Wildlife Photography from a respectful distance
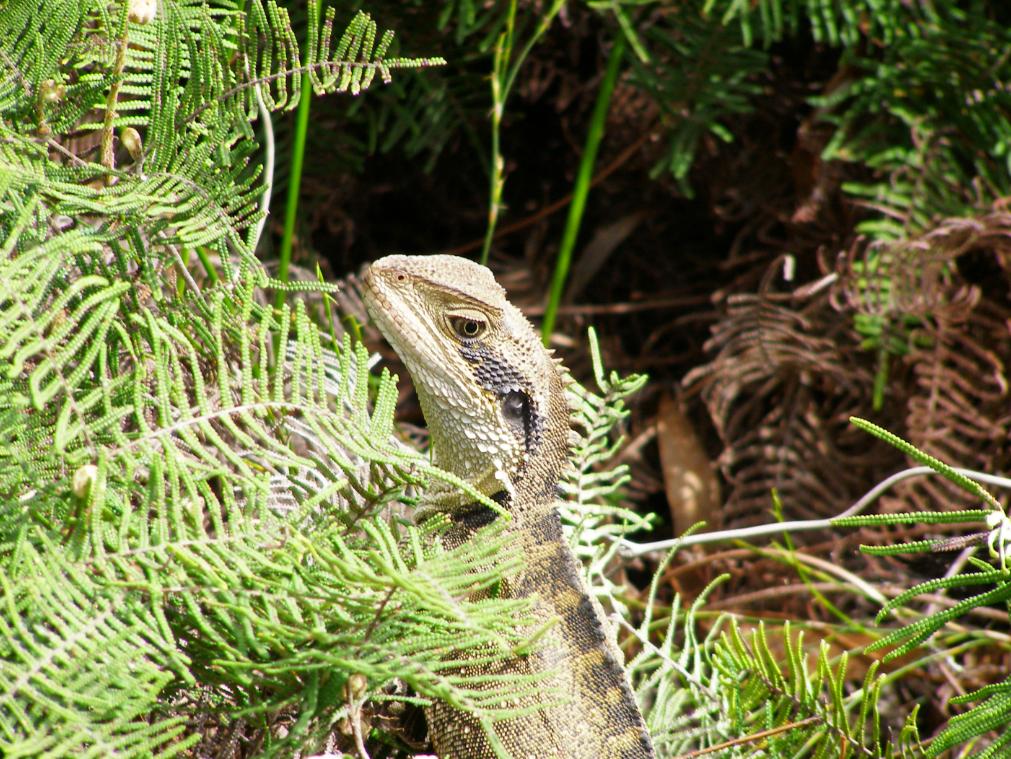 Eastern Water Dragon
(Physignathus lesueurii)
Taken for the benefit of the photograph, not the dragon
Photo by Editor in Blue Mountains, Australia, 20061112, photo © under ^Creative Commons]
Click image to enlarge
Eastern Water Dragon
(Physignathus lesueurii)
Taken for the benefit of the photograph, not the dragon
Photo by Editor in Blue Mountains, Australia, 20061112, photo © under ^Creative Commons]
Click image to enlarge
.
Wildlife photography is not about humanising wildlife for entertainment. It ought to be about awareness, wonder and respect for wildlife and their habitat.
Zoology may be about technical understanding of the structure and classification of the animal kingdom, but since Darwin we have realised that animals are so much more complex creatures of behaviour and integral to ecology than just being taxidermied museum specimens for public display.
Zoos are just an extension of museums for the benefit of public entertainment. But they do not respect wildlife in their habitat.
 [Source: ^http://katialglobal2viceduau.global2.vic.edu.au/personal-learning/]
[Source: ^http://katialglobal2viceduau.global2.vic.edu.au/personal-learning/]
.
In their habitat and ecological context, photographed wildlife may be better appreciated and valued for their integral role in Nature. But at a respectful distance.
.
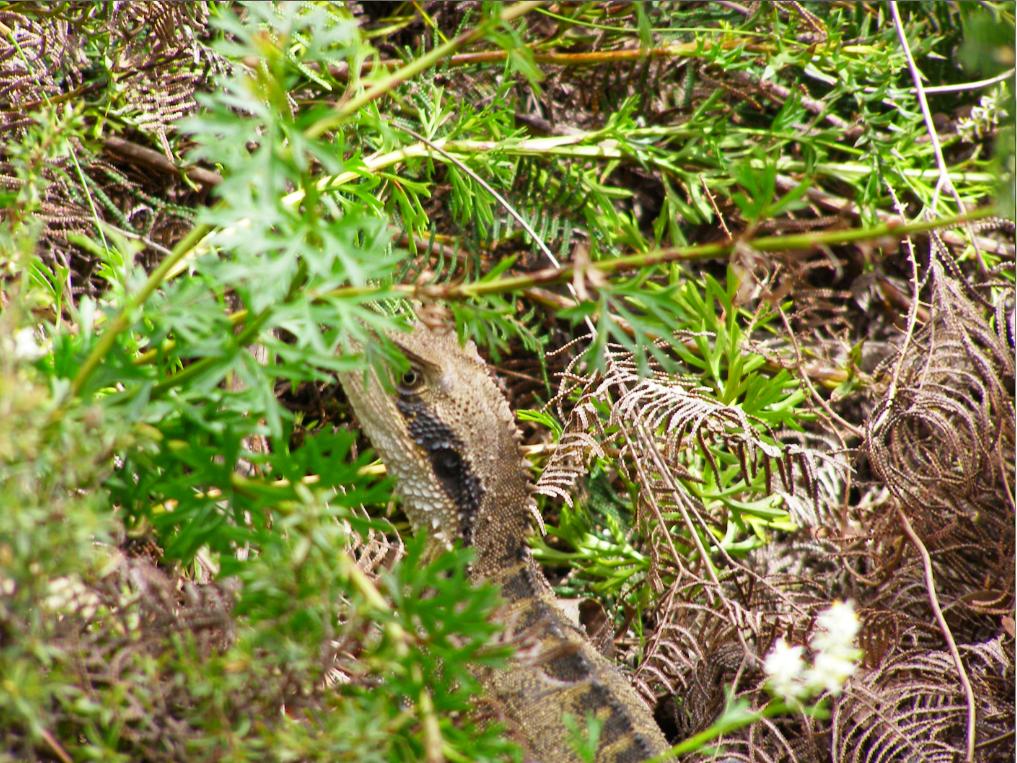 Not for the camera, but naturally obscured in its habitat
A more interpretative photo, but still too close.
Photo by Editor 20061112, photo © under ^Creative Commons]
Not for the camera, but naturally obscured in its habitat
A more interpretative photo, but still too close.
Photo by Editor 20061112, photo © under ^Creative Commons]
.
“The two basic processes of education are knowing and valuing”
~ Robert J. Havighurst (1900-1991).
.
.
.
Empathy for Other Species is the Key to Ethical Wildlife Photography
.
[Source: “Empathy for Other Species is the Key to Ethical Wildlife Photography”, by Jim Robertson, ^http://www.wildwatch.org/Binocular/bino01/empathy.html].
<< A deep admiration for Nature has led many to another level of appreciation–the craft of wildlife photography.
Unfortunately, not all who photograph wildlife do so out of caring and with respect for our fellow beings. In fact, the behavior of many photographers, both amateur and professional, can only be described as disrespectful, disruptive and sometimes dangerous to the animals they are photographing.
For example, every spring in Yellowstone you are sure to see a large group of photographers standing around–or even sitting on lawn chairs–talking loudly right outside some poor badger’s birthing den, waiting for the family to emerge. Though these folks may think nothing of the clamor of a rowdy bar or ball game, how would they like to live next door to that bar or ball field, or wake up to the racket of an expectant crowd of photojournalists right outside their bedroom window?
In response to this kind of ill-behavior, which invariably results in the harassment or endangerment of wildlife, informal guidelines have been established to spell out just how close, in yards or feet, one should get to an individual animal, depending on that species’ tolerance zone.
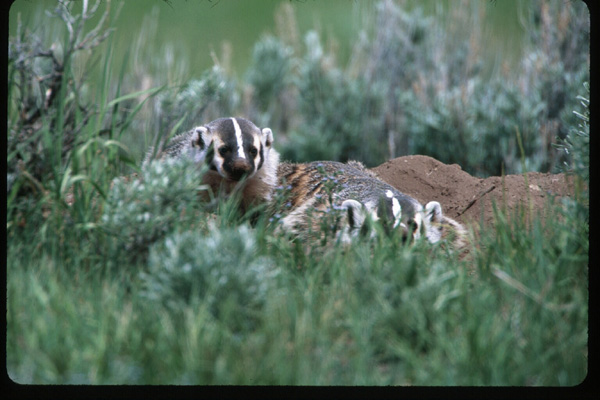 Badger Den
This mother and young badger were photographed across the road from their den using a 600mm telephoto lens and a 2X multiplier
Photo © Jim Robertson
^http://www.wildwatch.org/Binocular/bino01/empathy.html]
Badger Den
This mother and young badger were photographed across the road from their den using a 600mm telephoto lens and a 2X multiplier
Photo © Jim Robertson
^http://www.wildwatch.org/Binocular/bino01/empathy.html]
.
But rather than memorizing numbers and gauging distances, perhaps it would be easier for photographers and wildlife observers to apply The Golden Rule in each and every situation.
However, instead of the old, oversimplified rule, “Do unto others as you would have them do unto you,” why not adopt a revised golden rule that takes into account the differences between ourselves and other species? Maybe something like, “Do unto others as you think they would have you do unto them.” In other words, try to envision what the animals’ needs and self interests are and take into consideration how their lives in the wild are different from our own.
Empathy, the intellectual or emotional identification with another — or the ability to relate to others — is essential for maintaining ethical standards when photographing wildlife.
Last spring I watched from a distance as the annual gathering of noisy photographers was posted outside the entrance of a badger den. They were so deep in conversation and oblivious to their surroundings that none of them noticed as the mother badger finally made a break for it in hopes of procuring food for her young.
The day before, I had photographed the same badger den from across a road with a 600mm telephoto lens fitted with a 2X extender to bring the subject in closer without actually getting close. Because I remained on the opposite side of the road and well away from the den, quietly giving them the space they needed to engage in their activities and enjoy the sunny day, the badger and her young came and went freely, without paying me any notice.
.
The Poor Man’s Super-Telephoto Lens:
.
<< The lens of choice among the serious pro wildlife photographers I know seems to be the 600mm ƒ/4 super-telephoto. It’s great for subjects that won’t let you get close, is incredibly sharp, and autofocuses quickly and accurately. However, it costs over $7,000.
That being just a bit beyond my budget, when I really need “reach,” I turn my $1,200 300mm ƒ/4 lens into a 600mm ƒ/8 by attaching a $300 2x teleconverter between the lens and camera body.Also known as tele-extenders, teleconverters are available from the major lens manufacturers for their long lenses, and offer three major benefits.
First, as just cited, they’re an economical way to get superlong focal lengths. And they’re not just for the budget-challenged. Pros use them, too—a 1.4x converter turns that monster 600mm into an 840mm; a 2x converter, into a 1200mm.
The second benefit of the teleconverter is that it doesn’t change the lens’ minimum focusing distance. Add a 2x converter to a 300mm lens that focuses down to five feet, and you have a 600mm lens that focuses down to five feet. (For comparison, my camera manufacturer’s 600mm super-telephoto won’t focus closer than 18 feet unless you attach it to an extension tube; but then it won’t focus out to infinity.)
The third teleconverter benefit is lack of bulk. A 300mm lens with a 2x teleconverter is much more compact than a 600mm ƒ/4 super-telephoto lens. (A 600mm ƒ/8 prime lens also would be smaller than the 600mm ƒ/4, but currently no one makes a 600mm ƒ/8. >>
[Source: ‘The Poor Man’s Super-Telephoto’, 20090421, by Mike Stensvold, ^http://www.outdoorphotographer.com/gear/lenses/the-poor-mans-super-telephoto.html].
A national Park like Yellowstone can be the perfect place for photographing animals without causing them undue stress. Since they know they are safe from hunting within park boundaries, “game species” are not so distrustful of human presence.
Although many species are easily viewable from park roadways, they are much less concerned about vehicles than people approaching on foot. Staying in your car makes wildlife feel more comfortable, and your vehicle makes a great blind for photographing animals calmly going about their business. Some of my best photos have been taken out of the window of my rig.
Other examples of photographer misconduct include trimming away vegetation–that may conceal a nest or den from people and predators–to get a clearer photo, throwing food to attract animals, and the all-too-common habit of yelling or honking at an elk, a bison or a family of bears so they will look toward the camera.
By using empathy we can begin to recognize changes in behavior and respect the signals animals use to convey to us that we are irritating them or getting too close for their comfort.
Every year irresponsible photographers are gored by bison, trampled by moose, or charged by bears. When these animals are annoyed to the point that they feel the need to defend themselves, chances are they will suffer or die for it in the end. Thoughtless conduct can also force animals to leave their familiar surroundings, interrupt natural activities necessary for survival, or even separate mothers from their young.
.
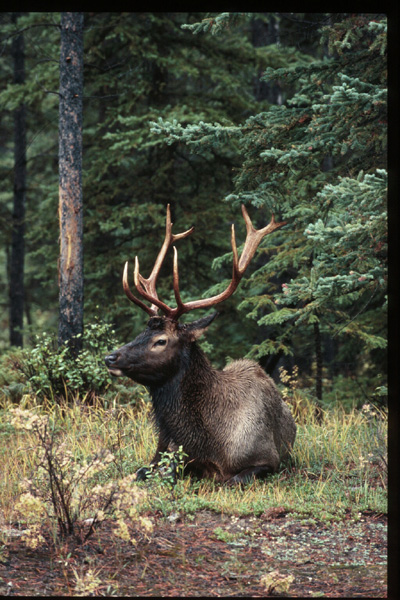 Bull Elk
This bull elk was photographed from my vehicle in Jasper National Park, Alberta, using a telephoto lens
Photo © Jim Robertson, ^http://www.wildwatch.org/Binocular/bino01/empathy.html]
Bull Elk
This bull elk was photographed from my vehicle in Jasper National Park, Alberta, using a telephoto lens
Photo © Jim Robertson, ^http://www.wildwatch.org/Binocular/bino01/empathy.html]
.
Outdoor Photographer magazine ran an article in January/February 2000 on “Tips for Photographing Eagles” with the sub-heading “A long lens, the right location and a sensitive approach can get you excellent images of these majestic birds”.
The author of the article, Bill Silliker, Jr. wrote, “If you don’t have a long lens, don’t push it. Ethical wildlife photography requires that we forego attempts to photograph wildlife when we’re not equipped for it or if the attempt might harass or somehow place the subject in jeopardy. Be satisfied with images that show an eagle in its habitat. Editors use those too.”
The other day a neighbour stopped by and, upon seeing the small herd of black-tailed deer who found refuge on my land, asked if I was a hunter. When I said, “No, I’m a wildlife photographer,” he shrugged and replied, “It’s all shooting.”
Well, yes and no.
The obvious, major difference is that the animals “shot” with a camera do not end up dead. But because there are similarities to hunting, many people approach wildlife photography with a similar mind-set. It’s laughable to see photographers in a national park camouflaged from head-to-toe, sometimes including face paint, photographing a bull elk as he calmly grazes alongside the road–fully aware of their presence. And I couldn’t count how many times I’ve seen tourists run right up to a bear, elk, bison, or moose with a tiny disposable camera to get their close-up “trophy” photo.
They seem to think it’s only fair–that they are entitled to get closer–since they don’t have a large telephoto for their camera. But if they were to examine their motives they would realize that their behaviour is not fair to the animal. Is their trophy more important than the well-being of the subject of their photo?
At the height of disregard, some photographers will use hounds fitted with radio collars to pursue and corner bears, bobcats, or cougars for close-up photos of these more elusive species. If they are “lucky”, they might even catch the animal snarling in response–just the way any number of hunting magazines like to portray them on their covers or in juicy, two-page fold-outs. But how would they feel if they had to flee for their lives, chased down by a pack of dogs until they were exhausted or treed, just so someone could get a picture of them?
Wildlife photography should not be thought of as a sport or challenge against nature, or against the animals who did not volunteer for the game. Would it be considered ethical to make sport of photographing unwilling human subjects?
Unethical practices of those who photograph wildlife for self-serving purposes have given the whole field a bad name. Bill McKibben, author of “The End of Nature” has proposed a moratorium on new wildlife photos, to prevent further aggravation of endangered animals. He argues there are plenty of photos already out there for use in prints and publications. As more incidents of unethical behaviour by photographers occur, the privilege of photographing wild animals will become more and more restricted.
Still, no amount of harassment or disruption of wildlife in any way justifies the increasingly popular use of game farms by so-called wildlife photographers.
Too often, the “wild” animal seen in a publication or promotional is actually a captive animal sentenced to life on a game farm. Game farms use high fences, costing upwards of $8,000.00 per mile, to keep their preferred, sometimes exotic species in. These fences also effectively keep the native migratory wildlife out, thereby taking up valuable habitat.
While many game farms profit directly from the hunting of animals in their enclosures, others appear relatively innocuous, charging only for public viewing and private photographic sessions with “wildlife models,” including crowd-pleasing kittens, cubs, or fawns bred specifically for that purpose. But as these animals get older and less photogenic, they are auctioned off as “surplus” to the highest bidders–a common practice of zoos as well. It is likely the same animals that appeared as cute babies on calendars, greeting cards, or other publications will end up a few years later at another game farm that does profit from the canned hunting of them.
.
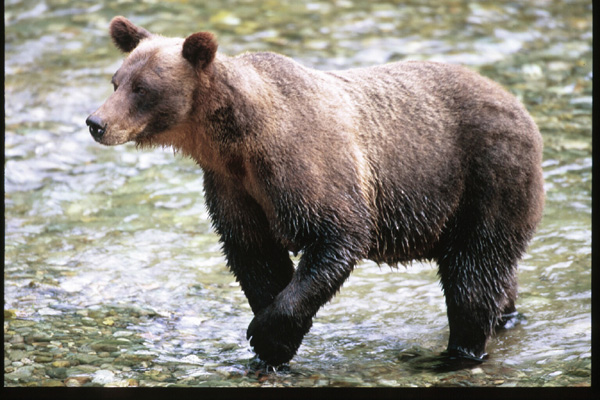 Grizzly Bear
Grizzly BearThis sow grizzly bear was photographed with a 600mm telephoto from a supervised Forest Service observation platform along Fish Creek, in Southeast Alaska. Photo © Jim Robertson ^http://www.wildwatch.org/Binocular/bino01/empathy.html]
.
Most photographers and photo editors do not differentiate between wild or captive animals when selling and publishing images. Using photos shot at game farms supports those who profit from exploiting animals by keeping them captive to serve as models for photographers, entertainment for tourists, or targets for trophy hunters. At the same time, these photos set a new, unnatural standard for closeness and intimacy with animals that the public expects to see in every future image.
And while on the subject of ethics, how ethical is it to top off a day of photographing waterfowl or ungulates with a dinner of poultry or red meat?
.
Don’t all living beings deserve our compassion and respect?
.
I had long heard that animals feel less threatened by someone who does not eat meat, but I wondered how long a human could survive without consuming the flesh of others. After six years as a vegan, I can attest to the fact that wild animals are not as fearful of me now, and that saying “no” to animal protein is healthier and easier than I ever would have imagined. >>
.
Tags: ethical wildlife photography, species tolerance zone, wildlife photography