Blue Mountains ongoing illegal dumping
Monday, July 16th, 2012 Illegal dumping in The Gully, Katoomba, Blue Mountains
Reported to local council and promptly removed by local council.
(Photo by Editor 20060702, image free in public domain, click to enlarge)
Illegal dumping in The Gully, Katoomba, Blue Mountains
Reported to local council and promptly removed by local council.
(Photo by Editor 20060702, image free in public domain, click to enlarge)
.
Illegal dumping is not unique to the Blue Mountains, but it continues to be an ongoing problem in this populated area that is situated upstream of the internationally valued Blue Mountains World Heritage Area.
Whereas litter is generally individual items of waste products improperly disposed of in the environment, illegal dumping is generally of a larger scale and premeditated. Both are illegal.
Both are selfish, lazy and disrespectful to society and the environment. The larger problem of illegal dumping involves the deliberate or unauthorised dumping, tipping or burying of waste on land that is not licensed or fit to accept that waste. People illegally dump bags of household rubbish, electronic equipment, furniture, mattresses, industrial wastes, construction and demolition materials, garden waste, packaging, tyres, old cars and soil.
It is bad enough that an increasingly populating society that is also increasingly consuming resources is also increasingly contributing to landfill for its waste. Worse is when that waste is illegally dumped and far worse when it is dumped in places that harm native ecology.
 Lawn Clippings dumped at remote Hargreaves Lookout Road,
west of Blackheath in protected bushland, Blue Mountains, New South Wales
(Photo by Editor 20080405, image free in public domain, click to enlarge)
Lawn Clippings dumped at remote Hargreaves Lookout Road,
west of Blackheath in protected bushland, Blue Mountains, New South Wales
(Photo by Editor 20080405, image free in public domain, click to enlarge)
.
Illegal dumping is more than just unsightly waste in an inappropriate location. It not only reduces property values and costs rate payers a substantial amount of money each year to clean up. Illegal dumping is inherently unnatural which means when dumped in a natural environment, the composition of the waste will have an adverse impact upon the natural ecology – it degrades and spoils local ecology. The waste does not have to be deemed ‘hazardous’ such as toxic chemicals, paints, solvents, fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides or asbestos for instance.
Lawn clippings and woodchips will cause a moist environment for bacteria and flies to breed and after rain the nutrients will flow and contaminate surrounding soils, vegetation and watercourses. This can be lethal to vulnerable and fragile flora and fauna, especially in Australia which naturally has low nutrient soils.
Illegally dumped waste can poison the soil and kill vegetation. The introduced nutrients such as acids will prevent the vegetation from regenerating and dependent wildlife from returning. Illegal dumping leads to long-term contamination of land, waterways, natural springs and groundwater, particularly when the waste is from an industrial source or contaminated soil.
 Subsoil and rubble (left) dumped in The Gully (Katoomba), alongside the old race track
(Photo by Editor 20070310, free in public domain, click to enlarge)
Subsoil and rubble (left) dumped in The Gully (Katoomba), alongside the old race track
(Photo by Editor 20070310, free in public domain, click to enlarge)
.
Illegal dumping can be dangerous to people (broken glass, syringes, nappies and medical waste, and carcinogenic substances like asbestos) but also it can attract rodents, insects and other vermin. It can provide an ideal breeding ground for mosquitoes and maggots. It can block waterways and stormwater drains, increasing the potential for flooding and erosion, and it can be a potential fire hazard.
The most common cause of illegal dumping in the Blue Mountains is typically on the side of a road where a motorist has carted the waste by trailer.
.
Perhaps it is time to outlaw trailers and to replace them with waste collection services only provided by local council.
.
After all, if there is no means available to cart waste except by hand, the volume of illegal dumping will be reduced and the ability of illegal dumping to be away from residential areas and in natural areas will also be reduced.
Of course trucks can cart larger quantities of waste, but fewer people have access to trucks. This does not mean that greater regulation cannot be imposed on truck drivers. Perhaps every truck load needs to be registered and inspected by local council authorities, or an effective penalty imposed – say $5000 or a custodial sentence.
.
Whatever an effective mix of solutions, unless governments are serious about addressing the problem, illegal dumping shall continue unabated.
.
Lenient law enforcement or the absence thereof, contribute to illegal dumping behaviour – and be clear, we are dealing with a human behavioural issue here.
 In 2001, hundreds of tonnes of sand and rubble from the Soldiers Pinch upgrade to the Great Western Highway (Mount Victoria) was dumped by the RTA in The Gully over the top of an Upland Swamp. Permission was given by the Blue Mountains City Council, but without any community consultation.
Subsequent actions by the Council involved planting on top of the compressed rubble, instead of properly removing it.
(Photo by Editor 20060702, 5 years on from the 2001 dumping little had grown.
Image free in public domain, click image to enlarge)
In 2001, hundreds of tonnes of sand and rubble from the Soldiers Pinch upgrade to the Great Western Highway (Mount Victoria) was dumped by the RTA in The Gully over the top of an Upland Swamp. Permission was given by the Blue Mountains City Council, but without any community consultation.
Subsequent actions by the Council involved planting on top of the compressed rubble, instead of properly removing it.
(Photo by Editor 20060702, 5 years on from the 2001 dumping little had grown.
Image free in public domain, click image to enlarge)
.
Shaping correct responsible behaviour requires a combination of a ‘carrot’ incentive and ‘stick’ deterrent approach. If waste is collected from households like weekly garbage, then the incentive for illegal dumping is reduced. Why go to the trouble of driving somewhere to dump when it can be collected from your residence? Similarly, if the cost of collection is low, the incentive to utilise the collection service is stronger.
As the cost of landfill fees is rising due to reducing number of suitable tip sites, some people in order to avoid disposal fees at landfills will choose to illegally dump to save money. the risk of getting caught is low and this is the core problem in trying to change this bad behaviour.
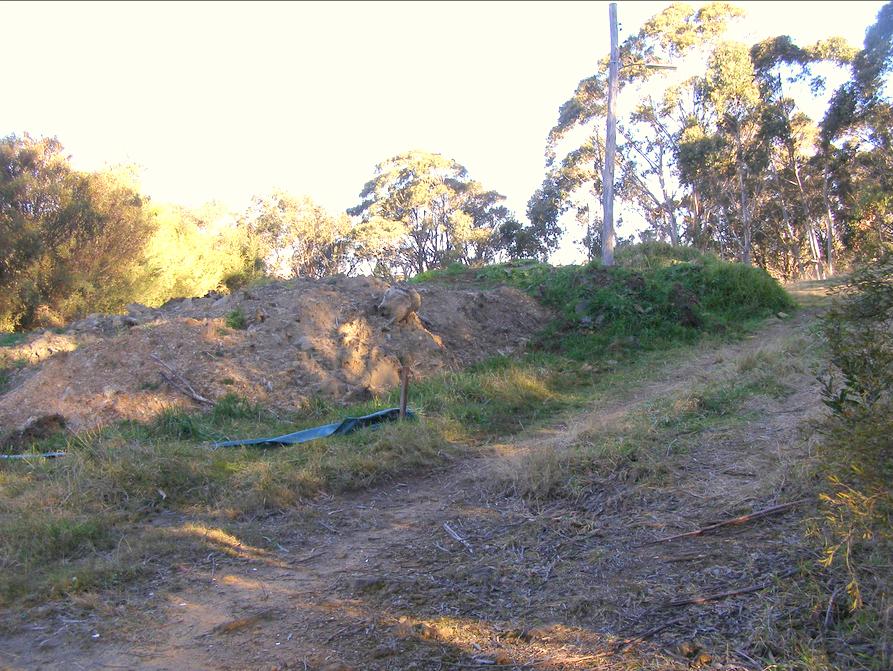 Over 20 tonnes of rubble dumped in The Gully by Sydney Water as part of its Sewerage Amplification Project in 2005
(Photo by Editor 20120624, free in public domain, click image to enlarge)
Over 20 tonnes of rubble dumped in The Gully by Sydney Water as part of its Sewerage Amplification Project in 2005
(Photo by Editor 20120624, free in public domain, click image to enlarge)
.
Penalties for illegal dumping vary around the country. For instance, in Queensland under its Waste Reduction and Recycling Act 2011, there are a range of offences for litter and illegal dumping from $200 on the spot fine for littering through to $16,500 for illegal dumping of large domestic items such as fridges, garden refuse and construction material.
[Source: Townsville City Council, ^http://www.townsville.qld.gov.au/resident/environment/Pages/litter.aspx].
But most offenders do not get caught because the scale of monitoring is unwieldy and practically ubiquitous.
In Victoria , a landfill levy on all households has helped to fund a dedicated Illegal Dumping Strike Force team as part of the Environment Protection Authority in that State. It’s tasks are to support businesses to understand their legal requirements for managing waste and recyclable material, work with its council partners and other government agencies to share intelligence about dumping offences and hotspots, and to investigate and enforce against incidents of large-scale industrial waste dumping.
[Source: Victorian Government’s Environmental Protection Authority, ^http://www.epa.vic.gov.au/waste/prevent-illegal-dumping/default.asp].
 Household garbage illegally dumped in The Gully near the South Katoomba Rural Fire Brigade, July 2012
(Photo by Editor, 20120703, free in public domain, click image to enlarge)
Household garbage illegally dumped in The Gully near the South Katoomba Rural Fire Brigade, July 2012
(Photo by Editor, 20120703, free in public domain, click image to enlarge)
.
In the Hunter Valley of New South Wales, the Hunter and Central Coast Regional Environmental Management Strategy (HCCREMS) in its Illegal Dumping project is seeking to address illegal dumping in the region through a range of new initiatives.
- Designing and trialing a number of enforcement campaigns to gain further data on illegal dumping ‘hot spots’ and determine effective campaign styles
- Trialing different illegal dumping deterrence methods (barriers, cameras, gates, etc) to determine their effectiveness at stopping illegal dumping
- Collating illegal dumping data, take photographs and coordinate media and community awareness activities.
- Establishing an Illegal Dumping Regional Database using Microsoft Access database software to collate and analyse data collected by councils, from dumping sites. All incidents are entered into the database, which is linked to GIS and is able to produce maps of the locations in each council area.
- Allowing Councils to use the intelligence generated from the database to determine appropriate and effective inspection patrol regimes and where access control measures can be installed.
- Encouraging all councils to record incidents of illegal dumping on the incident forms developed by the Hunter Regional Illegal Dumping Group and forward these into HCCREMS for entry into the database.
- Illegal Dumping Deterrence Project – trialling deterrence measures including: motion-sensitive cameras, revegetation, fencing, signage and earth mounds.
- Illegal Dumping Education and Awareness campaign including facilitating media involvement
.
Sample Record of Illegal Dumping reported to Blue Mountains Council by residents
.
Jan 2008: Dumped Garden Refuse opposite 16 Garden St, Katoomba
 To The General Manager, BMCC
Emailed to council@bmcc.nsw.gov.au
To The General Manager, BMCC
Emailed to council@bmcc.nsw.gov.au
.
‘Sir,
I request for the removal of dumped garden refuse within a bushland adjacent Carlton Street, Katoomba, opposite 16 Garden Street (located at the corner of Garden St and Carlton St). The garden refuse contains weeds and is near a large rock.
Dumped building waste (opposite a recently built house at 20 Carlton St) and cut down trees are also present within the bushland.
Please see attached photographs.
Also, I recommend that Council arrange for its ranger to inform nearby local residents that it is illegal to dump garden refuse and building waste under the Protection of the Environment Operations Act and cut down trees under the Tree Preservation Order. Garden refuse smothers native vegetation, spreads weeds and increases bush fire danger.
As you will be aware, the cutting down of native trees for firewood reduces habitat and creates wood smoke pollution.’
.
Apr 2007: Opposite Megalong Lodge, 40 Acacia Street Katoomba
 .
.
To The General Manager, BMCC
Emailed to council@bmcc.nsw.gov.au
.
‘Sir,
I request Council removes a very large amount of dumped garden refuse within escarpment bushland, located adjacent Cliff Drive and across the road from Megalong Lodge, 40 Acacia St, Katoomba.
The dumped refuse is believed to have come from Megalong Lodge, as it is made up of white driveway pebbles, pine needles, Agapanthus and Rhododendron cuttings found on this property. A bush trail in direct line to the property also contains the cuttings. Grass clippings have also been dumped.
Urgent removal of the garden refuse is recommended, since exotic grass is beginning to grow within the escarpment bushland. The dumping was discovered in April 2007. Please see attached photographs.
Also request the ranger to inform nearby local residents that it is illegal to dump garden refuse under the Protection of the Environment Operations Act. Garden refuse is pollution and smothers native vegetation, spreads weeds and increases bush fire danger.‘
.
Dec 2007: Outside Katoomba Golf Club
 To The General Manager, BMCC
Emailed to council@bmcc.nsw.gov.au
To The General Manager, BMCC
Emailed to council@bmcc.nsw.gov.au
.
‘Sir,
I request for the removal of dumped grass clippings within bushland at Katoomba Golf Course, opposite 165 Narrow Neck Road, Katoomba. Dumped clippings are located next to the golf course entrance turnstile. The front lawn of 161 Narrow Neck Road had just been mown at the time of discovery of the still green clippings. Please see the attached photograph.
Also, I request a Council ranger to inform nearby local residents that it is illegal to dump grass cuttings under the Protection of the Environment Operations Act. Grass cuttings smother native vegetation, spread weeds and increase bush fire danger.’