructive activities such as new mining, logging, and illegal activities such as poaching and arson, and less than 5% of the Tarkine is protected as a National Park. The Tarkine’s future as a wild place hangs in the balance.
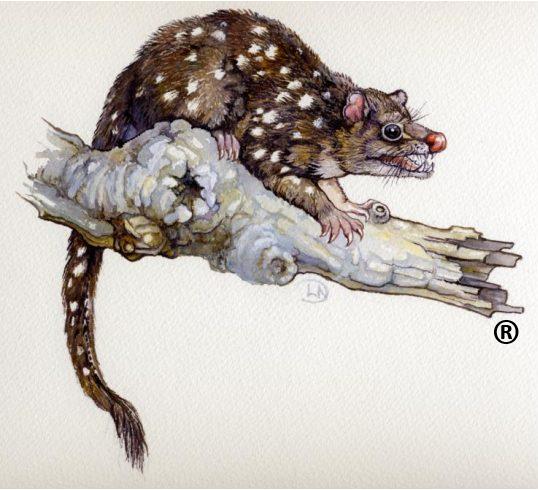
The Tarkine is the home to the last disease free population of the Tasmanian Devil. The Tasmanian Devil is being pushed to extinction by the fatal Devil Facial Tumour Disease. This disease has been estimated to have killed 80% of the Tasmanian Devil population in the past decade. As such the habitat of the Tarkine is critical to survival of this iconic species in the wild. Threats such as mining, logging and roading place the future of the Devil at risk..
 Tasmanian Devils heading towards extinction, following the Thylacine.
Tasmanian Devils heading towards extinction, following the Thylacine.Token funding in dribs and drabs by the Tasmanian Government toward Save the Tasmanian Devil Programme pales in the face of the Tasmanian Government encouraging ongoing destruction of the Devil’s critical habitat. [Source: Photo by Rhys Allen in article ‘Tarkine mines could be last straw for Tasmanian devils’, 20130115, by Hamish McCallum, Head, Griffith School of Environment at Griffith University, ^http://theconversation.com/tarkine-mines-could-be-last-straw-for-tasmanian-devils-114839]
.
Protecting the Tarkine
.
The campaign to protect The Tarkine began in the 1960s, when a formal conservation proposal was put forward by the then Circular Head Mayor Horace (Jim) Lane for the establishment of a ‘Norfolk Range National Park’. But Lane’s proposal was not realised.
From the late 1990s, the region came under increasing national and international scrutiny in a similar vein to the environmental protests surrounding Tasmania’s Franklin River and Queensland’s Daintree Rainforest. The case for protecting the Tarkine was significantly advanced with the Federal Government’s Forestry Package in 2005 adding 70,000 hectares to reserves in the Tarkine.
The environmentalist organisation Tarkine National Coalition, headed by Scott Jordan, has proposed the Tarkine be officially declared a national park, and with the support of many Tasmanians, wishes to ultimately see the Tarkine properly internationally protected as a World Heritage listed area for all time.
 Scott Jordan in The Tarkine
Scott Jordan in The Tarkine
.
In December 2009, the Tarkine was listed as a National Heritage Area following an Emergency National Heritage Listing sought by the Tarkine National Coalition to stop a proposed Tarkine Road, which would have coursed through old growth forest and detrimentally affected the natural values of undisturbed areas.
In 2013, while 80% of the Tarkine is now protected from logging, only 5% is protected from mining, and the Tasmanian Government still wants its tourist road bulldozed through it to destroy its wilderness values for tourism exploitation.
In December 2010, the incoming Federal Environment Minister Tony Burke allowed the emergency listing to lapse in the face of numerous mining proposals in the Tarkine.
.
Further Reading: ^http://tarkine.org/
.
Threats from Mining
.
The west coast region of Tasmania has a sad history of exploitative mining since the industrial Robber Baron era of the late 19th Century, when tin was discovered at Mount Bischoff, setting of a mining boom. Cooper was mined from Mount Lyell and smelted at nearby Queenstown from the 1890s. Zinc and lead were mined at Mt Read near Rosebery and nickel from Avebury near Zeehan, both along the southern fringe of the Tarkine. Gold has been from the Henty mine, mixed base metals from the Hellyer mine, and later iron ore extracted in large open cut pits at Savage River in the heart of The Tarkine.
Since 1965, ‘Savage River Mines‘ has been carving up a large slice of The Tarkine from its open-cut magnetite mine.
 Savage River Mine
Irrevocably carving out Tarkine wilderness, currently operated by Grange Resources Limited
Savage River Mine
Irrevocably carving out Tarkine wilderness, currently operated by Grange Resources Limited
.
Ironically, nearby Savage River National Park is recognised for its wilderness values:
.
<< The park protects the largest contiguous area of cool temperate rainforest surviving in Australia and acts as a refuge for a rich primitive flora, undisturbed river catchments, high quality wilderness, old growth forests, geodiversity and natural landscape values.
The western portion of the park includes the most extensive basalt plateaux in Tasmania that still retains a wholly intact forest ecosystem. The upper Savage River, which lends the park its name, runs through a pristine, rainforested river gorge system. The park contains habitat for a diverse rainforest fauna and is a stronghold for a number of vertebrate species which have suffered population declines elsewhere in Tasmania and mainland Australia.
The parks remoteness from human settlement and mechanised access, its undisturbed hinterland rivers and extensive rainforest, pristine blanket bog peat soils and isolated, elevated buttongrass moorlands ensure the wilderness character of the park. Like the vast World Heritage listed Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area to its south, the area is one of the few remaining temperate wilderness areas left on Earth. >>
.
[Sources: ‘Mining’, University of Tasmania, ^http://www.utas.edu.au/library/companion_to_tasmanian_history/M/Mining.htm; ‘Tasmania’s Mines’, Mineral Resources Tasmania (Tasmanian Government, ^http://www.mrt.tas.gov.au/portal/page?_pageid=35,831205&_dad=portal&_schema=PORTAL; ‘Savage River National Park’, Parks and Wildlife Service Tasmania, ^http://www.parks.tas.gov.au/?base=3732].
 American Robber Baron Robert Carl Sticht (1856-1922)
American metallurgist and General Manager of Mount Lyell Mining and Railway Company
Elitist exploiter of copper mining and smelting from Mount Lyell on Tasmania’ wild west coast
American Robber Baron Robert Carl Sticht (1856-1922)
American metallurgist and General Manager of Mount Lyell Mining and Railway Company
Elitist exploiter of copper mining and smelting from Mount Lyell on Tasmania’ wild west coast
.
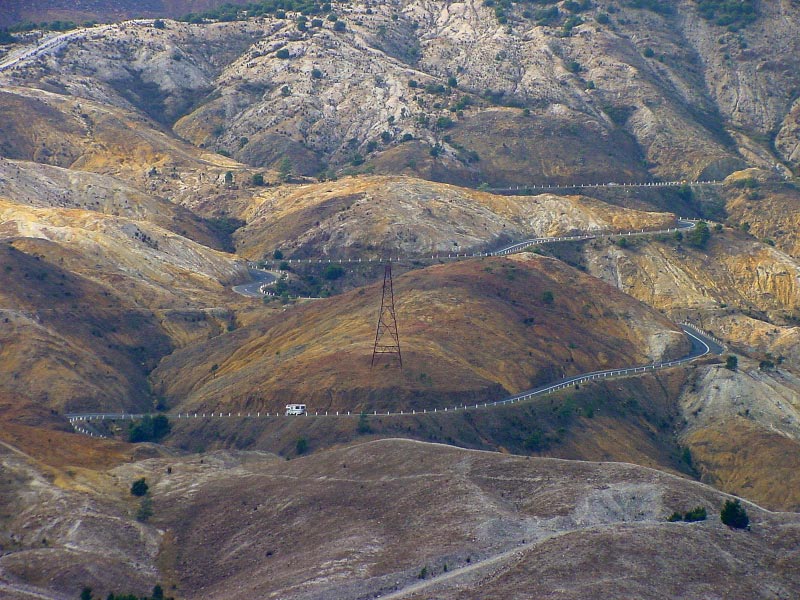 Sticht’s Mining Legacy to Tasmania
– a denuded moonscape above Queenstown caused by sulphuric acid associated with the copper mining and smelting.
The people of Queenstown were not left wealthy after the copper mine closed – the company profits went offshore – sound familiar?
Sticht’s Mining Legacy to Tasmania
– a denuded moonscape above Queenstown caused by sulphuric acid associated with the copper mining and smelting.
The people of Queenstown were not left wealthy after the copper mine closed – the company profits went offshore – sound familiar?
.
In 2013, there are ten new mines proposed for the Tarkine over the next five years, and the campaign to prevent this onslaught of destruction is heating up. Nine of these mines are Pilbara style open cut mines. The first two companies to submit for permits are Venture Minerals for their three proposed tin and iron ore mines at Mt Lindsay, and Shree Minerals for their proposed Nelson Bay River iron ore mine.
.
2011: Open Cut Mine proposed by Indian company, Shree Minerals
.
Indian-owned mining conglomerate, Shree Minerals, has proposed to develop an open pit magnetitie/hematite mine and processing plant near Nelson Bay River , approximately seven kilometres east of Temma village in northwest Tasmania. The proposed mine will target 4 million tonnes of the resource over a 10 year period producing 150,000 tonnes of product per year.
.
[Ed: This is in The Tarkine, but of course the term is deliberately omitted]
.
Parent company, Shree Minerals and Fuels, is headquartered at 51 M.I.G., Jain Mandir Road, Shanti Nagar, Housing Board, Katni, Madhya Pradesh, India. It is was established by millionaire, Vishwanath Garodia, and is currently owned by Vijay Garidia. The Shree Minerals Board of Directors is currently made up of Chairman Mr Sanjay Loyalka, Mr. Arun Kumar Jagatramka, Mr Mahendra Pal, Mr Andy Lau and Mr Amu Shah.
[Sources: ^http://www.shreemineralsandfuels.com/owners-profile.html; ^http://www.shreeminerals.com/scripts/page.asp?mid=11&pageid=13].
<< Shree Minerals has lodged a Development Application with a supporting Development Proposal and Environmental Management Plan (DPEMP) to Circular Head Council… (and) the Australian Government has declared the proposal a controlled action which will require assessment and approval under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999. This process will occur separately from the State Government process (which has approved the mine). >>
.
[Source: Tasmanian Government, ‘Shree Minerals Ltd Nelson Bay River Mine, (undated), ^http://epa.tas.gov.au/regulation/shree-minerals-ltd-nelson-bay-river-mine].
 Tasmanian Baby Boomer politicians in 2012 with Indian chairman of Shree Minerals, Sanjay Loyalka
[Source: Tasmanian Minerals Council, ^http://www.tasmanianmining.com.au]
Tasmanian Baby Boomer politicians in 2012 with Indian chairman of Shree Minerals, Sanjay Loyalka
[Source: Tasmanian Minerals Council, ^http://www.tasmanianmining.com.au]
.
<< With Tasmanian approvals in hand for mining at Nelson Bay River (NBR), Shree Minerals awaits Commonwealth Government approval, which is expected soon. Meanwhile, drilling will commence at NBR in November.
Shree Minerals (ASX:SHH) has re-affirmed that it is awaiting Commonwealth approvals for mining to commence at its Nelson Bay River Iron Project (NBR) in Tasmania.
Tasmanian approvals were received from:
– Circular Head Council, Tasmania;
– Environmental Protection Authority (EPA), Tasmania; and,
– Mineral Resources Tasmania (MRT) grant of Mining Lease
Shree said it expects a final decision from the Australian Commonwealth Government under EPBC Act, for which the final EIS has been published following response to submission received as a result of public exhibition of Draft EIS. Further that it expects to receive approval and a final decision is now expected soon.
Other highlights included:
– Grant of Mining Lease from Mineral Resources Tasmania (MRT) for mining at NBR has been received
– Maiden Reserves published and DSO mine plan for first 2 years finalised (October 2012).
– The 2011/12 fieldwork at Mt.Sorell has identified encouraging signs for the presence of Volcanic Hosted Massive
The production schedule for the first two years comprises mining of DSO iron ore. The DSO requires no further beneficiation to produce a marketable product. It only requires crushing and screening. Two separate DSO pits are planned in the first two years (comprising DSO South Pit and DSO North Pit, which is within the BFO resources) with following total resultant pit quantity of 815,000 tonnes at 57.5% iron (Fe):
The DSO is a first, lucrative stage of mining at NBR. It involves minimal CAPEX and no infrastructure CAPEX.
Development stages at NBR
Development of the project involves three stages. The first stage is to develop two relatively shallow opencut mines to produce direct shipping grade hematite ore.
This direct shipping ore (DSO) only requires crushing and sizing to produce the DSO product. Each pit will produce a separate grade of DSO product.
The south pit has a higher DSO grade and will be mined first with the product transported to Port Latta for export. The north DSO pit, situated above the main magnetite orebody will follow. It has a lower DSO grade.
Stage two involves the continuation of mining of the northern DSO opencut. Here the stage one DSO hematite oxide cap is surrounded by lower grade ore considered to have the potential to be processed to produce a commercial beneficiated oxide product (BFO). Processing the BFO material is considered to be stage two of the project.
Stage three of the project involves the opencut mining of the deep magnetite orebody beneath the oxide cap. This magnetite ore will require processing to produce commercial grade magnetite products and the BFO processing plant will be modified to achieve this objective.
Earlier studies demonstrated that the magnetite ore can produce two products, a dense media magnetite (DMM) product suitable for coal washery applications or a blast furnace pellet (BFP) magnetite product.
Suppliers are few in number for the higher value DMM product and mining generally occurs on a small scale. This would suit the Nelson Bay Iron Project.
Shree is planning to commence drilling at the NBR and Rebecca Creek tenements during the second week of November. Documentation for approval to drill ~3500 m to improve resource category and further extension of resources and geotechnical studies at the Project was submitted to the Minerals and Resources Tasmania. >>
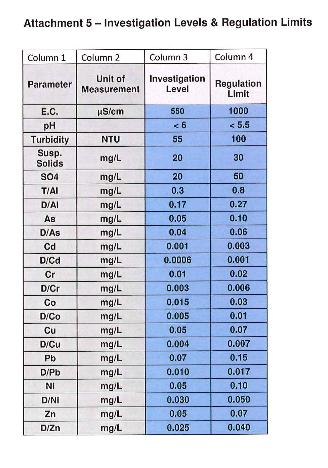 The Mine’s expected Heavy Metal products/tailings cocktail
The Mine’s expected Heavy Metal products/tailings cocktail(Copper, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, Cobalt, Nickel and Zinc, as well as Arsenic and sulphuric acid)
.
[Source: ‘Is Shree Minerals the next iron ore producer in Australia?’, 20121029, by Proactive Investors, ^http://www.proactiveinvestors.com.au/companies/news/35093/is-shree-minerals-the-next-iron-ore-producer-in-australia-35093.html].
Shree Mining Gloat
.
<< Shree Minerals chairman Sanjay Loyalka presented to over 175 investors this week at the ‘Stars in 2013′ investor forum in Sydney – and outlined the company’s pathway to production. Shree is positioned to become Australia’s next iron ore producer when the company commences production from the Nelson Bay River Project in Tasmania in mid-2013.
Shree Minerals presented to brokers, fund managers and investors this week in Sydney at Proactive Investors “Stars in 2013” investor forum – and focused on how the company will become Australia’s next iron ore producer. The production schedule for the first two years comprises the mining of DSO iron ore, which requires no further beneficiation to produce a marketable product.
Shree is targeting iron ore production in mid-2013 from the Nelson Bay River Project which is located in the west coast of Tasmania, in an area rich with infrastructure which includes being close to roads and port.
Shree has a memorandum of understanding with nearby miner Grange Resources for use of port Latta, and has an off-take contract MOU in-place with a large international trading house.
All approvals are in place for developing the mine including; Environmental Protection Authority (EPA), Tasmania; Mineral resources Tasmania (MRT) grant of Mining Lease; and Commonwealth Government under EPBC Act.
Highlighting the prospectivity of the area, it hosts world class mines including Grange Resources’ Savage River, Vedanta’s Mt Lyell, Unity Mining’s Henty and MMG’s Roseberry and Avebury.
Shree’s Nelson Bay River Project has a goethite-hematite Inferred Resource of 1.4 million tonnes, magnetite Resources of 7.8 million tonnes at 38.3 DTR, and is capable of producing highgrade concentrates to produce Blast Furnace (BF) Pellets and Dense Media Magnetite (DMM). Importantly there is the opportunity for resource growth, considering that the current resource is only based on limited drilling at the north end of the Aeromagnetic Anomaly as the company focus in last two years has been the on permitting process and project development.
This exploration potential provides the opportunity for a substantial increase in scale and mine life.
The Nelson Bay River Project differentiates itself from other iron ore projects as it does not require large CAPEX in infrastructure, and importantly there is a local workforce available, which cuts costs compared to other producers who use the fly-in-fly-out model. >>
.
[Source: ‘Shree Minerals’ Sanjay Loyalka outlines path to iron ore production in front of 175 investors’, 20130125, by Proactive Investors, ^http://www.proactiveinvestors.com.au/companies/news/38728/shree-minerals-sanjay-loyalka-outlines-path-to-iron-ore-production-in-front-of-175-investors-38728.html].
Aug 2012: Tasmanian EPA recklessly approves Dark Side Ecology
.
.
<< The Tarkine National Coalition (TNC) has reacted with disbelief to the Tasmanian EPA’s approval of the Shree Minerals Nelson Bay River mine despite clearly incomplete and fraudulent information tendered by the proponent.
.
‘Shree EIS a mismatch of omissions, flawed assumptions and misrepresentations’
.
The Shree Minerals’ Environmental Impact Statement for the proposed Nelson Bay River open cut iron ore mine as a mismatch of omissions, flawed assumptions and misrepresentations. Key data on endangered orchids were missing, and projections on roadkill impacts on Tasmanian devil and Spotted tailed quoll were based on fanciful data known to contradict the company’s independent Traffic Impact Assessment.
.
Scott Jordan (TNC):
.
“The EPA seems to have abandoned rational science and accepted Shree Minerals’ assertion that a 1km long 220 metre deep open cut pit extending 170 metres below the level of the adjacent Nelson Bay River wont impact on hydrology.
The EPA also has chosen to accept Shree Minerals blatant contradictions and misrepresentations in the data relating to projections of Tasmanian devil roadkill from mine related traffic by accepting projections substantially lower than Shree Minerals’ own expert produced Traffic Impact Assessment. This increase of traffic will, on the company’s formulae, result in up to 32 devil deaths per year, not the 3 per year in presented in the data accepted by the EPA.”
.
This failure comes within days of Federal Environment Minister Tony Burke’s decision to absolve himself of responsibility for conducting environmental assessments by allowing the Tasmanian Government to conduct the EPBC assessments for mining projects in the Tarkine.
“Is this really the assessment regime that Tony Burke want to oversee the protection of the environment in the Tarkine?”, asks Jordan. Decisions on Commonwealth environmental approvals and local council approvals have not been granted at this point. Unlike the Venture Minerals projects, the Shree Minerals also has a concurrently running Commonwealth assessment. >>
.
Senator Christine Milne, leader of the Australian Greens:
.
“The Tasmanian Government EPA’s approval of the Shree Minerals mine confirms exactly why Tony Burke is wrong to trust this agency with the assessment of new mines in the Tarkine. Shree Minerals has no friends in the Tasmanian mining industry. The company fudged their data on likely impacts on the Tasmanian Devil – yet here they are securing Tasmanian Government approval.
“The ball is now in Tony Burke’s court. He should reject Shree’s mine, which still has to pass federal environmental approvals tests. He must reverse his decision to let Venture Mineral’s three mines be assessed by the Tasmanian Government.
“By not heritage listing the Tarkine, Tony Burke has washed his hands of responsible environmental protection and approval of the Tarkine rainforest and the threatened Tasmanian Devil, and now we see the consequences.”
.
The Tasmanian Greens will write to Tasmania’s Environment Protection Authority seeking further information over a decision to approve an iron ore mine at Nelson Bay River. >>.
 Alex Schaap, Tasmanian EPA Director
Under fire over nondisclosure of a heavy metals spill from a tailings dam spill at Grange Resources Savage River mine into surrounding waterways in early 2013.
[Source: ‘Tasmania’s Environment Protection Agency is on notice’, 20130318, by Isla Macgregor, Tasmanian Public and Environmental Health Network, ^http://tasmaniantimes.com/index.php?/weblog/article/tasmanias-environment-protection-agency-is-on-notice/]
Alex Schaap, Tasmanian EPA Director
Under fire over nondisclosure of a heavy metals spill from a tailings dam spill at Grange Resources Savage River mine into surrounding waterways in early 2013.
[Source: ‘Tasmania’s Environment Protection Agency is on notice’, 20130318, by Isla Macgregor, Tasmanian Public and Environmental Health Network, ^http://tasmaniantimes.com/index.php?/weblog/article/tasmanias-environment-protection-agency-is-on-notice/]
.
Greens Member for Braddon (Tasmania), Paul O’Halloran MP:
.
“Serious concerns have been raised about the reliability and accuracy of information provided to the EPA by the mine proponent, Shree Minerals. The public should be able to have full confidence in the capacity of agencies like the EPA to independently assess these controversial mining projects and to test the accuracy and rigour of the data they are provided.
“Critical details regarding the impact on threatened species appear to be missing or inconsistent with previously released data, and the potential hydrological impacts have not been fully assessed. “When you consider that the mine itself will be well below the level of the nearby Nelson Bay River, it’s hard to see how this will not impact on the area’s hydrology.
“If the Commonwealth uses the same questionable data for its assessment for the project, then the Tasmanian public will be rightly sceptical when their final decision is handed down.” >>
.
[Sources: ‘EPA’s approval of Shree Minerals’ incomplete environmental reports a farce’, 20120801, by Scott Jordan, Campaign Coordinator Tarkine National Coalition, ^http://tasmaniantimes.com/index.php?/weblog/article/epas-approval-of-shree-minerals-incomplete-environmental-reports-a-farce/]; ‘ Greens seek answers over Shree Minerals Assessment’, by Paul O’Halloran MP, Greens Member for Braddon, 20120727, ^http://tasmaniantimes.com/index.php?/weblog/article/epas-approval-of-shree-minerals-incomplete-environmental-reports-a-farce/].
Sep 2012: Mainland unions weigh into Tarkine v Mining debate
.
National Secretary of the Australian Workers’ Union Paul Howes discusses the union’s campaign to promote mining in Tasmania.
.
 National Secretary of the Australian Workers’ Union Paul Howes addressing a rally in Hobart,
with Tasmanian Premier Lara Giddings in the background.
[Source: ^http://www.tasmanianmining.com.au]
National Secretary of the Australian Workers’ Union Paul Howes addressing a rally in Hobart,
with Tasmanian Premier Lara Giddings in the background.
[Source: ^http://www.tasmanianmining.com.au]
.
ABC Television Transcript:
.
<< EMMA ALBERICI, PRESENTER: To discuss the AWU’s campaign, I was joined earlier in our Hobart studio by the union’s national secretary, Paul Howes.
Paul Howes, welcome to Lateline.
PAUL HOWES, NATIONAL SECRETARY, AUSTRALIAN WORKERS’ UNION: Thanks, Emma.
EMMA ALBERICI: The Federal Environment Minister Tony Burke on the Tarkine issue has indicated he’s not predisposed to wholesale heritage listing. So what exactly are your concerns there?
PAUL HOWES: There is a very large campaign being run at the moment by the Greens and GetUp in particular, aiming to have the entire north-western region of Tasmania, known as the Tarkine, listed for World Heritage listing.
That would potentially close two existing mines, would have the impact of not having the go-ahead for a number of new mines in the region which need to be developed.
At the moment north-west Tasmania has unemployment of around 8.4 per cent, when you compare that to the national average of 5.2 per cent, you can see how hard times are in that part of Tasmania.
And to lose a minerals industry would be devastating for the entire state, but particularly for the north-west.
The mines in question and the potential mines in question take up less than 1 per cent of the land mass of the Tarkine and whilst we accept there are many areas of the Tarkine that should be protected and should be locked up from future development, we are concerned that this large-scale campaign will pressure the Federal Government into actually granting a listing which would potentially shutdown this very important industry for north-west Tasmania.
And our members that work in the sector have been concerned for a long time, their voices haven’t been heard in the debate, and that’s why they asked us to run this campaign so that their voices can be heard on the national stage about what they believe should continue to happen in the Tarkine, which is having nature and the mining industry co-existing as it has done for 120 years.
.
EMMA ALBERICI: On the process of heritage listing, you would be aware that current mines are not affected and current applications for mines equally are not affected?
PAUL HOWES: Well that’s not the case.
EMMA ALBERICI: It’s certainly the case as Tony Burke’s office explained it to us.
PAUL HOWES: If you look at the issue, for example, of Rosebery. Rosebery isn’t subject to the … the current mining operations at Rosebery isn’t subject to the listing, but Rosebery needs a new tailings dam, that new tailings dam has to be built in an area which would be subject to the listing.
If the new tailings dam can’t be built then Rosebery would should, equally for Savage River. Savage River needs to expand and move into new parts of ore bodies that would be in areas where that listing applies.
Look, I’m very hopeful and I think that Tony Burke will make the right decision, but equally it’s important that the voice of Tasmanian miners and Tasmanian communities in the north-west of the state are heard in this debate.
As we have seen in the proposals put forward by the national Tarkine coalition, if they were successful in their proposal a whole range of potential mines and exploration zones would be locked up. So that’s why we need to ensure that when the Federal Government makes a decision, that it does the right thing for the environment, everyone agrees with that, but we don’t hurt the Tasmanian economy and create a situation where we’ve had intergenerational mining in that part of Tasmania for 120 years being wiped off the map for the sake of frankly an ideological agenda being driven by a few.
.
EMMA ALBERICI: But Paul Howes, we do have to make the distinction here, no-one is suggesting mining’s going to be wiped off the map in Tasmania. You say yourself these are potential mines, these are not current mines, nor are they mines under current assessment.
PAUL HOWES: Yes, they are Emma. They are currently under assessment.
EMMA ALBERICI: Well if they are under assessment Tony Burke’s office tell us they are not affected by the heritage listing. Who is right?
PAUL HOWES: Hopefully that will be the case but the campaign being run by the national Tarkine coalition and by the Greens would have the effect, if it were successful, in shutting down, for example, the venture minerals site. That’s the outcome.
Now we are providing the alternative voice, which is saying these areas equate to roughly 1 per cent of the land mass of the Tarkine and we believe that those areas should be excluded. In terms of the current mines, as I explained only just a few minutes ago, yes, it is true to say that the existing mine site at Savage River and the existing mine site at Rosebery isn’t covered by the proposal, but where those mines have to expand just slightly down the road is covered by the proposal.
And if those expansions can’t go ahead, then the existing mine sites won’t be viable. It’s not just a simple matter of getting out the map and looking at where the current mining operations take place and where the proposed ones have been, there is the case that if the national Tarkine coalition’s proposal goes ahead, you would see the mine life of a mine like Rosebery being cut drastically short.
I’m not in the business of running campaigns when we don’t have to, I would be more than happy to see a sensible campaign run by the environmental lobby that would actually result in carving out the minerals zones. But if you just log on to the national Tarkine coalition website, yourself, you’ll see that a large part of their campaign is about stopping the potential mines that should go ahead in the next couple of years, from actually happening.
.
EMMA ALBERICI: Some of the current approvals being sought are possibly going to endanger… possibly going to put at risk some endangered species. You would accept surely that some of those do need protection?
PAUL HOWES: Absolutely and once again, we are talking about an environmental footprint of less than 1 per cent of the Tarkine region. You are talking about areas which have been portrayed, particularly by GetUp, for example, as saying as being virgin or untouched rainforest, where it’s just not the case.
There has been widespread mining activity across the Tarkine for 120 years. Many of the areas that have actually featured in GetUp ads are actually areas which used to be mining facilities. In fact there was a famous ad that GetUp ran in The Sydney Morning Herald with a picture of the Environment Minister Tony Burke looking at a tree – he was standing on an old mining trail.
The point is that, yes, we need to do what we can to protect endangered species and yes we should lock up those areas of the region that deserve environmental protection, but we should also look at the facts in the cold hard light of day and recognise that there is the ability to have sustainable mining practices engaged right across that region and at the same time do the right thing by the environment.
.
EMMA ALBERICI: If we can move on to the Greens more broadly, you’ve been attacking them for the better part of the last few months pretty consistently. Is this part of a deliberate strategy to sort of re-establish Labor as an entity in its own right, to kind of divorce itself from the Greens on the political stage?
PAUL HOWES: In terms of the campaign that we have launched here in Hobart today, it’s a campaign that members of my union asked us to run, and I’m responding to the wishes of our members. That’s what membership based organisations do. Our union does campaign against companies, against governments and against political parties which pose direct threats to the job security of our members.
In the form of the Greens, whilst there are many policies that I do agree with the Greens on, overall their economic policies are ones which would lead to wide sections of the membership of the AWU being left out of work. That’s why we have been, for a very long period of time – it predates even my time as secretary of the union – been very strident and forthright in our criticism of a lot of the policies.
I’m pleased that we have seen over the last few months more people in the Labor movement stepping up to the plate, actually taking on the Greens, actually calling into question many of their policies which for too long have gone unquestioned. Ultimately I do think they should be held to account. I don’t think the Labor Party needs to differentiate itself because ultimately the Labor Party is a separate party.
The Labor Party and the Labor movement has very different values to the values of the Greens and whilst there might be some similarities in some areas, at the end of the day the type of Australia that the Labor movement wants to see and the type of Australia the Greens want to see are two very different types of Australia.
.
EMMA ALBERICI: Recently you have compared the Greens to One Nation and to the DLP. Have you gone too far there? What is it about the Greens that you fear?
PAUL HOWES: I don’t fear the Greens. Things that I fear I normally run away from. I don’t fear the Greens.
EMMA ALBERICI: You clearly fear their impact on your party.
PAUL HOWES: What I have said is I think it’s incumbent upon the Labor movement to actually take up the fight to the Greens, that we shouldn’t shy away from articulating the alternative vision that we see for this country.
Now as I said, there are many Greens policies which are similar to views that I hold, but ultimately on the key questions about work, the value of work, the type of economy we have, which is I think fundamental to the nature of what it is to be Australian – the Greens and the Labor movement are worlds apart.
My view has been for a long time that we should articulate that, we should take up that fight and that we should actually demonstrate that our values are different, their values are theirs.
Now of course, voters will be free to choose between the two, but we actually need to articulate those differences in our views and policies proudly and strongly.
.
EMMA ALBERICI: Is there a fear that voters won’t be able to see a difference between the two?
PAUL HOWES: I think occasionally that might be the case. I think of late, we have seen substantial differences. I was proud to be standing on the steps of Tasmanian Parliament today with the Tasmanian Premier Lara Giddings, who was very strongly backing our campaign about the Tarkine.
That clearly demonstrates she disagrees strongly with her colleagues in the minority government here in Tasmania, and that’s important. It’s important to traditional Labor voters, particularly in rural and regional Tasmania and important to working-class Labor voters right across the country to know that the Labor Party – still right across the nation, stands up for the values of work and believes in the need to have a diversified economy.
Ultimately, what the Labor Party does in government, state or federal, is up to them. But as a member of the Labor movement and our union has strongly believed for a long time that this is a fight that’s worth having.
.
EMMA ALBERICI: Finally, the new government in Queensland has today slashed just shy of 3,000 jobs in its Health Department.
What intelligence are you getting from your Queensland colleagues about how much further the job cuts are likely to go?
PAUL HOWES: We are very proud to represent over 10,000 workers in the Queensland Health Department and we are disappointed that Campbell Newman today in his announcement hasn’t articulated where these job cuts are going to happen.
We fear that it will be frontline workers in the hospitals that will be cut. If that happens, we will see a decrease in patient care right across Queensland. What we are seeing here is an aggressive and scary attack on services right across Queensland, but particularly in the Health Department.
Queensland Health has had a lot of problems for a long period of time, but cutting staff, stripping back services, outsourcing essential services across Queensland hospitals, is not the way to resolve issues in Queensland Health.
In fact, it will send Queensland Health back into the dark ages and frankly, we are fearful, in fact we are very strongly fearful and we suspect that this is only the beginning of deeper and harder cuts to come from Campbell Newman, once again betraying his promises to the Queensland people that he made right before the election.
.
EMMA ALBERICI: Right Paul Howes we have to leave it there but thank you very much for your time.
PAUL HOWES: Thank you, Emma. >>
.
[Source: ‘Paul Howes locks horns with the Greens over anti-mining campaign’, 20120907, Australian Broadcasting Corporation (television), Reporter Emma Alberici, ^http://www.abc.net.au/lateline/content/2012/s3585805.htm].
 [Source: Kudelka’s view,
^http://www.themercury.com.au/article/2012/05/12/327401_tasmania-news.html]
[Source: Kudelka’s view,
^http://www.themercury.com.au/article/2012/05/12/327401_tasmania-news.html].
Dec 2012: Burke approves Shree Mine based on dodgy submission
. Federal Environment Minister, Tony Burke in The Tarkine
Federal Environment Minister, Tony Burke in The Tarkine
.
<< Environment Minister, Tony Burke, today approved Shree Mineral’s Nelson Bay River Magnetite and Hematite Mine in north-west region of Tasmania with 29 strict conditions.
.
Mr Burke:
.
“The approval conditions will ensure the mine will be built and operated in strict accordance with national environment law. By imposing these 29 approval conditions I am satisfied the project can now go ahead without any unacceptable impacts on matters of national environment significance such as nationally listed threatened and migratory species and their habitat.
In making my approval I am requiring Shree Minerals to comply with a number of key environmental conditions and actions. My decision is based on a thorough and rigorous assessment of the proposal, with extensive opportunity for public consultation.
Key aspects of the approval conditions include:
- the development of a site-wide management plan for the protection of nationally threatened species at the mine site and for travel to and from the mine site
- the undertaking of targeted pre-clearance surveys for the nationally listed masked-owl, spot-tailed quoll, Tasmanian devil and Tasmanian wedge-tailed eagle
- environmental awareness training for all staff, contractors and visitors to the site.
.
“In addition I am requiring Shree Minerals to take specific actions to mitigate and avoid the threat of road kill to nationally threatened species, especially the Tasmanian devil.
I am requiring that mine vehicles travel only during daylight hours and abide by appropriate speed limits within and to and from the mine site and that they provide bus transport to limit the amount of traffic on nearby roads.
I am also requiring that Shree Minerals report all deaths of nationally threatened species from road kill caused by the operation of the mine. This information will be recorded on their website and updated at least every three months.
If reported road kill is in excess of predicted levels, the conditions require that Shree Minerals pay additional compensation or provide new resources for further environment programs to support threatened species in and near the site.
“I am also requiring Shree Minerals to fund and resource a Tasmanian Devil monitoring strategy on the mine site. The strategy will need to involve at least ten infrared monitoring cameras and be consistent with the work being done by Save the Tasmanian Devil Program.”
.
Each year Shree Minerals is required to report on their compliance with the approval conditions and publish this information on their website.>>
.
[Source: ‘Environment Minister Approves Shree Minerals Nelson Bay River Mine’ (media release), The Hon Tony Burke MP, Minister for Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities, 20121218, ^http://www.environment.gov.au/minister/burke/2012/mr20121218.html].
Burke allows mining disturbance to colour his purist view:
“I was expecting to see a pristine area pretty much covered in rainforest. The truth of the industrial history and current industrial activity in the Tarkine was quite different to those images”
.
 Tony Burke considers a plan for world heritage listing during a visit to the Tarkine
[Source: Photo by Peter Mathew, ‘Labor accused of betraying Tarkine forests by favouring mining in heritage decision’, by Matthew Denholm, The Australian (with AAP), 20130208, ^http://www.theaustralian.com.au/national-affairs/tony-burke-backs-away-from-tarkine-protection/story-fn59niix-1226573268457]
Tony Burke considers a plan for world heritage listing during a visit to the Tarkine
[Source: Photo by Peter Mathew, ‘Labor accused of betraying Tarkine forests by favouring mining in heritage decision’, by Matthew Denholm, The Australian (with AAP), 20130208, ^http://www.theaustralian.com.au/national-affairs/tony-burke-backs-away-from-tarkine-protection/story-fn59niix-1226573268457]
.
Burke lets mining wounds open up Tarkine to circling vultures
.
<<The large expanse of land known as the Tarkine is currently host to around 60 mineral exploration licences, with 10 mines proposed for development over the next few years. The mineral rich area is also largely undisturbed, with temperate rainforests, open plains, diverse flora, and a stronghold of healthy Tasmanian Devils. The approval of the Nelson Bay River magnetite mine marks the beginning of a new chapter in the Tasmanian discourse over the benefits of exploiting natural resources over the preservation of unique natural heritage.
There are existing mines in the Tarkine region on the West Coast of Tasmania; the iron ore mine in Savage River managed by Grange Resources, the Hellyer Mine managed by Bass Metals and the Rosebery Mine managed by MMG.
A long history of mining in the area is coming face to face with a growing awareness of its unique natural and cultural significance.
Yesterday’s approval of a magnetite mine adjacent to the Nelson Bay River by Federal Environment Minister Tony Bourke is the first of several proposed new mining ventures in the area, after nearly twenty years of no new mining approvals in the state.
The interest in superior steel products is creating an increased demand for magnetite across Australia, which, after being processed, provides a consistently higher iron content in comparison to hematite ore.
The magnetite mined from the proposed open cut pit is also used to create magnetic iron oxides used in magnetic storage, for example in the magnetic layer of hard disks.
Twenty-nine conditions from Federal Environment Minister Tony Burke accompany the approval of Shree Minerals’ Nelson River Bay mangenite mine, largely directed at protecting native flora and fauna.
Included in the environmental conditions are $48,000 fines if Tasmanian Devils are killed by vehicle movement, if more than two are killed within a 12 month period.
As Tasmania takes a respite from the ongoing debate over how to restructure a floundering forestry industry, reactions to the magnetite mine approval have been swift.
Leon Compton spoke to some stakeholders in the approval on Statewide Mornings, beginning with Ian Woodward, principal environmental scientist for Tasmanian firm Pitt and Sherry, who prepared the environmental assessment report.
“In terms of the environmental significance, both the state and commonwealth assessments have been very comprehensive.”
“There are no threatened plant species on the site, there is a very low likelihood of threatened fauna, there might be one or two Tasmanian Devils that use the area.”
Shree Minerals has also committed to road transport movement during the day time, and limited speed conditions.
“Minister Burke’s concerns were confined to threatened species listed under Federal legislation, the EPA’s assessment in the Tasmanian jurisdiction was very much more comprehensive and considered all environmental matters including ground disturbance, water management, potential for acid drainage and how that would be mitigated and managed.”
The mine footprint is about 150 hectares, and will consist of two open cut pits that are designed to contain the possibility of acid generating materials being uncovered.
Exposed rock can generate acid as it oxidises, and there are examples of acidic poisoning of rivers from previous mining activities in the region.
Most famously, the King River is described as the most polluted river in Australia, a result of mining prctices at Mount Lyell on its tributary, the Queen River.
The Whyte River and Savage River, which both flow into the Pieman River, and the Arthur River at the northern end of the Tarkine, all suffer from acidity as a result of previous mining practices.
Scott Jordan, from the Tarkine National Coalition, believes that the proposed mine will have a massive effect upon the hydrology on the area around the site.
“This mine will be 225 metres deep, it will be 170 metres below the level of the adjacent Nelson Bay River, it will 60 metres below sea level.”
“In the referal that went to the Commonwealth, there were 16 Commonwealth listed threatened species identified within the five kilometre radius of the site.”
He questioned the assertions made by Pittt and Sherry regarding Tasmanian Devil numbers and the traffic impact assessment.
“They submitted to the Commonwealth that there would be an increase in road traffic affecting Tasmanian Devils of 32 percent, when in fact the Traffic Impact Assessment tells them that they would be looking at about 320 per cent.”
Asked why we have yet to hear from state green cabinet members, Mr Jordan said, “These decisions are made by a minister, they are not made by a cabinet, and so I would expect that the Green members of cabinet are just as upset about this as I am, and I expect that we will see them voicing that concern.”
Leon Compton also spoke with Circular Head Mayor Daryl Quilliam who vouched for the benefits of the proposed mine for the region.
“It’s not only good for our area, it’s good for Tasmania becvause of the investment that is happening overseas and good for the region in that jobs will be created right along the North West Coast.”
Asked about the environmental concerns Mr Quilliam said, “Everybody is welcome to their opinion, and that is fine, but you’ve got to stop and realise that there has been five or six years of planning for this mine, and just to go through the rigorous process it goes through now, all those environmental issues have been looked at.”
“Mines are not like they used to be 40 or 50 years ago, where you just dig a hole and leave a hole.”
Mr Quilliam discounted the area as the last refuge of the Tasmanian Devil, and cited Woolnorth as being more likely as that region.
“If there are protests, well I am sorry, but our local people, and I would say 80 to 85 percent of our local people are supporting that mine, will need to protest against them as well.”
Mr Quilliam called for people to work together to protect the region, and thinks that there is no reason why all values cannot be upheld. >>
.
[Source: ‘Tarkine focus on Nelson Bay River’, 20121219, by Tim Walker (Cross Media Reporter), ABC, ^http://www.abc.net.au/local/stories/2012/12/19/3657638.htm].
Tasmanian Devil’s extinction by a thousand cuts
.
<< Just a week before Christmas, Environment Minister Tony Burke approved Shree Minerals’ mine near Temma in the Tarkine region of north-west Tasmania. Perhaps he hoped the announcement would get lost in the Christmas and New Year “silly season”, because this approval is likely to be extraordinarily controversial: the mine is in an area currently proposed for World Heritage listing and is also in the last remaining stronghold of the Tasmanian devil.
The Tasmanian devil is threatened with extinction by an infectious cancer. Since its first discovery in north-eastern Tasmania in 1996, the cancer has inexorably spread westward, reducing Tasmanian devil populations by at least 80%.
Only the north-west remains undiseased. There are indications that the devil populations in the north-west have slightly different genetic composition from those in the remainder of Tasmania and may perhaps harbour some individuals with genotypes resistant to this lethal disease.
Tony Burke’s press release and his approval of 18 December explicitly recognise the threat that this mine will pose to Tasmanian devils: the developers are required to donate $350,000 to the Save the Tasmanian Devil Program Appeal to compensate for the mine’s unavoidable impact.
Within the limited area of the mine site itself, there will certainly be impacts on wildlife, including devils. More seriously, the ore will need to be trucked out by road for about 150km. Almost all of this distance will be through habitat of undiseased Tasmanian devils.
As scavengers, devils are particularly susceptible to being killed on roads, as they feed on the carcasses of other animals, such as possums or wallabies, which have previously been run over. As anyone who has driven in Tasmania will know, roadkill of Tasmanian Devils is not new. The problem is that its impact on the viability of the species as a whole is much greater now than it has been in the past, given that roadkill is additional to mortality imposed by facial tumour disease. This and other proposed mines will substantially increase total vehicular traffic in the remote north west of Tasmania.
The approval contains several conditions intended to mitigate this threat of roadkill to devils. These include an obligation to report all incidents of roadkill, a requirement that most travel to and from the mine site must occur during daylight hours and reduced speed limits of 50 km/h or less close to the mine site. But most of the distance mine trucks will travel through devil habitat on their way to port will be outside the reduced-speed-limit area.
A penalty of $48,000 will be applied to each Tasmanian devil in excess of two per year killed on the road by mine vehicles. This sounds a strong disincentive in principle, but I wonder what will happen in practice. There will be an even stronger incentive for vehicle operators to simply throw a carcass off the road into the bush rather than admit to killing a devil and incurring this substantial financial penalty.
More generally, this example highlights a problem with Australian environmental regulation. Up to 10 mine developments are currently proposed for the Tarkine area. The impact of each one individually might perhaps be acceptable in terms of increased risk of impacts on Tasmanian devil populations. But the impact of all 10 in aggregate will certainly be much less acceptable.
If mines are evaluated individually, we risk a scenario of “death by 1000 cuts”. The appropriate way to evaluate the risk would be to take all of the proposed developments together and assess whether the joint effect of all can be handled without unacceptable risk to biodiversity conservation.
The fact that this mine development has been approved individually does not give me confidence this approach will be taken. >>
.
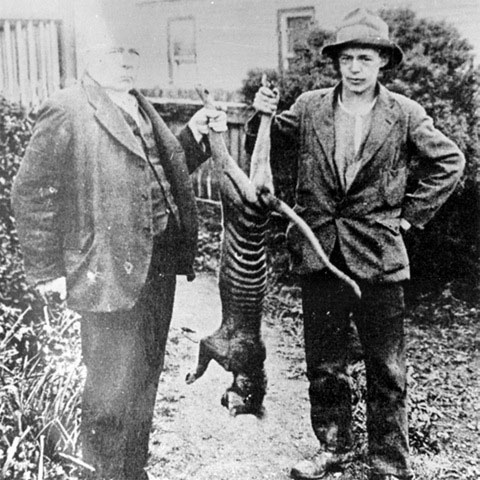 Different animal, same attitude
Different animal, same attitude
.
[Source: ‘Tarkine mines could be last straw for Tasmanian devils’, 20130115, by Hamish McCallum, Head, Griffith School of Environment at Griffith University, ^http://theconversation.com/tarkine-mines-could-be-last-straw-for-tasmanian-devils-11483].
Feb 2013: Tony Burke refuses Tarkine heritage listing
.
In December 2009, with wide recognition of its National Heritage values, The Tarkine was granted Emergency National Heritage listing by former Federal Environment Minister Peter Garrett, however this lapsed in December 2010 .
Despite the Australian Heritage Council (AHC) already recommending a 433,000 hectare National Heritage Area, Minister Burke has instructed the AHC to reassess the Tarkine. The reassessment deadline was extended to December 2013.
<<..Despite a 2010 Australian Heritage Commission recommendation for the listing of 433,000 hectares of the Tarkine, Mr Burke said on Friday he would only recognise its Aboriginal heritage.
Mr Burke said he had tried to find a boundary that would incorporate the natural values without delivering unacceptable social and economic outcomes.
”I simply haven’t been able to find a way to recognise the natural heritage values with a boundary that will find a balance,” he said. ”For this reason I have decided to only put the indigenous values on the national heritage list.”
Mr Burke said he acknowledged that his decision was not the outcome for the Tarkine that many groups were seeking. He said part of the Tarkine’s coastline would be entered on the National Heritage List as the Western Tasmania Aboriginal Cultural Landscape.
The decision was warmly backed by the local MHR and parliamentary secretary for Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry, Sid Sidebottom. ”Minister Burke has listened carefully to my representations on behalf of our region, and to the delegations of union members – particularly from the Australian Workers Unions – and of my local mayors,” Mr Sidebottom said.
The AWU under secretary Paul Howes mounted an ”Our Tarkine – Our Future” campaign promoting job opportunities in the region.
The move drew praise from a local MP, but sparked an angry response from Greens leader Christine Milne, who said the Minister had ”abandoned the Tarkine to the mining and timber industries”. Ms Milne said she was ”devastated”: ”If anyone has any doubt as to who is running the environment portfolio in Australia the answer is very clear: the mining industry.
”I have been campaigning for the Tarkine for a very long time . . . Tony Burke has completely sold out the environment for logging and mining.”
She called on Mr Burke to release the heritage council’s latest recommendations, made in a report to the government last December. >>
.
[Source: ‘No’ to Tarkine environment listing’, 20130208, by Andrew Darby (Hobart correspondent for Fairfax Media) with Jonathan Swan, ^http://www.smh.com.au/environment/no-to-tarkine-environment-listing-20130208-2e2bo.html].
Apr 2013: Conservationists find a qualified doctor to save the wounded Tarkine
.
<< Mining in Tasmania’s Tarkine region is being challenged as conservationists take their battle to the federal court.
The Tarkine National Coalition has lodged a case in the Federal Court seeking a review on Federal Environment Minister Tony Burke’s decision approving Shree Minerals iron ore mine.
Campaign co-ordinator Scott Jordan said Burke approved the mine without knowing the impacts it could have on the endangered Tasmanian devil.
“We will argue that Minister Burke has not acted in accordance with the provisions of the Environmental Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act, and as such the approvals granted are invalid,” Jordan said. “This mine should not have received approval, and we are asking the court to rule against it. “
Debate erupted over the application for mining developments in the region last year, with Federal Environment Minister Tony Burke rejecting a National Heritage listing for the area.
Debate continues to rages between environmental groups who want mining developments halted and companies and potential employees who say opening up the Tarkine region to mining is crucial in the future economic prosperity of Tasmania.
Earlier this year, Tasmania’s Premier Lara Giddings said three new mining projects were expected in the region following Burke’s rejection of the National Heritage listing.
Giddings said she expected Venture Minerals’ proposal for a $200 million tin mine at Mount Lindsay to be approved, creating 1000 jobs.
She said that developments like Venture’s Riley Creek mine and the approved Shree Metals mine at Nelson Bay were signs that mining investment would grow in Tasmania now that the “dark cloud” of the Tarkine national heritage nomination had been removed.
Environmentalists argue that open-cut mining will destroy the area and say that any decision to expand mining will result in irreversible contamination. >>
.
[Source: ‘Federal Court fight to stop Tarkine mine’, 20130404, by Vicky Validakis, Mining Australia, ^http://www.miningaustralia.com.au/news/federal-court-fight-to-stop-tarkine-mine].
Desperate times again drive Tasmanians to burn their house to stay warm
.
<< The Deputy Premier has defended the Labor-Greens Government at a pro-development and pro mining rally in north-west Tasmania.
The Unlock Tasmania Rally in Smithton yesterday heard from eight industry speakers, including representatives from the mining industry, and the Farmers and Graziers Association.
Organiser Joan Rylah estimates more than 3,000 people attended. Ms Rylah says the State Government has been influenced by minority fringe groups, while the majority’s concerns have been ignored. “These people are feeling that they have not been heard,” she said.
The Deputy Premier Bryan Green also addressed the crowd. He says times are tough, but the minority government is not to blame.
[Ed: Yes it is]
“It is an easy target,” he said. Mr Green says he shares the crowd’s frustrations at the court injunction launched by conservationists, banning work at the Shree Minerals mine at Nelson Bay River in the Tarkine until a legal hearing next week. >>
.
[Source: ‘North-west rally backs development’, 20130624, ABC, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/2013-06-24/pro-miners-rally-for-development/4774734?section=tas].
Jul 2013: Court overrules Burke’s Bias
.
 Federal Court of Australia
~ such an apt emblem
Federal Court of Australia
~ such an apt emblem
.
<< A conservation group (Save the Tarkine) has stopped an open cut iron ore mine in Tasmania’s Tarkine region which it says threatened the Tasmanian devil. The Federal Court has ruled that the Federal Environment Minister’s approval of Shree Minerals’ open cut mine at Nelson Bay River was invalid.
Then minister Tony Burke approved the mine last December, imposing nearly 30 conditions to protect the devil and other threatened species.
The far north-west is considered one of the last disease-free areas for the state’s devil population.
Environmental group Save the Tarkine sought a judicial review of the decision, arguing Mr Burke did not act in accordance with the Environment Protection Act.
The group’s Scott Jordan was in the Federal Court in Melbourne to hear the judgement.
“It’s a great day for the Tarkine and it’s a great day for the Tasmanian Devil that was placed under threat by this mining proposal,” he said. “The Minister’s been given a clear message; that short cuts to get mines over the line in the Tarkine won’t be tolerated.”
Save the Tarkine has flagged it will continue to fight any other proposed mines in the area.
“They shouldn’t be taking short cuts to get mining projects up like the Tarkine. This is an area that shouldn’t be mined,” Mr Jordan said.
The $20 million project was expected to employ 70 workers and was the first mine approved in Tasmania in 26 years.
A spokesman for the new Federal Environment Minister, Mark Butler, says the decision is being examined. “The Minister will carefully consider the court’s decision before proceeding further,” he said.
.
Ruling disappoints Tasmanian Premier and local Circular Head Mayor
.
Tasmania’s Premier Lara Giddings says it is disappointing.
“We would have hoped to have seen Shree Minerals go ahead,” she said.” “We see it as economically sustainable, environmental sustainable and important investment that will help create jobs in the mining industry. “We will now of course review the Federal Court decision and see what Government can do to assist that company.”
Circular Head mayor Daryl Quilliam has called it a sad day for the whole state. “While I respect the court’s decision…I just think it gives any investors who want to invest in Tasmania, probably puts a query for them and whether they’re going to continue to invest in Tasmania,” the mayor said.
 Circular Head mayor Daryl Quilliam
Same Baby Boomer age group, same Baby Boomer mindset
Circular Head mayor Daryl Quilliam
Same Baby Boomer age group, same Baby Boomer mindset
.
Despite the ruling, he is optimistic Shree will proceed with its plans. “I expect that they’ll have to deal with some issues that have been raised by the court and I wouldn’t expect that it’ll knock it in the head completely.” “But it will certainly slow up the process and I just hope that they continue on and do whatever is necessary to make it valid.”
Tasmanian Liberal Senator Eric Abetz says most sensible Tasmanians would want the mine to go ahead.
“It is important for our state to harness our mineral wealth and our forestry wealth and the Government has been busy in destroying job opportunities in both areas and in the one area where they’ve made an exception, they’ve mucked it up,” he said.
 Tasmanian Eric Abetz MP
Same Baby Boomer age group, same Baby Boomer mindset
Tasmanian Eric Abetz MP
Same Baby Boomer age group, same Baby Boomer mindset
.
The Commonwealth will pay the legal bill from the court challenge. >>
.
Read Federal Court Ruling:
.
Case Citation: ‘Tarkine National Coalition Incorporated v Minister for Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities [2013] FCA 694’
^http://www.judgments.fedcourt.gov.au/judgments/Judgments/fca/single/2013/2013fca0694
.
[Source: ‘Federal Court ruling halts Shree Mineral’s $20m Tarkine mine’, 20130717, by Zoe Edwards, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/2013-07-17/court-decides-tarkine-mine27s-fate/4825230].
The industrial fight persists to exploit the last of Natural Tasmania
.
<< The Federal Court’s decision to halt work on an iron ore mine in Tasmania’s remote Tarkine region has spooked the industry, but the State Government has vowed to help fight it.
In December, the then Federal Environment Minister Tony Burke approved $20 million plans by Shree Minerals to build an open cut mine in the north west, the last disease-free stronghold of the Tasmanian devil.
Justice Shane Marshall has upheld a claim by the lobby group Save the Tarkine that Mr Burke did not properly take into account conservation advice about the endangered species and ruled its approval invalid.
Terry Long of the Minerals Council says it could scare off potential investors. “It’s been challenged on a detail in the court and knocked over. So from Tasmania’s point of view it’s a worry into the future, I mean it’s going to be difficult to get people to take on projects in the state under the circumstances.”
But Tasmania’s Resources Minister, Bryan Green, is viewing the ruling as a setback that can be resolved easily. Mr Green says he will be asking the new Environment Minister, Mark Butler, to quickly reconsider the project, taking into account the conservation report on the Tasmanian Devil. “This is a setback but it’s not the end of the process by any stretch of the imagination.
“Because from what I can see, based on the Federal Court’s decision, other than this administrative error the approvals process is sound,” said Mr Green.
The Premier Lara Giddings believes the mining proposal is economically and environmentally sustainable. “We will now of course now review the Federal Court decision and see what Government can do to assist that company to be able rectify any problems that the Federal Court has identified and ensure we can get that investment back on the right track,” said Ms Giddings.
The Greens leader Nick McKim does not think the Federal Court decision paints Tasmania as a risky place to invest. “The decision says nothing about the investment environment in Tasmania and says everything about the need for the Commonwealth Minister to follow a lawful process,” he said.
.
Jobs blow for struggling region
.
The mine was expected to employ seventy workers. The earthmoving contractor, Rodney Collins, says he employs 10 people and was looking to recruit more. He says the court’s decision is a kick in the guts. “You know there’s (sic) thirty new people who can’t have a job and at the moment after today we don’t know what we’re going to do with the people working for us at the moment,” he said.
Another three Tarkine mining projects are awaiting approval. Shree Minerals says it “followed the approval process to the letter of the law and beyond, with the best possible scientific advice. “For the project to be set aside on appeal is disappointing in the extreme.”
The (new) Environment Minister replacing Tony Burke, Mark Butler MP, now with the title Minister for the Environment, Heritage and Water; says he is carefully considering the court’s ruling before deciding his next step. >>
.
[Source: ‘fight-to-restore-tarkine-mine-approval, 20130717, ABC, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/2013-07-17/fight-to-restore-tarkine-mine-approval/4826860].
Tasmanian Minerals Council can’t help itself’
.
<< Calls by Tasmanian Minerals Council chief Terry Long, Tasmanian Deputy Premier Bryan Green and Braddon MP Sid Sidebottom for some kind of technical or administrative fix to yesterdays Federal Court decision to set aside approvals for the Nelson Bay River mine in the Tarkine, are both uninformed and an example of the kind of corrupted process that resulted in the Federal Court decision.
“The failure of the Minister and his department to consult the Approved Conservation Advice was not an administrative oversight. The Approved Conservation Advice is the key source of advice on which the Minister must rely to determine how best to protect the Tasmanian devil in any assessment,” said Save the Tarkine Campaign Coordinator, Scott Jordan.
“You can’t just add it to the appendix after the event and publish the same decision. The court didn’’t say the Minister forgot to list it, it actually said the Minister failed to consult it at all,”
“The comments by Long, Green and Sidebottom show an example of trying to solve a problem by repeating the action that created it”.
“The Minister must either let the court decision stand as the final judgement, appeal to the full bench of the Federal Court, or go back to the start of the process and conduct a proper legal assessment. Anything short of this will end up back before a court on exactly the same grounds”. >>
[Source: ‘No quick fix for Tarkine mine’, 20130718, media release by Scott Jordan, Campaign Coordinator, Save the Tarkine].
.
Further Reading:
.
[1] >Environmental-Assessment-Report-Shree-Nelson-Bay-River-Magnetite-Mine-EPA-2012.pdf (4.8MB, 50 pages, PDF)
.
[2] >Tasmania’s Tarkine vulnerable to reckless mining
.
[3] >Save the Tarkine from Venture Minerals
.
[4] >Miners eyeing off The Tarkine, just don’t get it!
.
[5] >Shree Minerals invasion into the fragile Tarkine
.
[6] >Tasmania’s white raptor endangered in Tarkine
.
[7] >Tasmania’s Tarkine Wilderness ENDANGERED!
.
[8] >Tarkine’s above ground values are for eternity
.