Posts Tagged ‘deforestation’
Wednesday, December 5th, 2012
 Click above image to play video: ‘Appetite for Destruction: China’s trade in illegal timber’ Click above image to play video: ‘Appetite for Destruction: China’s trade in illegal timber’
.
China is the World’s Top Buyer of Illegal Timber driving deforestation.
<<BEIJING: China, emergent superpower and the world’s second biggest economy, is effectively standing on the sidelines as its exponential growth devastates forests in a trade worth billions of dollars a year.
In the new report Appetite for Destruction: China’s Trade in Illegal Timber, launched today in Beijing, the London-based Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA) reveals that China is now the single largest international consumer of illegal timber, importing wood stolen by organised criminal syndicates on a massive scale.
In the past 10 years, significant progress has been made to protect shrinking forests around the world from the devastating impacts of illegal logging. As major timber-consumers, the United States the European Union and Australia have now taken legislative steps to exclude stolen timber from their markets, while key producer countries such as Indonesia have dramatically improved enforcement against illegal logging.
Yet although China has taken vigorous and laudable steps to protect and re-grow its own forests, it has simultaneously nurtured a vast and ravenous wood processing industry reliant on importing most of its raw materials.
“China is now effectively exporting deforestation around the world,” said Faith Doherty, head of EIA’s Forests Campaign.
“Any further meaningful progress to safeguard the forests of the world is being undermined unless the Chinese Government acts swiftly and decisively to significantly strengthen its enforcement and ensure that illegal timber is barred from its markets.”
EIA investigators has been conducting field investigations into flows of illicit timber, including working undercover and posing as timber buyers, since 2004 in China, Indonesia, Laos, Madagascar, Mozambique, Myanmar, the Russian Far East and Vietnam.
Appetite for Destruction examines the extent and impacts on these countries of China’s voracious consumption, and features several case studies from countries whose forests are being severely depleted.
“This report makes a clear and concise case for action by China,” added Doherty. “The burden of making any further progress in the international fight against deforestation, illegal logging and the criminal networks behind it now rests squarely on its shoulders.”>>
.
 Chinese have become the worst deforesters on Earth Chinese have become the worst deforesters on Earth
.
.
1. The Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA) is a UK-based Non Governmental Organisation and charitable trust (registered charity number 1145359) that investigates and campaigns against a wide range of environmental crimes, including illegal wildlife trade, illegal logging, hazardous waste, and trade in climate and ozone-altering chemicals.
2. Read and download Appetite for Destruction at http://www.eia-international.org/?p=6379.
[Source: Environmental Investigation Agency, 62-63 Upper Street, London N1 0NY, UK, ^www.eia-international.org, ^https://vimeo.com/54229395 ]
.
The Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA) is an independent campaigning organisation committed to bringing about change that protects the natural world from environmental crime and abuse.
Sunday, March 4th, 2012
Some wee satire….

Dozer Rights
.
We are built to do a job
We do that job well
We clear unwanted rubbish,
debris, obstacles, clear roads, bushes, pesky trees,
in some god forsaken places – people and their homes
.
It’s not our fault we’re gaudy yellow
Can’t miss us that way!
We often work solo
in the middle of nowhere
And we go all day
We work hard! ..努力加油 “loh lik gah yau!“
.
But we’re persecuted
Many hate us
They don’t understand
It’s not our fault
We’re just following orders
It’s a dozers lot
We have rights too.
.
 A bulldozer flattens out coastal sand dunes to make way for Donald Trump’s golf course
Aberdeenshire, Scotland A bulldozer flattens out coastal sand dunes to make way for Donald Trump’s golf course
Aberdeenshire, Scotland
.
 Dozer clearing the way Dozer clearing the way
.
 Dozers in Rosella Waters, doing it for permaculture in the Atherton Rainforest
(The Permaculture Research Institute on the USA)
…they wouldn’t let us back home Dozers in Rosella Waters, doing it for permaculture in the Atherton Rainforest
(The Permaculture Research Institute on the USA)
…they wouldn’t let us back home
.
 Smoko Smoko
.
 Dozers helping out for new housing in Brazil Dozers helping out for new housing in Brazil
.
 Dozers helping out in Sumatra for pulp wood
. Dozers helping out in Sumatra for pulp wood
. Dozers helping out for Palm Oil Dozers helping out for Palm Oil
.
 Dozer respect for riparian habitat Dozer respect for riparian habitat
.
 Dozers having a wee afternoon doze
. Dozers having a wee afternoon doze
.
 23 year old International Solidarity Movement activist Rachel Corrie
— about to be crushed by an Israeli bulldozer 20030317 23 year old International Solidarity Movement activist Rachel Corrie
— about to be crushed by an Israeli bulldozer 20030317
.
 Greg Schnabel, 28, from Chicago, said the protesters were in the house of Dr. Samir Masri. Greg Schnabel, 28, from Chicago, said the protesters were in the house of Dr. Samir Masri.
“Rachel was alone in front of the house as we were trying to get them to stop,” he said. “She waved for the bulldozer to stop and waved. She fell down and the bulldozer kept going. We yelled ‘stop, stop,’ and the bulldozer didn’t stop at all. It had completely run over her and then it reversed and ran back over her.”
-from Ha’aretz
^http://www.indybay.org/newsitems/2003/03/17/15838231.php
.
 See, they just don’t understand See, they just don’t understand
.
Postcript:
.
We added the Israeli human tragedy to this article afterwards.
We were shocked and consider this event of 2003 murderously barbaric, and so not to be forgotten to history.
We include it to convey a message of comparison to readers that the unacceptable horror inflicted by humans on non-humans is comparable to the unacceptable horror humans continue to inflict upon themselves.
When one reflects about ‘humanity’ one considers the status well below ‘ecology’. Such distinguishing sadistic human motives are not part of non-human ecology.
.
What is CRIME?
.
Clearly current definitions of crime – its prevention, policing and presecution are inadequate…human and non-human.
It is when the human injustice hits home, that when compared with non-human injustice one starts to realise that injustice should not be selective.
.
Read About the ‘International Solidarity Movement‘
.
^http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_Solidarity_Movement
.
Thursday, February 23rd, 2012
The following article is a press release by UK-based NGO, The Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA), of 20120124 entitled ‘Conservation on the Front Line – Muara Tae’s Last Stand Against Big Palm Oil’
 Their ancient rainforest home clearfelled for bloody Palm Oil,
now these Orang-utans are homeless in their own homeland
[Source: ^http://www.pdnphotooftheday.com/2010/05/4673]
(Click photo to enlarge) Their ancient rainforest home clearfelled for bloody Palm Oil,
now these Orang-utans are homeless in their own homeland
[Source: ^http://www.pdnphotooftheday.com/2010/05/4673]
(Click photo to enlarge)
.
MUARA TAE, EAST KALIMANTAN (Borneo, Indonesia):
The fate of a Dayak indigenous community, deep in the interior of East Kalimantan (Borneo) demonstrates how Indonesia must safeguard the rights of indigenous people if it is to meet ambitious targets to reduce emissions from deforestation.
 Cleared land at Muara Tae
(c) EIA/Telapak Cleared land at Muara Tae
(c) EIA/Telapak
.
The Dayak Benuaq of Muara Tae, in West Kutai Kabupaten (Indonesia), today face a two-pronged assault from palm oil companies aggressively expanding into their ancestral forests. Together with Indonesian NGO Telapak, the community is manning a forest outpost around the clock in a last ditch attempt to save it from destruction.
The London-based Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA) has witnessed at first-hand the Dayak Benuaq’s struggle, and how their sustainable use of forests could help Indonesia deliver on its ambitious targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
EIA Forests Team Leader Faith Doherty said: “There are more than 800 families in Muara Tae relying on the forests for their food, water, medicine, culture and identity. Put simply, they have to keep this forest in order to survive.
 Villagers on cleared land at Muara Tae
(c) EIA/Telapak Villagers on cleared land at Muara Tae
(c) EIA/Telapak
.
“The rhetoric from the President of Indonesia on curbing emissions by reducing deforestation is strong but on the front line, where indigenous communities are putting their lives at risk to protect forests, action is sorely missing.
“Giving these communities, such as the Dayak Benuaq, the rights they deserve is a vital step to reduce catastrophic levels of deforestation in Indonesia.”
President Yudhoyono has pledged to reduce carbon emissions across the archipelago by 26 per cent by 2020 against a business-as-usual baseline, alongside delivering substantial economic growth.
 Self-serving bullshit artist
– take your pick Self-serving bullshit artist
– take your pick
.
Plantation expansion will inevitably be a significant element of growth, but it has historically been a major driver of emissions and it is widely acknowledged that in order avoid them, expansion must now be directed to ‘degraded’ lands.
As a result of weak spatial planning, however, the forests of Muara Tae are identified as ‘APL’, a designation meaning they are not part of the national forest area and are open to exploitation. The theft of indigenous forests also raises serious questions as to what form of ‘development’ these plantations offer.
In indigenous communities such as the Dayak Benuaq of Muara Tae, Indonesia has perhaps its most valuable forest resource. It is due to their sustainable methods, honed over generations, that the forest even remains.
 Benuaq girl and ncap payang tree
(c) EIA/Telapak Benuaq girl and ncap payang tree
(c) EIA/Telapak
.
Telapak president Ambrosius Ruwindrijarto said:
“Together with the community, we have not only been protecting the last forests but also planting new Ulin and Meranti saplings to enhance it. These people are the true guardians of the forest and their fate is entwined with it.”
Muara Tae has lost more than half of its land and forests during the past 20 years to mining companies. The impact has been tangible; the villagers’ water source has dried up and they must now routinely make a 1km journey to collect clean water.
The remaining forest is home to a large number of bird species including hornbills, the emblem of Borneo. There are about 20 species of reptiles and it is also a habitat for both proboscis monkeys and honey bears.
 Indonesia’s Environment Minister Gusti Hatta,
all talk..so…’what does an Orang-Utan look like?‘
. Indonesia’s Environment Minister Gusti Hatta,
all talk..so…’what does an Orang-Utan look like?‘
.
The latest land-grabs have taken place since January 2010, when the local Bupati (regional government official), Ismail Thomas, issued plantation permits to two palm oil companies: Malaysian-owned PT Munte Waniq Jaya Perkasa (PT MWJP) and PT Borneo Surya Mining Jaya, a subsidiary of Sumatran logging, mining and plantation conglomerate Surya Dumai.
While the Norwegian Government has been instrumental in financially backing efforts to reduce deforestation in Indonesia through the REDD+ initiative, it has also invested in the parent company of PT MWJP through its sovereign wealth fund.
Pak Singko, a leader of the Dayak Benuaq of Muara Tae, said: “We are calling for help from people everywhere in protecting our forests and ancestral land. We are being squeezed from all sides by mining and plantation companies.
.
“This is the last remaining forests that we have and the only land we have to survive.
If my forests are gone, our lives will end.”
 Cargill’s ecological facism for its self-serving Palm Oil
The destruction of primary rainforest by Duta Palma. West Kalimantan, Borneo.
Cargill was a key purchaser of palm oil from this notorious rainforest destroyer up until 2008. Cargill’s ecological facism for its self-serving Palm Oil
The destruction of primary rainforest by Duta Palma. West Kalimantan, Borneo.
Cargill was a key purchaser of palm oil from this notorious rainforest destroyer up until 2008.
[Source: Photo: David Gilbert/RAN, ^http://www.flickr.com/photos/rainforestactionnetwork/5551935164/]
(Click photo to enlarge)
.
The above photo is from an investigative report from Rainforest Action Network that presents evidence that (US conglomerate) Cargill is operating two undisclosed palm oil plantations in West Kalimantan, Indonesia.
 Cargill’s pathetic claim of its Corporate Responsibility in Indonesia Cargill’s pathetic claim of its Corporate Responsibility in Indonesia
[Source: Cargill corporate website: ^http://www.cargill.com.au/en/index.jsp].
.
When William Wallace Cargill founded our company in 1865, he deliberately set out to ensure that we earned and maintained a reputation for integrity, which he saw as a key differentiator in those times.
Corporate responsibility is part of everything we do. It is a company-wide commitment to apply our global knowledge and experience to help meet complex economic, environmental and social challenges wherever we do business. It is a process of continually improving our standards, our actions and our processes. Corporate responsibility extends not only to our own operations but to our wider communities and is based on four commitments:
- We will conduct our business with high levels of integrity, accountability and responsibility.
- We will develop ways of reducing our environmental impact and help conserve natural resources.
- We will treat people with dignity and respect.
- We will invest in and engage with communities where we live and work.
We recognize our continued success depends on the growth and health of our communities and partners, as well as the vitality and conservation of our natural resources. We are working with a diverse group of global, national and local organizations to support responsible economic development, help protect the environment and improve communities.
 Forced eviction, forced immigration
Orang-Utan orphans fleeing their ravaged parents and their ravaged ancestral homes
Forced eviction, forced immigration
Orang-Utan orphans fleeing their ravaged parents and their ravaged ancestral homes
Present us an American citizen accepting of such home eviction!
.
ED: Cargill’s eco-rape and eco-plunder policy across Indonesia’s vulnerable Borneo (Kalimantan) demonstrates that Cargill’s above public relations spiel is clearly crap! This is a wealthy United States corporate exploiting a poor country’s precious rainforest ecosystems, buggering local indigenous peoples and driving the extinction of the endangered Orang-Utan. If you work for Cargill or have shares in Cargill yoiu may as well be associated with the arms suppliers to the Syrian president Bashar al-Assad and his regime.
 Not just home invasion, but complete ecological erasion
Cargill is calling in the A-Bomb to Orang-Utans
What United States citizen would tolerate this?
911 is being inflicted on vulnerable species by the United States Not just home invasion, but complete ecological erasion
Cargill is calling in the A-Bomb to Orang-Utans
What United States citizen would tolerate this?
911 is being inflicted on vulnerable species by the United States
.
.
 Cargill’s worldwide president and COO Gregory R. Page
His life won’t end in devastation, but he drives devastation in vulnerable Kalimantan – in secret! Cargill’s worldwide president and COO Gregory R. Page
His life won’t end in devastation, but he drives devastation in vulnerable Kalimantan – in secret!
.
Further Reading:
.
[1] ‘Villagers face off against palm oil firm’s bulldozers‘, by EIA, 20111123, ^http://www.eia-international.org/villagers-face-off-against-palm-oil-firms-bulldozers
.
[2] ‘Orangutan ‘killers’ on trial over slaughtering primates for pest control at palm oil plantation‘, by Damien Gayle, Daily Mail, 20120208, ^http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2097946/Orangutan-killers-trial-slaughtering-primates-pest-control-palm-oil-plantation.html
.
Tags: ancient rainforest, Cargill, deforestation, deforestation in Indonesia, EIA, Environmental Investigation Agency, forest exploitation, Gregory R. Page, Gusti Hatta, Hillary Clinton, Indonesia, Indonesian palm oil plantations, Kalimantan, Logging, logging Borneo, Meranti, Murara Tae, orang-utan, palm oil, palm oil plantations, payang tree, President of Indonesia, PT Borneo Surya Mining Jaya, PT Munte Waniq Jaya Perkasa, Sumatran logging, Surya Dumai, Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono, Telapak, Ulin, United States
Posted in Kalimantan (ID), Orang-utans, Threats from Farming | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Saturday, January 7th, 2012
 Cathcart State Forest (NSW) being logged in 2011
[Source: Australian Forests and Climate Alliance ^http://forestsandclimate.net/newsouthwales] Cathcart State Forest (NSW) being logged in 2011
[Source: Australian Forests and Climate Alliance ^http://forestsandclimate.net/newsouthwales]
.
Most of Australia’s native vegetation cover, over 75% of that predating the 1788 Colonial Invasion, has been ‘cleared’ – a euphemism for deforested, logged, destroyed, killed.
Today, as one travels around Australia and sees vasts areas of unproductive, degraded, denuded and abandoned farmlands – one questions why destroy more fragile environment? Yet the exploitative bastards are still hell bent on killing more native forest and bushland, even though they can’t properly manage the ‘already ‘cleared’ lands they’ve got. It is a short sighted insatiability, harking to a 19th Century ‘old blighty’ mindset of taming the land. It is deluded thinking that just because the native vegetation is green and looks fertile that it can be replaced for pasture and cropping and that new cleared land will be any different to that already cleared.
The Liberal-Labor governments and their rural National mates haven’t given a toss throughout the entire 20th Century and still couldn’t give a toss.
 Recent land clearing in the Daly River catchment area
Northern Territory, Australia.
Photo: Environment Centre NT Recent land clearing in the Daly River catchment area
Northern Territory, Australia.
Photo: Environment Centre NT
.
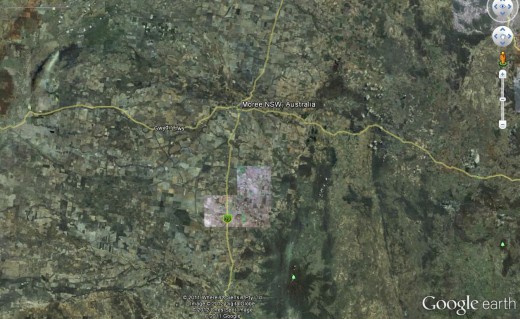 Moree region New South Wales – mainly deforested
Visit Google Earth and zoom into any area of NSW and see that most of it has been deforested
(click image to enlarge) Moree region New South Wales – mainly deforested
Visit Google Earth and zoom into any area of NSW and see that most of it has been deforested
(click image to enlarge)
.
Still across Australia in 2011, thousands of hectares of native forests continue to be deforested – albeit for farming, logging and development, or just bizarre bushfire abandonment. Not only is this occurring on private land, but in State Forests, which most people think are protected. Native forests on land are being cleared branded by State governments as ‘State Forests’ are simply not protected.
The native trees, flora and fauna are not protected from logging, bushfire, State-sanctioned arson (aka ‘hazard reduction‘), State napalming (aka indiscriminate ‘hazard reduction‘), indiscriminate State aerial poisoning with 1080, wildlife poaching, 4WD hooning, trail bike hooning, or even backpacker murdering. The watercourses (and the interconnected groundwater aquifers), that flow through State Forests are not protected from fishing, stormwater run-off, mine tailing contamination, farm pesticide and herbicide, industrial pollution.
.
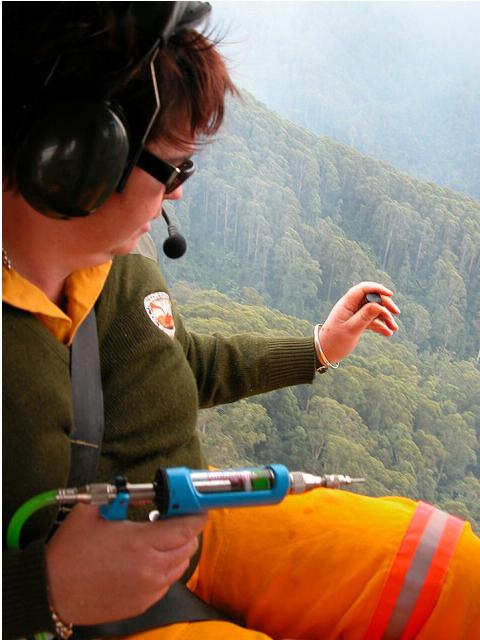 Helicopter Aerial Incendiary
Over Bindarri National Park, 20km south-west of Coffs Harbour, New South Wales
Yes, even our National Parks and Wildlife Service sets indiscriminate fires to National Parks! Helicopter Aerial Incendiary
Over Bindarri National Park, 20km south-west of Coffs Harbour, New South Wales
Yes, even our National Parks and Wildlife Service sets indiscriminate fires to National Parks!
.
For the likes of taxpayer funded government industrial loggers ‘State Forest’ is a euphemism ‘for not logged yet‘. This applies to the likes of Forestry Tasmania, VicForests, Forests NSW, Forestry SA (spot the naming trend), as well as the more aptly Queensland Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries, and likewise the Forest Products Commission of Western Australia.
It seems that doesn’t matter whether there is proof that there is an endangered and protected species such as the Long-Footed Potoroo in the Cann Valley State Forest or Drummer State Forest in Victoria, or protected Koalas in the Murrah/Mumbulla State Forests of New South Wales, or three identified endangered species, the wedge-tailed eagle, the swift parrot and the wielangta stag beetle in Tasmania’s Wielangta State Forests, the Liberal-Labor governments of those States turn a blind eye to deforestation.
It is only when self-funded local communities take the respective government logger to the Supreme Court and win that logging stops momentarily, such as in the recent Victorian Supreme Court case Environment East Gippsland Inc v VicForests [2010] VSC 335. In 2006, the Victorian State Government committed to increasing the conservation parks and reserves within the broader Brown Mountain area. Disregarding its elected master and ignoring any concerns for the ecological Precautionary Principle, State industrial logger VicForests, got stuck in with its mechanical clearfelling of old growth forests in the Brown Mountain area.
Not-for profit group Environment East Gippsland (EEG) self-funded and obtained numerous studies of the area indicated the presence of important threatened and rare species. EEG requested the Minister for Environment and Climate Change, Gavin Jennings, to make an interim conservation order to conserve critical habitat of the endangered Long-footed Potoroo, Spotted-tailed Quoll, Sooty Owl, Powerful Owl and Orbost Spiny Crayfish at Brown Mountain. Even then, the Minister for Environment and Climate Chang did not grant a conservation order, but instead increased the conservation area surrounding Brown Mountain. It took the overriding legal authority of the Supreme Court to stop the Victorian Government and its delinquent logger trashing protected old growth habitat.
 Victorian Labor Minister for Environment (etc), 2007-2010 Victorian Labor Minister for Environment (etc), 2007-2010
.
In March 2010, Forests NSW began controversial logging operations in the Mumbulla State Forest, south of Bermagui on the state’s far south coast. Despite being criticised, after a recent survey identified the forest as a key colony for the region’s remaining koala population, Forests NSW Regional Manager Ian Barnes says the logging must go ahead across 240 hectares of the forest, in order to satisfy a supply agreement with the timber industry.
 Deforestation is all about lining ones pockets out of ecological wanton exploitation
It’s a ‘wam bam thank you mam’ approach no different to what the Vikings did to the British in the eight Century.
Colonial Australians and their descendants are doing the same to Australian ecology in the 19th, 20th and 21st Centuries. Deforestation is all about lining ones pockets out of ecological wanton exploitation
It’s a ‘wam bam thank you mam’ approach no different to what the Vikings did to the British in the eight Century.
Colonial Australians and their descendants are doing the same to Australian ecology in the 19th, 20th and 21st Centuries.
Mr Barnes says the logging will not affect the koala habitat. “We’ve taken quite some effort to avoid any possible conflict there,” he says. “As anybody who reads the recent report will know, the koalas have been found in the eastern side of the forest, and our logging is planned for the western part, as far away as we can get from the koalas.”

Despite assurances, anti-logging campaigners have organised a vigil in the forest in an attempt to stop the logging. Conservationist Prue Acton says the activity will devastate the koala population.
“Why risk the only healthy koala colony left in the far south coast. For what? “ she said. “95% of what is going to be logged is going to end up at the Eden woodchip mill, be shipped to Japan for cheap copy-paper. What a disgrace.”
The Greens MP Lee Rhiannon says the Premier should put the protection of koalas ahead of the interests of logging companies. “The New South Wales Government has refused to end logging in the south east native forest but they should step in and stop the destruction of the koala habitat,” she said.
[Source: ‘Logging begins near key koala habitat‘, ABC, 20100330, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2010/03/30/2859615.htm?site=southeastnsw]
.
‘Loggers are clearing bushland at rising rate‘
[Source: ‘Loggers are clearing bushland at rising rate’, by Ben Cubby, Sydney Morning Herald, 20111221, ^http://www.theherald.com.au/news/national/national/general/loggers-are-clearing-bushland-at-rising-rate/2399764.aspx?storypage=0]

The amount of bushland being cleared by logging in NSW soared last year to the highest level since state-wide records began in 1988. An area equivalent to 138,400 football fields was cleared for crops, forestry or infrastructure, says a government report.
The Office of Environment and Heritage said the rise in logging was probably cancelled out by regrowth, leading to no net loss of trees, though its most recent survey took place in 2008, before the land clearing spike. It said the reasons for the logging increase were unclear.
”[The] most likely factors relate to market demand and favourable climatic conditions and [they] can be expected to fluctuate over time,” a department spokesman said. ”It is also possible that recent changes in forestry methods are more readily detectable by satellite monitoring.”
Environment groups said the annual vegetation report was evidence that logging companies were operating in an unrestrained manner.
Bushfires remain the biggest destroyer of forests in the state, leading to a net loss of 48,300 hectares in 2010, the report said.
.
But logging activities now come a close second, accounting for the removal of 42,700 hectares of trees in 2010. This is up from 31,000 hectares the previous year, and an average of about 21,000 hectares a year since 1988.
About 21,200 hectares of bushland was cleared in 2010 to make new areas for crops and grazing, while 5300 hectares were cut down to make way for roads, factories and housing.
”The NSW government is currently conducting a review of native vegetation controls,” said the chief executive of the Nature Conservation Council of NSW, Pepe Clarke. ”They should take this report as a warning – what is required are stronger land- clearing laws that do more to protect the environment, not weaker ones.”
The Wilderness Society said the government had ”failed in its promises to restrain land clearing, resulting in rapid and accelerating degradation of wildlife habitat and water catchments.”
The most recent State of the Environment report found that there had been no net loss of ”woody cover” across NSW between 2003 and 2008.
”This is because, although clearing has occurred over that period, there has also been an equivalent amount of regrowth including government sponsored environmental and forestry planting programs conducted by private landholders and state forests, within crown forests areas,” the department said.
”Notwithstanding no net loss over the whole state, some regions have experienced net declines in woody cover.”
The report uses the international definition of ”woody cover”, which includes land at least 20% covered by the crowns of trees higher than 2 metres, a description which would include relatively open country.
The introduction of a satellite monitoring system for land clearing last year appears to have increased the level of prosecution for illegal land clearing on private property. On crown lands, the number of prosecutions has increased threefold, from a low base, since 2007.
In 2010, the government received 471 reports of suspected illegal land clearing.
.
‘Landowners sent satellite images identifying land clearing‘
[Source: ‘Landowners sent satellite images identifying land-clearing’, NSW Department of Environment (etc), Media release: 14 May 2010, ^http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/media/DecMedia10051404.htm]
.
NSW Department of Environment Climate Change and Water (DECCW) today began a high tech education campaign to encourage compliance with native vegetation laws by sending letters to landholders including before and after satellite pictures identifying land clearing.
DECCW Director-General Lisa Corbyn said the letters were part of an ongoing education program to encourage compliance with the laws and inform landowners of the proper channels available to them if they want to clear native vegetation.
“We’ve been using satellite technology for some time to identify changes in vegetation cover that may warrant further investigation,” Ms Corbyn said.
“Now we are also using the technology as an education tool. From today, advisory letters will be sent to landowners including before and after satellite pictures showing that vegetation has been cleared on their land.”
Ms Corbyn said the letters aim to inform to the landowner that the satellite imagery has picked up that vegetation had been cleared and highlight the proper channels available to them under the legislation to allow clearing of native vegetation, such as property vegetation plans.
The letters support other tools used by DECCW to encourage compliance with the legislation, including strategic investigations, prosecutions, penalty notices, stop work orders, remedial directions, warning and advisory letters.
The letter also alerts landowners to incentive funding available to restore and protect native vegetation on their properties.
The Native Vegetation Act was introduced in 2003 to bring an end to broadscale land-clearing in NSW. Since then, more than 400,000 hectares of native vegetation has been conserved or rehabilitated on private land through property vegetation plans (PVPs) and 1.6 million hectares has been managed for thinning and invasive native scrub management.
.
Over 60 % of the native vegetation in NSW has been cleared, thinned or substantially disturbed.
.
The impacts of native vegetation clearing have included the extinction of 77 plant and animal species, soil erosion, increased dryland salinity and a decline in water quality.’
.
2003: ‘Clearing rate in NSW 116,000 to 216,000 hectares per year: NSW Govt report’
[Source: ‘Clearing rate in NSW 116,000 to 216,000 hectares per year: NSW Govt report’, by Stephanie Peatling, Environment Reporter, Sydney Morning Herald, 20031117, ^http://www.sydneyalternativemedia.com/id64.html]
.
The equivalent of up to 200,000 football fields may be illegally stripped of native trees and grass each year in NSW, figures suggest.
The first estimates on the extent of the clearings, which the Department of Natural Resources field staff prepared for the Government’s vegetation taskforce, suggest the figure could be as high as 100,000 hectares a year. The figures show between 150,000 hectares and 560,000 hectares were illegally cleared between 1997 and 2002.
The advice is the first official guess at NSW’s illegal clearance levels. The highest rates are in the Barwon, Central West and Far West regions where much of NSW’s remaining native vegetation is located.
The figures have shocked environmentalists, who stress the urgency of making changes to the state’s natural resource management system, which Parliament is debating this week.
A Wilderness Society campaigner, Francesca Andreoni, said: “The new system needs to be fair to everyone, particularly farmers doing the right thing.
“The shocking extent of illegal clearing confirms the urgent need for the Government to implement its decision to end broadscale clearing.”
Figures recording the rate of illegal land clearing each year are almost impossible to compile because it so hard to charge people who breach native vegetation laws. There is also a complicated system of exemptions which allow people to clear land for purposes such as maintaining fire access trails.
Monitoring illegal clearing is potentially dangerous for departmental compliance officers. After reports of illegal clearing earlier this year on a property near Nyngan, in the state’s west, department officers were prevented from entering the property by an angry crowd of up to 150 people.
.
When the amount of land illegally cleared is added to land that is legally approved for clearance, the department estimates between 700,000 hectares and 1.3 million hectares of land were cleared between 1997 and 2002.
.
The figures suggest clearing was faster than the Department of Natural Resources’ previously admitted figure of about 60,000 hectares a year. That figure would give NSW the second-highest clearing rate in the country behind Queensland.

Debate on the Government’s package to overhaul native vegetation laws, based on an election promise to end broad-scale clearing, will take place this week. Last month the Premier, Bob Carr, announced a $406 million deal between farmers and environmentalists to end broad-scale clearing.
Most of the money is expected to go towards such things as tree planting and fencing waterways to help counter salinity and erosion. But local authorities may also compensate farmers for not clearing land. Clearing will still be allowed where it is deemed environmentally necessary.
Under the new system, natural resource management is being overhauled. Thirteen catchment management authorities will replace 19 catchment management boards, 20 regional vegetation committees and 33 water management committees.
Scientists often name land clearing as one of Australia’s most urgent environmental concerns. It contributes to soil salinity, loss of biodiversity and greenhouse gas emissions because carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere when the cleared timber is disposed of, usually through burning.
.
‘Green groups attack logging growth’
[Source: ‘Green groups attack logging growth’, by David Bancroft, My Daily News, 20111229, ^http://www.mydailynews.com.au/story/2011/12/29/green-groups-attack-logging-growth/]
.
Environment groups have banded together to criticise the level of logging occurring in New South Wales. The Nature Conservation Council, The Wilderness Society, National Parks Association, the Northern Inland Council for the Environment and the North Coast Environment Council have issued a joint warning that iconic and endangered species are being threatened by land clearing.
 Illegal deforestation for fire wood, near Taralga, on the western edge of the Blue Mountains
Source: ^http://www.orchidsaustralia.com/article_%20conservation_no3.htm Illegal deforestation for fire wood, near Taralga, on the western edge of the Blue Mountains
Source: ^http://www.orchidsaustralia.com/article_%20conservation_no3.htm
.
In a joint press release, the groups said the NSW annual report on native vegetation released by the Office of Environment and Heritage (Ed. yet another money wasting name change) this month showed 2009/10 was the “worst year on record for clearing of native bushland”.
.
The Wilderness Society campaigns manager Belinda Fairbrother said the report showed that in 2009/10 an area equating to 138,400 football fields was cleared for crops, forestry or infrastructure.
.
“This is higher than any other year since records commenced in 1988 and shows the NSW Government has failed in its promises to restrain land clearing, resulting in rapid and accelerating degradation of wildlife habitat and water catchments,” she said.
North Coast Environment Council president Susie Russell said the report made a sad end to the International Year of Forests.
“The area cleared for forestry in 2009/10 was almost five times greater than it was in 1988/89,” she said.
“It reveals a massive increase in the rate and intensity of logging in NSW, which will be causing untold damage to the extraordinary high diversity forests of north-east NSW.”
Nature Conservation Council chief executive officer Pepe Clarke said land clearing was recognised as the single greatest threat to wildlife in Australia.
“It causes the death of birds and animals, the extinction of species, leads to the poisoning of soils from salinity and makes a major contribution to global warming,” he said.
.
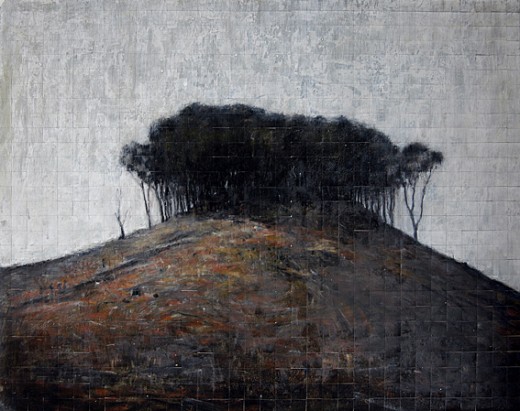 The Liberal-Labor Party ‘Island Vision’ for Australia’s State Forests
‘The Hill’ (Penrose State Forest, NSW) 2007, drawing by James King The Liberal-Labor Party ‘Island Vision’ for Australia’s State Forests
‘The Hill’ (Penrose State Forest, NSW) 2007, drawing by James King
^http://www.jamesking.com.au/drawings.html
.
Tags: 1788 Colonial Invasion, Cathcart State Forest, deforestation, Eden woodchip mill, fire wood, Forests NSW, Google Earth, hazard reduction, Helicopter Aerial Incendiary, Island Vision for Australian State Forests, koala habitat, land clearing, Logging, Long-footed Potoroo, Murrah/Mumbulla State Forests, not logged yet, Orbost Spiny Crayfish, Powerful Owl, precautionary principle, Sooty Owl, spotted-tailed quoll, State-sanctioned Arson, VicForests, Wielangta State Forests
Posted in Koalas, Owls, Quolls, Threats from Bushfire, Threats from Deforestation, Threats from Farming | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Thursday, October 13th, 2011
If you go down into the woods today you’re sure in for a big surprise…but in Tasmania’s South-West it ain’t no teddy bear’s picnic.
One has to first get past the many infamous locked gates. Forestry Tasmania (aka the State-sanctioned corporate logger) is sure to have locked its steel gates for very good reason – Forestry Tasmania doesn’t want the public to know the truth about what it is doing to Tasmania’s remaining wild forests.
 Forestry Tasmania’s locked gate on the public road to the top of Mount Tim Shea
(Suspiciously this public access road was deemed unfit for public travel coincidentally around the same time as Forestry Tasmania opened its ‘Adventure Hub’ in Maydena,
and equally coincidentally one of the hills they charge people for a ride to the top from reads ‘Adventure Hub’).
(Photo by Alan Lesheim) Forestry Tasmania’s locked gate on the public road to the top of Mount Tim Shea
(Suspiciously this public access road was deemed unfit for public travel coincidentally around the same time as Forestry Tasmania opened its ‘Adventure Hub’ in Maydena,
and equally coincidentally one of the hills they charge people for a ride to the top from reads ‘Adventure Hub’).
(Photo by Alan Lesheim)
.
 Rugged Mount Tim Shea, South-West Tasmania Rugged Mount Tim Shea, South-West Tasmania
Photo by Forestry Tasmania
^http://www.forestrytas.com.au/topics/2008/06/maydena-adventure-hub-opportunities
.
 Locked Gate on Five Road in the Upper Florentine Locked Gate on Five Road in the Upper Florentine
(connects to Cook’s Track which enters the Gordon River Road short of Camp Flozza)
(Photo by Alan Lesheim)
.
Forestry Tasmania has hundreds of these padlocked gates throughout Tasmania’s wild forests.
The Wilderness Society’s spokesperson Amanda Sully said “Forestry Tasmania have a locked boom gate over the Huon Valley Wilderness and are refusing entry. This is just one of hundreds of gates on forestry roads in Tasmania.
“It’s very clear who is locking up the forests. People are sick and tired of seeing log truck after log truck coming from the clear felling behind these padlocked gates.
These are publicly-owned forests.
Forestry Tasmania is supposed to manage them for the benefit of all Tasmanians, not just the loggers” Ms Sully concluded.
.
[Source: ‘Forestry Tasmania – Locking up our forests‘, ^http://www.wilderness.org.au/campaigns/forests/19980924_mr
.
 Forestry Locked Gate on Blue Road, northern section of the Upper Florentine Valley Forestry Locked Gate on Blue Road, northern section of the Upper Florentine Valley
(Photo by Alan Lesheim)
.
.
Author Anna Krien was on a quest for the truth described in her revealing expose book of 2010 into what’s stihl happening in Tasmania’s wild forests:
~
‘Most people travelling through Tasmania will never know of the long-running hide-and-seek taking place in the labyrinth of logging roads beyond the bitumen.
Sightseers walk among 300-year-old trees, some of them 90 metres tall, in the Styx Big Tree Reserve, chainsaws can be heard in the distance.
The road into this attraction is lined with stage sets of wilderness.
At the rise of a hill, just before the nose of the car tilts downwards, passengers might glimpse a balding peak, a fleeting insight into the world behind the verge.’
~
[Source: ‘Into the Woods: The Battle for Tasmania’s Forests‘, 2010 by Anna Krien pp.25-26, published by Black Inc. ^http://www.blackincbooks.com/books/woods, includes video interviews].
.
So, this Editor, half way through the book, last month flew down to Hobart, hired a car and retraced the author’s journey into Tasmania’s South-West …
.
 Driving west along the old Hydro Electrical Commission’s (HEC) Gordon River (Access) Road,
through Forestry’s logging town of ‘Westerway’ Driving west along the old Hydro Electrical Commission’s (HEC) Gordon River (Access) Road,
through Forestry’s logging town of ‘Westerway’
.
Noticeably, when driving out of Hobart I passed clearly wealthy residential suburbs, yet driving along the Gordon River Road these few isolated hamlets are not wealthy. Their construction mostly seems temporary like mining companies would construct while the mine delivers. The highway through the hamlets of Westerway, Fitzgerald and Maydena seems only for forest access, not for community.
I parked the car and walked through Maydena.
There is only the odd person out and about. The place seems impoverished – one small primary school, a notable lack of shops, lack of amenities, and little sign of any vibrant community.
It’s as if the profits from logging have driven right through the guts of these local villages and on to big corporations eastward.
.
 Past the National Park Hotel
where Tasmania’s champion wood-chopper ‘Big Dave’ holds pride of place above the pub’s fire place. Past the National Park Hotel
where Tasmania’s champion wood-chopper ‘Big Dave’ holds pride of place above the pub’s fire place.
.
 Driving through Forestry’s old logging town of ‘Fitzgerald’
. Driving through Forestry’s old logging town of ‘Fitzgerald’
.
.
 Driving through the old logging town of ‘Maydena’
– a closed so-called ‘Adventure Hub’ on the left, yet its diesel bowser (circled) open for Forestry Tasmania vehicles and observed in used by Editor 20110928. Driving through the old logging town of ‘Maydena’
– a closed so-called ‘Adventure Hub’ on the left, yet its diesel bowser (circled) open for Forestry Tasmania vehicles and observed in used by Editor 20110928.
.
Reminiscent of Australia’s 1850s Gold Rush, Tasmanian folk would have been lured west by Forestry to the promise of bountiful tall timber delivering reliable logging income and the promise of building personal wealth.
But along the Gordon River Road there is a stark absence of Forestry wealth. Instead it seems Forestry has abandoned these Gordon River Road communities.
What Forestry has done is to sell out Tasmania’s traditional woodcraft industry for short term profit from flogging quality Tasmanian hardwood as cheap asian woodchips, destroying Tasmania’s forests timber communities in the process. Then Gunns got greedy and Tasmania’s timber reputation has deteriorated thereafter.
Now Forestry Tasmania are clearfelling and selling out Tasmania’s rare forests to the asians direct, to the likes of Ta Ann. Forestry Tasmania is no more than a corporate pimp of Tasmanian rare forest heritage.
.
“The road into this attraction is lined with stage sets of wilderness.”
 Driving further west along the HEC Gordon River Road
– bulldozed in 1964 through 64km of pristine wilderness forest by the Hydro Electric Commission, and
funded by the then Menzies federal government at a cost of £2.5 million (likely twenty times that in today’s terms – i.e. $50 million.
. Driving further west along the HEC Gordon River Road
– bulldozed in 1964 through 64km of pristine wilderness forest by the Hydro Electric Commission, and
funded by the then Menzies federal government at a cost of £2.5 million (likely twenty times that in today’s terms – i.e. $50 million.
.
 Gordon River Road – signposted logging country Gordon River Road – signposted logging country
.
“At the rise of a hill, just before the nose of the car tilts downwards, passengers might glimpse a balding peak”
 The balding peak of Forestry Tasmania’s cable logging…’a fleeting insight into the world behind the verge’.
(Photo by editor 20110928 while on Gordon River Road heading west) The balding peak of Forestry Tasmania’s cable logging…’a fleeting insight into the world behind the verge’.
(Photo by editor 20110928 while on Gordon River Road heading west)
.
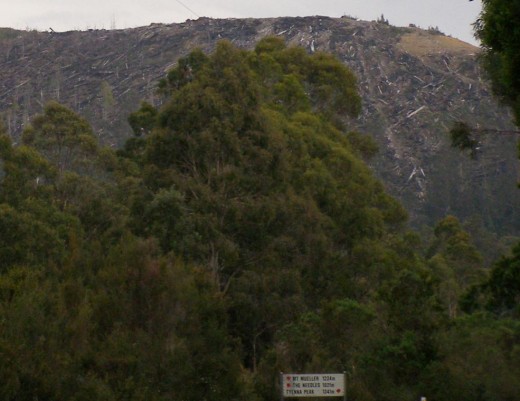 An entire hill of wild Tasmanian forest savagely cabled logged bare by Forestry Tasmania
Tourists can now see this from Gordon River Road.
(Photo by editor 20110928. Click photo to enlarge.)
An entire hill of wild Tasmanian forest savagely cabled logged bare by Forestry Tasmania
Tourists can now see this from Gordon River Road.
(Photo by editor 20110928. Click photo to enlarge.)
.
 Beyond the lock gates lies the ecological holocaust
(Photo by editor 20110928. Click photo to enlarge.) Beyond the lock gates lies the ecological holocaust
(Photo by editor 20110928. Click photo to enlarge.)
.
 Styx Valley Holocaust
(Photo by Rob Blakers) Styx Valley Holocaust
(Photo by Rob Blakers)
.
 Tasmania’ s Styx Holocaust
September 2011 (Photo by Alan Lesheim)
Tasmania’ s Styx Holocaust
September 2011 (Photo by Alan Lesheim)
.
 Forestry Tasmania’s Killing Fields
Forestry Tasmania’s Killing Fields
.
 Cambodia’s Khmer Rouge Killing Fields
(Human mass murder comparable to Tasmania’s mass forest murder
– both crimes consistently against life) Cambodia’s Khmer Rouge Killing Fields
(Human mass murder comparable to Tasmania’s mass forest murder
– both crimes consistently against life)
.
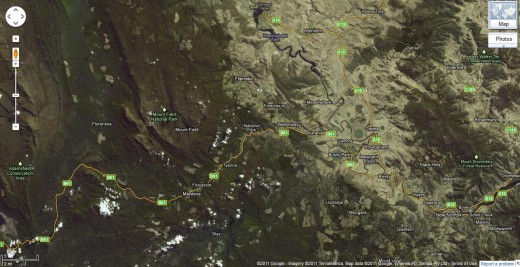 Google Maps (September 2011) satellite view of the forest rape by Forestry Tasmania
.
Google Maps (September 2011) satellite view of the forest rape by Forestry Tasmania
.
 . .
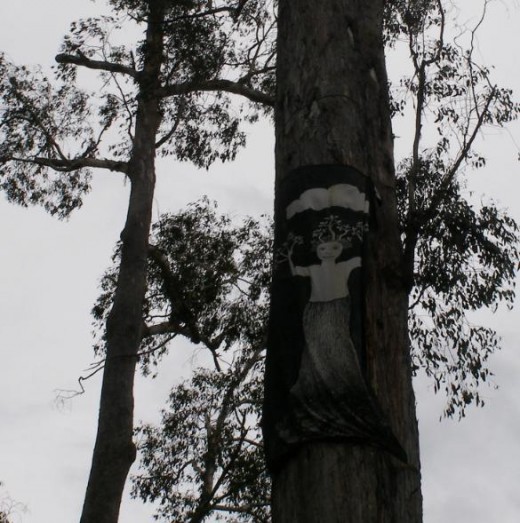 Camp Flozza’s symbolic goddess of the ancient Florentine Forest
~ eco-raped by Forestry Tasmania in its January 2009 raid
Camp Flozza’s symbolic goddess of the ancient Florentine Forest
~ eco-raped by Forestry Tasmania in its January 2009 raid
.
 And they wonder why the people protest and are prepared to be arrested?
(Photo of forest defender being arrested at Forestry Tasmania’s police raid on Camp Flozza,
Upper Florentine Valley, 13th January 2009) And they wonder why the people protest and are prepared to be arrested?
(Photo of forest defender being arrested at Forestry Tasmania’s police raid on Camp Flozza,
Upper Florentine Valley, 13th January 2009)
.
 Styx Valley Holocaust by Forestry Tasmania, September 2011
(Photo of editor 20110928. Click photo to enlarge.)
Styx Valley Holocaust by Forestry Tasmania, September 2011
(Photo of editor 20110928. Click photo to enlarge.)
.
.
Forestry Tasmania padlocks gates 10 kilometres from clearfell around a protected Wedge-tailed Eagle nest
[Source: ‘Loggers breach eagle nest protection laws again‘, Bob Brown, 20090827, ^http://bob-brown.greensmps.org.au/category/issues/environment/forestry/wielangta]
‘In the breeding season, a clear felling operation in Tasmania’s wild Upper Huon Valley has breached guidelines by smashing down forests next to an endangered Tasmania’s Wedge-tailed eagles’ nest. The Tasmanian Wedge-tailed eagle, with wingspan up to 3 metres, are one of the Earth’s 6 largest eagle species.

“After repeated controversies about woodchip operations burning or destroying eagle nests and causing failure of nesting because of bulldozers and chainsaws operations near nests, this failure of protection in the Huon is inexcusable. It makes a mockery of logging industry propaganda,” said Australian Greens Leader Bob Brown.
“The Ministers for Forestry and Environment who are responsible for Australia’s rare and endangered species don’t know, and don’t act in any helpful way.”
“It is as if the Howard Government never left office. These ministers have washed their hands of their role in the Wedge-tailed eagles’ fate. Logging laws in Tasmania state that a minimum of 10 hectares be left around an eagle’s nest,” said Senator Brown.
Forestry Tasmania has erected locked gates 10 kilometres from the nest logging site preventing public or media inspection.’
.
Footage of the logged area and nest available here (on YouTube):

.
.
Meanwhile Forestry Tasmania on its ‘Adventure Forests‘ website promotes its ‘Top of the World Tour‘ from Maydena…

…’Go wild where eagles soar…Make the escape to the Eagle’s Eyrie on a Top of the World Tour.You’ll experience all the fun of the Railtrack Rider as you travel into the heart of the forest to explore long-abandoned bush heritage, before emerging to an alpine wonderland and an eagle’s eye view over the Tasmanian wilderness. There’s plenty of time for indulgence as well, with an individually-prepared gourmet lunchbox and fine regional wines enjoyed in the fireside comfort of the Eagles Eyrie.’
^http://adventureforests.com.au/maydena
.
.
‘The real voyage of discovery consists not in seeking new landscapes
but having new eyes’
~ Marcel Proust, French novelist
Tags: Anna Krien, Cable Logging, Camp Flozza, deforestation, Fitzgerald, Florentine Valley Holocaust, Forestry Holocaust, Forestry Locked Gates, Forestry Tasmania, Gordon River Road, having new eyes, Into the Woods, Maydena, Maydena Adventure Hub, Mount Tim Shea, National Park hotel, Styx Big Tree Reserve, Styx Forest, Styx Valley, Styx Valley Holocaust, Ta Ann, Tasmania, Tasmania's Ancient Forests, Tasmania's South West, Tasmania's Wild Forests, Upper Florentine Forest, Wedge-tailed Eagle, Westerway, wild forests
Posted in Eagles, Tasmania (AU), Threats from Deforestation, Threats to Wild Tasmania | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Friday, August 26th, 2011
 Who does one believe?… Who does one believe?…
Greenwash Tick
.
.
.
Tuesday 23-Aug-2011:
‘Paper manufacturer loses green credentials’
by Liz Hobday, ABC News, 20110823, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/2011-08-23/paper-manufacturer-loses-green-credentials/2851982/?site=melbourne, accessed 20110825]
.
The Wilderness Society says Australian Paper cannot meet environmental standards. The manufacturer of Reflex paper has lost part of its international environmental certification, after withdrawing from an audit of its wood supplies.

The Forest Stewardship Council was auditing Australian Paper, to check that the wood used to make Reflex paper is not sourced from high conservation value forests.
Luke Chamberlain from the Wilderness Society says the company withdrew from the process, because it cannot meet environmental standards.
“The makers of Reflex paper get their wood from the Victorian State Government native forest logging arm VicForests,” he said.
 “VicForests log in endangered species habitat. They log old growth forests in East Gippsland and the central highlands” “VicForests log in endangered species habitat. They log old growth forests in East Gippsland and the central highlands”

Australian Paper says its products are not sourced from high conservations value forests threatened by logging.
Shaun Scallan from Australian Paper says they withdrew because the audit process changed while it was underway.
“We pulled out because of a change in the definition of part of the standard late in the piece, which did not allow us enough time to then satisfy that changed definition,” he said.
.
.
Meanwhile the same Shaun Scallan of Australian Paper just the day prior on Monday 22 August 2011 posts his media release:
.
‘Australian Paper retains FSC Chain of Custody Certification’…?
by Shaun Scallan, Australian Paper, 20110822, ^http://australianpaper.com.au/media/2478/AP%20FSC%20audit%20release%20FINAL%20Aug%2022_2011.pdf, accessed 20110825
.
‘Australian Paper has successfully retained Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) Chain of Custody certification (FSC-C002059) in its latest audit. Auditor Rainforest Alliance confirmed that under the certification Australian Paper may continue to produce FSC-certified product based on sourcing of material from FSC-certified operations and recycled content, as allowed under the FSC rules for Mixed and Recycled product.
.
“We are pleased to have retained our FSC Chain of Custody certification,” Australian Paper CEO Mr Jim Henneberry said.
“Australian Paper has held Chain of Custody certification since 2006. However, we have decided to remove the Controlled Wood component from our certification at this time as there has been uncertainty around the interpretation of key elements of the standards.”
.
“Advice received by Rainforest Alliance from FSC International around the interpretation of the Standard was received after the physical audit had been completed. This left insufficient time for us to address and so we elected to withdraw Controlled Wood from our certification.” Mr Henneberry said.
.
Australian Paper remains committed to ensuring that fibre supplies come from internationally recognised, third party certified sources and also regards the Australian Forestry Standard and PEFC as benchmark certifications under this policy. The majority of wood supplied to Australian Paper is certified to the Australian Forestry Standard.
.
“We are also continuing to consult with a wide range of stakeholders as part of our Future Fibre Strategy review,” Mr Henneberry said.
“It is vital that we achieve the best balance between the environment, the health of regional communities and our ongoing competitiveness. We look forward to sharing outcomes from this review in due course.”
.
.
Meanwhile, we have the boss of Nippon Paper (the Japanese company that owns the misnomer ‘Australian Paper’) declaring Nippon Paper is going gang-busters to become a top global pulp and paper company…(at any cost?)
 ‘Since I was appointed president of Nippon Paper Group, Inc. in 2008, I have been pursuing “growth-oriented management.” This means exploring every possibility with a consistently positive stance, actively seizing opportunities, achieving the growth needed to become one of the top pulp and paper companies worldwide, as set out in the Group Vision 2015, and developing corporate value that meets the expectations of all stakeholders.’ ~ President of Nippon Paper Group, Yoshio Haga. [Source: ^http://www.np-g.com/e/about/president.html] ‘Since I was appointed president of Nippon Paper Group, Inc. in 2008, I have been pursuing “growth-oriented management.” This means exploring every possibility with a consistently positive stance, actively seizing opportunities, achieving the growth needed to become one of the top pulp and paper companies worldwide, as set out in the Group Vision 2015, and developing corporate value that meets the expectations of all stakeholders.’ ~ President of Nippon Paper Group, Yoshio Haga. [Source: ^http://www.np-g.com/e/about/president.html]
 . .
.
Meanwhile, the stated Charter of Nippon Paper Group includes:
.
‘6. Active involvement with environmental issues assures that…’
.
- ‘We shall promote afforestation projects, to create and make effective use of sustainable forest resources.’
- ‘We shall promote energy conservation, the use of wastepaper and other measures to effectively use resources that are limited in quantity.’
- ‘We shall manage and reduce all types of discharge and waste generated in the course of corporate activities.’
- ‘We shall research and develop manufacturing technologies, and products and services that are in harmony with the environment.’
.
[Source: ^http://www.np-g.com/e/about/charter.html#shead2]

Editor: It is suspicious when a Japanese company is more than content to log and irrevocably destroy another country’s old growth forests, while Japan’s own old growth forests around Mt Fuji remain sacrosanct.
‘In spite of the abundant natural resources, logging is not commonly practiced in the forests of Japan. Japan Forests are venerated and protected since they provide essential soil cover and help in water conservation. All Species are encouraged to grow in the Forests in Japan , from the broad-leaved deciduous to the evergreen coniferous types. There are also many forests which grow near volcanic areas, destroyed and then rejuvenated every time an eruption occurs. The Aokigahara Forest at the base of Mount Fuji is one such forest. Locals as well as tourist camp, trek and hike through these dense forests of Japan to explore their unusual natural beauty.
‘Some Japan Forests are designated as Sacred Forests . These forests generally contain an ancient religious Shrine, usually worshiping the Shinto religion and are protected from trespassing and destruction. These forest shrines are still venerated as national treasures.
.
Some of the sacred forests in Japan are-
- The Forest of the Yahiko Jinja has many trees like the Cedar, Cypress and Oaks. The Shrine has a sacred Chinquapin tree as well.
- The Forest of Atsuta Jinja is an important Shinto Shrine, housing one the three important Shinto relics – the holy sword of Kusanagi-no-tsurugi. The forest has evergreens like the Japanese Camellia Sakaki, camphor trees, Ilex and Japanese Honeysuckle.
- The Forest of Kashima Jingu has over 800 species of trees like varieties of Cedar, Fir and Oak. The Kashima Jingu is an important shrine of the Kanto Area. The forest has been designated as a Wildlife Protection area for the rare birds in the region.
- The Forest of Shimogamo Jinja covers over 495 hectares and has many different species of deciduous trees like the Zelkova, the Elm and the Hackberry. The Shrine itself has 53 buildings which have been designated as National Heritage Architecture.
- The Forest of the Kirishima Jingu covers and area of 887 hectares. Located near the Mount Kirishima Volcano, the forest has been destroyed and then recovered for over 60 times.
- The Forest of the Kasuga Taisha is home to the beautiful podocarpus Nagi. The forest also contains many species of evergreens and shrubs. Trees like the Kasuga, the Andromeda and the Ichii also grow there. People from all over Japan visit the venerated shrine in the quarterly pilgrimages.‘
[Source: ^http://www.mapsofworld.com/japan/japan-tourism/forests-in-japan.html]
 Japan’s sacred Aokigahara Forest Japan’s sacred Aokigahara Forest
.
Ethics question for Yoshio Haga (President of Nippon Paper Group):
What moral right do the Japanese have to consider their own native old growth Aokigahara Forest more sacred than Australia’s sacred native old growth forests such as those across East Gippland?
 Stump of Brown Mountain’s sacred 600 year old Mountain Ash old growth tree.
It was logged by VicForests in November 2008 for Nippon Paper’s Reflex Paper. Stump of Brown Mountain’s sacred 600 year old Mountain Ash old growth tree.
It was logged by VicForests in November 2008 for Nippon Paper’s Reflex Paper.
.
.
In light of VicForests recent civil prosecution in the Victorian Supreme Court, Nippon Paper Group’s association with VicForests calls into question the reputation of Nippon Paper Group and its brand Reflex Paper:
.
‘VicForests has been stopped from harvesting certain coupes in the Brown Mountain forest in East Gippsland containing old growth forest
– habitat for rare and threatened species – until the completion of steps implementing the precautionary principle.’
.
.
.
‘Environment East Gippsland Inc v VicForests – The precautionary principle in action’
22 November 2010:
[Source: Blake Dawson (Lawyers), ‘Environment Matters’, 20111122, ^http://www.blakedawson.com/Templates/Publications/x_article_content_page.aspx?id=60457, accessed 20110825]
.
.
In Brief:.
- ‘The Victorian Supreme Court decision in Environment East Gippsland Inc v VicForests firmly embeds the approach to the precautionary principle laid down in Telstra Corporation Limited v Hornsby Shire Council (2006).’
- ‘The case makes it clear that the precautionary principle can be the subject of an enforceable obligation.’
- ‘The case also makes it clear that the precautionary principle applies both at the strategic and operational stages of a project or undertaking.’
- ‘The fact that VicForests complied with its forestry approvals was not enough to satisfy the Court that it had met its obligations with regard to the precautionary principle.’
.
‘In Environment East Gippsland Inc v VicForests [2010] VSC 335 conservation group Environment East Gippsland (EEG) won a landmark injunction against VicForests, a state-owned timber business with responsibility for commercial timber harvesting in Victoria’s state forests.
VicForests has been stopped from harvesting certain coupes in the Brown Mountain forest in East Gippsland containing old growth forest – habitat for rare and threatened species – until the completion of steps implementing the precautionary principle.
In this case, Justice Osborn of the Supreme Court of Victoria undertook a thorough analysis of the application of the precautionary principle in the context of a detailed legislative regime aimed at balancing biodiversity protection and commercial timber harvesting. The case embeds the approach to the precautionary principle laid down by Chief Justice Preston of the Land and Environment Court of New South Wales, in Telstra Corporation Limited v Hornsby Shire Council (2006) 67 NSWLR 256.’
.
The lead-up to the litigation
.
‘The Brown Mountain forests in Victoria’s East Gippsland contain old growth forests and provide habitat for rare and threatened species such as the Powerful Owl, the Spotted-tailed Quoll (mainland Australia’s largest marsupial carnivore) and the Long-footed Potoroo. However, these areas are also amongst the most productive timber harvesting forests in Victoria and play a crucial role in Victoria’s sustainable timber industry.
In 2006, the Victorian State Government committed to increasing the conservation parks and reserves within the broader Brown Mountain area. Nevertheless, in 2008 commercial logging in the Brown Mountain area began.
After numerous studies of the area indicated the presence of important threatened and rare species, EEG requested the Minister for Environment and Climate Change, Gavin Jennings, to make an interim conservation order to conserve critical habitat of the endangered Long-footed Potoroo, Spot-tailed Quoll, Sooty Owl, Powerful Owl and Orbost Spiny Crayfish at Brown Mountain. The Minister did not grant a conservation order, but instead increased the conservation area surrounding Brown Mountain.
Having failed to obtain undertakings from VicForests that it would not proceed to log the Brown Mountain coupes, EEG sought interlocutory injunctive relief. An interlocutory injunction restraining logging was granted by Justice Forrest on 14 September 2009 (see our article Environmental litigation heats up with some significant wins for public interest litigants in our 2 October 2010 edition of Environment Matters ), pending the outcome of the full proceedings before Justice Osborn in the Supreme Court of Victoria.’
.
The legislative regime
.
‘Logging of state forests in Victoria is regulated by a complex scheme of legislation, codes of practice, management plans and procedures, described by Osborn J as “labyrinthine”. The principal legislation includes the Forests Act 1958 (Vic) (Forests Act), Sustainable Forests (Timber) Act 2004 (Vic) (SFT Act), Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act 1988 (Vic) and Conservation, Forests and Lands Act 1987 (Vic).’
.
Responsibilities for timber harvesting and forestry management
.
‘VicForests is a state-owned corporation, established in 2004 to undertake the harvesting of timber in Victoria’s state forests. The Secretary to the Department of Sustainability and Environment (DSE) has overarching responsibility for managing state forests and timber harvesting within forests under the Forests Act.’
.
Legal challenge
.
‘EEG sought an injunction restraining VicForests from harvesting four coupes at Brown Mountain containing old growth forest. It also sought declarations that timber harvesting within the coupes by VicForests in accordance with the current forestry regime would be unlawful.
EEG argued that the current conservation measures for the Brown Mountain coupes did not meet the requirements of the regulatory system, which addresses the preservation of conservation values and in particular the protection of endangered species. EEG also argued that VicForests had failed to implement the precautionary principle.
VicForests took issue with EEG’s standing to sue. Further, it denied the presence of a number of endangered species and argued that the logging of the Brown Mountain coupes would take place under a legislative framework that adequately protects endangered species and would, therefore, be lawful. It also argued that it was DSE’s responsibility to stipulate any further requirements for habitat protection in accordance with the regulatory regime.’
.
EEG’s standing
.
‘Following the settled High Court authority that standing to bring such proceedings depends on the plaintiff’s “special interest” in the subject matter of the litigation (Australian Conservation Foundation v Commonwealth (2000) 200 CLR 591), Osborn J was satisfied that EEG had a relevant “special interest” because:
- EEG uses the coupes to a greater degree than the general public (for example, the group has a “Valley of the Giants Old Growth Forests Walk” through the affected coupes);
- EEG’s predecessor was involved in the consultative process for the formulation of the applicable forest management plan; and
- the government has previously recognised EEG’s status as a body representing this sector of the public interest.’
.
The precautionary principle [Ed: once again]
.
‘The VicForests case firmly embeds in Australian environmental jurisprudence the approach to the precautionary principle laid down by Chief Justice Preston of the Land and Environment Court of New South Wales, in Telstra Corporation Limited v Hornsby Shire Council (2006) 67 NSWLR 256 (Telstra). Justice Osborn’s decision in VicForests is the first Supreme Court application of the Telstra principles.
The precautionary principle is integrated throughout the Victorian forestry regime’s many instruments.
Following Preston CJ’s two-fold test in Telstra, Osborn J stressed that the precautionary principle is a test of common sense. There must be:
- a threat of serious or irreversible environmental damage; and
- scientific uncertainty as to the environmental damage.
Justice Osborn stated:
Once both of these conditions or thresholds are satisfied, a precautionary measure may be taken to avert the anticipated threat of environmental damage, but it should be proportionate … [The] degree of precaution appropriate will depend on the combined effect of the seriousness of the threat and the degree of uncertainty.
It is a “wherever practicable” test.
In practice, this meant that once the two-fold test was satisfied by EEG, VicForests had the onus of proving that the threat posed by logging the coupes did not exist or was negligible. Because it could not do this, the question then became:
- whether the threat was able to be addressed by adaptive management measures (in this case the requirement for surveys and management zone reviews); and
- whether the measure alleged to be required (here the permanent injunction against logging the coupes) was proportionate to the threat in issue.
Justice Osborn carefully examined the legislative regime and held that it is not intended that VicForests only apply the precautionary principle at the strategic planning stage:
VicForests is specifically required to apply it [the precautionary principle] having regard to the results of monitoring and research as they come to light during operations. … The requirements of the precautionary principle fall to be considered in the light of the whole of the evidence bearing on these matters as it now is and not as it was at the time VicForests completed planning.
Justice Osborn stressed, however, that the precautionary principle sits within a wider statutory regime that takes into account principles of sustainable development.
He held that unless VicForests complied with the requirements of the applicable Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act Statements and with conditions stated in the relevant allocation order (under the Forests Act) and the Timber Release Plan (under the SFT Act), logging at Brown Mountain would be unlawful.
This meant that VicForests could not rely on its current approvals to log the coupes because DSE had not, for example, changed zonings in the coupes to reflect the presence of threatened species. VicForests had an ongoing, active duty to apply the precautionary principle, which included responding to new information as it became available.
Importantly, Osborn J stressed that the precautionary principle can be the subject of an enforceable obligation.’
.
Outcome
.
‘Justice Osborn ordered that VicForests stop harvesting until various measures had been completed to respond to the detection of endangered species and to implement a precautionary approach with respect to their potential extinction. The required measures included:
- creating or amending special management zones, special protection zones and retained habitat areas to protect the Long-footed Potoroo, Greater Gliders and Yellow-bellied Gliders (as relevant);
- undertaking further surveys for the Giant Burrowing Frog, Large Brown Tree Frog and Spotted-tailed Quoll; and
- completing a current review of the Powerful Owl and Sooty Owl Management Areas,
to the satisfaction of the Director, Biodiversity Policy and Programs, DSE.
The difficulty for the Court in formulating its orders was that the power to act on the evidence of rare and endangered species and implement the required legislative and policy changes lies not with VicForests, against whom the injunction was sought, but with DSE.
Justice Osborn overcame this difficulty by stopping VicForests from logging until certain actions are undertaken, these actions being DSE responsibilities. VicForests had maintained throughout proceedings that it would comply with any changes to the regulatory regime made by DSE, and this was accepted by the Court.
.
Significance of the decision
.
This case firmly embeds the approach to the precautionary principle laid down by Chief Justice Preston in Telstra Corporation Limited v Hornsby Shire Council (2006) 67 NSWLR 256.
Justice Osborn’s decision makes it clear that:
- The precautionary principle can be the subject of an enforceable obligation.
- Parties having an obligation to apply the precautionary principle cannot demonstrate compliance with the principle solely through departmental approval of their actions or relevant approvals under the regulatory regime; the precautionary principle is an active obligation that applies throughout operations, requiring parties to respond to new information as it arises.
- The precautionary principle applies throughout all stages of operation, not just the strategic planning (or approvals) stage.
The decision has broader implications because:
- The precautionary principle is embedded in many other statutory regimes in Victoria and around Australia, apart from the Victorian legislative regime for forestry and the protection of endangered species. The decision has implications for any statutory regime in which the principle is enshrined.
- Although VicForest is a state-owned enterprise operating within a highly regulated environment, there is scope for the decision to be applied to other types of entities operating within industries where the precautionary principle is relevant.
Furthermore, a decision of the Supreme Court of Victoria has strong precedent value, and is likely to be adopted by the Supreme Courts of other States, and perhaps even higher courts or courts with federal jurisdiction.
.
Action points
.
Parties under an obligation to apply the precautionary principle need to be aware that:
- to implement the precautionary principle as per the principles laid down in Telstra, parties need to ask:
- is there a real threat of serious or irreversible damage to the environment?
- if yes, is it attended by a lack of full scientific certainty (in the sense of material uncertainty)?
- if yes, is the threat non-existent or negligible?
- if no, is the threat able to be addressed by adaptive management and is the measure alleged to be required proportionate to the threat in issue?
- the principle must be applied at both the strategic decision making stage of a project, and throughout the operational stage; and
- it may not be sufficient to simply obtain and comply with project approvals – parties need to proactively respond to new information as it arises throughout the operational stage.’
.
..
.
Further Reading:
.
[1] >Vicforests’ Ecological Genocide
.
[2] ‘Nippon buys Maryvale mill‘, by Ian McIlwraith, The Age newspaper, 20090217, ^http://www.theage.com.au/business/nippon-buys-maryvale-mill-20090216-89bu.html, accessed 20110826]
.
‘Paperlinx will take a $600 million hit on its half year results and the future of its Tasmanian operations is under review after last night unveiling the partial sale of its Australian papermaking business.
Japan’s Nippon Paper Group will buy most of Australian Paper, which includes the Maryvale pulp mill in Gippsland, for more than $700 million, including taking on attached debt and a three-year profit share agreement.
Money from the sale, expected to be completed in June, will go to reducing PaperlinX’s debt burden to about $340 million…’
[Editor: So Paperlinx was in debt to the Australian Tax Office by over a billion dollars? How can Australia’s pulp industry be profitable then?]
.
[3] Australian Paper Watch website (providing information about the logging of Victoria’s forests to make paper products such as Reflex by Nippon Paper and their ‘subsidiary’ Australian Paper), ^http://www.australianpaper.forests.org.au/
.
[4] Nippon Paper’s Maryvale Mill Upgrade, ^http://www.reflex.com.au/2008-Maryvale-Mill-Upgrade/
‘Australian Paper has a long history in the La Trobe Valley in Gippsland, Victoria, dating back to 1937 when established. Today, the Mill is Australia’s largest integrated pulp and paper operation. In response to global paper trends and changing consumer expectations for our products, Australian Paper (Nippon Paper subsidiary) embarked on a major upgrade of the Maryvale Pulp Mill in 2006 which was completed in December 2008. With an investment of $350 million, the upgrade significantly expanded the Mill’s production of bleached pulp capacity and delivered a range of safety, health and environmental benefits.’
.
[5] ‘Loggers, activists clash over forest‘, by Adam Morton, The Age newspaper, 20110817, August 17, 2011, ^http://www.theage.com.au/victoria/loggers-activists-clash-over-forest-20110816-1iwew.html
.
‘Conservationists have held up timber workers in a fiercely contested area of native forest on Melbourne’s fringe for nearly a month, chaining themselves to bulldozers and climbing trees scheduled for logging.
The protest, which has led to at least 10 arrests, is expected to reach a climax today as activists and local residents march into the logging coupe outside Toolangi in Victoria’s central highlands.
Protest organisers claim they have evidence the coupe is home to the endangered Leadbeaters Possum, which scientists say is under threat after Black Saturday bushfires wiped out up to half its habitat. But the Department of Sustainability and Environment says there has been no sign of live possums. Department spokeswoman Kim Payne said one tree in the coupe had hollows that showed evidence of possum use. That tree would be left standing, but the coupe did not meet the legal criteria of prime possum habitat and could otherwise be logged.
Sarah Rees, director of Healesville-based group My Environment, said it was cruel to think a possum could be protected by retaining a single tree while taking away the forest around it. She said logging was hurting central highlands communities.
.
”Tourism based on the state forest is far more important to the local economy than forestry and the two cannot co-exist,” she said.
The conflict over the Toolangi State Forest was the focus of a public meeting in the area late last week when logging opponents verbally clashed with forestry workers, who accused the activists of restraint of trade. One contractor said he had lost about $80,000 due to the protests.

David Walsh, spokesman for state commercial timber agency VicForests, said the Toolangi protests had cost forest workers significant time. Only about a quarter of the 19-hectare coupe had been harvested. He said gates raised to ensure public safety had been damaged. ”VicForests believes these are legal harvesting operations which comply with the detailed legislative framework governing native timber harvesting in Victoria,” he said.‘
.
Editor: The legal doctrine of ‘restraint of trade’ sought to be applied in the commercial exploitation and destruction of old growth forests, is an invalid excuse. It is a contemptible euphemism for a ‘right to rape’ old growth ecology that is being contrived by commercial lawyers profiting from the exploiters ~ a case of the morally bankrupt collaborating with the damned.
[6] Ethical Paper website, ^http://www.ethicalpaper.com.au/
.
[7] My Environment website, ^http://www.myenvironment.net.au/

.
– end of article –
Tags: Aokigahara Forest, Atsuta Jinja, Australian Forestry Standard, Australian Paper, Chain of Custody certification, deforestation, East Gippsland, EEG, endangered species habitat, Environment East Gippsland, Environment East Gippsland Inc v VicForests, Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act, Forest Stewardship Council, Forestry Standard Certification, FSC, FSC audit process, FSC Chain of Custody Certification, FSC International, FSC-C002059, Future Fibre Strategy, Giant Burrowing Frog, Greater Glider, Greenwash Tick, Kashima Jingu, Kasuga Taisha, Kirishima Jingu, Large Brown Tree Frog, Leadbeaters Possum, Logging, Long-footed Potoroo, Maryvale Pulp Mil, My Environment, Nippon Paper Group, PEFC, Powerful Owl, precautionary principle, pulp and paper, Rainforest Alliance, Reflex Paper, restraint of trade, right to rape, sacred forest, Shimogamo Jinja, Shinto religion, Sooty Owl, The Wilderness Society, Timber Release Plan, Toolangi State Forest, TWS, VicForests, Yahiko Jinja, Yellow-bellied Glider
Posted in Gippsland (AU), Owls, Potoroos, Quolls, Reptiles, Threats from Deforestation | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Thursday, July 28th, 2011
The following article was initially posted 20090414 by Tigerquoll on CanDoBetter.net:.

The UN position in 1992 on conserving native forests of the world:
.
‘At the 1992 United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) the forest issue was among the most controversial, polarizing developing and developed countries.
In Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, intense negotiations among governments at UNCED resulted in the Non-legally Binding Authoritative Statement of Principles for a Global Consensus on the Management, Conservation and Sustainable Development of all Types of Forests, also known as the “Forest Principles”, as well as Chapter 11 of Agenda 21: Combating Deforestation.”

.
..
1992 Report of the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development [UNCED]
(Rio de Janeiro, 3-14 June 1992)
Extract from ‘Annex III’:
[NON-LEGALLY BINDING AUTHORITATIVE STATEMENT OF PRINCIPLES FOR A GLOBAL CONSENSUS ON THE MANAGEMENT, CONSERVATION AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF ALL TYPES OF FORESTS]

.
PREAMBLE
(a) The subject of forests is related to the entire range of environmental and development issues and opportunities, including the right to socio-economic development on a sustainable basis.
(b) The guiding objective of these principles is to contribute to the management, conservation and sustainable development of forests and to provide or their multiple and complementary functions and uses.
(c) Forestry issues and opportunities should be examined in a holistic and balanced manner within the overall context of environment and development, taking into consideration the multiple functions and uses of forests, including traditional uses, and the likely economic and social stress when these uses are constrained or restricted, as well as the potential for development that sustainable forest management can offer.
(d) These principles reflect a first global consensus on forests. In committing themselves to the prompt implementation of these principles, countries also decide to keep them under assessment for their adequacy with regard to further international cooperation on forest issues.
(e) These principles should apply to all types of forests, both natural and planted, in all geographical regions and climatic zones, including austral, boreal, subtemperate, temperate, subtropical and tropical.
(f) All types of forests embody complex and unique ecological processes which are the basis for their present and potential capacity to provide resources to satisfy human needs as well as environmental values, and as such their sound management and conservation is of concern to the Governments of the countries to which they belong and are of value to local communities and to the environment as a whole.
(g) Forests are essential to economic development and the maintenance of all forms of life.
(h) Recognizing that the responsibility for forest management, conservation and sustainable development is in many States allocated among federal/national, state/provincial and local levels of government, each State, in accordance with its constitution and/or national legislation, should pursue these principles at the appropriate level of government.

.
PRINCIPLES/ELEMENTS
.
1. (a) States have, in accordance with the Charter of the United Nations and the principles of international law, the sovereign right to exploit their own resources pursuant to their own environmental policies and have the responsibility to ensure that activities within their jurisdiction or control do not cause damage to the environment of other States or of areas beyond the limits of national jurisdiction.
(b) The agreed full incremental cost of achieving benefits associated with forest conservation and sustainable development requires increased international cooperation and should be equitably shared by the international community.
2. (a) States have the sovereign and inalienable right to utilize, manage and develop their forests in accordance with their development needs and level of socio-economic development and on the basis of national policies consistent with sustainable development and legislation, including the conversion of such areas for other uses within the overall socio-economic development plan and based on rational land-use policies.
(b) Forest resources and forest lands should be sustainably managed to meet the social, economic, ecological, cultural and spiritual needs of present and future generations. These needs are for forest products and services, such as wood and wood products, water, food, fodder, medicine, fuel, shelter, employment, recreation, habitats for wildlife, landscape diversity, carbon sinks and reservoirs, and for other forest products. Appropriate measures should be taken to protect forests against harmful effects of pollution, including air-borne pollution, fires, pests and diseases, in order to maintain their full multiple value.
(c) The provision of timely, reliable and accurate information on forests and forest ecosystems is essential for public understanding and informed decision-making and should be ensured.
(d) Governments should promote and provide opportunities for the participation of interested parties, including local communities and indigenous people, industries, labour, non-governmental organizations and individuals, forest dwellers and women, in the development, implementation and planning of national forest policies.
3. (a) National policies and strategies should provide a framework for increased efforts, including the development and strengthening of institutions and programmes for the management, conservation and sustainable development of forests and forest lands.
(b) International institutional arrangements, building on those organizations and mechanisms already in existence, as appropriate, should facilitate international cooperation in the field of forests.
(c) All aspects of environmental protection and social and economic development as they relate to forests and forest lands should be integrated and comprehensive.
4. The vital role of all types of forests in maintaining the ecological processes and balance at the local, national, regional and global levels through, inter alia, their role in protecting fragile ecosystems, watersheds and freshwater resources and as rich storehouses of biodiversity and biological resources and sources of genetic material for biotechnology products, as well as photosynthesis, should be recognized.
5. (a) National forest policies should recognize and duly support the identity, culture and the rights of indigenous people, their communities and other communities and forest dwellers. Appropriate conditions should be promoted for these groups to enable them to have an economic stake in forest use, perform economic activities, and achieve and maintain cultural identity and social organization, as well as adequate levels of livelihood and well-being, through, inter alia, those land tenure arrangements which serve as incentives for the sustainable management of forests.
(b) The full participation of women in all aspects of the management, conservation and sustainable development of forests should be actively promoted.
6. (a) All types of forests play an important role in meeting energy requirements through the provision of a renewable source of bio-energy, particularly in developing countries, and the demands for fuelwood for household and industrial needs should be met through sustainable forest management, afforestation and reforestation. To this end, the potential contribution of plantations of both indigenous and introduced species for the provision of both fuel and industrial wood should be recognized.
(b) National policies and programmes should take into account the relationship, where it exists, between the conservation, management and sustainable development of forests and all aspects related to the production, consumption, recycling and/or final disposal of forest products.
(c) Decisions taken on the management, conservation and sustainable development of forest resources should benefit, to the extent practicable, from a comprehensive assessment of economic and non-economic values of forest goods and services and of the environmental costs and benefits. The development and improvement of methodologies for such evaluations should be promoted.
(d) The role of planted forests and permanent agricultural crops as sustainable and environmentally sound sources of renewable energy and industrial raw material should be recognized, enhanced and promoted. Their contribution to the maintenance of ecological processes, to offsetting pressure on primary/old-growth forest and to providing regional employment and development with the adequate involvement of local inhabitants should be recognized and enhanced.
(e) Natural forests also constitute a source of goods and services, and their conservation, sustainable management and use should be promoted.
7. (a) Efforts should be made to promote a supportive international economic climate conducive to sustained and environmentally sound development of forests in all countries, which include, inter alia, the promotion of sustainable patterns of production and consumption, the eradication of poverty and the promotion of food security.
(b) Specific financial resources should be provided to developing countries with significant forest areas which establish programmes for the conservation of forests including protected natural forest areas. These resources should be directed notably to economic sectors which would stimulate economic and social substitution activities.
8. (a) Efforts should be undertaken towards the greening of the world.
All countries, notably developed countries, should take positive and transparent action towards reforestation, afforestation and forest conservation, as appropriate.
(b) Efforts to maintain and increase forest cover and forest productivity should be undertaken in ecologically, economically and socially sound ways through the rehabilitation, reforestation and re-establishment of trees and forests on unproductive, degraded and deforested lands, as well as through the management of existing forest resources.
(c) The implementation of national policies and programmes aimed at forest management, conservation and sustainable development, particularly in developing countries, should be supported by international financial and technical cooperation, including through the private sector, where appropriate.
(d) Sustainable forest management and use should be carried out in accordance with national development policies and priorities and on the basis of environmentally sound national guidelines. In the formulation of such guidelines, account should be taken, as appropriate and if applicable, of relevant internationally agreed methodologies and criteria.
(e) Forest management should be integrated with management of adjacent areas so as to maintain ecological balance and sustainable productivity.
(f) National policies and/or legislation aimed at management, conservation and sustainable development of forests should include the protection of ecologically viable representative or unique examples of forests, including primary/old-growth forests, cultural, spiritual, historical, religious and other unique and valued forests of national importance.
(g) Access to biological resources, including genetic material, shall be with due regard to the sovereign rights of the countries where the forests are located and to the sharing on mutually agreed terms of technology and profits from biotechnology products that are derived from these resources.
(h) National policies should ensure that environmental impact assessments should be carried out where actions are likely to have significant adverse impacts on important forest resources, and where such actions are subject to a decision of a competent national authority.
9. (a) The efforts of developing countries to strengthen the management, conservation and sustainable development of their forest resources should be supported by the international community, taking into account the importance of redressing external indebtedness, particularly where aggravated by the net transfer of resources to developed countries, as well as the problem of achieving at least the replacement value of forests through improved market access for forest products, especially processed products. In this respect, special attention should also be given to the countries undergoing the process of transition to market economies.
(b) The problems that hinder efforts to attain the conservation and sustainable use of forest resources and that stem from the lack of alternative options available to local communities, in particular the urban poor and poor rural populations who are economically and socially dependent on forests and forest resources, should be addressed by Governments and the international community.
(c) National policy formulation with respect to all types of forests should take account of the pressures and demands imposed on forest ecosystems and resources from influencing factors outside the forest sector, and intersectoral means of dealing with these pressures and demands should be sought.
10. New and additional financial resources should be provided to developing countries to enable them to sustainably manage, conserve and develop their forest resources, including through afforestation, reforestation and combating deforestation and forest and land degradation.
11. In order to enable, in particular, developing countries to enhance their endogenous capacity and to better manage, conserve and develop their forest resources, the access to and transfer of environmentally sound technologies and corresponding know-how on favourable terms, including on concessional and preferential terms, as mutually agreed, in accordance with the relevant provisions of Agenda 21, should be promoted, facilitated and financed, as appropriate.
12. (a) Scientific research, forest inventories and assessments carried out by national institutions which take into account, where relevant, biological, physical, social and economic variables, as well as technological development and its application in the field of sustainable forest management, conservation and development, should be strengthened through effective modalities, including international cooperation. In this context, attention should also be given to research and development of sustainably harvested non-wood products.
(b) National and, where appropriate, regional and international institutional capabilities in education, training, science, technology, economics, anthropology and social aspects of forests and forest management are essential to the conservation and sustainable development of forests and should be strengthened.
(c) International exchange of information on the results of forest and forest management research and development should be enhanced and broadened, as appropriate, making full use of education and training institutions, including those in the private sector.
(d) Appropriate indigenous capacity and local knowledge regarding the conservation and sustainable development of forests should, through institutional and financial support and in collaboration with the people in the local communities concerned, be recognized, respected, recorded, developed and, as appropriate, introduced in the implementation of programmes. Benefits arising from the utilization of indigenous knowledge should therefore be equitably shared with such people.
13. (a) Trade in forest products should be based on non-discriminatory and multilaterally agreed rules and procedures consistent with international trade law and practices. In this context, open and free international trade in forest products should be facilitated.
(b) Reduction or removal of tariff barriers and impediments to the provision of better market access and better prices for higher value-added forest products and their local processing should be encouraged to enable producer countries to better conserve and manage their renewable forest resources.
(c) Incorporation of environmental costs and benefits into market forces and mechanisms, in order to achieve forest conservation and sustainable development, should be encouraged both domestically and internationally.
(d) Forest conservation and sustainable development policies should be integrated with economic, trade and other relevant policies.
(e) Fiscal, trade, industrial, transportation and other policies and practices that may lead to forest degradation should be avoided. Adequate policies, aimed at management, conservation and sustainable development of forests, including, where appropriate, incentives, should be encouraged.
14. Unilateral measures, incompatible with international obligations or agreements, to restrict and/or ban international trade in timber or other forest products should be removed or avoided, in order to attain long-term sustainable forest management.
15. Pollutants, particularly air-borne pollutants, including those responsible for acidic deposition, that are harmful to the health of forest ecosystems at the local, national, regional and global levels should be controlled.’

.
.
The UN position in 2007:
.
‘Following nearly 3 years of intense negotiations, starting from UNFF5 and culminating at UNFF7, the Non-Legally Binding Instrument on All types of Forests was adopted on 28 April 2007. The Instrument was adopted by the UN General Assembly (Resolution 62/98) on 17 December 2007.
The purpose of this instrument is:
(a) To strengthen political commitment and action at all levels to implement effectively sustainable management of all types of forests and to achieve the shared global objectives on forests;
(b) To enhance the contribution of forests to the achievement of the internationally agreed development goals, including the Millennium Development Goals, in particular with respect to poverty eradication and environmental sustainability;
(c) To provide a framework for national action and international cooperation.’

– end of article –
.
.
Rainforest Reality, 2011:
.
‘Deforestation in Brazil’s Amazon Region Increases 400% in One Year’ [ May 2011]
[20110520, hispanicallyspeakingnews.com]
.
‘Brazil is reporting a dramatic increase in deforestation in the Amazon that has the country’s environmental protectionists and some government officials troubled. In just one year – March/April of 2010 -2011 – Brazil’s Amazon has seen a 400 percent increase in the amount of acres that have undergone deforestation – 25,451 acres to 146,533, according to satellite images from the Brazilian space research institute.
Environmental protectionists believe the increased demand for cattle and soy are behind the decision to clear so many acres, while other blame the government for not being hesitant in regards to laws to regulate deforestation. The country’s Environmental Minister Izabella Teixeira said she was troubled to see the satellite images, and said the government would establishing a special panel to address the matter.
Currently, Brazilian law states that 80 percent of the land in the Amazon region must remain forested, and that has been in place since 1934. Still, deforestation advocates claim additional clearing is needed. In the state of Mato Grosso, deforestation occurs in large part to make room for soybean production.’
.
[Source: ^ http://www.hispanicallyspeakingnews.com/notitas-de-noticias/details/deforestation-in-brazils-amazon-region-increases-400-in-one-year/7782/, accessed 20110728]

Editor’s comment: ‘This the consequence of ‘non-legally binding UN ‘Forest Principles’.’
.
.
Read More:
.
[1] United Nations Forum on Forests, ^http://www.un.org/esa/forests/
[2] Mongabay.com, ^http://www.mongabay.com/brazil.html
[3] Greenpeace.org, ^http://www.greenpeace.org/international/en/press/releases/second-largest-rate-of-amazon/
[4] Greenpeace campaign to save the Amazon, ^http://www.greenpeace.org/international/en/campaigns/forests/amazon/
[5] ‘Deforestation in decline but rate remains alarming, UN agency says‘, UN News Centre, ^http://www.un.org/apps/news/story.asp?NewsID=34195
[6] ‘REDD’, The United Nations Collaborative Programme on Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation in Developing Countries, ^http://www.un-redd.org/
[7] ‘UN: $40bn a year could halve deforestation worldwide‘, by Will Nichols, 20110606, Business Green, ^http://www.businessgreen.com/bg/news/2076417/-usd40bn-halve-deforestation-worldwide
.
(above references accessed 20110728)
.
– end of article –
Tags: Agenda 21: Combating Deforestation, Amazon forest, deforestation, Forest Principles, old growth conservation, old growth forest, Rainforest Reality, soybean, tigerquoll, U.N. Principles, UNCED, UNFF
Posted in Amazon (BR), Threats from Deforestation, Threats from Farming | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Friday, July 22nd, 2011
The following article was initially posted by Tigerquoll 20090408 on CanDoBetter.net:
.
 © Photo EEG 2009 © Photo EEG 2009
.
Radiocarbon-testing has confirmed that a giant rare old-growth Eucalyptus regnans located in its natural forest habitat on East Gippsland’s Brown Mountain has been chainsawed by VicForests, despite it being scientifically confirmed to be at least 500 years old.
No regard has been made for the existence value of a Victorian 500 year old natural asset, nor the habitat requirements for the typical arboreal animals and forest owls dependent on this old growth habitat tree or its associative forest dependent habitat. Under State-
sanction, ignorant VicForest butchers have plundered, ransacked and run.
 © Photo EEG 2009 © Photo EEG 2009
.
Manager, Victorian Department of Sustainability and Environment, Orbost, Steve DeVoogd, has been formally advised that this chainsawing of rare old growth forest is an offence committed under the section 46(1) of the Sustainable Forests (Timber) Act 2004. The action is also a breach of Code of Forest Practices (CFP). VicForests Chairman, Warren Hodgson, Board members Monica Gould, Jim Houghton, Fiona McNabb, Bob Smith, Susan Walpole, and Chief Executive Officer David Pollard should all be sacked forthwith. VicForests token ‘vision’ ‘purpose’ and ‘values’ which profess motherhood notions of ‘sustainable’, ‘environmentally responsible’ and ‘ethical’ are but ‘Mugabean’. This 500 year old tree epitomises the reality of Brumby’s ‘Sustainability Charter for State forests.
Botanist Steve Mueck has worked for the Victorian Department of Natural Resources and Environment and is now a consultant in the private sector. He says radiocarbon dating of eucalypts is unusual and the result in this case is significant.
“Current forest managements practices are looking at harvesting on rotation times in the vicinity of 80 to 120 years with the perception that that’s a particularly long period of time,” he said.
“Now it is, I suppose, in the context of a human lifetime, but it is a very, very short period of time in comparison to the age in which many of the components that live in these forests can in fact get to in a natural system.”
Back in the 1860s timber workers and naturalists emerged from the forests with stories of massive trees towering to immense heights and as wide as houses.
Government botanist Ferdinand von Mueller recounted the existence of a tree as high as the Egyptian Pyramids at 480 ft (144m) and another fallen tree in the Dandenong Ranges over 400 ft (120m). A giant was sighted in the Otways with a girth of 64 ft (19m).
VicForests senseless decapitation of one of the last Victorian giants is a harbinger of extinction to Victoria’s old growth forests.
It’s like grabbing an old ANZAC from a ‘march past’ and slitting his throat.
 © Photo EEG 2009 © Photo EEG 2009
.
.
Comments:
.
‘Victorian Labor’s “sustainable” principles are thin and shallow’
by Vivienne 20090410:
.
In 2006 the Labor Party pledged to “protect remaining significant stands of old growth forest currently available for timber harvesting by including them in the National Parks and reserves system”.
This promise was blatantly broken.
The trees on of Brown Mountain have not burned for 200 years despite repeated fire threats. The resistance of these old forests to bushfire is evident. This area is also the home of several highly endangered native species.
Clear felling of old growth forests has continued despite their critical role in storing carbon and providing water for the depleted Snowy River catchment.
The Victorian government states that 90% of our forests are preserved. However, only 16% of Victoria is protected, and over 80 percent of what is logged in East Gippsland ends up as mere woodchips!
Clearing 10% of our forests is plainly too much considering that Victoria remains the most cleared and damaged State of Australia.
Our Brumby government is guilty of serious eco-destruction and policy violation, and any claims of “sustainable” principles are demonstrated to be thin and shallow.
.
– end of article –
Tags: biodiversity, Brown Mountain, Brumby's 'Sustainability Charter for State forests, Code of Forest Practices, deforestation, Department of Sparks and Embers, East Gippsland logging, John Brumby, save our forests, Sustainable Forests (Timber) Act 2004, VicForests, Victoria's old growth forests, Victorian Department of Sustainability and Environment, Victorian Labor
Posted in Gippsland (AU), Threats from Deforestation | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
|
|
 Click above image to play video: ‘Appetite for Destruction: China’s trade in illegal timber’
Click above image to play video: ‘Appetite for Destruction: China’s trade in illegal timber’ Chinese have become the worst deforesters on Earth
Chinese have become the worst deforesters on Earth









 Dozers having a wee afternoon doze
.
Dozers having a wee afternoon doze
.