Blue Gum Forest still not valued by RFS
Tuesday, December 20th, 2011 The Blue Gum Forest’s fire-scarred trees of December 2006
some of which have graced the Grose Valley in the Blue Mountains for hundreds of years.
Photo: Nick Moir (Source: Sydney Morning Herald, 20111211, Front Page)
The Blue Gum Forest’s fire-scarred trees of December 2006
some of which have graced the Grose Valley in the Blue Mountains for hundreds of years.
Photo: Nick Moir (Source: Sydney Morning Herald, 20111211, Front Page)
.
The following articles are drawn from those by Gregg Borschmann, the first of which hit the front page of the Sydney Morning Herald on Monday 11th December 2006, following the massive bushfire conflagration that coalesced in the Grose Valley on 23rd November 2006.
From the community’s perspective, no noticeable lessons have been since learned by the Rural Fire Service (RFS) responsible. The prevailing bushfire management culture is that unless private property is directly, bushland is not valued and so not defended from bushfire. Indeed the approach is to let a bushfire burn as a defacto hazard reduction, so long as it doesn’t threaten human life or property. The RFS does not consider bushland an asset worth protecting from bushfire no matter what its conservation value, so with such a mindset such an ecological tragedy could well happen again.
.
‘The ghosts of an enchanted forest demand answers’
.
[Source: ^http://www.smh.com.au/news/national/the-ghosts-of-an-enchanted-forest-demand-answers/2006/12/10/1165685553891.html].
‘More than seventy years ago this forest inspired the birth of the modern Australian conservation movement. Today Blue Gum Forest stands forlorn in a bed of ash. But was it unnecessarily sacrificed because of aggressive control burning by firefighters focused on protecting people and property? That is the tough question being asked by scientists, fire experts and heritage managers as a result of the blaze in the Grose Valley of the upper Blue Mountains last month.
As the fate of the forest hangs in the balance, the State Government is facing demands for an independent review of the blaze amid claims it was made worse by control burning and inappropriate resources.
This comes against a backdrop of renewed warnings that Australia may be on the brink of a wave of species loss caused by climate change and more frequent and hotter fires. There are also claims that alternative “ecological” approaches to remote-area firefighting are underfunded and not taken seriously.
In an investigation of the Blue Mountains fires the Herald has spoken to experienced fire managers, fire experts and six senior sources in four agencies and uncovered numerous concerns and complaints.
- It was claimed that critical opportunities were lost in the first days to contain or extinguish the two original, separate fires.
- Evidence emerged that escaped backburns and spot fires meant the fires linked up and were made more dangerous to property and heritage assets – including the Blue Gum Forest. One manager said the townships of Hazelbrook, Woodford and Linden were a “bee’s dick” away from being burnt. Another described it as “our scariest moment”. Recognising the risk of the backburn strategy, one fire officer – before the lighting of a large backburn along the Bells Line of Road – publicly described that operation as “a big call”. It later escaped twice, advancing the fire down the Grose Valley.
- Concerns were voiced about the role of the NSW Rural Fire Service Commissioner, Phil Koperberg.
- Members of the upper Blue Mountains Rural Fire Service brigades were unhappy about the backburning strategy.
- There were doubts about the mix and sustainability of resources – several senior managers felt there were “too many trucks” and not enough skilled remote-area firefighters.
- Scientists, heritage managers and the public were angry that the region’s national and international heritage values were being compromised or ignored.
- There was anecdotal evidence that rare and even common species were being affected by the increased frequency and intensity of fires in the region.
- Annoyance was voiced over the environmental damage for hastily, poorly constructed fire trails and containment lines, and there were concerns about the bill for reconstruction of infrastructure, including walking tracks.
The fire manager and ecologist Nic Gellie, who was the fire management officer in the Blue Mountains for the NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service during the 1980s and ’90s, says the two original fires could have been put out with more rapid direct attack.
“Instead, backburning linked up the two fires and hugely enlarged the fire area … what we saw would be more accurately described as headfire burning, creating hot new fire fronts. While it protected the town of Blackheath, the plateau tops burnt intensely – and that created new problems both for management of the fire and the protection of biodiversity.
“When extreme fire weather, hot days and high winds arrived as predicted, the expanded fire zone was still not fully contained – and that was the cause of most of the high drama and danger that followed.”
In that dramatic week, Mr Gellie confronted Mr Koperberg with his concerns that the commissioner was interfering with the management of the fire by pushing hard for large backburns along the northern side of towns in the Blue Mountains from Mount Victoria to Faulconbridge, along what is known in firefighting circles as the “black line”.
The Herald has since confirmed from numerous senior sources that “overt and covert pressure” from head office was applied to the local incident management team responsible for fighting the fire.
There were also tensions relating to Mr Koperberg’s enthusiasm for continuation of the backburning strategy along the black line – even when milder weather, lower fuel levels and close-in containment were holding the fire.
Several sources say the most frightening threat to life and property came as the fire leapt onto the Lawson Ridge on “blow-up Wednesday” (November 22) – and that those spot fires almost certainly came from the collapse of the convection column associated with the intensification of the fire by the extensive backburns.
The Herald has also confirmed that
- The original fire lit by a lightning strike near Burra Korain Head inside the national park on Monday, November 13, could not be found on the first day. The following day, a remote area fire team had partly contained the fire – but was removed to fight the second fire. The original fire was left to burn unattended for the next couple of days;
- An escaped backburn was responsible for the most direct threat to houses during the two-week emergency, at Connaught Road in Blackheath. However, at a public meeting in Blackheath on Saturday night, the Rural Fire Service assistant commissioner Shane Fitzsimmons played down residents’ concerns about their lucky escape. “I don’t want to know about it. It’s incidental in the scheme of things.”
 Blackheath escarpment broadscale backburn – “incidental in the scheme of things“?
(Photo by Editor 20061209, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge)
Blackheath escarpment broadscale backburn – “incidental in the scheme of things“?
(Photo by Editor 20061209, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge)
.
Mr Koperberg, who is retiring to stand as a Labor candidate in next year’s state elections, rejected the criticisms of how the fire was fought.
He told the Herald: “The whole of the Grose Valley would have been burnt if we had not intervened in the way we did and property would have been threatened or lost. We are looking at a successful rather than an unsuccessful outcome.
“It’s controversial, but this is world’s best backburning practice – often it’s the only tool available to save some of the country.”
The commissioner rejected any criticism that he had exerted too much influence. “As commissioner, the buck stops with me. I don’t influence outcomes unless there is a strategy that is so ill-considered that I have to intervene.”
Mr Koperberg said it was “indisputable and irrefutable” that the Blue Mountains fire – similar to fires burning now in Victoria – was “unlike any that has been seen since European settlement”, because drought and the weather produced erratic and unpredictable fire behaviour.
.
 Phil Koperberg
NSW Rural Fire Service Commissioner at the time of the Grose Fire
Phil Koperberg
NSW Rural Fire Service Commissioner at the time of the Grose Fire
.
The district manager of the Blue Mountains for the Rural Fire Service, Superintendent Mal Cronstedt, was the incident controller for the fire.
Asked if he would do anything differently, Mr Cronstedt answered: “Probably.” But other strategies might have also had unknown or unpredictable consequences, he said.
Jack Tolhurst, the deputy fire control officer (operations) for the Blue Mountains, said: “I am adamant that this fire was managed very well. We didn’t lose any lives or property and only half the Grose Valley was burnt.”
Mr Tolhurst, who has 50 years’ experience in the Blue Mountains, said: “This fire is the most contrary fire we have ever dealt with up here.”
John Merson, the executive director of the Blue Mountains World Heritage Institute, said fire management was being complicated by conditions possibly associated with climate change.
“With increased fire frequency and intensity, we are looking at a fundamental change in Australian ecosystems,” he said. “We will lose species. But we don’t know what will prosper and what will replace those disappearing species. It’s not a happy state. It’s a very tough call for firefighters trying to do what they think is the right thing when the game is no longer the same.
“What we are seeing is a reflex response that may no longer be appropriate and doesn’t take account of all the values we are trying to protect.”
 Grose Valley incinerated 23rd November 2006
(Photo by Editor 20061209, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge)
Grose Valley incinerated 23rd November 2006
(Photo by Editor 20061209, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge)
..
‘The burning question’
.
[Source: ^http://www.smh.com.au/news/national/the-burning-question/2006/12/10/1165685553945.html].
‘A bushfire scars a precious forest – and sparks debate on how we fight fire in the era of climate change.
.
“Snow and sleet are falling on two bushfires burning in the Blue Mountains west of Sydney.” ~ ABC Radio, November 15 (2006).
The news report was almost flippant, something that could happen only in Dorothea Mackellar’s land of drought and flooding rains. Later that evening, two weeks from summer, Sydney had its coldest night in more than a century.
Over the past month – as an early summer collided with a late winter and a decade-long drought – NSW and Victoria have battled more than 100 bushfires. But of them all, last month’s Blue Mountains blaze reveals tensions and systemic problems that point to a looming crisis as bushfire fighters struggle to protect people, property, biodiversity and heritage values in a world beset by climate change.
The tensions have always been there – different cultures, different ways of imagining and managing the landscape. Perhaps they are illustrated by a joke told by two Rural Fire Service crew in the Blue Mountains. “How does the RFS put out a fire in your kitchen? By backburning your sitting room and library.” The joke barely disguises the clash between the imperative of saving lives and homes, and the desire to look after the land, and the biodiversity that underpins our social and economic lives.
For fire managers, whose first priority will always be saving people and property, the equation has become even more tortured with a series of class actions over fires in NSW and the ACT. As one observer put it: “These guys are in a position where they’re not going to take any chances. No one will ever sue over environmental damage.”
For bushfire management the debate tentatively started a couple of decades ago. The challenge was to do what poets, writers and painters have long grappled with – coming to terms with a country whose distinctiveness and recent evolutionary history have been forged in fire. Drought and climate change now promise to catapult that debate to centre stage.
It is perhaps no accident that such a defining fire has occurred in one of the great amphitheatres of the Australian story, the Grose Valley in the upper Blue Mountains. Charles Darwin passed by on horseback in 1836, and described the valley as “stupendous … magnificent”.
The Grose has long been a microcosm of how Australians see their country. In 1859 some of the first photos in Australia were taken in the valley. Proposals for rail lines and dams were forgotten or shelved. The first great forest conservation battle was fought and won there in 1931-32.
But now the valley is under threat from an old friend and foe – fire.
Ian Brown has worked on dozens of fires in the Blue Mountains. He is a former operations manager for the National Parks and Wildlife Service.
“All fires are complex and difficult, and this sure was a nasty fire … But we need lots of tools in the shed. Those hairy, big backburns on exposed ridges so close to a blow-up day with bad weather surprised me. Frightened me even.”
For Brown, even more worrying is the trend.
“Parts of the Grose have now burnt three times in 13 years and four times in 24 years. Most of those fires started from arson or accident. Many of the species and plant communities can’t survive that sort of hammering.”
Ross Bradstock, a fire ecologist, agrees. Professor Bradstock is the director of the new Centre for the Environmental Risk Management of Bushfires at the University of Wollongong, which is funded by the Department of Environment and Conservation and the Rural Fire Service. He says Australia stands out as one of the countries whose vegetation may be most affected by climate change.
Bradstock says that in south-eastern Australia the potential for shifts in fire frequency and intensity are “very high … If we’re going to have more drought we will have more big fires.”
But the story is complicated and compounded by the interaction between drought and fire. The plants most resistant to fire, most able to bounce back after burning, will be most affected by climate change. And the plants that are going to be advantaged by aridity will be knocked over by increased fire frequency. “In general, the flora is going to get whacked from both ends – it’s going to be hit by increased fire and climate change. It’s not looking good.”
.
Wyn Jones, an ecologist who worked for the wildlife service, says the extremely rare drumstick plant, Isopogon fletcheri, is a good example. There are thought to be no more than 200 specimens, restricted to the upper Grose. Last week, on a walk down into the Blue Gum Forest, Jones found three – all killed by the fire.
.
The NSW Rural Fire Service Commissioner, Phil Koperberg, has been a keen supporter of Bradstock’s centre. Asked if he agreed with the argument that the Grose had seen too much fire, Mr Koperberg replied: “It’s not a comment I disagree with, but had we not intervened in the way we did, the entire Grose Valley would have been burnt again, not half of it.”
The great irony of the fire is that it was better weather, low fuels and close-in containment firefighting that eventually stopped the fire – not big backburns.
Remote area firefighting techniques have been pioneered and perfected over recent decades by the wildlife service. In 2003 a federal select committee on bushfires supported the approach. It recommended fire authorities and public land managers implement principles of fire prevention and “rapid and effective initial attack”.
Nic Gellie, a fire ecologist and former fire manager, has helped the wildlife service pioneer ecological fire management. The models are there – but he says they have not been used often enough or properly.
Doubts have been expressed about the sustainability of the current remote area firefighting model. It is underfunded, and relies on a mix of paid parks service staff and fire service volunteers. Most agree the model is a good one, but not viable during a longer bushfire relying on volunteers.
The Sydney Catchment Authority pays $1 million for Catchment Remote Area Firefighting Teams in the Warragamba water supply area. It has always seemed like a lot of money. But it looks like a bargain stacked against the estimated cost of $10 million for the direct costs and rehabilitation of the Grose fire.
Curiously, one unexpected outcome of the great Grose fire may be that the valley sees more regular, planned fire – something the former wildlife service manager Ian Brown is considering.
“If climate change means that the Grose is going to get blasted every 12 years or less, then we need more than just the backburning strategy. We need to get better at initial attack and maybe also look at more planned burns before these crises. But actually getting those burns done – and done right – that’s the real challenge.”
It may be the only hope for Isopogon fletcheri.
 Fletcher’s Drumstricks (Isopogon fletcheri)
http://www.anbg.gov.au
Fletcher’s Drumstricks (Isopogon fletcheri)
http://www.anbg.gov.au
.
.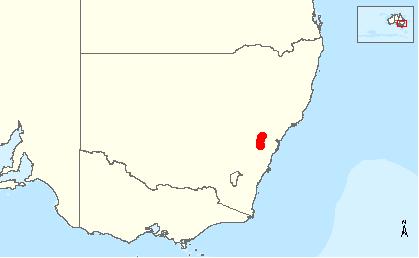 Distribution of Isopogon fletcheri is restricted to a very small area in the Blackheath district of the Blue Mountains.
Given restricted distribution, it is susceptible to local extinction due to environmental and demographic uncertainty and in particular pathogens such as Phytophthora cinnamomi.
Distribution of Isopogon fletcheri is restricted to a very small area in the Blackheath district of the Blue Mountains.
Given restricted distribution, it is susceptible to local extinction due to environmental and demographic uncertainty and in particular pathogens such as Phytophthora cinnamomi.What needs to be done to recover this species? Continued habitat protection.
http://www.threatenedspecies.environment.nsw.gov.au/tsprofile/profile.aspx?id=10440
.
.
What price now?
.
[Source: ^http://www.smh.com.au/news/national/what-price-now/2006/12/10/1165685553948.html?page=2].
The Blue Gum Forest stands tall, straight and surreal in a fire-ground of still smouldering ash. Three weeks ago it was intensely burnt during bushfires in the Grose Valley. The future of the iconic forest – some trees are thought to be 200 to 300 years old – now hangs in the balance.
Last week the massive white-trunked blue gums were dropping their scorched leaves to reveal a stark and unrecognisable forest of tall trunks, bare limbs and fallen logs.
The director of the Colong Foundation for Wilderness, Keith Muir, did not speak out during the fires, but now he wants answers.
.
-
“Could the Blue Gum have been saved using other firefighting strategies that also protected life and property?
-
Was the fire that burnt this very special forest made more intense, unpredictable and extensive by massive backburning operations?
-
Was the Blue Gum sacrificed for the sake of a de facto fuel reduction exercise that didn’t consider heritage values?
-
We need answers. We need an independent inquiry. This is too important to happen again.”
.
In the early 1930s the Herald supported a campaign by bushwalkers to save the Blue Gum from grazing and agricultural development. It was the first successful Australian conservation campaign to protect an almost pure stand of tall mountain blue gum ( Eucalyptus deanei) on about 40 hectares of river flats in the rugged Grose Valley of the upper Blue Mountains. The bushwalkers raised £130 to buy the lease covering the forest and create the Blue Gum Forest Reserve.
The Herald visited the Blue Gum Forest again last week with a forest ecologist, Wyn Jones, and Ian Brown, former National Parks and Wildlife Service operations manager with overall responsibility for fire management. In 1994 Jones, then an ecologist with the service, helped to describe scientifically the rare and newly discovered Wollemi pine. He first saw the Blue Gum Forest more than 40 years ago. He has been involved with it professionally and as a bushwalker ever since.
He said the forest would re-shoot and regrow, but it remains to be seen when and how. He predicted its immediate future would be decided over the next six months. That would depend largely on the vagaries of climate. Severe wind storms, a hot dry summer or even persistent rain, fungal growth and insect attack could all compromise the forest’s ability to bounce back quickly.
More uncertain and potentially bleak is the long-term prognosis. Jones said changing fire regimes caused by humans could be further complicated by climate change, a recipe for more frequent and hotter fires.
The Blue Gum Forest has been burnt four or five times in less than 50 years: by wildfire in 1957, possibly 1968, and in 1982, 1994 and 2006.
“Without human interference , this forest may have been burnt once or perhaps twice in 50 years, not five times,” Jones said.
Jones is convinced cracks in majestic gums were caused by the fire. If they are deep enough to effectively ringbark the surviving trees, then the demise of the forest promises to be a slow and painful affair.
“The old Blue Gum Forest is gone,” he said. “We don’t know what the Blue Gum of the future will look like. We could be heading for strange and very different days.”
===========
‘Friends of the giants’
.
In 1931 the Herald’s conservation reporter, J.G. Lockley, writing under the name Redgum, led a campaign to save the Blue Gum Forest.
“To destroy the trees would be unforgivable vandalism .. if they are permitted to stay, they will stand straight and true for many generations … Every acre on which those grey gums are growing should be reserved for the distant days, when the nation will know the true worth of the giant trees, which are not understood.”
.
‘Blue Gum Lessons’
.
(Editor’s letter in the Blue Mountains Gazette, 20061220).
‘One of our most precious natural heritage assets, the Blue Gum Forest, has been allowed to be scorched by bushfire. This demands an independent enquiry into current fire fighting practices to ensure such a tragedy is not repeated.
Not a witch hunt, but what is needed is a constructive revision into improving bushfire fighting methods incorporating current research into the issue. The intensity and frequency of bushfires have become more prevalent due to disturbances by man, including climate change.
An enquiry should consider the assets worth saving; not just lives, homes and property but natural assets of the World Heritage Area. Fire fighting methods should seek to protect all these values. It seems back-burning, however well-intentioned, burnt out the Blue Gum. This is unacceptable. What went wrong? The future survival of our forests depends on how we manage fire.’
.
A Grose Valley Fire Forum was held at Mount Tomah on Saturday 17th February 2007, but the public were denied entry.
An independent enquiry was never conducted. A public enquiry was never conducted.