2006 Grose Valley Fires – any lessons learnt?
Wednesday, January 18th, 2012On Sunday 13th November 2006 two separate bushfire ignitions were believed to have been started by lightning just west of the Grose Valley of the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area, according to the Rural Fire Service (RFS). One ignition was located outside the small rural village of Hartley Vale in a valley referred to as Lawsons Long Alley, while the other was in rugged bushland at Burra Korain Head about 4 km east of the village of Mount Victoria. Ten days later catastrophe…
 Pyrocumulus cloud as the Grose Valley goes up in smoke on 23rd November 2006
Pyrocumulus cloud as the Grose Valley goes up in smoke on 23rd November 2006
.
‘Two bushfires that were believed to have been started by lightning strikes on Monday are burning in the Blue Mountains National Park. A fire burning 2 km north of Mount Victoria has burnt out about 1100 hectares of private property and parkland and is burning on both sides of the Darling Causeway. The Darling Causeway remains closed to traffic and motorists are advised to use the Great Western Highway and Bells Line of Road as alternate routes.
A second fire burning about 5 km north of Blackheath in the Grose Valley has burnt out about 500 hectares of parkland. Waterbombing aircraft are slowing the progress of the fire as it is burning in difficult and inaccessible terrain.’
[Source: New South Wales Rural Fire Service Blue Mountains website, Fire Name: Lawsons Long Alley, Time Message Issued: 1700, Date Message Issued: 16/11/06, ^http://lists.rfs.org.au/mailman/listinfo/bluemountains-info].
At the time the RFS reported that the ‘fire is not threatening any properties or homes at this stage‘, but it was this reassurance that lulled the fire fighting effort into a false sense of security. Over the coming days the fires were not earnestly suppressed but instead allowed to burn out of control as neither were ‘threatening any properties or homes at this stage‘. Famous last words. Worse was that a series of broadscale backburns were started by the RFS at Hartley Vale, Blackheath and along Bells Line of Road – each of which at times got out of control.
.
Comparison with 2003 Canberra Firestorm
.
Three years prior, four ignitions that had been purportedly been sparked by lighting on 8th January 2003 were allowed to burn out of control in remote bushland outside Canberra, Australian Capital Territory (ACT), and starting outside the ACT in NSW. At the time, those fires were deemed not to be threatening any properties or homes at that stage too. Ten days later, the four fires – McIntyre’s Hut Fire, the Bendora Fire, the Stockyard Spur Fire and the Mount Gingera Fire all coalesced into what became known as the 2003 Canberra Firestorm in which four people perished.
 McIntyre’s Hut Fire 20030108 – distant, isolated and remote at this stage.
Ten days later it became the 2003 Canberra Firestorm
McIntyre’s Hut Fire 20030108 – distant, isolated and remote at this stage.
Ten days later it became the 2003 Canberra Firestorm.
Three years hence, the two bushfires west of the Grose Valley after seven days had coalesced into what has become known as the 2006 Grose Valley Fires that ended up incinerating 14,070 hectares of wild bush habitat, including the iconic Blue Gum Forest down in the Grose Valley inside the Greater Blue Mountains World heritage Area .
Both catastrophic bushfires were ultimately the responsibility of the RFS in New South Wales to suppress in order to prevent them becoming uncontrollable firestorms. The RFS failed catastrophically on both occasions with RFS Commissioner Phil Koperberg at the helm. The lessons from the 2003 Canberra Firestorm had not been heeded.
 An aerial view of a fire-devastated Chauvel Circle in the suburb of Chapman on 21st January, 2003 in Canberra,
where 15 of 20 homes in the street were destroyed by fire.
Four people were killed and 419 homes destroyed when the fires being fought on five fronts swept through the nation’s capital.
(Photo by Daniel Berehulak, Getty Images)
An aerial view of a fire-devastated Chauvel Circle in the suburb of Chapman on 21st January, 2003 in Canberra,
where 15 of 20 homes in the street were destroyed by fire.
Four people were killed and 419 homes destroyed when the fires being fought on five fronts swept through the nation’s capital.
(Photo by Daniel Berehulak, Getty Images)
.
According to the report of the official enquiry into the 2003 Canberra Firestorm by ACT Coroner Maria Doogan, she states:
‘During the inquiry it was submitted that the severity of the firestorm could not have been foreseen. I do not accept this. Australia has a recorded history of extreme fire events dating back to at least 1851. As discussed in Chapter 7 (of the Coroner’s Report), CSIRO fire expert Phil Cheney predicted several years ago a conflagration of the type experienced in January 2003. He made his prediction on the basis of information in the report of one of the seven inquiries that have been held since 1986 to examine various aspects of the ACT’s emergency services.
‘The point to make here is that experiences in life, be they good or bad, serve no useful purpose if we fail to learn from them. It is hoped, therefore, that the many lessons that can be learnt from this catastrophe in the ACT are in fact learnt and result in positive action, not just supportive words and shallow promises.’
[Source: ‘The Canberra Firestorm: Inquest and Inquiry into Four Deaths and Four Fires between 8 and 18 January 2003’, Vol 1, Ch1, pp.2-3., by ACT Coroner].
Blue Mountains Council’s response to the 2006 Grose Valley Fires
.
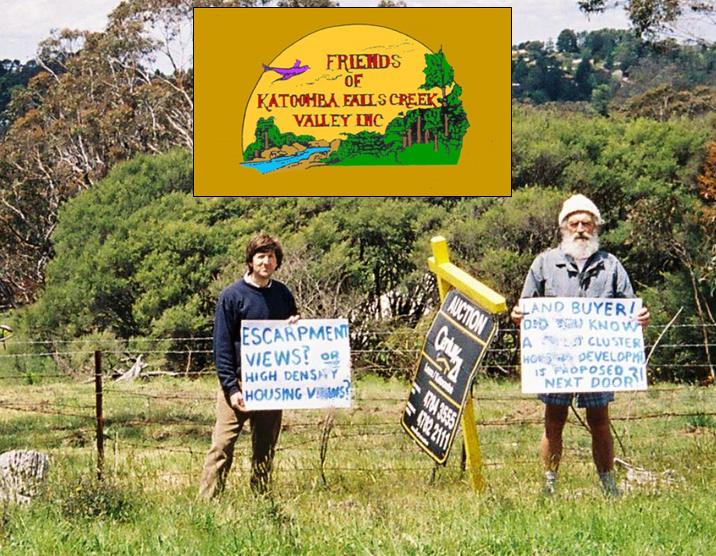
The 2006 Grose Valley Fires coalesced into a conflagration on Thursday 23rd November 2006 down in the World Heritage Grose Valley. Many in the local Blue Mountains community were outraged that this could have been allowed to have occurred. Public demands for answers finally led Blue Mountains Council two months later on Tuesday 30th January 2007 to agree to support the call of ‘concerned residents’ for the New South Wales Government to undertake a thorough, independent review of the Grose Valley Fires.
It is important to note that at the time there was a Labor Government in New South Wales, which was ultimately held responsible for both the 2003 and 2006 bushfire emergency responses.
The following is a copy of the official meeting minutes of Blue Mountains Council’s Ordinary Meeting of 20070130, two months after the 2003 Grose Valley Fires:
.
‘A Motion was moved by Councillors (Terri) Hamilton (Independent) and (Daniel) Myles (Liberal):
.
1. That the Council gratefully acknowledges the efforts of all the volunteers, professionals and agencies that worked together to control the recent Grose Valley Fire.
.
2. That the Council, in order that improvements in fire management can continue for the Blue Mountains and other parts of NSW, as a matter of urgency, writes to the Premier of New South Wales, the Hon Morris Iemma, stating it supports the call of concerned residents on the New South Wales Government, which appeared on page 13 of the Blue Mountains Gazette of 6 December, 2006, as follows:
“1. Undertake a thorough, independent review of the Grose Valley Fire, involving all stakeholders with particular attention to the following questions:
- Were fire detection and initial suppression timely and adequate?
- Were resources adequate, appropriate and supported?
- Were the adopted strategies the best available under the circumstances?
- Could other strategies of closer containment have offered lower risk to the community, better firefighter safety, higher probabilities of success, lower costs and less impact on the environment?
- Was existing knowledge and planning adequately utilised?
- Is fire management funded to the most effective way?
2. Ensure adequate funding is available for post-fire restoration, including the rehabilitation of environmental damage.
3. Fund more research to improve understanding of fire in the Blue Mountains landscape and methods for fire mitigation and suppression.
4. Improve research and training in strategies for controlling fires in large bushland areas.
5. Improve pre-fire planning to support decision-making during incidents.
6. Improve systems to ensure that local fire planning and expertise is fully utilised during incidents, and that the protection of the natural and cultural values of World Heritage areas and other bushland are fully considered.”
.
3. That the independent review includes addressing the questions raised by Blue Mountains Conservation Society:
a. The Blue Mountains City Council therefore supports the following adopted position of the Blue Mountains Conservation Society and would like the review to address the following questions:
i. In what circumstances are back burning from the “Northern Strategic Line” and the Bells Line of Road appropriate?
ii. What can be improved to ensure that lightning strikes or arson fires are contained as quickly as possible?
iii. What can be done to better manage fire risk in the Grose Valley in terms of preparation and suppression to minimise damage to people, property and biodiversity?
iv. What is needed to allow remote area fire teams to be able to work at night when conditions are more benign?
v. How can funding of bushfire management and suppression be changed to reduce overall costs to the community. (Federal funding of suppression under section 44 means funding for trail maintenance and planning is limited.)
.
b. If practicable, would the review also address the following?
i. The World Heritage Area contains a number of threatened species and ecological communities that, in addition to the direct threats associated with climate change, are particularly vulnerable to increased fire frequency and intensity.
ii. The effects on biodiversity of the fire regimes in the Grose Valley over the last 40 years, where there has been a succession of large intense wild fires without sufficient interval between them.
iii. Climate change predictions suggest a probability of more frequent and more intensive fire events, with significant implications for fire management and integrity of ecosystems.
iv. The Blue Mountains City Council also supports and requests involvement in the forum being organised by the Director of the Central Branch of the National Parks and Wildlife Service, Bob Conroy, on the 17 February 2007.
.
4. That the Council emphasises that the requested review should be of a scientific and technical nature.
.
5. That a copy of this letter be forwarded to the Minister for Emergency Services, the Hon Tony Kelly, the Member for the Blue Mountains, the Hon. Bob Debus, and the New South Wales Opposition Leader, Peter Debnam.
.
Upon being PUT to the Meeting, the MOTION was CARRIED, the voting being:
FOR:
- Fiona Creed (Liberal)
- Terri Hamilton (Independent)
- Pippa McInnes (Greens)
- Daniel Myles (Liberal)
- Kerrin O’Grady (Greens)
- Lyn Trindall (Blue Mountains First
.
AGAINST:
- Mayor Jim Angel (Labor)
- Kevin Frappell (Labor)
- Alison McLaren (Labor)
- Adam Searle (Labor)
- Chris Van der Kley (Liberal) and Chair of Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee
 The Hartley Vale backburn 20061115 escaped up Hartley Vale Road and over the Darling Causeway (above) toward the Grose Valley to the right
(Photo by Editor 20070204, free in pubic domain, click to enlarge)
The Hartley Vale backburn 20061115 escaped up Hartley Vale Road and over the Darling Causeway (above) toward the Grose Valley to the right
(Photo by Editor 20070204, free in pubic domain, click to enlarge)
..
Editor’s Note:
Ahead of the Blue Mountains Council voting for the above motion, two Labor Councillors, Clr Chris Van der Kley (also Chair of the Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee) and Clr Kevin Frappell (Labor) moved an alternative motion, however it was lost upon voting. This proposed alternative motion was labelled an ‘amendment’ but it was significantly different in detail. The proposed amendment excluded calls for an independent review (per the first item in the original motion).
This proposed amendment also excluded asking the six key questions put by the concerned residents such as ‘Were fire detection and initial suppression timely and adequate?‘, ‘Is fire management funded to the most effective way?‘, etc.
This proposed amendment also excluded that part of Item 1 which recommended strategic improvements to bushfire management such as ‘Ensure adequate funding is available for post-fire restoration, including the rehabilitation of environmental damage‘ and ‘Fund more research to improve understanding of fire in the Blue Mountains landscape and methods for fire mitigation and suppression‘, etc.
This proposed amendment instead drew upon the view of the leadership of the Blue Mountains Conservation Society at the time that considered an independent enquiry would equate to criticism and assigning blame and so be politicised. This did however include advocating “an interagency and technical review process, to tease out the lessons learned.”
.
The Amendment (although lost in the Council voting) is important for the record and read as follows:
1. That the Blue Mountains City Council gratefully acknowledges the efforts of all the volunteers, professionals and agencies that worked together to control the recent Grose
Valley fire.
.
2. That the Blue Mountains City Council supports the recent position adopted by the Blue Mountains Conservation Society in relation to the Grose Valley fire in November
2006. We note and support the position of the Society when it says,
“The circumstances of the bushfire are complex and it is not in anyone’s interest for criticism or blame to be apportioned. However, there is much to be gained by looking at what was done and how it can be improved. The Society does not therefore support a large public inquiry and its attendant politicisation. Instead, the Society advocates an interagency and technical review process, to tease out the lessons learned.”
.
3. That the Blue Mountains City Council therefore supports the following adopted position of the Blue Mountains Conservation Society and would like the review to
address the following questions:
- In what circumstances are back burning from the “Northern Strategic Line” and the Bells Line of Road appropriate?
- What can be improved to ensure that lightning strikes or arson fires are contained as quickly as possible?
- What can be done to better manage fire risk in the Grose Valley in terms of preparation and suppression to minimise damage to people, property and biodiversity?
- What is needed to allow remote area fire teams to be able to work at night when conditions are more benign?
- How can funding of bushfire management and suppression be changed to reduce overall costs to the community. (Federal funding of suppression under Section 44 means funding for trail maintenance and planning is limited.)
.
If practicable, would the review also address the following?
- The World Heritage Area contains a number of threatened species and ecological communities that, in addition to the direct threats associated with climate change, are particularly vulnerable to increased fire frequency and intensity.
- The effects on biodiversity of the fire regimes in the Grose Valley over the last 40 years, where there has been a succession of large intense wild fires without
sufficient interval between them. - Climate change predictions suggest a probability of more frequent and more intensive fire events, with significant implications for fire management and
integrity of ecosystems. - That the Blue Mountains City Council also supports and requests involvement in the forum being organised by the Director of the Central Branch of the National Parks and Wildlife Service, Bob Conroy, on the 17 February 2007.
.
Upon being PUT to the Meeting, the AMENDMENT was LOST, the voting being:
FOR:
- Mayor Jim Angel (Labor)
- Kevin Frappell (Labor)
- Alison McLaren (Labor)
- Adam Searle (Labor)
- Chris Van der Kley (Liberal, and Chair of Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee)
.
AGAINST:
- Creed (Liberal)
- Hamilton (Independent)
- McInnes (Greens)
- Myles (Liberal)
- O’Grady (Greens)
- Trindall (Blue Mountains First)
.
[Source: Blue Mountains Council’s Ordinary Meeting, 20070130, Minute No. 7, File Ref. C01095. Subject: ‘Grose Valley Fire’, pp.15-16].
Editor’s Analysis:
.
- Similar failure by the RFS and the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) to muster all available necessary resources to suppress and extinguished both the Lawson’s Long Alley and Burra Korain Head fires, demonstrated that lessons from the 2003 Canberra Firestorm had not been learnt. Critical time was lost in the initial days of the ignitions at both to effectively suppress the fires while they were of a small size and weather conditions relatively favourable to enable suppression.
- The RFS strategy to apply excessive broadscale backburning on multiple fronts at at Hartley Vale, Blackheath and Bells Line of Road exacerbated the complexity and scale of both fires and in the most part contributed to the conflagration of all the fires down in the Grose Valley on 23rd November 2006
- The shortcoming of not mustering all necessary resources to suppress and extinguish bushfires, irrespective of whether a fire is immediately affecting property and homes or not, is flawed, negligent and only heightens the inherent risk of a bushfire escalating out of control. The risk of a bushfire escalation into uncontrollable firestorm is heightened as time allows for the prospect of worsening bushfire weather conditions – increased wind, wind gusts, wind direction, temperatures, and lowering humidity – contributory factors in both the respective Canberra and Grose Valley Fires. There is no indication that this operational culture has changed.
- That a bushfire is situated in inaccessible terrain is not an excuse for bushfire management not to muster all airborne and RAFT resources to suppress and extinguish it as soon as feasibly possible
- After local community realisation that the bushfire had overrun the Grose Valley including burning through the iconic Blue Gum Forest on 23rd November, an informal collection of local ‘concerned residents‘ formed numbering 143 and co-ordinated by Blue Mountains resident Ian Brown. By Wednesday 6th December, within days of the fire finally being suppressed (3rd Dec), this informal group had collectively paid for a full page letter in the Blue Mountains Gazette newspaper costing $2,131.40(page 13). The letter was entitled ‘Burning Issues – fire in the Grose Valley – A statement funded and supported by concerned residents‘. The context was that detailed in Council’s carried motion above.
- Blue Mountains Council’s response was simply a manifestation of the “supportive words and shallow promises” whom ACT Coroner Maria Doogan had cautioned in the Coroner’s Report into the 2003 Canberra Firestorm. No effective Council follow up to its supportive words was undertaken. Sure per Council’s carried motion, Council’s then acting General Manager, Dave Allen, sent off the letter with supportive words to the NSW Premier Morris Iemma, on 20th February 2007, but Council took no other review or enquiry action.
- In the Central Blue Mountains, there are three government agencies responsible for bushfire management – the New South Wales Rural Fires Service, the National Parks and Wildlife Service as part of the NSW Department of Environment (what ever its frequently changing title) and Blue Mountains Council. Collectively these three bodies have co-operated under the Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee, which was/is chaired by Blue Mountains Councillor Chris van der Kley.) and is responsible for planning in relating to bush fire prevention and coordinated bush fire fighting, as well as responsible for advising the Commissioner on bush fire prevention; mitigation and coordinated bush fire suppression. Included on the Committee is also the Commissioner of the RFS, and a nominated representative respectively from the NSW Fire Brigades, Forests NSW, NPWS, the Local Government Association of NSW, the Shires Association of NSW, the NSW Rural Fire Service Association, NSW Police, a nominee of the Minister for the Environment (then Bob Debus), a representative of the Nature Conservation Council of NSW, a person appointed by the Minister on the recommendation of the NSW Farmers Association, a representative of the Department of Community Services and a representative of the Department of Lands. In March 2008, the Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee (BMBFMC) staged a series of community workshops on the Plan’s review process. The Plan was approved on 14th December 2000 with a required review every five years. So by the Grose Valley Fire, the Plan was a year out of date and by March 2008 the Plan was three years out of date.
- It is not surprisingly that the above proposed amendment to the Council letter to the NSW Premier excluded calls for an independent review. Those who proposed the motion and who voted for it were either all Labor Party members or in the case of Liberal Councillor Chris Van Der Kley, Chair of the Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee who was operationally involved. An independent enquiry and the proposed strategic improvements to the bushfire management establishment would have likely revealed operational and government failings and recommended changes to the RFS structure, strategies, and management and importantly to its culture. The amendment was rejected anyway due to Labor having insufficient votes on Council.
- On Sunday 13th November 2006 two separate bushfire ignitions were believed to have been lit by lightning just west of the Grose Valley of the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area by the RFS. Following a back burn/hazard reduction burn that had got out of control up Hartley Vale Road and crossed the Darling Causeway, on Wednesday 15th November the RFS declared a formal escalation to a Section 44 bushfire emergency. This four day delay in detection and suppression is unexplained by the RFS.
- Despite the calls by the concerned residents (with Blue Mountains Council’s supportive words) for the ‘NSW Government to undertake a thorough, independent review of the Grose Valley Fire, involving all stakeholders, so such independent review was done.
- The local Labor member for the NSW Seat of Blue Mountains at the time and NSW Minister for the Environment was Bob Debus MP, who categorically refused requests for either an independent review or a public review into the management of the Grose Valley Fires.
- The Blue Mountains Conservation Society (BMCS) similarly rejected calls for a public enquiry, stating “the circumstances of the bushfire are complex and it is not in anyone’s interest for criticism or blame to be apportioned. However, there is much to be gained by looking at what was done and how it can be improved. The Society does not therefore support a large public inquiry and its attendant politicisation. Instead, the Society advocates an inter-agency and technical review process, to tease out the lessons learned.” It needs to be pointed out that key committee members of the BMCS were/are also active members of the RFS, which raises the issue of and actual or perceived conflict of interest.
- There were two reviews of sorts, none independent and none public.
- On Tuesday 19th December 2006 there was apparently an ‘Inter-Agency Review‘ which took place at Katoomba behind closed doors by members of bushfire management and operating personnel involved in the fire fighting. Despite requests by this Editor, no minutes or reports of that meeting were ever forthcoming. The meeting was internal and secret.
- On Saturday 17th February 2007, there was a ‘Grose Valley Fire Forum‘ held at Mount Tomah organised by Director of the Central Branch of the National Parks and Wildlife Service, Bob Conroy, and the Blue Mountains World Heritage Institute. Only selected participants were permitted to attend – mainly from the bushfire management, fire experts and selected members of the Blue Mountains Conservation Society. A copy of the report of that forum will be publicised on this website shortly.
- Following ongoing community concerns about the lack of transparency, no evidence of any lessons being learned from the Grose Valley Fires and even of a cover up into some of the operational decisions, in January 2007 Bob Debus MP announced a suggestion of there being an Environmental Summit to be staged in the Blue Mountains to provide the first public forum into important environmental issues affecting the Blue Mountains region, notably to discuss the Grose Valley Fire. Well, by the time the summit eventuated it was over a year later and held on the weekend of 23rd and 24th February 2008. By then Bob Debus had moved to federal politics (though still representing the Blue Mountains via the Seat of Macquarie. The summit was chaired by the RFS Commissioner responsible for the 2006 Grose Valley Fires, Philk Koperberg (now local Labor MP) and even the bushfire Incident Controller of the 2006 Grose Valley Fires, RFS Superintendent Mal Cronstedt, was in attendance. However, the summit was now called a conference and the agenda had expanded to many issues including Energy, Social Systems, Natural Systems and Water. Discussion about bushfire was restricted to a two hour workshop and so available time to the Grose Fire to one or two questions which copped only official spiel. It was a classic Labor tactic or stalling on accountability until the community gives up or forgets.
- Since 2006, the Blue Mountains community still doesn’t know whether in the 2006 Grose Valley Fire or currently:
- Fire detection and initial suppression was/is timely and adequate?
- Whether bushfire management resources were/are adequate, appropriate and supported?
- Whether in the Grose Valley Fire the adopted strategies were the best available under the circumstances?
- Whether other strategies of closer containment could have offered lower risk to the community
- Whether currently it has better firefighter safety, higher probabilities of success, lower costs and will cause less impact on the environment?
- Whether existing knowledge and planning is adequately utilised?
- Whether bushfire management is funded to the most effective way?
- Is adequate funding available for post-fire restoration, including the rehabilitation of environmental damage?
.
Another three years hence, in the Blue Mountains we have witnessed from afar the catastrophic Victorian ‘Black Saturday’ Bushfires of 7th February 2009.
.
Another three years hence in 2012, have we learnt anything?
.