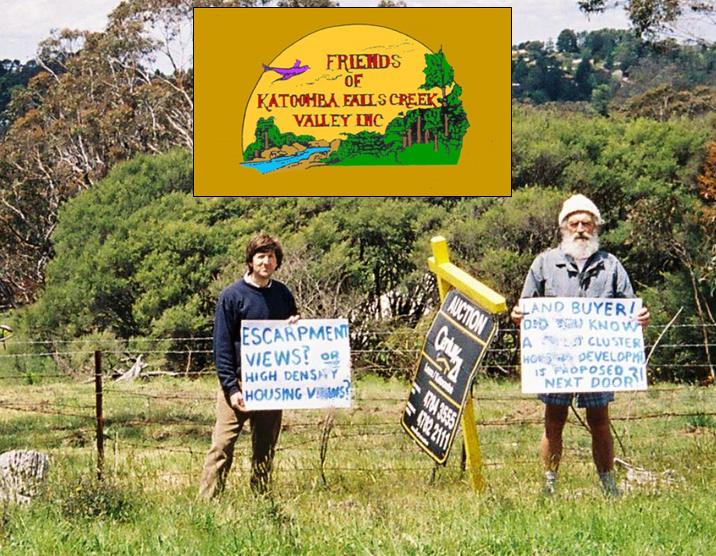
Katoomba Golf Club’s escarpment vandalism
Friday, July 5th, 2013 Katoomba Golf Club this week has been placed into administration – about time!
[Photo by Editor, 20130507, Photo © under ^Creative Commons]
Katoomba Golf Club this week has been placed into administration – about time!
[Photo by Editor, 20130507, Photo © under ^Creative Commons]
.
Actor Bing Crosby used to famously play golf back in the 1950s, but in 2013 who plays golf but the last of retired male Baby Boomers? The sport is a ‘has been’ and most courses have been constructed necessitating broadscale habitat destruction, and arrogantly so.
Golf’s origins date back to 15th Century Scotland and to the exclusive pastime of its landed gentry – male gentry, one for Gentlemen Only Ladies Forbidden. Along with croquet and lawn bowls, it dates to a bygone era – up there with duelling, archery practice and pheasant hunting.
This week we learn about the demise of another golf club struggling to attract new members as its 20th Century members ‘pass on’.
In the Blue Mountains west of Sydney, the Katoomba Golf Club as registered body formed just over a hundred years ago back in 1911. The land on which Katoomba Golf Club sited Katoomba Golf Course after the war in May 1923, had few previous owners in historic times.
A brief reflection on relevant colonial history
In the 18th Century, the island continent we now call Australia, was considered ‘undiscovered’ by the then dominant global European powers that be. In 1768, the then head of state of the Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, King George III commissioned his Royal Navy to undertake a world expedition voyage under the command of Lieutenant James Cook (combined with Botanist Joseph Banks of the Royal Society) to the south Pacific Ocean aboard HMS Endeavour, which took place between 1768 to 1771. Amongst the voyage’s prescribed tasks were to observe the 1769 transit of Venus across the Sun (3–4 June that year), and to seek evidence of the postulated Terra Australis Incognita or “undiscovered southern land”, plus other exploratory, naturalist and mapping duties.
In April 1770, the voyage famously became the first known European expedition to reach the east coast of Australia, mapping the coastline and making landfall near present-day Point Hicks, and then proceeding north to Botany Bay, naming the land New South Wales.
On 21st August 1770, Cook’s exploration party stepped ashore on an island in the Torres Strait situated 2km off now Cape York Peninsula (since called Possession Island) and declared possession of this “undiscovered southern land” to the British Crown. This was on the basis of unilateral possession – the land perceived as ‘terra nullius’, being Latin for ‘land belonging to no one’, because Cook and Banks considered there were few ‘natives’ along the coast and deduced that there would be fewer or none inland.
Subsequently, the British colonial First Fleet arrived at Botany Bay then Port Jackson in 1788 to establish a British convict settlement was set up in New South Wales.. The Proclamation of NSW Governor Richard Bourke in 1835 implemented the legal principle of terra nullius in Australian law as the basis for British settlement, 47 years later. Such were the powers that prevailed at the time. Various ‘frontier wars’ were waged sporadically between the Aboriginal peoples and the vastly out-weaponed British military and colonists for 46 years (1788-1934). By 1901, Australia was universally declared a unified federated nation state – The Commonwealth of Australia.
This island continent had been ‘legally owned’ (possessed) by the British Crown since Cook’s authorised declaration of possession in 1770. From 1788, the British penal colony of New South Wales was ruled by successive British military governors of the Colony of New South Wales. Until 1824, the military governors of New South Wales were absolute rulers with rights granted to them under an Act of the British Parliament of 1787. The only power superior to them being the British Parliament at Westminster in London, England.
History is history.
So, back to the land of Katoomba Golf Course – obtained historical written records show that the land site was then ‘legally owned’ by the London Chartered Bank of Australia from at least as far back as the 1870s. Katoomba was then not a settlement. Only a sandstone rock quarry ‘The Crushers‘ is historically documented to be in the area to supply ballast for the new railway line roll-out from the 1860s to 1874 when a railway siding was built. It appears that soon afterwards, English migrant (entrepreneurial merchant, miner then property developer) John Britty North acquired vast acreage around the south western area of The Crushers, which would become called the township of Katoomba.
Thus far, our research has not revealed how the local council happened to acquire the land of what would become granted to Katoomba Golf Club in 1920 to deforest the bushland for a golf course. In 1889, Blue Mountains Council did not exist, rather it was one of a number of smaller regional municipal councils across the central Blue Mountains, then it being termed the Katoomba Municipal Council Incorporated).
This is an historic legal document we have obtained that reveals the original deal dated 28th January 1920 between the Katoomba Golf Club and the then local council. At the time the deal was in fact legally between ‘The South Katoomba Land Company Limited‘ and ‘The Council of the Municipally of Katoomba‘. The former was the registered legal body that certain local business owners had established as a legal entity, and the then legally named local council.
 Loading...
Loading...
Now this is a good revealing read. How’s these stated legal requirements for instance:
-
“Council at its own expense… (read Clause 1), (read Clause 2)”
-
(Clause 3) “THAT the said Council its successors and assign will not at any time erect on the said land any dwelling house or other building except a golf club house or a tennis court or croquet cloub house or a club house for any other purpose for recreation as allowed by paragraph (a) 2 and sheds outhouses stables and other buildings in connection herewith.”
The land was then owned by the then Katoomba Council (i.e. by the local community). The land was acquired from the local council for £1500 by property developers under the name of the South Katoomba Land Company. Was the escarpment land paid for, loaned or gifted? A nearby Gully was acquired a generation later from the Katoomba Council via a £27,000 loan to build a motor racing track, but the loan was never repaid.
So golf playing at the Katoomba Golf Club was in full swing from the 1920’s, and when Bing Crosby was playing during the post War 1950’s, golf was in its heyday. But by the end of the 1980s for reasons of waning interest, other competing interests for a four hour round of golf, busy lifestyles and basic economics; the Baby Boomer golf fad was fading. This was not just across Australia, but across America and elsewhere. Read the article at the end of this one by Nancy Keate, in The Wall Street Journal.
[Source: ‘Is Economy Or Lack Of Interest Hurting Golf?’, 20110523, by Ian Hutchinson , ^http://www.golfnewsnow.ca/2011/05/23/is-economy-or-lack-of-interest-hurting-golf/] .
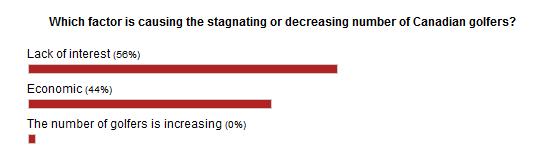
Is Economy Or Lack Of Interest Hurting Golf?
“Over the past week, we’ve been discussing the declining number of golfers, both in Canada and the United States, a topic sparked by this story (see below) by Gene Yasuda of Golfweek.
Of course, the U.S. numbers used by Yasuda were provided by the National Golf Foundation, but here in Canada, we have no recent official numbers to go by, so it could be argued that there’s no cause for alarm about the number of Canadian golfers.
Some might even be tempted to lean on the crutch that Canada is among the world leaders in golfers per capita. Even if that is still the case, it doesn’t necessarily mean that the number of golfer isn’t dwindling.
All golf operators need to do is look out on their fairways and compare the number of golfers out there today to what it was five or 10 years ago to come to a realistic conclusion on how the number of golfers is affecting their businesses and whether it’s up, down or stagnant.
Of course, that number may be affected by the number of golf courses in a saturated market, but the feeling I get from different regions of the country leads me to believe that the number of overall golfers in this country is stagnating at best. If only there were numbers to back that up.
The consensus in the Golfweek story is that the U.S. numbers are affected mainly by the struggling American economy more than a lack of interest in the game.
Here in Canada, however, we’ve come out of the economic downturn a lot quicker that the U.S., but economic factors such as the price of gas and other inflation and the possibility of rising interest rates may be playing a part.
On the other hand, Canadian golf may be feeling the competition from other entertainment and recreation sources, which could indicate a waning interest in the game. While economic pressures on golfers might be a temporary factor, waning interest is more long term.
Which of those two factors do you feel is affecting the number of golfers in Canada? That’s the subject of this week’s GNN Poll.”
U.S. golf participation falls for third consecutive year
May 9, 2011 [SOURCE: http://golfweek.com/news/2011/may/09/us-golf-participation-falls-third-consecutive-year/]
“For the third consecutive year, the number of golfers in the U.S. declined, falling 3.6 percent to 26.1 million in 2010, according to the National Golf Foundation.
The slide, from 27.1 million golfers in 2009, wasn’t unexpected in light of the heavy toll the recession has had on the sport and the economy in general.
The silver lining, if any, according to NGF officials, is that the participation falloff is more linked to financial pressures rather than golf losing popularity among consumers.
“Multiple NGF studies of golfers since 2008 would attribute the gradual decline in golfers and rounds primarily to the impact of lower job security and concern over personal finances, not waning appeal for the game,” said Joe Beditz, NGF president and CEO.
The NGF supported that conclusion by citing golf’s continuing ability to attract “new” participants – in 2010 a total of 3.6 million, including 1.5 million first-time beginners and 2.1 million returning former golfers.
That gain, however, was negated by the loss of 4.6 million golfers who played in 2009 but not in 2010. According to the NGF, the number of new golfers held steady while the number of those who left the game decreased significantly. In recent years, golf industry leaders have been emphasizing improving the retention of golfers.
For all their efforts, though, the downward trend of participation remains a major concern. By comparison, the number of golfers in the U.S. in 2000 and 2005 was 28.8 million and 30 million, respectively.
Among the other findings:
- The number of “core” golfers (eight or more rounds annually) dropped to 14.8 million – down 3.6 percent from 15.3 million in 2009.
- “Occasional” golfers suffered a similar decline: a drop of 3.7 percent to 11.3 million from 11.8 million in 2009.
- The number of rounds played in 2010 was 475 million, down 2.3 percent from 486 million in the previous year. (By comparison, rounds played in 2000 and 2005 was 518 million and 500 million, respectively.)
The participation study defines a golfer as a person, age 6 or older, who plays at least one round of golf in a given year. Its results are “derived from a multi-sport study of 40,000 Americans, executed in conjunction with the Sporting Goods Manufacturers Association,” the NGF stated.
Yet, despite this general waning interest in golf and despite specifically the falling membership at both Katoomba and nearby Leura golf clubs, some Baby Boomers in complete denial decided in the 1990s to expand the Katoomba golf course from 9 holes to 18. [Editor’s Corrigendum: Correspondence received from an informed reader after publication, has confirmed that the golf course was in fact expanded from 9 holes to 18 holes circa 1927 (^Source). The development works circa 1995 instead relate to expansion of the course acquiring 5.6 hectares of adjoining community zoned woodland alongside Narrow Neck Road in order to build 13 townhouses and a resort hotel. Also circa 2007, a fairway/green was extended into bushland near Stuarts Road.] Further, they had grandiose notions of building a dozen new dedicated golfing townhouses next to the clubhouse, so perpetuating the ‘has-been’ American trend of the 1980s.
Where did the millions in development finance come from and how much was put up by local Blue Mountains Council negotiated behind closed doors claiming a dubious excuse fo commercial in confidence” dealing with this being zoned ‘Community Land‘ ?
Of course, this development necessitated a considerable acquisition of more surrounding bushland to be logged, the vegetation slashed and bulldozed, the soils landscaped, grassed and fertilised. This has meant permanent destruction of the ecosystem just like open cut mining. All this occurred immediately above and upstream of the Jamison Valley wilderness, now part of the Blue Mountains World Heritage Area.
.
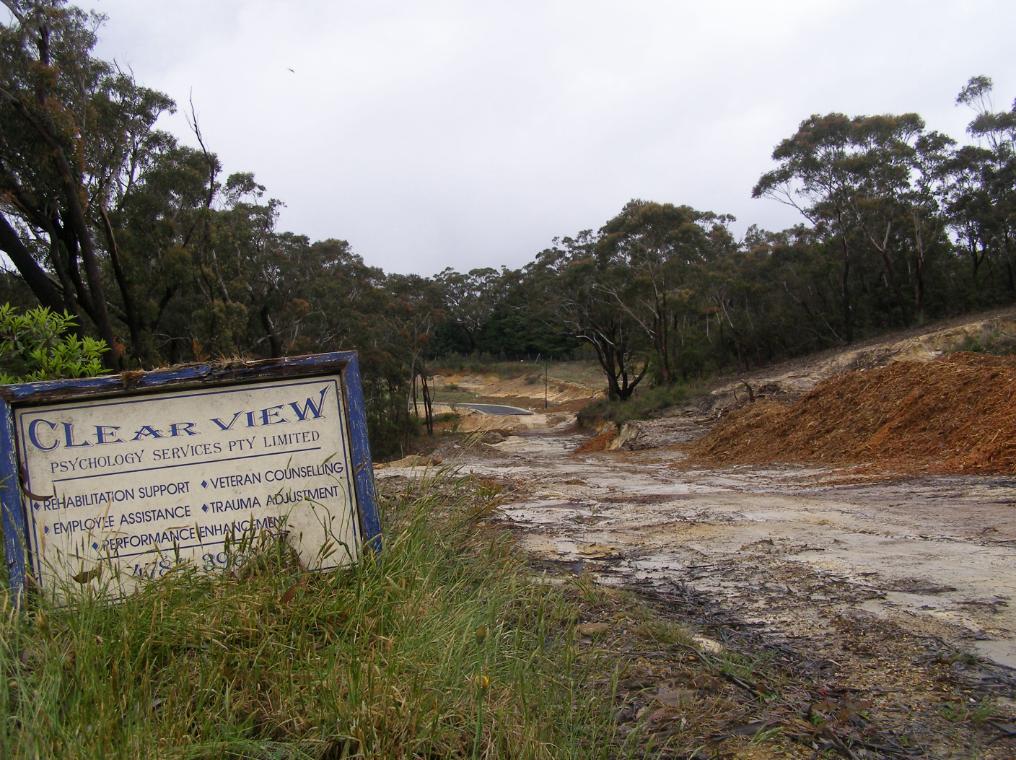
 Juxtaposition of the Katoomba Golf Club (light green coloured fairways) replacing virgin habitat across the escarpment; all so that a few retiring Baby Boomer men can selfishly play golf at the expense of Ecology.
[Source: Google Earth, 2013]
Juxtaposition of the Katoomba Golf Club (light green coloured fairways) replacing virgin habitat across the escarpment; all so that a few retiring Baby Boomer men can selfishly play golf at the expense of Ecology.
[Source: Google Earth, 2013]
.
During the construction of the additional nine holes [Editor’s Corrigendum: The construction instead related to building 13 townhouses and a resort hotel], the development proposal submitted to the local Blue Mountains Council, specified a new track would be constructed through adjacent bushland to connect two fairways. It was deceptive, because that track became a new wide fairway, complete with soil replacement, landscape contouring, grass seeding and fertilizer.
Repeated instances of sediment run-off from the construction were formally reported to the local Blue Mountains Council by concerned local residents, yet no remediation action was undertaken and no punitive fines were issued.
.
 Native bushland along the Blue Mountains escarpment slashed and woodchipped to expand the Katoomba Golf Club out to 18 holes
[Editor’s Corrigendum: The construction instead related to building 13 townhouses and a resort hotel]
[Photo by Editor, 20071110, Photo © under ^Creative Commons]
Native bushland along the Blue Mountains escarpment slashed and woodchipped to expand the Katoomba Golf Club out to 18 holes
[Editor’s Corrigendum: The construction instead related to building 13 townhouses and a resort hotel]
[Photo by Editor, 20071110, Photo © under ^Creative Commons]
.
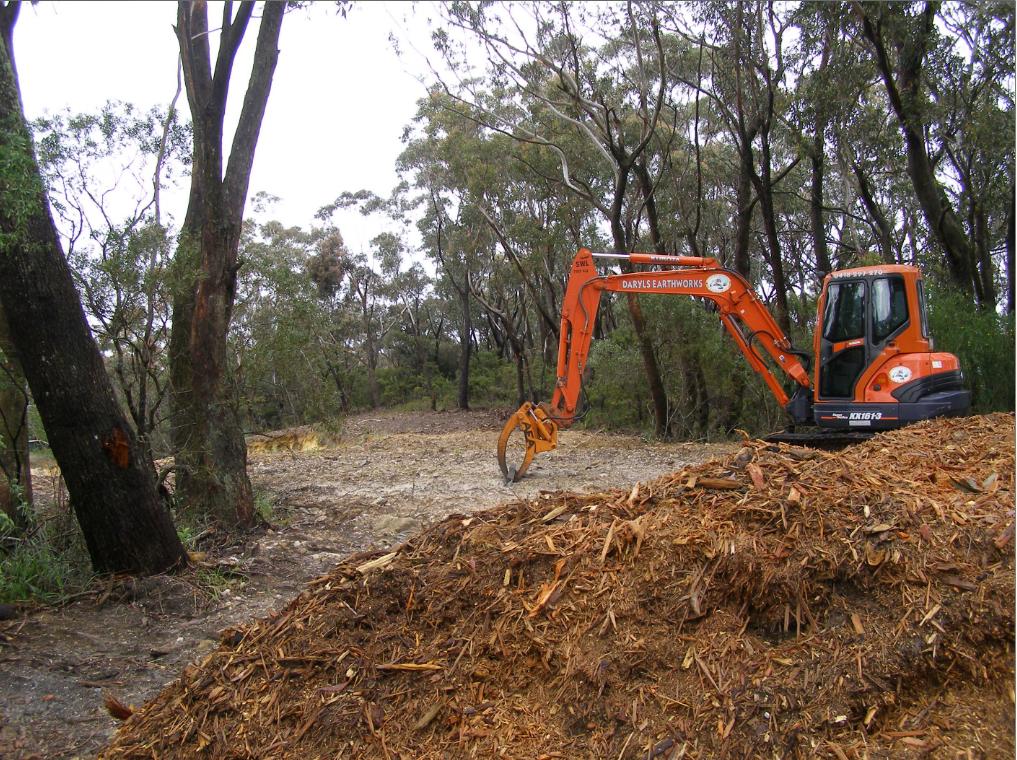
. Native bushland bulldozed to make way for golfing townhouses adjacent to the Katoomba Golf Club
Erosion and sediment run-off has been rife for years
[Photo by Editor, 20071110, Photo © under ^Creative Commons]
Native bushland bulldozed to make way for golfing townhouses adjacent to the Katoomba Golf Club
Erosion and sediment run-off has been rife for years
[Photo by Editor, 20071110, Photo © under ^Creative Commons]
.
Golf courses not only necessitate absolute ecological destruction in such places, but the ongoing maintenance of the fairways and greens demands constant fresh water irrigation. Irrigation, as with farming, risks causing saline intrusion into the groundwater.
The keeping of golfing greens green to uphold the lush traditional image, necessitates that golf courses use extensive amounts of chemical fertilizers containing elevated levels of nitrogen (as sulphate of ammonia), potash , sulphur and phosphorus, as well as the application of pesticides and herbicides. All such chemicals are toxic to Australian native vegetation and to aquatic wildlife in the downstream watercourses. Effectively they are environmental pollutants and so next to and upstream of vital World Heritage, use of such chemicals needs to be legally banned.
The local Blue Mountains Council has failed to monitor run-off from the construction activity into the surrounding natural environment. The custodian of the World Heritage Area, National Parks and Wildlife Service, simply isn’t interested.
.
. White Elephant golfing townhouses adjacent to the Katoomba Golf Club that have since stood vacant for years
White Elephant golfing townhouses adjacent to the Katoomba Golf Club that have since stood vacant for years[Photo by Editor, 20071110, Photo © under ^Creative Commons]
.
 << It’s big, blue and beautiful! Blue Mountains National Park is located just 60 kilometres west of Sydney. It is unique in it’s history, its wildlife and world famous scenery…includes the Grose Wilderness, dedicated for its wild unspoilt natural beauty. At Katoomba see the Three Sisters and Katoomba Falls… 300 kilometres of heritage walking tracks and hundreds of lookouts, most within easy reach of a string of train stations. It’s a wilderness made easy to get to! >>
<< It’s big, blue and beautiful! Blue Mountains National Park is located just 60 kilometres west of Sydney. It is unique in it’s history, its wildlife and world famous scenery…includes the Grose Wilderness, dedicated for its wild unspoilt natural beauty. At Katoomba see the Three Sisters and Katoomba Falls… 300 kilometres of heritage walking tracks and hundreds of lookouts, most within easy reach of a string of train stations. It’s a wilderness made easy to get to! >>[Source: NSW Government, ^http://www.visitnsw.com/destinations/blue-mountains/katoomba-area/blackheath/attractions/blue-mountains-national-park]
.
[Ed: No mention of golf in the tourism promotion these days]
.
Katoomba Golf Club R.I.P.
.
<<..“the locksmith has been in” and the club is no longer trading.
Unfortunately the club has temporarily closed its doors to the public. They have appointed administrators to handle the business. We are no longer employed. We, the staff thank all of you for your patronage, your friendship, your laughs and your well wishes – it has been a wonderful and memorable time for all of us. A bit of a sad day for us, so thank you. >>
[Source: ‘Katoomba Golf Club shuts its doors’, 20130703, Blue Mountains Gazette, print, p.5, ^http://www.bluemountainsgazette.com.au/story/1614280/katoomba-golf-club-shuts-its-doors/?cs=2062].
 Escarpment Karma?
Yet over 50 hectares of vital escarpment habitat has been lost
to a Baby Boomer selfish pastime.
Escarpment Karma?
Yet over 50 hectares of vital escarpment habitat has been lost
to a Baby Boomer selfish pastime..
Notice of First Meeting of Creditors of Company Under Administration
.
Company: Katoomba Golf Club Ltd
ACN: 000 952 992
Status: Administrators Appointed
Appointed: 01 July 2013
.
Meeting details:
Notice is given that a first meeting of the creditors of the Company, or a first meeting for each of the Companies, (for multiple companies), will be held:
Location: Katoomba Golf Club, Acacia Street, Katoomba New South Wales
Meeting date: 10 July 2013
Meeting time: 12:00PM
.
[Source: ASIC Insolvency Notices]..
.
‘Fore Sale – Luxury golf communities have hit a rough patch’
[Source: ‘Fore Sale – Luxury golf communities have hit a rough patch’, 20120724, by Nancy Keate, The Wall Street Journal, ^http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303703004577474563368632088.html].
 Photo Illustration: Jeff Huang
Photo Illustration: Jeff Huang
.
<< After years of aggressive golf course expansion, interest in golf declined just as the market for luxury homes plunged. Now, once-pricey real estate is available at below-par prices. Selling a lot for $1.
Debbie Bowers and her husband, tired of life in their cold Ohio town, spent eight years looking for a home near a sunny luxury golf course in a Southern state. Everything they saw was too expensive. Then this past May, they got a call: A lot was available at South Carolina’s Colleton River Plantation, one of the country’s premiere golf communities—for free.
Prices at luxury private golf communities are crashing, done in by rampant overdevelopment, the economic downturn and waning national interest in the sport. Nancy Keates has details on Lunch Break.
The seller was even willing to pay the $15,000 club initiation fee and the first year of $17,000 annual membership dues at Colleton River, which includes three celebrity-designed courses (two by Jack Nicklaus, one by Pete Dye), a Stan Smith-designed tennis center and a new 6,000-square-foot fitness center. Mrs. Bowers, 55, met her husband that day at the site and signed the papers. They’re now building a 3,000-square-foot house that should be finished by November.
The past two decades saw an unprecedented boom in the building of high-end golf courses linked to luxury real-estate communities. Betting that aging Baby Boomers would embrace golf as their pastime of choice, the National Golf Foundation set a goal of building “A Course a Day” beginning in 1988. Real-estate developers teamed up with top-name golf-course architects, building exclusive communities adjacent to courses, and requiring homeowners to pay annual club dues—sometimes even if they didn’t play. Then, in a moment of spectacularly bad timing, both the golf industry and the real-estate market took a nose-dive at once.
Now, private golf communities are dealing with the fallout. Many sellers are dropping their prices radically, in some cases even paying people to take their land. Gated communities that once traded on their exclusivity are aiming to appeal to a wider swath of buyers, building family-friendly “village centers” with ice cream shops, hiking trails and bowling alleys. A few are even “repurposing” by reducing courses to nine holes from 18 and selling off the reclaimed land.
At golf communities near Bluffton, S.C., like Belfair Plantation, Colleton River Plantation and Berkeley Hall, several lots that initially sold for at least $150,000 are now on sale for $1 apiece. Investors who bought but never built on the sites are trying to unburden themselves of the thousands of dollars—typically $12,000 to $17,000—they still have to pay in annual club dues.
At the Mizner Country Club in Delray Beach, Fla., which has an Arnold Palmer golf course, a lakefront home with five bedrooms, a pool and a spa is asking $795,000. It sold for $1.6 million in 2007. A lot in Horseshoe Bay Resort, near Austin, Texas, that sold previously for $300,000, is on sale for $39,000.
In Bend, Ore., interior designer Ronda Fitton and her husband paid $500,000 for a lot at Pronghorn, a gated community with golf courses designed by Tom Fazio and Jack Nicklaus, in 2006. A similar-size lot sold for $10,000 earlier this year. Ms. Fitton is hopeful values will go up but she says the lot is “worth nothing now. It’s a real bummer.” (Lot prices exclude membership fees.) Lots at Rams Hill in Borrego Springs, Calif. are also selling for about $10,000, compared with $100,000 at the peak.
The housing downturn is partly responsible. But the crash in value has been exacerbated by a development binge that resulted in too many courses just as the sport of golf began to fade in popularity.
From 1990 to 2003, some 3,000 new courses were built in the U.S., swelling the total number of courses nationally by 19% and costing about $20 billion, according to the National Golf Foundation.
Many of these new courses were inextricably linked to the luxury-real-estate market. About 40% of the courses built during the 1990s were tied to real-estate communities—a shift from the previous decades, when that number was closer to 18% and the vast majority of golf courses didn’t have people living on them. The golf courses were the lure to get people to buy houses: The bigger the name of the architect who designed them, the greater the prestige and the more expensive the real estate.
Soon after, however, the sport started to lose its allure. The percentage of the overall population in the U.S. that plays golf is down over the past 10 years, from 11.1% in 2000 to 9.2% in 2010, according to the National Golf Foundation.
Last year the number of rounds played in the U.S. dropped to 463 million from 518 million in 2000. The number of golfers fell to 25.7 million in 2011 from 28.8 million in 2000. A net of more than 350 golf courses have been closed since 2005. In 2011, more than 150 courses closed, outpacing the 19 courses that debuted last year.
Compounding the problem: Real-estate developers didn’t think about the viability of the golf courses themselves, says Art West, founder of Golf Course Advisors, a golf-course consulting company. Many of these courses designed by brand-name golf-course architects were championship-level, too difficult for the average player. They took a long time to play and cost millions a year to maintain, pushing up annual dues.
“It was a perfect storm,” says David Hueber, former president and CEO of the National Golf Foundation, who wrote a paper called ” ‘Code Blue’ for U.S. Golf Course Real Estate Development” stemming from research for his Ph.D. in real-estate development at Clemson University.
Across the country, about 2,000 of the 16,000 golf courses are “financially distressed,” according to the National Golf Foundation. Mr. Hueber estimates that 4,000 to 5,000 golf courses will be in financial danger if they don’t change their model.
Membership fees for many clubs have tumbled. The initiation fee at Old Palm Golf Club in Palm Beach Gardens, Fla., which was as high as $250,000 in 2007, is now down to $175,000, while the fee at Tiburon Golf Club in Naples, Fla., is now at $50,000, compared with $145,000 at its peak.
In some parts of the country, the premium that home buyers are willing to pay for a house on a golf course versus a house that isn’t on a course has dropped to about 25%, from 50% in 2007, says Doug Schwartz, who runs the sales, marketing and homebuilding operations for WCI Communities, in Bonita Springs, Fla., which currently owns four golf communities. Lisa Treu, an agent with the Treu Group in Palm Beach County, says homes on golf courses in Southeast Florida could at one time command a 25% premium over non-golf-course homes; that premium has now dropped to about 10%, she says. (Some areas are still strong, like Palm Springs, Calif., where agents say the premiums are as much as 35%).
“There are a lot of people who would like to get out of here because of the economy,” says Don Davis, who with his wife bought a house in South Carolina’s Colleton River for $970,000 in 2001. The couple, who have loved living in the community but want to move back to Atlanta to be closer to their grandchildren, say it doesn’t make financial sense to move without selling their house because they’d still have to pay the community’s annual membership dues of some $17,000. Their house, listed at $775,000, hasn’t had any offers in its six months on the market.
Real-estate agent Dick Datz of Carolina Realty Group says Belfair and Colleton River are offering agents a $5,000 bonus when they sell a $1 lot; otherwise the commission would be pennies. Rob Norton, president of the Colleton River Plantation Board, says houses in the community are selling and there’s lots of new construction. It’s mostly the people who bought the land as an investment who are having a hard time, he says.
Some developers are recasting their golf communities to appeal to a broader swath of home buyers, including more families and young people. One example: Tuscany Reserve, a 450-plus-acre private golf community in Naples, Fla., which had about $200 million invested in its infrastructure, including a golf course designed by Pete Dye and Greg Norman, before it went bankrupt. Florida developer Syd Kitson recently bought the community for $30 million and changed the name to Talis Park, which he thought sounded more youthful. Instead of building a clubhouse as planned, Mr. Kitson, will build a “village center” with a cafe, a spa and walking paths. Homes are now expected to be in the $700,000-to-$2 million range instead of up to $6 million, as originally intended.
“The model of a country club in its current form is gone forever,” says Mr. Kitson.
After seeing sharp decreases in its sale prices, Pronghorn, the gated community in Bend, Ore., opened its gates, launching a 48-suite lodge in 2010 and inviting the public to use one of its two golf courses. The Resort Group, a resort operator based in Honolulu, Hawaii, took over in February and announced it will bring in Auberge Resorts to manage the property, turning it into a five-star resort with a spa, three restaurants, two pools, tennis courts and a kids club.
The Cliffs—a group of eight residential developments spread among 20,000 acres between Greenville, S.C., and Asheville, N.C., with golf courses designed by Jack Nicklaus and Tom Fazio—filed for U.S. Bankruptcy Court protection in February, with estimated liabilities between $100 million and $500 million. A planned golf course for the Cliffs, designed by Tiger Woods, hasn’t been started. According to a 2007 news release, the Cliffs sold 40 lots in the $500,000 price range, and lots at that time couldn’t be purchased below $200,000. Earlier this year a lot sold in one high-end community for less than $10,000, according to real-estate agent Justin Winter.
Owners at the Cliffs, who tried to bail it out earlier by putting up $64 million to keep the club operating, say they are optimistic and are in the midst of a reorganization with Carlile Group, a diversified company based in Marshall, Texas. Carlile is working with two other groups.
Owners say the revamped club will have more options for membership. The initiation fee, which was $150,000, is now $50,000. “We are working diligently to find and deliver the best solution for all members and property owners at the Cliffs,” Steve Carlile of Carlile Group says in a statement.
Golf-course architect Bobby Weed of Bobby Weed Golf Design has been helping residential golf communities over the past few years “repurpose”—by compressing the properties. He is currently working on several proposals to shrink 18-hole courses to nine holes. At the Deltona Club in Deltona, Fla., he helped reduce the amount of land used by the clubhouse and the golf course to create a separate, 17-acre parcel for development.
The steep decline in prices is a boon for potential buyers, of course. “Now I’m getting worried I’m going to miss out if I don’t move quickly,” says Gordon Flach, 44, who has been looking for a golf resort home in Montana, Utah or Oregon for the past three years. Mr. Flach, who is part owner of a resort in the Bahamas, has his eye on a $425,000, 3,800-square-foot four-bedroom house in Pronghorn. A similar house was going for $1.1 million when he first started looking.
Ron Ruff, a 55-year-old semiretired anesthesiologist, got his lot at Pronghorn free about a year ago. The seller also kicked in part of the $115,000 reimbursement of his golf-club membership initiation fee he got back when he “sold” the land. Mr. Ruff says that he felt, despite the dire climate and other people thinking he was crazy, that Pronghorn has a “magical” feel and that the value would be realized again, just as he had seen happen in other areas before. His house is now complete.
John Reed, the original developer of Colleton River Plantation, Belfair Plantation and Berkeley Hall, concedes there are too many golf-course communities. “There’s a train wreck in the industry now,” he says. “We overbuilt and the market stopped.” He had Pete Dye and Tom Fazio design a golf course for his latest development, called Hampton Lakes, but decided to nix it in favor of a 165-acre freshwater fishing and boating lake.
“The best golf course we ever did is 9 feet underwater,” he jokes. >>