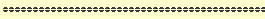Archive for the ‘Threats from Deforestation’ Category
Sunday, February 19th, 2012
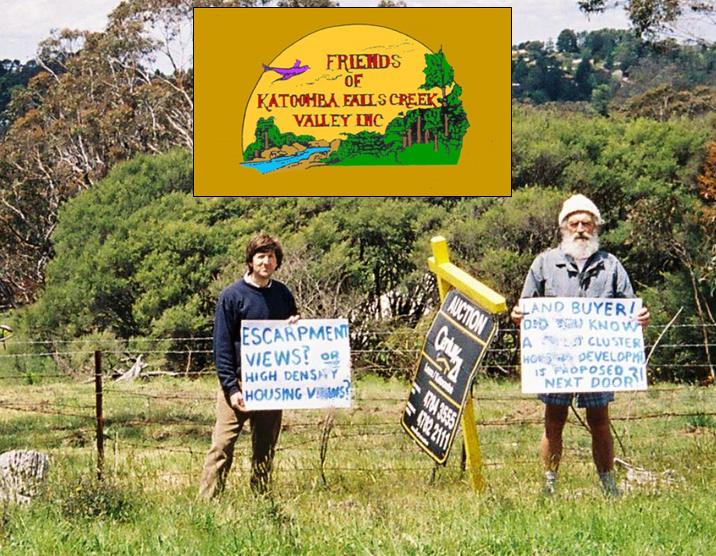
This article was initially posted by Tigerquoll 20120202 as a comment on the Tasmanian Times newspaper to an article entitled ‘Gunns’ Pulp Mill lifeline extended – community will protest‘ by Anne Layton-Bennett, Friends of The Tamar Valley (20120201).
 . .
The ANZ Bank publicly claims it has adopted the Equator Principles of the World Bank’s International Finance Corporation (IFC).
These are ‘voluntary standards designed by the World Bank’s International Finance Corporation (IFC) to help banks identify and manage social and environmental risks associated with the direct financing of large projects‘ – i.e. Natural Resource projects like Gunns Pulp Mill.
[Source: ANZ Bank website, ^ http://www.anz.com/aus/values/environment/Equator.asp]
.
“ANZ has voluntarily committed to fund only new projects that can be developed and operated according to sound social and environmental standards.”
~ ANZ website
 ANZ Bank’s new brand represents a bank “for the people”
For the people or for its executives? ANZ Bank’s new brand represents a bank “for the people”
For the people or for its executives?
.
As at 1 Jan 2012, the IFC’s Equator Principles Performance Standard 3 ‘Resource Efficiency and Pollution Prevention” states that its aim is
- To avoid or minimize adverse impacts on human health and the environment by avoiding or minimizing pollution from project activities.
- To promote more sustainable use of resources, including energy and water.
- To reduce project-related GHG emissions.
.
ANZ’s prominent project finance client, Gunns and its planned Tamar Valley Pulp Mill project seems set to fail each of these objectives in its airborne emissions and waste water. In September 2007, the ANZ was ranked the most sustainable bank globally by the Dow Jones Sustainability Index. So what is the ANZ Bank not telling the IFC?
 A Gunns Woodchip Mill at Longreach, Tasmania A Gunns Woodchip Mill at Longreach, Tasmania
.
 . .
IFC’s Sustainability Framework – 2012 Edition:
Performance Standard 6: ‘Biodiversity Conservation and Sustainable Management of Living Natural Resources’
Clause 14: The client will not significantly convert or degrade natural habitats, unless all of the following are demonstrated:
- No other viable alternatives within the region exist for development of the project on modified habitat;
- Consultation has established the views of stakeholders, including Affected Communities, with respect to the extent of conversion and degradation;8 and
- Any conversion or degradation is mitigated according to the mitigation hierarchy.
. Gunns Clearfell of Tasmanian Heritage
© Photo by Alex Wise
Source: ^http://www.alexwisephotography.net/blog/2008/11/08/tasmania-clearfelling/ Gunns Clearfell of Tasmanian Heritage
© Photo by Alex Wise
Source: ^http://www.alexwisephotography.net/blog/2008/11/08/tasmania-clearfelling/
.
Clause 17: In areas of critical habitat, the client will not implement any project activities unless all of the following are demonstrated:
- No other viable alternatives within the region exist for development of the project on modified or natural habitats that are not critical
- The project does not lead to measurable adverse impacts on those biodiversity values for which the critical habitat was designated, and on the ecological processes supporting those biodiversity values
- The project does not lead to a net reduction in the global and/or national/regional population13 of any Critically Endangered or Endangered species over a reasonable period of time;
- A robust, appropriately designed, and long-term biodiversity monitoring and evaluation program is integrated into the client’s management program.
.
Back to ANZ’s website…
‘ANZ will comply with the Principles for all project finance proposals, regardless of their size, and apply the same Equator Principles standards to all projects in all countries.’
.
These people don’t think so..
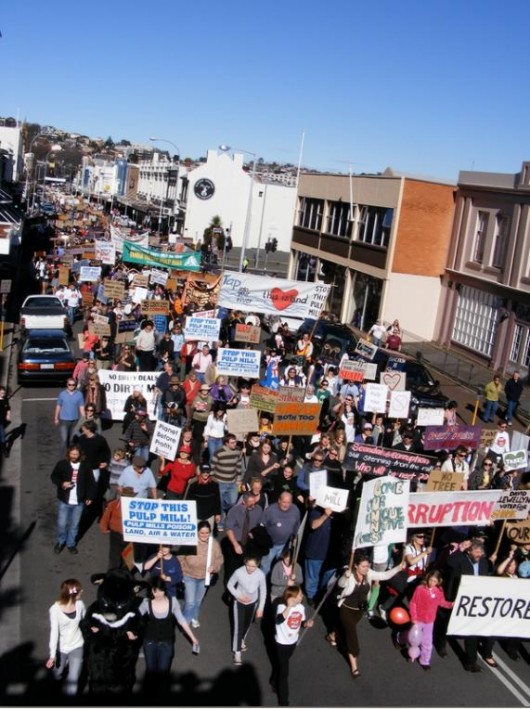 Pulp Mill protest, Launceston Tasmania
A pulp mill for the people? Pulp Mill protest, Launceston Tasmania
A pulp mill for the people?
.
Grassroots community action group in Tasmania, Pulp the Mill Alliance, continues to oppose Gunns’ proposed Tamar Valley Pulp Mill for the following reasons:
- Toxic effluent in Bass Strait
- Threats to the livelihood and lifestyle of thousands of Tamar Valley residents
- Fresh water usage
- Possible future use of native forests
- The draconian and undemocratic Section 11 of the Pulp Mill Assessment Act
- Lack of an independent, transparent assessment of a “critically non-compliant” mill
- Lack of public hearings and community consultation
- A complete lack of integrity on Gunns’ part
.
The No Pulp Mill Alliance is undertaking a national campaign to warn the ANZ that if they renew their debt facility to Gunns Ltd then we will renew our national campaign targeting ANZ as the bank that is financing the corruptly approved, environmentally destructive, divisive, and financially risky Tamar Valley pulp mill.
‘We will be placing national advertisements, undertaking direct actions, sending letters/petitions, and anything else it takes to let ANZ know that we don’t want them to finance the Gunns’ Tamar Valley pulp mill.’
With Gunns’ share price at its lowest ever and a capital equity of only $82 million, Gunns Ltd is in serious financial trouble. It is selling everything to try and get its pulp mill built. In fact, the name Gunns Ltd could now be considered as synonymous with the Tamar Valley Pulp Mill.
Gunns has a net debt of $616 million, of which the primary financing facility – a $350 million senior debt facility – is maturing in January 2012. ANZ is the primary financing facility and thus is the Aussie Bank that keeps Gunns standing. Current site works taking place to prepare for construction of the proposed pulp mill are directly financed by the ANZ bank.
Gunns’ Chairman stated in his Annual General Meeting speech in November 2011 that Gunns Ltd is in discussion with ANZ to extend the debt with the: “objective of these discussions is to provide financing terms which facilitate the completion of the asset sale program and financial close of the Bell Bay pulp mill project.”
 Gunns’ pulp mill site on the Tamar River, Tasmania Gunns’ pulp mill site on the Tamar River, Tasmania
.
We demand that ANZ do not extend the debt facility for Gunns Ltd, and warn ANZ that if it does announce an extension of the debt facility, then our national campaign will result in letting its customers know worldwide that it is backing a polluting project that does not comply with the Equator Principles.’
[Source: ANZ Campaign to stop funding the Pulp Mill, ^http://www.pulpthemill.org/]
 . .
The current ten banks committed to Gunns in a syndicated loan are gambling solely on the go ahead and profitability of the proposed Pulp Mill.
Whereas Gunns once had a reliable cash inflows stream from multiple revenue streams – plantation sales including interstate, sawmilling, and hardware earlier on, all non pulp mill assets are being treated as “non-core”.
This strategy has already shown to be poor by the fire sale desperation of these assets in order to maintain operating cash flow to remain solvent, while the myopic focus on the proposed $2.3 billion Bell Bay pulp mill drives the Gunns’ Board. Gunn’s revenue strategy is hedged on one big risky pulp mill – risky from the point of view of fickle international market demand and pulp commodity prices, mired by political controversy and considerable community opposition to the mill.
It’s equivalent to gambling all the $340 Million on the red to win on the roulette wheel.
These banks must be privy to some revenue guarantees and that is likely from ‘commercial in confidence’ assurances from the Tasmanian Labor Party.
.
Tigerquoll
Suggan Buggan
Victoria
.
Further Reading:
.
[1] World Bank’s International Finance Corporation (IFC) Equator Principles , ^ http://www.equator-principles.com/
.
[2] Pulp the Mill Alliance Inc. ^ http://www.pulpthemill.org/
.
[3] Friends of the Tamar River, ^ http://ftv.org.au/
.
[4] TAP, ^ http://www.tapvision.info/
.
[5] The Wilderness Society (Tasmania), ^ http://www.wilderness.org.au/regions/tasmania
.
[6] Tasmanian Times (forum), ^ http://tasmaniantimes.com.au/, ‘Tasmanian Times is a forum of discussion and dissent – a cheeky, irreverent challenge to the mass media’s obsession with popularity, superficiality and celebrity’. Article: ^ http://tasmaniantimes.com/index.php?/article/gunns-pulp-mill-lifeline-extended-community-will-protest/
.
[7] Tasmania Clearfelling, Alex Wise Photography, ^ http://www.alexwisephotography.net/blog/2008/11/08/tasmania-clearfelling/
.
Tags: ANZ Bank, Equator Principles, for the people, Gunns, Gunns Pulp Mill, IFC, International Finance Corporation, Natural Resource Projects, pulp mill pollution, Toxic effluent, World Bank
Posted in Tasmania (AU), Threats from Deforestation | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Sunday, January 22nd, 2012
Tags: Bill Kelty, Blueprint for Tasmania's Forest, Conservation Agreement, Contractors Voluntary Exit Grants, ENGO, ENGO Report of Logging breaching IGA, Environmental NonGovernment Organisation, FIAT Submission to Legislative Council, Forest Reserve Map, Forestry Tasmania, Giddings Labor Government, Gillard Labor Government, Heads of Agreement, Independent Verification Group Terms of Reference, interim reserves, National Partnership Agreement, Protecting Private Forests, Tasmanian Forest Contractors Exit Assistance Program, Tasmanian Forests Agreement, Tasmanian Forests Agreement Independent Verification Group, Tasmanian Forests IGA, Tasmanian Forests Intergovernmental Agreement (IGA), Tasmanian Forests Interim Report, Tasmanian Forests Statement of Principles, Tasmanian Regional Forest Agreement, Timber Workers for Forests
Posted in Tasmania (AU), Threats from Deforestation, Threats to Wild Tasmania | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Sunday, January 15th, 2012
 Tasmania’s magnificent ‘Weld Forest’
~ one of Tasmania’s rare ancient forests constantly threatened
by Tasmanian Government recidivist logger ‘Forestry Tasmania’ Tasmania’s magnificent ‘Weld Forest’
~ one of Tasmania’s rare ancient forests constantly threatened
by Tasmanian Government recidivist logger ‘Forestry Tasmania’
.
Australia’s Gillard Labor Government yesterday (20120114) announced an ‘interim legal protection for 428,000 ha’ ahead of tomorrow’s scheduled return of recidivist logging.
This appears good news which obviously the Gillard media release intends. But the process is duplicitous and sly.
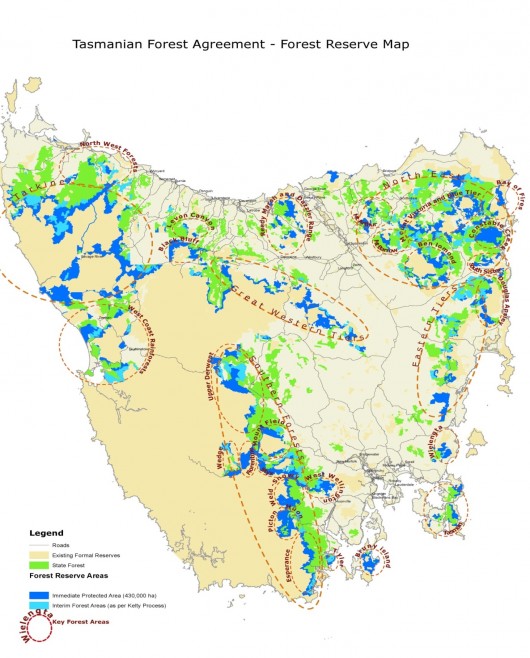
Tasmania’s 2011 Forests Agreement is a community agreement about public forest protection involving taxpayer funded Forestry Tasmania so what moral right does the Labor Party have to deny the process being public – i.e. transparent and open? Why is the forest map not publicly online showing the updates of the discussions? Which 1950ha get the chainsaw and why?
This is the only available map. [Read Tasmanian Forest Protection Map 2011]
Professor Jonathan West, Chair of the Independent Verification Group has a lot to answer for. Why has he not voiced outrage publicly of Forestry Tasmania’s illegal logging of the 430.000 hectares of native forests protected in Interim Reserves under the Agreement?
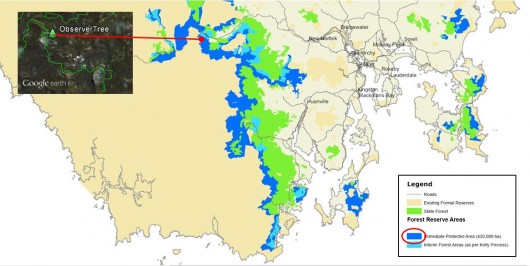
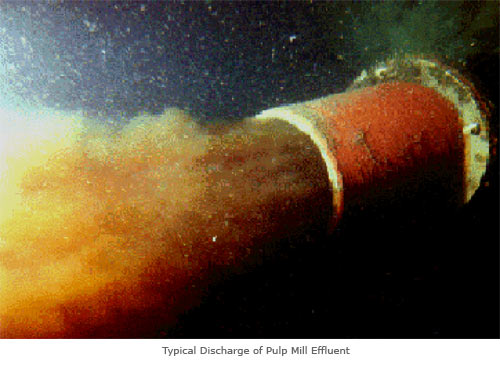
Relative position of the local Tasmanian community protest tree sit The Observer Tree
For ongoing updates visit The ObserverTree.org
.
 Tasmania’s Forest Defender – Miranda Gibson
stationed in a eco-Tree Sit 60 metres above the Styx Valley Forest floor
Visit: The ObserverTree.org
…waiting for Australia’s Prime Minister Julia Gillard to honour her personal promise to Tasmanians to protect Tasmanian old growth forests for perpetuity.
. Tasmania’s Forest Defender – Miranda Gibson
stationed in a eco-Tree Sit 60 metres above the Styx Valley Forest floor
Visit: The ObserverTree.org
…waiting for Australia’s Prime Minister Julia Gillard to honour her personal promise to Tasmanians to protect Tasmanian old growth forests for perpetuity.
.
572,000 hectares of Tasmania’s remaining old growth
…’as agreed‘ Julia!
.
‘Tassie forests deal like a Gunn to the head’
[Source: ‘Tassie forests deal like a Gunn to the head’, by political journalist Bruce Montgomery in Hobart, ^http://www.crikey.com.au/2011/09/06/tasmanian-forrests-deal-gillard-and-giddings/]above the Styx
.
‘The $276 million agreement that Prime Minister Julia Gillard and Tasmanian Premier Lara Giddings flaunted only a month ago as the ultimate peace deal to end the 40-year war in Tasmania’s forests is dead in the water. It comes as no surprise to those who have sought to interpret the poorly drafted provisions of the intergovernmental agreement (IGA) signed by Gillard and Giddings and those of the agreement that preceded it, the so-called Statement of Principles.
The Statement of Principles was the product of those purporting to represent the Tasmanian forest industry and the conservation movement to achieve a peace, most recently under the guidance of former ACTU secretary Bill Kelty.
Both documents appear to have been the work of plant operators rather than draftspeople. Grammar and proofing blunders aside, the giant flaw in both agreements has been the right of conservation groups to identify and nominate another half a million hectares of Crown land in Tasmania to be annexed into reserves, perhaps to the status of national parks or World Heritage, in order to neuter, by law, the timber industry in Tasmania and to pay alms to its victims.
Private foresters, who manage 26% of the total forest cover, were excluded from the negotiations on the pretext that the talks did not involve forests on private land, yet clause 31 of the IGA specifically drags 885,000 hectares of private forests into the equation.
Such a deal, whether concluded at NGO or government level, was never going to pass Tasmania’s Upper House, the Legislative Council. If it did come to pass, it would seal the fate of the Labor-Green governments in Canberra and Hobart as far as Tasmanian voters were concerned.
The premise for the Statement of Principles and the IGA was that the major industrial player, Gunns, was getting out of native forest logging in favour of plantations in order to swing public and banker support behind its $2.5 billion pulp mill proposal at Long Reach on the Tamar River.
In effect, Gunns was about to place all its eggs in one basket, a world-scale pulp mill using only plantation timber. Both agreements hinged on Gunns getting government compensation for its departure from public native forests, yet the mood in Tasmania has clearly been that Gunns should get nothing; its exit from native forests was being made on purely commercial grounds; it was immaterial that it had residual rights to use the public native forests.
If the Giddings government had been responsible for giving Gunns one red cent from the overall $276 million compensation package for the IGA, it would have faced political and electoral oblivion.
We don’t know what Gunns was offered in the end. It is thought to have been $23 million, but on the proviso that it pay its debts to Forestry Tasmania, a disputed $25 million.
Yesterday the Tasmanian government confirmed Gunns had rejected the offer, though Gunns, which has been in a trading halt on the stock exchange since August 8, said nothing.
Assuming that is right, it has the option to place those forest rights on the market. Since the IGA depends on those forests being protected, the keystone to the agreement is gone.’
.
‘Tasmanian forest deal riles green groups‘
[Source: ‘Tasmanian forest deal riles green groups’, by Lanai Vasek and Matthew Denholm, ‘The Australian’, 20120113, The Australian: ^http://www.theaustralian.com.au/national-affairs/tasmanian-forest-deal-riles-green-groups/story-fn59niix-1226243780040]
.
The Gillard Labor Government has announced interim legal protection for 428,000 ha of Tasmania’s forests, but has been accused of reneging on a deal to deliver a larger logging ban.
 Australia’s 27th Prime Minister, The Hon. Julia Gillard (June 2010 – ?)
In her vital and privileged position, she has the power, influence, connections and taxpayer resources
to protect Tasmania’s 572,000 hectares of old growth native forests consistent with the IGA.
As usual, it comes down to political will, courage and innovative thinking – which is what we expect of our leaders. Australia’s 27th Prime Minister, The Hon. Julia Gillard (June 2010 – ?)
In her vital and privileged position, she has the power, influence, connections and taxpayer resources
to protect Tasmania’s 572,000 hectares of old growth native forests consistent with the IGA.
As usual, it comes down to political will, courage and innovative thinking – which is what we expect of our leaders.
.
Environment Minister Tony Burke announced the move today after the Greens suspended normal relations with the government in protest at continues logging of areas deemed sensitive.
The new Conservation Agreement with the Tasmanian Government falls 1950ha short of the forest protection promised under last year’s intergovernmental agreement (IGA) between the Gillard and Giddings governments.
This provoked an angry reaction from environment groups, who said it had “shaken” their confidence in the two governments’ ability to deliver a broader agreement to protect up to 572,000ha.
And Greens leader Bob Brown said it was “a blueprint for the destruction of more than 20 square kilometres of high-conservation value forests”.
…The agreement provides legal protection to the area until an independent process decides how much of the larger area of 572,000ha deserves protection and can be locked up without harming existing timber contracts.
Mr Burke said the new interim deal was good for both forest conservation and jobs and would allow all parties to focus on supporting the longer-term independent verification process, expected to complete by June.
“With this agreement in place, all parties can now concentrate their efforts on assisting the important work of the Independent Verification Group, which is assessing the conservation values of the entire 572,000ha nominated by environmental non-governmental organisations, in addition to verifying long-term timber supply requirements,” Mr Burke said.
“This is a good result for Tasmania’s forestry industry, for local jobs and communities while protecting Tasmania’s iconic forests.”
However, the Wilderness Society, the Australian Conservation Foundation and Environment Tasmania all condemned the two governments for allowing logging in the 1950 ha, saying this included iconic, ancient forests in the Styx Valley, Weld Valley and The Tarkine, including endangered species habitat.
Earlier this week Greens leader Bob Brown said he would not resume his regular meetings with Julia Gillard once parliament returns next month unless she committed to ending logging. This afternoon, Senator Brown said he remained open to ad-hoc talks with Ms Gillard, who will visit Tasmania on the weekend, but accused her of reneging on the promise to protect the full 430,000ha in the IGA announced in August last year.
.
How is Tasmania’s Premier Lara Giddings dealing with the colonial cultural right to log Tasmania’s remaining ancient forests?
Only when Tasmania’s condemned old growth forest is ultimately logged, will neanderthal loggers ugg…
.
‘Where’s me big trees gone’ ?
 . .
Bill Kelty’s drafting of the IGA was a contradictory hoodwink
.
While the public message is $276 million (no less) to exit native forests and a logging moratorium, what is Lara Giddings saying privately to Forestry that we see its business as usual pursuing old growth logging self-righteously on its perceived right to log?
Under the conservation agreement, the Tasmanian government agency Forestry Tasmania is restrained from logging swathes of disputed public forest while the deal is settled. However, evidence has been found of Forestry Tasmania continuing to penetrate its logging deep into these wilderness forests. Meanwhile the contradictory message by the Giddings Labor Government to the Tasmanian forest industry is that it has a ‘guaranteed wood supply‘.
Perhaps having the $276 million cake she says its ok to log the forest too!
In 2004 the Timber Workers for Forests (TWFF) defended their “statutory requirement that a minimum of 300,000 m3 of high quality Eucalypt veneer and sawlog be made available annually.” It’s ‘Logging Statutory Requirement‘ versus ‘Native Logging Moratorium‘ allowing a duplicitous and sly parallel government message process.
Bill Kelty’s drafting of the IGA was worse that a compromise. Its complex and contradictory legalese was a hookwink. Kelty’s wording allowed Forestry to have its cake and eat it. On the one hand it promises Conservation (lumped as “ENGO’s”) under Clauses 25, 26 and 27 …”The State will immediately place the 430,000 ha of native forest…into Informal Reserves.”
While at the same time it also guarantees Forestry wood supply for the remaining industry under Clause 17…”At least 155 000 thousand cubic metres per year of high quality sawlog, by regulation, 265 000 metres per year of peeler billets, a speciality timber supply, noting that the industry claim is 12,500 cubic metres per year, subject to verification.”
So Forestry has has a window of logging opportunity to go for it while Professor Jonathan West’s Independent Verification Group decides the exact boundaries of the 430,000 and 572,000 for either protection or the chainsaw (Clause 20). That decision was due 31st Dec 2011, two weeks ago.
.
“It is little wonder that many Tasmanians now worry that the woodchippers’ greed destroys not only their natural heritage, but distorts their parliament, deforms their polity and poisons their society. And perhaps it is for that reason that the battle for forests in Tasmania is as much about free speech and democracy – about a people’s right to exercise some control over their destiny, about their desire to have a better, freer society – as it is about wild lands.”
[Source: ‘Out of Control: The tragedy of Tasmania’s forests’, by Richard Flanagan, in The Monthly, May 2007, ^http://www.themonthly.com.au/monthly-essays-richard-flanagan-out-control-tragedy-tasmania-s-forests-512]
.
 Logging invades Tasmania’s South-West wilderness in the Huon valley,
not far downstream of the above photo.
This logging is ruining the integrity of the adjacent Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area
whose boundaries have been drawn to protect the treeless mountaintops
and leave the forested valleys to the loggers. Logging invades Tasmania’s South-West wilderness in the Huon valley,
not far downstream of the above photo.
This logging is ruining the integrity of the adjacent Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area
whose boundaries have been drawn to protect the treeless mountaintops
and leave the forested valleys to the loggers.
.
Tags: Bill Kelty, Forestry Tasmania, Gillard Labor Government, Independent Verification Group, Julia Gillard, Labor Party, Lara Giggings, old growth forest, recidivist logging, Tasmania, Tasmanian Forests Intergovernmental Agreement, Weld Forest
Posted in + Wild Tasmania, Tasmania (AU), Threats from Deforestation | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Saturday, January 7th, 2012
 Cathcart State Forest (NSW) being logged in 2011
[Source: Australian Forests and Climate Alliance ^http://forestsandclimate.net/newsouthwales] Cathcart State Forest (NSW) being logged in 2011
[Source: Australian Forests and Climate Alliance ^http://forestsandclimate.net/newsouthwales]
.
Most of Australia’s native vegetation cover, over 75% of that predating the 1788 Colonial Invasion, has been ‘cleared’ – a euphemism for deforested, logged, destroyed, killed.
Today, as one travels around Australia and sees vasts areas of unproductive, degraded, denuded and abandoned farmlands – one questions why destroy more fragile environment? Yet the exploitative bastards are still hell bent on killing more native forest and bushland, even though they can’t properly manage the ‘already ‘cleared’ lands they’ve got. It is a short sighted insatiability, harking to a 19th Century ‘old blighty’ mindset of taming the land. It is deluded thinking that just because the native vegetation is green and looks fertile that it can be replaced for pasture and cropping and that new cleared land will be any different to that already cleared.
The Liberal-Labor governments and their rural National mates haven’t given a toss throughout the entire 20th Century and still couldn’t give a toss.
 Recent land clearing in the Daly River catchment area
Northern Territory, Australia.
Photo: Environment Centre NT Recent land clearing in the Daly River catchment area
Northern Territory, Australia.
Photo: Environment Centre NT
.
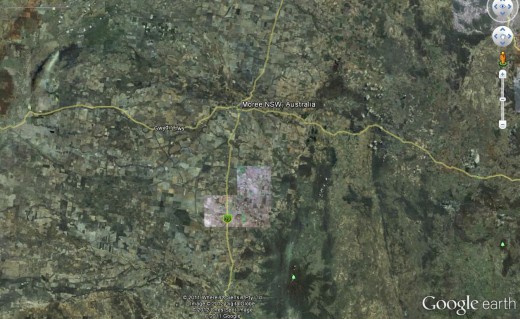 Moree region New South Wales – mainly deforested
Visit Google Earth and zoom into any area of NSW and see that most of it has been deforested
(click image to enlarge) Moree region New South Wales – mainly deforested
Visit Google Earth and zoom into any area of NSW and see that most of it has been deforested
(click image to enlarge)
.
Still across Australia in 2011, thousands of hectares of native forests continue to be deforested – albeit for farming, logging and development, or just bizarre bushfire abandonment. Not only is this occurring on private land, but in State Forests, which most people think are protected. Native forests on land are being cleared branded by State governments as ‘State Forests’ are simply not protected.
The native trees, flora and fauna are not protected from logging, bushfire, State-sanctioned arson (aka ‘hazard reduction‘), State napalming (aka indiscriminate ‘hazard reduction‘), indiscriminate State aerial poisoning with 1080, wildlife poaching, 4WD hooning, trail bike hooning, or even backpacker murdering. The watercourses (and the interconnected groundwater aquifers), that flow through State Forests are not protected from fishing, stormwater run-off, mine tailing contamination, farm pesticide and herbicide, industrial pollution.
.
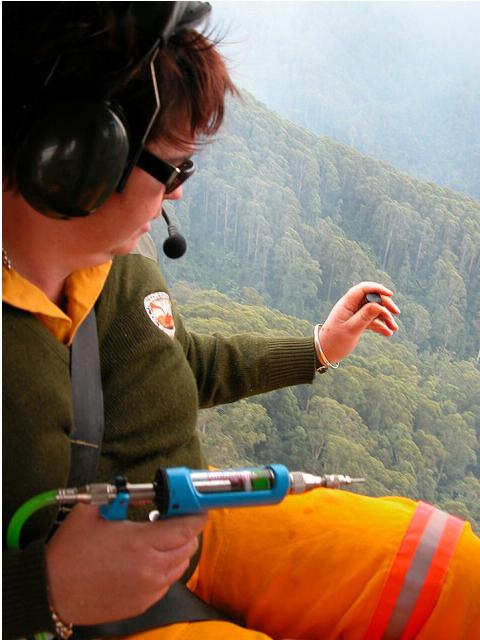 Helicopter Aerial Incendiary
Over Bindarri National Park, 20km south-west of Coffs Harbour, New South Wales
Yes, even our National Parks and Wildlife Service sets indiscriminate fires to National Parks! Helicopter Aerial Incendiary
Over Bindarri National Park, 20km south-west of Coffs Harbour, New South Wales
Yes, even our National Parks and Wildlife Service sets indiscriminate fires to National Parks!
.
For the likes of taxpayer funded government industrial loggers ‘State Forest’ is a euphemism ‘for not logged yet‘. This applies to the likes of Forestry Tasmania, VicForests, Forests NSW, Forestry SA (spot the naming trend), as well as the more aptly Queensland Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries, and likewise the Forest Products Commission of Western Australia.
It seems that doesn’t matter whether there is proof that there is an endangered and protected species such as the Long-Footed Potoroo in the Cann Valley State Forest or Drummer State Forest in Victoria, or protected Koalas in the Murrah/Mumbulla State Forests of New South Wales, or three identified endangered species, the wedge-tailed eagle, the swift parrot and the wielangta stag beetle in Tasmania’s Wielangta State Forests, the Liberal-Labor governments of those States turn a blind eye to deforestation.
It is only when self-funded local communities take the respective government logger to the Supreme Court and win that logging stops momentarily, such as in the recent Victorian Supreme Court case Environment East Gippsland Inc v VicForests [2010] VSC 335. In 2006, the Victorian State Government committed to increasing the conservation parks and reserves within the broader Brown Mountain area. Disregarding its elected master and ignoring any concerns for the ecological Precautionary Principle, State industrial logger VicForests, got stuck in with its mechanical clearfelling of old growth forests in the Brown Mountain area.
Not-for profit group Environment East Gippsland (EEG) self-funded and obtained numerous studies of the area indicated the presence of important threatened and rare species. EEG requested the Minister for Environment and Climate Change, Gavin Jennings, to make an interim conservation order to conserve critical habitat of the endangered Long-footed Potoroo, Spotted-tailed Quoll, Sooty Owl, Powerful Owl and Orbost Spiny Crayfish at Brown Mountain. Even then, the Minister for Environment and Climate Chang did not grant a conservation order, but instead increased the conservation area surrounding Brown Mountain. It took the overriding legal authority of the Supreme Court to stop the Victorian Government and its delinquent logger trashing protected old growth habitat.
 Victorian Labor Minister for Environment (etc), 2007-2010 Victorian Labor Minister for Environment (etc), 2007-2010
.
In March 2010, Forests NSW began controversial logging operations in the Mumbulla State Forest, south of Bermagui on the state’s far south coast. Despite being criticised, after a recent survey identified the forest as a key colony for the region’s remaining koala population, Forests NSW Regional Manager Ian Barnes says the logging must go ahead across 240 hectares of the forest, in order to satisfy a supply agreement with the timber industry.
 Deforestation is all about lining ones pockets out of ecological wanton exploitation
It’s a ‘wam bam thank you mam’ approach no different to what the Vikings did to the British in the eight Century.
Colonial Australians and their descendants are doing the same to Australian ecology in the 19th, 20th and 21st Centuries. Deforestation is all about lining ones pockets out of ecological wanton exploitation
It’s a ‘wam bam thank you mam’ approach no different to what the Vikings did to the British in the eight Century.
Colonial Australians and their descendants are doing the same to Australian ecology in the 19th, 20th and 21st Centuries.
Mr Barnes says the logging will not affect the koala habitat. “We’ve taken quite some effort to avoid any possible conflict there,” he says. “As anybody who reads the recent report will know, the koalas have been found in the eastern side of the forest, and our logging is planned for the western part, as far away as we can get from the koalas.”

Despite assurances, anti-logging campaigners have organised a vigil in the forest in an attempt to stop the logging. Conservationist Prue Acton says the activity will devastate the koala population.
“Why risk the only healthy koala colony left in the far south coast. For what? “ she said. “95% of what is going to be logged is going to end up at the Eden woodchip mill, be shipped to Japan for cheap copy-paper. What a disgrace.”
The Greens MP Lee Rhiannon says the Premier should put the protection of koalas ahead of the interests of logging companies. “The New South Wales Government has refused to end logging in the south east native forest but they should step in and stop the destruction of the koala habitat,” she said.
[Source: ‘Logging begins near key koala habitat‘, ABC, 20100330, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2010/03/30/2859615.htm?site=southeastnsw]
.
‘Loggers are clearing bushland at rising rate‘
[Source: ‘Loggers are clearing bushland at rising rate’, by Ben Cubby, Sydney Morning Herald, 20111221, ^http://www.theherald.com.au/news/national/national/general/loggers-are-clearing-bushland-at-rising-rate/2399764.aspx?storypage=0]

The amount of bushland being cleared by logging in NSW soared last year to the highest level since state-wide records began in 1988. An area equivalent to 138,400 football fields was cleared for crops, forestry or infrastructure, says a government report.
The Office of Environment and Heritage said the rise in logging was probably cancelled out by regrowth, leading to no net loss of trees, though its most recent survey took place in 2008, before the land clearing spike. It said the reasons for the logging increase were unclear.
”[The] most likely factors relate to market demand and favourable climatic conditions and [they] can be expected to fluctuate over time,” a department spokesman said. ”It is also possible that recent changes in forestry methods are more readily detectable by satellite monitoring.”
Environment groups said the annual vegetation report was evidence that logging companies were operating in an unrestrained manner.
Bushfires remain the biggest destroyer of forests in the state, leading to a net loss of 48,300 hectares in 2010, the report said.
.
But logging activities now come a close second, accounting for the removal of 42,700 hectares of trees in 2010. This is up from 31,000 hectares the previous year, and an average of about 21,000 hectares a year since 1988.
About 21,200 hectares of bushland was cleared in 2010 to make new areas for crops and grazing, while 5300 hectares were cut down to make way for roads, factories and housing.
”The NSW government is currently conducting a review of native vegetation controls,” said the chief executive of the Nature Conservation Council of NSW, Pepe Clarke. ”They should take this report as a warning – what is required are stronger land- clearing laws that do more to protect the environment, not weaker ones.”
The Wilderness Society said the government had ”failed in its promises to restrain land clearing, resulting in rapid and accelerating degradation of wildlife habitat and water catchments.”
The most recent State of the Environment report found that there had been no net loss of ”woody cover” across NSW between 2003 and 2008.
”This is because, although clearing has occurred over that period, there has also been an equivalent amount of regrowth including government sponsored environmental and forestry planting programs conducted by private landholders and state forests, within crown forests areas,” the department said.
”Notwithstanding no net loss over the whole state, some regions have experienced net declines in woody cover.”
The report uses the international definition of ”woody cover”, which includes land at least 20% covered by the crowns of trees higher than 2 metres, a description which would include relatively open country.
The introduction of a satellite monitoring system for land clearing last year appears to have increased the level of prosecution for illegal land clearing on private property. On crown lands, the number of prosecutions has increased threefold, from a low base, since 2007.
In 2010, the government received 471 reports of suspected illegal land clearing.
.
‘Landowners sent satellite images identifying land clearing‘
[Source: ‘Landowners sent satellite images identifying land-clearing’, NSW Department of Environment (etc), Media release: 14 May 2010, ^http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/media/DecMedia10051404.htm]
.
NSW Department of Environment Climate Change and Water (DECCW) today began a high tech education campaign to encourage compliance with native vegetation laws by sending letters to landholders including before and after satellite pictures identifying land clearing.
DECCW Director-General Lisa Corbyn said the letters were part of an ongoing education program to encourage compliance with the laws and inform landowners of the proper channels available to them if they want to clear native vegetation.
“We’ve been using satellite technology for some time to identify changes in vegetation cover that may warrant further investigation,” Ms Corbyn said.
“Now we are also using the technology as an education tool. From today, advisory letters will be sent to landowners including before and after satellite pictures showing that vegetation has been cleared on their land.”
Ms Corbyn said the letters aim to inform to the landowner that the satellite imagery has picked up that vegetation had been cleared and highlight the proper channels available to them under the legislation to allow clearing of native vegetation, such as property vegetation plans.
The letters support other tools used by DECCW to encourage compliance with the legislation, including strategic investigations, prosecutions, penalty notices, stop work orders, remedial directions, warning and advisory letters.
The letter also alerts landowners to incentive funding available to restore and protect native vegetation on their properties.
The Native Vegetation Act was introduced in 2003 to bring an end to broadscale land-clearing in NSW. Since then, more than 400,000 hectares of native vegetation has been conserved or rehabilitated on private land through property vegetation plans (PVPs) and 1.6 million hectares has been managed for thinning and invasive native scrub management.
.
Over 60 % of the native vegetation in NSW has been cleared, thinned or substantially disturbed.
.
The impacts of native vegetation clearing have included the extinction of 77 plant and animal species, soil erosion, increased dryland salinity and a decline in water quality.’
.
2003: ‘Clearing rate in NSW 116,000 to 216,000 hectares per year: NSW Govt report’
[Source: ‘Clearing rate in NSW 116,000 to 216,000 hectares per year: NSW Govt report’, by Stephanie Peatling, Environment Reporter, Sydney Morning Herald, 20031117, ^http://www.sydneyalternativemedia.com/id64.html]
.
The equivalent of up to 200,000 football fields may be illegally stripped of native trees and grass each year in NSW, figures suggest.
The first estimates on the extent of the clearings, which the Department of Natural Resources field staff prepared for the Government’s vegetation taskforce, suggest the figure could be as high as 100,000 hectares a year. The figures show between 150,000 hectares and 560,000 hectares were illegally cleared between 1997 and 2002.
The advice is the first official guess at NSW’s illegal clearance levels. The highest rates are in the Barwon, Central West and Far West regions where much of NSW’s remaining native vegetation is located.
The figures have shocked environmentalists, who stress the urgency of making changes to the state’s natural resource management system, which Parliament is debating this week.
A Wilderness Society campaigner, Francesca Andreoni, said: “The new system needs to be fair to everyone, particularly farmers doing the right thing.
“The shocking extent of illegal clearing confirms the urgent need for the Government to implement its decision to end broadscale clearing.”
Figures recording the rate of illegal land clearing each year are almost impossible to compile because it so hard to charge people who breach native vegetation laws. There is also a complicated system of exemptions which allow people to clear land for purposes such as maintaining fire access trails.
Monitoring illegal clearing is potentially dangerous for departmental compliance officers. After reports of illegal clearing earlier this year on a property near Nyngan, in the state’s west, department officers were prevented from entering the property by an angry crowd of up to 150 people.
.
When the amount of land illegally cleared is added to land that is legally approved for clearance, the department estimates between 700,000 hectares and 1.3 million hectares of land were cleared between 1997 and 2002.
.
The figures suggest clearing was faster than the Department of Natural Resources’ previously admitted figure of about 60,000 hectares a year. That figure would give NSW the second-highest clearing rate in the country behind Queensland.

Debate on the Government’s package to overhaul native vegetation laws, based on an election promise to end broad-scale clearing, will take place this week. Last month the Premier, Bob Carr, announced a $406 million deal between farmers and environmentalists to end broad-scale clearing.
Most of the money is expected to go towards such things as tree planting and fencing waterways to help counter salinity and erosion. But local authorities may also compensate farmers for not clearing land. Clearing will still be allowed where it is deemed environmentally necessary.
Under the new system, natural resource management is being overhauled. Thirteen catchment management authorities will replace 19 catchment management boards, 20 regional vegetation committees and 33 water management committees.
Scientists often name land clearing as one of Australia’s most urgent environmental concerns. It contributes to soil salinity, loss of biodiversity and greenhouse gas emissions because carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere when the cleared timber is disposed of, usually through burning.
.
‘Green groups attack logging growth’
[Source: ‘Green groups attack logging growth’, by David Bancroft, My Daily News, 20111229, ^http://www.mydailynews.com.au/story/2011/12/29/green-groups-attack-logging-growth/]
.
Environment groups have banded together to criticise the level of logging occurring in New South Wales. The Nature Conservation Council, The Wilderness Society, National Parks Association, the Northern Inland Council for the Environment and the North Coast Environment Council have issued a joint warning that iconic and endangered species are being threatened by land clearing.
 Illegal deforestation for fire wood, near Taralga, on the western edge of the Blue Mountains
Source: ^http://www.orchidsaustralia.com/article_%20conservation_no3.htm Illegal deforestation for fire wood, near Taralga, on the western edge of the Blue Mountains
Source: ^http://www.orchidsaustralia.com/article_%20conservation_no3.htm
.
In a joint press release, the groups said the NSW annual report on native vegetation released by the Office of Environment and Heritage (Ed. yet another money wasting name change) this month showed 2009/10 was the “worst year on record for clearing of native bushland”.
.
The Wilderness Society campaigns manager Belinda Fairbrother said the report showed that in 2009/10 an area equating to 138,400 football fields was cleared for crops, forestry or infrastructure.
.
“This is higher than any other year since records commenced in 1988 and shows the NSW Government has failed in its promises to restrain land clearing, resulting in rapid and accelerating degradation of wildlife habitat and water catchments,” she said.
North Coast Environment Council president Susie Russell said the report made a sad end to the International Year of Forests.
“The area cleared for forestry in 2009/10 was almost five times greater than it was in 1988/89,” she said.
“It reveals a massive increase in the rate and intensity of logging in NSW, which will be causing untold damage to the extraordinary high diversity forests of north-east NSW.”
Nature Conservation Council chief executive officer Pepe Clarke said land clearing was recognised as the single greatest threat to wildlife in Australia.
“It causes the death of birds and animals, the extinction of species, leads to the poisoning of soils from salinity and makes a major contribution to global warming,” he said.
.
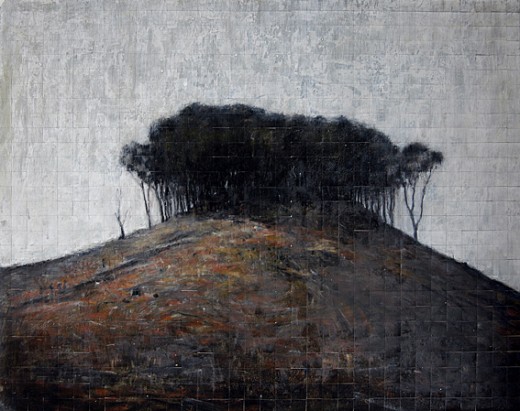 The Liberal-Labor Party ‘Island Vision’ for Australia’s State Forests
‘The Hill’ (Penrose State Forest, NSW) 2007, drawing by James King The Liberal-Labor Party ‘Island Vision’ for Australia’s State Forests
‘The Hill’ (Penrose State Forest, NSW) 2007, drawing by James King
^http://www.jamesking.com.au/drawings.html
.
Tags: 1788 Colonial Invasion, Cathcart State Forest, deforestation, Eden woodchip mill, fire wood, Forests NSW, Google Earth, hazard reduction, Helicopter Aerial Incendiary, Island Vision for Australian State Forests, koala habitat, land clearing, Logging, Long-footed Potoroo, Murrah/Mumbulla State Forests, not logged yet, Orbost Spiny Crayfish, Powerful Owl, precautionary principle, Sooty Owl, spotted-tailed quoll, State-sanctioned Arson, VicForests, Wielangta State Forests
Posted in Koalas, Owls, Quolls, Threats from Bushfire, Threats from Deforestation, Threats from Farming | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Wednesday, January 4th, 2012
 Carcinogenic Dioxin labeled as ‘Agent Orange’
was used as a widespread ecological exterminator by the United States and Australian
governments in last century’s US War Against the Vietnamese People Carcinogenic Dioxin labeled as ‘Agent Orange’
was used as a widespread ecological exterminator by the United States and Australian
governments in last century’s US War Against the Vietnamese People
.
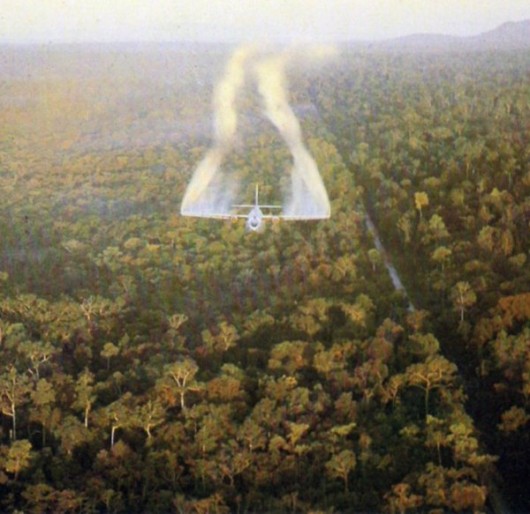
Agent Orange is the code name for one of the herbicides and defoliants used by the US military as part of its herbicidal warfare program, Operation Ranch Hand, during the Vietnam War from 1961 to 1971.
A 50/50 mixture of 2,4,5-T and 2,4-D, it was manufactured for the US Department of Defense primarily by Monsanto Corporation and Dow Chemical. The herbicides used to produce Agent Orange were later discovered to be contaminated with TCDD, an extremely toxic dioxin compound. It was given its name from the color of the orange-striped 55 US gallons (210 L) barrels in which it was shipped, and was by far the most widely used of the so-called “Rainbow Herbicides”.
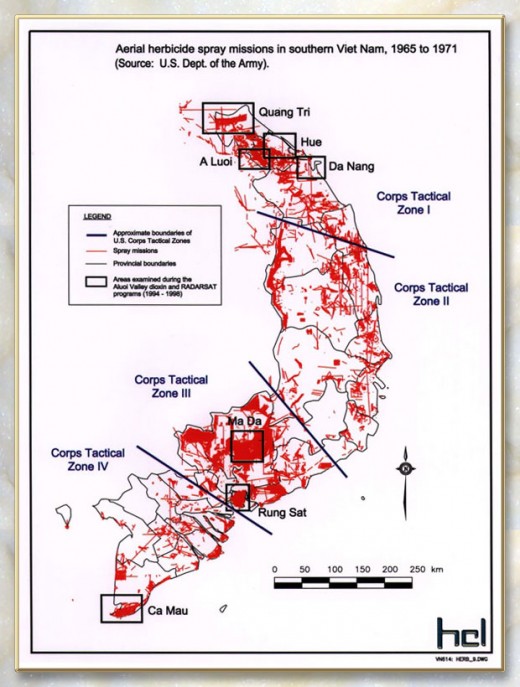
During the Vietnam war, between 1962 and 1971, the US Army sprayed 20,000,000 US gallons (80,000,000 L) of chemical herbicides and defoliants in Vietnam, eastern Laos and parts of Cambodia, as part of Operation Ranch Hand. The program’s goal (Ed: tactical theory) was to defoliate forested and rural land, depriving guerrillas of cover; another goal was to induce forced draft urbanization, destroying the ability of peasants to support themselves in the countryside, and forcing them to flee to the US dominated cities, thus depriving the guerrillas of their rural support base and food supply. [Read More]
Source: US Veterans Contact Point & Information Center, ^http://www.usvcpic.us/?p=1835]
.
 United States Congress approval of widespread defoliant poisoning
of Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia
The US Military code named it ‘Operation Ranch Hand’
during the US declared Vietnam War from 1961 to 1971
^http://www.the-savage-flsjr.com/img/new%20page%203.htm United States Congress approval of widespread defoliant poisoning
of Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia
The US Military code named it ‘Operation Ranch Hand’
during the US declared Vietnam War from 1961 to 1971
^http://www.the-savage-flsjr.com/img/new%20page%203.htm
.
Agent Orange Human Effect:
.
‘It is the war that will not end. It is the war that continues to stalk and claim its victims decades after the last shots were fired (2). The use of Agent Orange still has an effect on the citizens of Vietnam today. It has poisoned their food and creating health concerns. This chemical has been reported to cause serious skin diseases as well as a vast variety of cancers in the lungs, larynx, and prostate. Children in areas exposed to Agent Orange, or have parents who were exposed to agent orange during the war, have been affected and have multiple health problems–including cleft palate, mental disabilities, hernias, and extra fingers and toes, and many other birth defects.’
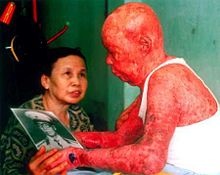
‘Recent laboratory tests of human tissue samples ( blood, fat tissue, and breast milk) taken from veterans who were exposed during the war and people living in sprayed areas revealed levels of dioxin higher than levels found in people living in non-sprayed areas of Vietnam as well as people living in industrialised countries. The most noteworthy are the levels of dioxin in breast milk. The high level of dioxin in nursing mothers shows how contamination spreads and bio-acumulates from mothers to their children (5).
Epidemiological studies show an elevated rate of diseases and disorders in people exposed to dioxin. These include high rates of cancers, abnormalities during pregnancies, neurological and metabolic disorders, and especially birth defects.’

Agent Orange Environmental Effect:
.
The consequences of spraying these toxic chemicals continue to have devastating effects on the environment. Millions of gallons of Agent Orange caused a great ecological imbalance.
.
‘It destroyed timber, wild animals and forest products.’
.
Without forest cover to retain water, flooding in the rainy season and drought in the dry season has adversely affected agricultural production. Topsoil is easily washed away, further hindering forest recovery. While the uplands have been and continue to be eroded, the lowlands have become choked with sediment, further increasing the threat of flooding.
[Source: ^ http://vietnamartwork.wordpress.com/war-end-agent-orange-effect/]
.
 Deforested and still contaminated Cam Lo, Vietnam
(Photo by Dr. P.T. Dang, 2004) Deforested and still contaminated Cam Lo, Vietnam
(Photo by Dr. P.T. Dang, 2004)
.
‘Over 30 years after the war, forest ecosystems on these hills south west of Cam Lo and most landscape in Quang Tri Province, Vietnam, damaged by Agent Orange and by heavy bombing have not been able to recover.
Dioxins in the soil, river bed, and in the food chain are serious sources of health threat; bomb craters (encircled) dotted the landscape, obstruct farming and provide excellent breeding ground for malaria, dengue and other disease transmitted mosquitoes; and unexploded ordnance (UXO’s) still buried in the ground continue to be extremely hazardous to people living in the area.’
[Source: ^http://www.tc-biodiversity.org/vn_ecorestoration_e1.htm]
.
‘Agent Orange cancer deaths probe – Innisfail forests’
.
[Source: ‘Agent Orange cancer deaths probe’, The Australian, sourced from AAP, 20080518, ^http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/agent-orange-cancer-deaths-probe/story-e6frg6oo-1111116372310]  Agent Orange ‘secretly tested’over the rainforest
at the back of Innisfail, Far North Queensland, Australia in 1966 Agent Orange ‘secretly tested’over the rainforest
at the back of Innisfail, Far North Queensland, Australia in 1966
by the Australian Regular Army
.
‘Concerns that cancer deaths are higher in a north Queensland town where the Army tested chemical weapons at the start of the Vietnam War will be investigated by the (Queensland) state government, Premier Anna Bligh says. Australian military scientists sprayed the toxic defoliant Agent Orange on rainforest in the water catchment area of Innisfail in 1966, Fairfax reported today.
The sprayed site, where jungle has never regrown, lies on a ridge about 100 metres above the Johnstone River, which supplies water for the town in the state’s far north.
Figures from the Queensland Health Department show 76 people died from cancer in the town of almost 12,000 in 2005, 10 times the state’s average and four times the national average.
“Any concerns these residents have can and will be investigated thoroughly just as we have when there’s been complaints about unusual cancer rates at workplaces,” Ms Bligh told reporters in Brisbane.
“I would encourage these residents who have any concerns to talk to the Environmental Protection Agency.”
Ms Bligh would not say whether the Army should come clean about its testing of Agent Orange in the region.
“I am not even sure what the facts are behind any Defence Force action in that area,” she said.
“If there has been any suggestion the Defence Force has any matters they should deal with I would encourage people to talk to the federal government and we will be doing the same.”
Researcher Jean Williams, who has been awarded the Order of Australia Medal for her work on the effects of chemicals on Vietnam War veterans, found details of the secret tests at Innisfail in Australian War Memorial archives.
“These tests carried out between 1964 and 1966 were the first tests of Agent Orange and they were carried out at Gregory Falls near Innisfail,” she told Fairfax.
“I was told there is a high rate of cancer there but no one can understand why.
“Perhaps now they will understand.”
.
Ms Williams found three boxes of files in the archives, with one file, marked “considered sensitive”, showing the chemicals 2,4-D, Diquat, Tordon and diemthyl sulphoxide (DMSO) were sprayed on the rainforest.
.
“It was considered sensitive because they were mixing together all the bad chemicals, which just made them worse,” she said.
Innisfail RSL president Reg Hamann, who suffers cancer after being exposed to Agent Orange while fighting in Vietnam, said his children had been born with health issues.
“The amount of young people in this area who die of leukaemia and similar cancers to what I got from Agent Orange is scary.
“The authorities are scared of digging into it as there would be lots of law suits.”

.
Agent Orange being used in the Amazon – July 2011
[Source: ‘Vietnam Era Weapon Being Used to Clear the Amazon’, by Stephen Messenger, Business / Corporate Responsibility, TreeHugger, 20110705, ^http://www.treehugger.com/corporate-responsibility/vietnam-era-weapon-being-used-to-clear-the-amazon.html]
.
Agent Orange is one of the most devastating weapons of modern warfare, a chemical which killed or injured an estimated 400,000 people during the Vietnam War — and now it’s being used against the Amazon Rainforest.
According to officials, ranchers in Brazil have begun spraying the highly toxic herbicide over patches of forest as a covert method to illegally clear foliage, more difficult to detect that chainsaws and tractors.
.
In recent weeks, an aerial survey detected some 440 acres of rainforest that had been sprayed with the compound — poisoning thousands of trees and an untold number of animals, potentially for generations.

Officials from Brazil’s environmental agency IBAMA were first tipped to the illegal clearing by satellite images of the forest in Amazonia; a helicopter flyover in the region later revealed thousands of trees left ash-colored and defoliated by toxic chemicals. IBAMA says that Agent Orange was likely dispersed by aircraft by a yet unidentified rancher to clear the land for pasture because it is more difficult to detect than traditional operations that require chainsaws and tractors.
Last week, in another part of the Amazon, an investigation conducted by the agency uncovered approximately four tons of the highly toxic herbal pesticides hidden in the forest awaiting dispension. If released, the chemicals could have potentially decimated some 7,500 acres of rainforest, killing all the wildlife that resides there and contaminating groundwater. In this case, the individual responsible was identified and now faces fines nearing $1.3 million.
According to a report from Folha de São Paulo, the last time such chemicals were recorded in use by deforesters was in 1999, but officials say dispensing the devastating herbicide may become more common as officials crack down on the most flagrant types of environmental crime.
“They [deforesters] have changed their strategy because, in a short time, more areas of forest can be destroyed with herbicides. Thus, they don’t need to mobilize tree-cutting teams and can therefore bypass the supervision of IBAMA,” says Jerfferson Lobato of IBAMA.
While Agent Orange was originally designed to clear forest coverage in combat situations, its use became a subject of controversy due to its impact on humans and wildlife. During the Vietnam War, the United States military dispersed 12 million gallons of herbicide, impacting the health of some 3 million, mostly peasant, Vietnamese citizens, and causing birth defects in around 500 thousand children. Additionally, the chemical’s effect on the environment have been profound and lasting.
Last month, over three decades after Agent Orange was last used in Vietnam, the US began funding a $38 million decontamination operation there. Meanwhile, in the Brazilian Amazon, the highly toxic chemical was being discovered anew and sprayed over the rainforest.
.
  . .
Tags: 245T, 24D, Agent Orange, Amazon forest, Australian Government, birth defects, chemical herbicides, defoliants, dioxin, Dow Chemical, Gregory Falls, Innisfail, Jean Williams, Johnstone River, Mekong Delta, Monsanto Corporation, Operation Ranch Hand, TCDD, United States, Vietnam war, Vietnam War veterans
Posted in Amazon (BR), Mekong (VN), Threats from Deforestation, Threats from War | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Friday, December 30th, 2011
What area of old growth native forest has been saved from business-as-usual deforestation as a result of the United Nation’s declaration of 2011 as the International Year of Forests?
 In Tasmania frankly it’s been logging Business-as-Usual
for taxpayer-funded ‘Forestry Tasmania’
(Source: Still Wild Still Threatened,
^http://observertree.org/2011/12/22/mirandas-daily-blog-day-8/) In Tasmania frankly it’s been logging Business-as-Usual
for taxpayer-funded ‘Forestry Tasmania’
(Source: Still Wild Still Threatened,
^http://observertree.org/2011/12/22/mirandas-daily-blog-day-8/)
.
UN International Year of Forests 2011 – ‘Global Objectives‘?

This is (was) the official UN website: ^http://www.un.org/en/events/iyof2011/
.
Well, at the time of writing, the public relations material on the official UN website conveys a general message that the ‘Forests 2011‘ programme is intended “to strengthen global efforts to improve the state of forests” and draws upon its dedicated subsidiary United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF), adopting four Global Objectives:
- Reverse Forest Loss – reverse the loss of forest cover worldwide through sustainable forest management, including protection,restoration, afforestation and reforestation, and increase efforts to prevent forest degradation.
- Enhance Forest-based Benefits – economic, social and environmental benefits, including by improving the livelihoods of forest-dependent people.
- Increase Sustainably Managed Forests – including protected forests, and increase the proportion of forest products derived from sustainably managed forests.
- Mobilize Financial Resources – reverse the decline in official development assistance for sustainable forest management and mobilise significantly-increased new and additional financial resources from all sources for the implementation of sustainable forest management.
.
[Source: ^ http://www.un.org/en/events/iyof2011/forests-for-people/global-objectives/]
.
Sounds encouraging, but where are the stated deliverables?, key result areas?, key performance indicators?, programme targets?, UN budget to achieve these global objectives? Where is the implementation plan and the delegated implementation task force?
The website is thick on its public relations message, but thin on substance. In the absence of any mention of the means to achieve these four objectives, my initial reaction is that it is more motherhood and perhaps just about ‘raising awareness‘. But don’t we already know that deforestation is a critical global problem?

.
The aim of the UN International Year of Forests 2011 seems to have merely been “to raise awareness and strengthen the sustainable management, conservation and sustainable development of all types of forests for the benefit of current and future generations“.
.
It just sounds like more Forestry spin!
.
And ‘sustainable forest management‘ is a familiar phrase and one bandied about not by environmentalists, but by forestry industry – i.e. industrial loggers. Type ‘sustainable forest management’ in Google at look at the websites results:
- Australian Government Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry (i.e. derives revenue from logging)
- Australian Forest Education Alliance (AFEA) – includes members from Australian Forest Products Association, Forests NSW, Forest Education Foundation Tasmania, Forest and Wood Products Australia, Primary Industries and Resources South Australia, Forestry Sustainable Forestry Program (Southern Cross University), NSW Forest Products Commission WA, VicForests (i.e. all derive revenue directly from logging, or subsidised by industrial loggers)
- Forestry Tasmania (i.e. derives revenue from logging)
- Forests NSW (i.e. derives revenue from logging)
- Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (encouraged forest be used for wood production)
- The Institute of Foresters of Australia
- Department of Sustainability and Environment (Victoria) (encouraged logging and burning of native forests)
- etc.

.
UN International Year of Forests 2011 – ‘Global Achievements‘?
.
The only other information that may be gleaned from the official UN site covers topics such as promotional events, films, photos, collaborative global partner organisations plus some forest statistics, a few online publications but that’s about it. So today on 30th December 2011 as the International Year for Forests draws to a close, what has the UN programme actually achieved?
What area of the world’s native forests has been protected from otherwise business-as-usual deforestation? What has stopped Forestry Tasmania and its band of loggers from their business-as-usual holocaust treatment of Tasmania’s endangered ancient native forest ecosystems?
Answer: More PR funding for the UN’s next programme?
.
Australian Government’s endorsement of International Year of Forests 2011
.
Rather than convey an assessment here, I shall just quote from the Australian Government’s website dedicated to supporting this programme (before it vanishes):
.
[Source: ^ http://www.internationalyearofforests.com.au/]
.
Australia’s Forests
.
‘Australia has some of the most beautiful and productive forest areas in the whole world. These fantastic and magical places mean a lot of different things to different people. Some of us work with the wood from the forests. Some work with the creatures that live in the forests. Some of us live in the forests and some of us play in the forest (camping, hiking, exploring) and some of us just love looking and being in a forest!
‘Without a doubt what ever your use, be it a little or a lot, Australian’s should be proud of Australia’s forests!
‘The United Nations announced 2011 as the International Year of Forests. Australians can unite and celebrate our sustainably managed forests and the diversity that our forests bring to our lives. Our forests give us wood that we use every single day and these very same forests give us the best playground that our kids could ever hope for. Australia’s forests are used by everyone and are the best in the world!

.
Ministers Address
.
‘Australia has about 4 per cent of the world’s forests on 5 per cent of the world’s land area, and has one of the best managed forestry sectors in the world.
‘The nation’s forests, and the products they produce, provide significant employment, environmental and recreational benefits to communities across Australia. Australia’s forestry and wood manufacturing sector employs nearly 76,000 people, many in regional areas, and generates around $7 billion worth of wood and paper products annually.
‘Across the nation the forests in conservation reserves cover over 23 million hectares. These reserves provide recreational benefits for communities and contribute to the 12 billion tonnes of carbon stored by Australian forests. Industry and government have been working hard to make sure our forests remain sustainable and viable for the long-term.

‘The Australian Government recognise the importance of World Forestry Day and the International Year of Forests and has actively supported both initiatives. This year the Gillard Government intends to release legislation to ban the importation of timber products that have not been legally harvested. This law will contribute to global efforts to stop illegal logging, provide for sustainable forest products made in Australia and reduce unfair competition. The Gillard Government remains committed to promoting sustainable forestry initiatives and encourages people to celebrate the International Year of the Forest.’
Senator Joe Ludwig,
Minister for Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry
.
And guess who’s embraced the 2011 International Year of Forests with public relations relish?
.
 Forestry Tasmania Forestry Tasmania
“Congratulations to Forestry Tasmania (FT) who held a successful Tasmanian launch of International Year of Forests. Held in Hobart on 25 January the ‘forest in the city’ event proved to be a popular summer holiday diversion with a steady stream of families, shoppers and naturalist flowing in to the Melville Street Dome throughout the afternoon.”
.
[Source: ^http://www.internationalyearofforests.com.au/news.php]
.
.
‘International Year of Forests 2011 off and running in Tasmania’
.
[Source: Forestry Tasmania website, 20110131, ^http://www.forestrytas.com.au/news/2011/01/international-year-of-forests-2011-off-and-running-in-tasmania?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed:+forestrytas+%28ForestryTas.com.au+News+and+Topics%29]
..
‘Forestry Tasmania (FT) kicked off its celebrations for the United Nations International Year of Forests 2011 with an open day at the ‘forest in the city’ in its Hobart headquarters on 25 January. The event proved to be a popular summer holiday diversion, with a steady stream of families, shoppers and naturalists flowing into the Melville Street Dome throughout the afternoon. Their curiosity was rewarded by science and fire fighting displays, indoor abseiling, and even the opportunity for the young (and young at heart) to have their photo taken with ‘Krusty’, FT’s very own giant freshwater crayfish.
 Forestry Tasmania’s promotional campaign for the International Year of Forests 2011
…to educate children early on that Forestry is good for native forests.
Tasmania’s endangered Giant Freshwater Crayfish just loves loggers destroying its habitat.
Get ’em while they’re young Bob! Forestry Tasmania’s promotional campaign for the International Year of Forests 2011
…to educate children early on that Forestry is good for native forests.
Tasmania’s endangered Giant Freshwater Crayfish just loves loggers destroying its habitat.
Get ’em while they’re young Bob!
.
Forestry Tasmania’s General Manager Corporate Relations and Tourism, Ken Jeffreys, said the open day was just a taste of things to come, with a 12-month calendar of events planned to celebrate the International Year of Forests.
“We have a number of exciting projects scheduled over the next year, such as the opening of new accommodation at Tahune, to be called the AirWalk Lodge.
“This development will, for the first time, see family accommodation available at one of Tasmania’s most highly visited tourism attractions. It will allow our guests to spend a full day experiencing all of the activities on offer at the AirWalk, as well as the many other attractions on offer in the Huon Valley.
“The year will also see a number of high-profile sporting events on state forest, including mountain biking and the multi-sport Ben Lomond Descent.
“And one of our bursary recipients, Shannon Banks, is going to attempt to visit all 52 of our recreation and tourism attractions around the State over the year. She’ll be writing a blog about her adventures, which we hope will inspire Tasmanians to experience the wonders of the forests in their own backyard.”
.
Mr Jeffreys said FT’s staff were excited by the opportunities presented by the International Year of Forests 2011.
“This year, we want to show the community that we are proud of the work we do to ensure the full range of forest values are maintained in perpetuity. Our staff worked hard to create displays for the launch that were fun and informative. The public’s reception showed us that there is a great deal of interest, and open-mindedness, about the way our forests are managed.”
.
Speech notes Simon Grove (Conservation Biologist with Forestry Tasmania – Division of Forest Research & Development):
.
‘Before I hand over to Rebecca White MHA to officially launch the International Year of Forests, I’ve been asked to say a few words about what our forests mean to the people that work here in Forestry Tasmania. Since our values come from our personal life-experiences, all I can do is tell you my own story, while recognising that every one of us here has their own story too.
I work as a researcher, a conservation biologist, with Forestry Tasmania. In some ways I deal with the meat in the sandwich that is forestry today – what does nature have to say about how we manage – or should manage – the forests in our care? But I want to start at the beginning. Life is all about discovery, learning and figuring things out, and I was lucky to discover early in life that nature, and forests, can be an excellent source of inspiration and experimentation. So here are a few of my naturalists’ memories, going back to toddlerdom.
I remember:
- Figuring out that earthworms have bristles that work like legs – if you fill an empty milk-bottle with worms and then leave the milk-bottle in the kitchen, the worms climb out and slither all over the kitchen floor.
- Learning that if I sat very still in the woods, I could watch the native mice going about their lives – and I could even catch them in my hands – but that they would bite my little sister’s hands if she tried the same thing.
- Learning that bumblebees loved the nectar of honeysuckle flowers as much as I did – and that they wouldn’t sting if I picked them up to enjoy the sensation of having them buzzing around in my cupped hands – but that they would sting my little sister’s hands if she tried the same thing.
- Discovering that it wasn’t only nasty wasps that filled the summer air with their droning, but beautiful flower-loving hoverflies – but little sisters aren’t always good at telling them apart.
- Realising that hungry ground-beetles eat lizards if you keep them in the same cage and don’t feed them.
- Learning that baby starlings abandoned by their parents get too hot if you try and incubate them on the boiler.
- Discovering that tadpoles kept in a glass jar don’t turn into frogs unless you give them some land to climb out onto.
- Realising that flower-presses were designed for delicate plants such as dandelions, and not for cacti.
- Learning that seashells brought back from the beach get very smelly if they still have their animals in them.
- Discovering that puffball fungi give off clouds of spores if you wee on them.
- Discovering that blackbirds’ eggs taste as good as chooks’ eggs if you fry them up on a camping stove in the garden.
- Figuring out that foxes eat cherries – you can find the stones in their poos.
- Figuring out that I could make wonderfully whiffy stink-bomb mixture by adding all sorts of sordid ingredients – dog-poo, apple-cores, ink – to the liquid accumulating in the bottom of a tree-hollow; but that if I then added real chemical stink-bomb ingredients to this then I ended up with dead-maggot stew instead.
.
We all have stories like this. (Ed: perhaps only at FT) In retrospect, we can see that they make us who we are today. Our challenge is to ensure that the next generation is encouraged to explore and experiment too.
I didn’t grow up in Tasmania, but the other side of the world in England. But I don’t think it would have made much difference to my outlook as a child. Nature’s all around us, and children the world over are tuned into it. If it’s nurtured, as it was in me, the empathy for nature can grow. Otherwise it may die away. The presence here today of so many families and children is testament to the amount of nurturing going on around us – which is wonderful to see. And what better place to do so than in our forests.
Some of us are lucky in that as adults we still get to liberate our inner child from time to time – every day if we’re very lucky. That’s how I’ve managed to live my life since leaving school – right through the years of university study; of working with nature conservation organisations in the UK; of working in Uganda as a conservation trainer in the forest department and in Indonesia as a training adviser on an international sustainable forest management project. It’s how I lived my life when I was researching rainforest insects in North Queensland for my PhD. And it’s how I have done so for the past decade as a conservation biologist here at Forestry Tasmania.
And despite what you might expect from media coverage of forestry issues, I don’t feel alone. Many people working in forestry here in Tasmania are naturalists at heart, and many more who wouldn’t call themselves naturalists nevertheless have a deep appreciation for the bush and an understanding of what makes it tick. Not so much sawdust in our veins, as bushdust – an empathy with the forests, and a recognition that we humans are not so much their lords and masters as their stewards.
My brother and I used to call chainsaws ‘long bottoms’, because to my ear they sounded like someone doing a very long fart. Later in my youth I came to see them as the conservationist’s friend, as we went about clearing wildling pines invading the heathland where rare birds nested. Today I know that chainsaws also have more prosaic functions – people use them to harvest trees so that they can be turned into products that we all use, such as timber and paper. This would be a tragic end for the forest if harvest were indeed the end-point. But it’s not, because experience shows that the elements of nature displaced by the harvest begin to move straight back in almost as soon as the chainsaws fall silent, and the forest begins to regrow and to fill with life again.
A background in natural history is good for making connections – among species and among natural processes. We learn that eagles feed on pademelons that graze on grasses and browse on young saplings; eagles nest in the old trees that grew up after the last wildfire and that escaped the browsing of pademelons; fungi and beetles recycle the trees – and even the eagles and pademelons – once they die. Eagles, trees, fungi, pademelons and beetles are all connected. Those of us steeped in natural history and ecology also make connections between humans and the rest of nature. We’re the original environmentalists. We recognise that the world faces not only a GFC but also a GEC – a global environmental crisis. I should emphasise that this crisis is not the outcome of sustainable forestry. But it is the cumulative outcome of all of our growing material demands outstripping the planet’s ability to supply. We all – especially our children – have to deal with the consequences.
In this context, we still expect the world’s remaining forests to be reservoirs of nature and yet to continue to supply our material and spiritual needs. It’s a big ask, but it can be done – certainly so in a place like Tasmania, with all the expertise in forestry and conservation at our disposal.
If I’ve discovered one big theme about the natural world during my life, it is that nature, for all its fragility, is remarkably resilient – think how forests recover after a bushfire. And the main take-home message from the forestry Masters course that I took at Oxford all those years ago, reinforced by daily experience since then, is that forestry is as much about people as it is about trees. Connecting the two concepts I come to a heartening conclusion. Through the increasing value that all of us place on our forests, they look set to become landscapes not of conflict but of reconciliation. Let’s see if we can use this International Year of Forests to further that end.
I’d now like to formally hand over to Rebecca White MHA, so that she can officially launch this International Year of Forests as Forestry Tasmania’s Ambassador.’
.
(Tasmanian) State Labor Member for Lyons and International Year of Forests Ambassador, Rebecca White MP, was on hand to officially launch Forestry Tasmania’s celebrations for 2011. She said the UN’s theme for the year, ‘celebrating forests for people’, had struck a deep chord with her.
“This theme resonated deeply with me, as it conveys the need to manage forests for many values, including conservation and sustainable development. It means that these values, which are often portrayed as being in conflict, are in fact intertwined. It also recognises that people are central to the effective management of forests.
“With careful, scientifically driven management, such as we have in Tasmania, there need not be a contradiction between conserving biodiversity and providing wood products and other non-commercial values from forests.
 Forestry Holocaust of the Tarkine, October 2009
Forestry Holocaust of the Tarkine, October 2009
.
“While not all values may be delivered in any one area of forest, they are delivered across the entire landscape. While there are of course a number of challenges confronting the forest industry at present, it’s nonetheless important to remember that our state forests provide skilled employment for thousands of Tasmanians, and indirect employment for many more in our rural and regional communities.
“And of course, our state forests also provide clean drinking water to our towns and cities, they store the equivalent of 24% of Tasmania’s carbon emissions each year, and they provide a host of recreation activities and tourism attractions that appeal to locals and visitors alike.”
 Upper Florentine old growth forest clearfelled by Forestry Tasmania in 2009,
situated behind Forest Defenders’ Camp Flozza
(Photo by Editor 20110928, free in public domain, click to enlarge) Upper Florentine old growth forest clearfelled by Forestry Tasmania in 2009,
situated behind Forest Defenders’ Camp Flozza
(Photo by Editor 20110928, free in public domain, click to enlarge)
.
World Deforestation Clock
.
- Each year about 13 million hectares of the world’s forests are lost due to deforestation, but the rate of net forest loss is slowing down, thanks to new planting and natural expansion of existing forests.
- From 1990 to 2000, the net forest loss was 8.9 million hectares per year.
- From 2000 to 2005, the net forest loss was 7.3 million hectares per year – an area the size of Sierra Leone or Panama and equivalent to 200 km2 per day.
- Primary forests are lost or modified at a rate of 6 million hectares per year through deforestation or selective logging.
- Plantation forests are established at a rate of 2.8 million hectares per year.
.
NOTE: 13,000,000 hectares/year = .412 hectares/sec
[Source of statistics: FAO Forest Resources Assessment 2005]
See the World Deforestation Clock at http://www.cifor.org/defclock.
.
Tags: clearfell, Corporate Relations, Forestry Holocaust, Forestry spin, Forestry Tasmania, giant freshwater crayfish, Logging, logging business as usual, sustainable forest management, tarkine, UN International Year of Forests, UN International Year of Forests 2011, United Nations Forum on Forests, Upper Florentine Forest, Upper Florentine Valley
Posted in Tasmania (AU), Threats from Deforestation, Threats from Greenwashing, Threats to Wild Tasmania | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Friday, December 30th, 2011
This is a scab: . .
These are Forestry Scabs:
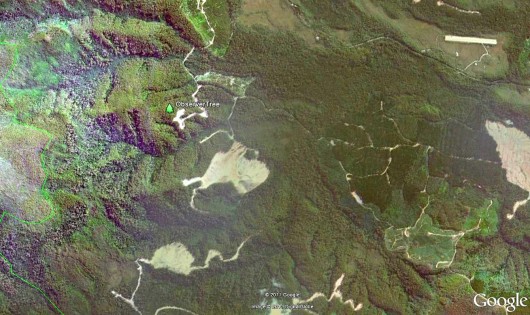 Forestry Scabs of clearfelled Tasmanian endangered old-growth forests
Google Earth reveals the clearfell truth behind the Forestry propaganda
(Click satellite image to enlarge – note environmental protestors’ ObserverTree)
To download Google Earth software (93MB), go to: ^http://www.google.com/earth/index.html Forestry Scabs of clearfelled Tasmanian endangered old-growth forests
Google Earth reveals the clearfell truth behind the Forestry propaganda
(Click satellite image to enlarge – note environmental protestors’ ObserverTree)
To download Google Earth software (93MB), go to: ^http://www.google.com/earth/index.html
.
This is an aerial close up of Forestry Scabs:
 Forestry Scabs pocking the endangered Upper Florentine Forest, 2011 Forestry Scabs pocking the endangered Upper Florentine Forest, 2011
.
 This is the ‘Forestry Plunder’
Old Growth which in the case of the Styx Valley, Forestry Tasmania labelled ‘Coupe SX015‘ This is the ‘Forestry Plunder’
Old Growth which in the case of the Styx Valley, Forestry Tasmania labelled ‘Coupe SX015‘
.
Recall 2006: ‘Forests protected: another tall story‘
.
[Source: ‘Forests protected: another tall story”, in Tasmanian Times, 20060327, ^http://tasmaniantimes.com/index.php/article/forests-protected-another-tall-story]
.
Two days after the election the police moved into the Styx Valley to apprehend a small band of protesters. An arrest was made and a 70-metre-tall tree holding a protest platform was blown up! Cable logging was set to resume in the Styx Valley of the Giants.
Yet last year both the state and federal Governments claimed that they had saved the giant trees of the Styx. Indeed, they claimed to have resolved the entire forests debate.
This week’s developments have given the lie to those claims. Not only is logging making a comeback in the Styx; it is also about to start in parts of the Weld and Upper Florentine that have never before seen a chainsaw. Other key areas are likely to follow, from the Tarkine in the far north-west, where there are still 400 square kilometres of threatened oldgrowth forest, to South Sister on the East Coast, Bruny Island in the south and the beleagured north-east highlands.
The Styx case is a classic example of how the governments deal with forest issues. One of the new reserves they have promised to create is the 336-hectare Styx Tall Trees Forest Reserve. This reserve occurs on either side of Skeleton Road, the road up which 4000 people marched on a cold, drizzly day in July 2003 to protest at logging.

The Reserve’s southern boundary occurs very close to the huge stump on which speakers at the rally delivered their speeches. The reserve contains several well-known giants, including the Chapel Tree — an 85-metre-tall giant which is the second most massive known living thing in Tasmania. It also contains the Mount Tree and Icarus Dream, which, at 96 and 97 metres respectively, are the tallest known trees in the Southern Hemisphere. The Two Towers, Gothmog, the Perfect Tree and the Andromeda Twins are other registered giants within the reserve.
Declaration of this reserve will be very welcome. However, cold hard scrutiny reveals that very little loggable forest has been conceded by the industry here. About 20 hectares were already in the informal Andromeda Reserve, which contains some of the tall trees mentioned above. In addition, Forestry Tasmania’s Giant Trees policy and protocols, adopted in the wake of the El Grande debacle, require the establishment of buffers of at least 100 metres radius around each registered giant. The abundance of giant trees in this patch of forest means that logging had already been severely curtailed.
In essence, the creation of the Styx Tall Trees Reserve is a minimalist recognition that little logging could have proceeded amongst these statuesque giants anyway.
.
Protected the bare minimum area
.
A look at the mapped boundaries of the reserve shows them to be very convoluted. That’s because the reserve has been designed to accommodate areas planned for logging.
Last year, Forestry Tasmania scheduled 26-hectare coupe SX18F. This created a cable-logged cut on the steep slopes immediately south-east of the Reserve. The imminent destruction of the tall oldgrowth forests in coupe SX15A will mark the southern edge of the reserve. Immediately west of the reserve is the already-logged SX13D and the scheduled SX13K. Later in the logging schedule come SX18E and SX13J.
 Forestry Tasmania logging the Styx Valley of its ancient old growth Forestry Tasmania logging the Styx Valley of its ancient old growth
.
The conclusions to be drawn from this are simple.
Forestry Tasmania protected the absolute bare minimum area of tall-eucalypt forest in the Styx Tall Trees Forest Reserve.
.
“Forestry Tasmana is now embarking on a program of ringing the reserve with new coupes. This appears to be an obvious bid to pre-empt any future expansion of the reserve. This strategy will have the effect of isolating the giants from adjacent protective forest. The reserve will become increasingly prone to the ‘edge effects’ of fire, wind and disease. This situation is not assisted by the messy design of the reserve.”
.
Forestry Tasmania will claim that it has protected these giants and met all of its legislated obligations. In fact, Forestry Tasmania has still failed to meet the targets set in the RFA for the protection of oldgrowth Eucalyptus regnans — the tallest flowering plant on Earth.
The Howard Government has been a party to this sham, providing millions of dollars of taxpayers’ funds to the logging industry and state government as ‘compensation’.

.
‘Forests Onslaught to Follow Election’
.
by Geoff Law, Tasmanian Campaign Coordinator, The Wilderness Society, 20060318, comment to an article in the Tasmanian Times of a speech made by Richard Flanagan, Parliament House Rally, Hobart, 16 March 2006, ^http://tasmaniantimes.com/index.php?/article/we-will-not-give-up/]
.
‘An onslaught of burning, logging and clearing in Tasmania’s forests will follow Saturday’s election, according to the Wilderness Society.
“New logging operations in the Styx, South Sister, Weld and Jackeys Marsh, huge new areas of tree-clearing, and another 30,000 hectares of burning are set to follow the election,” said the Society’s Tasmanian Campaign Coordinator, Geoff Law.
The burning program is set out in a brochure about forestry burn-offs distributed by Forestry Tasmania and FIAT in the Derwent Valley Gazette on Wednesday. It says: This autumn, the forest industry plans to prepare about 30,000 hectares of land for planting or sowing in patches scattered across Tasmania.
Logging is also poised to move into contentious forests in the Upper Florentine, at South Sister and unprotected parts of the Tarkine.
Mr Law said that his warning was based on:
- Forestry Tasmania’s attempt to log coupe SX15A in the Styx Valley, which was put on hold two weeks ago after the efforts of a handful of protesters. The logging machinery is poised and ready to go as soon as the election is out of the way.
- Forestry Tasmania’s interim draft Three Year Plan which has scheduled almost 16,000 hectares of tree-clearing for this calendar year as well as logging at South Sister, Jackeys Marsh, in the Weld and Upper Florentine Valleys and unprotected parts of the Tarkine
- The brochure on burning, which presents ‘Facts about the forest industry’s planned burning program during Autumn’ and which foreshadows 30,000 hectares of burning this autumn.’
 A Styx Legacy
A Eucalyptus regnans giant stump is all that remains of one of the huge trees
felled to make way for the logging road in coupe SX 15A in the Styx Valley.
^http://www.lexicon.net/peterc/Tasmania/Tas01.htm A Styx Legacy
A Eucalyptus regnans giant stump is all that remains of one of the huge trees
felled to make way for the logging road in coupe SX 15A in the Styx Valley.
^http://www.lexicon.net/peterc/Tasmania/Tas01.htm
.
‘Forestry Tasmania’s Sustainability Charter for Threatened species, communities and habitats‘
.
“Aim: Maintain viable populations of all existing animal and plant species and communities found in State forests.
This will involve:
- Increasing understanding of ecology and habitats of threatened species and communities and implementing appropriate management
- Active participation in the management of threatened species, communities and habitats
- Implementing specific strategies to protect threatened species and their habitats.”
.
 A rare giant Eucalyptus regnans of the nearby Upper Florentine
(Photo by Editor 20110928, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge) A rare giant Eucalyptus regnans of the nearby Upper Florentine
(Photo by Editor 20110928, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge)
.
2012 Year of the Forestry Scab?
.
In late 2011 and now going into 2012, Forestry Tasmania are at it again, trying to clearfell the Styx Valley of its old growth.
Get the lastest from the forest protest at The ObserverTree below Mount Mueller in the Styx Valley.
.
Tags: Andromeda Twins, Chapel Tree, coupe SX15A, Eucalyptus regnans, forestry scab, Forestry Tasmania, Google Earth, Gothmog, Icarus Dream, Mount Tree, old growth forest, Perfect Tree, Styx Forest, Styx Tall Trees Forest Reserve, Styx Valley, Styx Valley of the Giants, Tasmania, Tasmanian Times, The ObserverTree, Two Towers, Upper Florentine Forest
Posted in Tasmania (AU), Threats from Deforestation, Threats to Wild Tasmania | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Wednesday, December 28th, 2011
 [Source: Xπr, Dublin, c.2007] [Source: Xπr, Dublin, c.2007]
.
In February 2010, at the advent of the Chinese Year of the Tiger, the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) reported that tigers were in crisis around the world. With as few as 3,200 left of this endangered species compared to 100,000 a century ago, it was clear that this would be the vital tipping point for tigers.
Two key causes of the tiger’s plight are (1) poaching to feed consumer demand for tiger body parts, mostly for use in traditional Asian medicines (TCM) and folk remedies, and (2) deforestation as more and more forests are cleared for paper and palm oil, tiger habitat disappears daily.
.
‘New Study shows Bengal Tiger’s Habitat in Danger’
.
[Source: ‘New Study shows Bengal Tiger’s Habitat in Danger’, World Wildlife Fund, 20100119, ^http://www.worldwildlife.org/who/media/press/2010/WWFPresitem14914.html]
..
A new study by WWF scientists and partner organizations has found global climate change could shrink Bangladesh’s Sundarbans tiger habitat by 96 %, potentially reducing the tiger population to fewer than 20 breeding individuals!
An estimated sea level rise of 11.2 inches above 2000 levels by 2070 means this unique mangrove ecosystem could disappear within half a century.
 Bengal Tiger (Panthera tigris tigris)
© naturepl.com/Francois Sevigny / WWF Bengal Tiger (Panthera tigris tigris)
© naturepl.com/Francois Sevigny / WWF
.
Sundarbans Delta
.
The Sundarbans delta is the largest mangrove forest in the world.
This UNESCO World Heritage Site is shared by India and Bangladesh and sits at the mouth of the Ganges River. It is home to an estimated 254-432 Bengal tigers, the only tiger population adapted to live in mangroves. The tigers here regularly swim between islands and are the only tigers to have crabs and other seafood as an important part of their diet.
The area is an amazing ecosystem that houses a plethora of species including the spotted deer (the tiger’s prey), water birds, many kinds of fish, marine mammals, crocodiles, and snakes. The landscape naturally protects the area from natural disasters such as cyclones, storm surges, and wind damage. The mangroves are home not only to endangered fauna like tigers, but also to several million people who depend on the Sundarbans for their livelihoods.
The Bengal tiger population has already been under threat from poaching and habitat destruction and loss, and research suggests that the seas may be rising faster than originally thought.
Worldwide, tigers occupy only 7 percent of their historic range with as few as 3,200 left in the wild. The study encourages local governments to take immediate action to conserve and expand mangroves while cracking down on poaching. It suggests that globally, countries should work strongly on reducing greenhouse gas emissions in order to save the Sundarbans.
.
The Siberian (Amur) Tiger – Conservation Threats
.
[Source: ^ http://www.wcsrussia.org/Wildlife/AmurTigers/ConservationThreats/tabid/1468/language/en-US/Default.aspx]
.
The Siberian tiger is a tiger subspecies inhabiting mainly the Sikhote Alin mountain region with a small subpopulation in southwest Primorye province in the Russian Far East. In 2005, there were 331–393 adult-subadult Amur tigers in this region, with a breeding adult population of about 250 individuals.
The main threats to the survival of the Siberian Tiger are (1) poaching, (2) habitat loss, and (3) illegal hunting of ungulates, which are tigers’ main prey (Ed: looks similar to a lama). Because they increase access for poachers, roads are another important threat to the Siberian tiger. Intrinsic factors such as inbreeding depression and disease are also potential threats to this big cat, but are less understood.
 The Siberian tiger (Panthera tigris altaica), also known as the Amur tiger The Siberian tiger (Panthera tigris altaica), also known as the Amur tiger
.
Poaching
.
Roads in Amur tiger habitat, Russian Far East Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) research has demonstrated that human-caused mortality accounts for 75-85% of all Amur tiger deaths. Current estimates indicate that 20-30 tigers are poached in the Russian Far East each year, although actual numbers may be higher.
Population modeling based on Siberian Tiger Project field data suggests that poaching rates exceeding 15% of the adult female population could have dangerous repercussions, especially as tigers have fairly low population growth rates compared to other big cats. Analysis of mortality data in Sikhote-Alin Biosphere Reserve indicates that poaching rates may be at least this high in a significant area of Russian tiger range.
Tigers are most commonly poached for their fur and for their body parts, such as bones, that are used in Traditional Chinese Medicine. The opening of the border between China and Russia after the fall of the Soviet Union has now made it possible to easily transport goods to Chinese markets and beyond. Although tigers are a protected species in Russia, enforcement agencies have very limited ability to catch convict poachers, and, even when this happens, fines are relatively small and disincentives insufficient. Poaching problems are further exacerbated by low incomes in many rural areas of the Russian Far East – sale of a tiger skin and bones represents a substantial source of income for poor people in remote villages.
It is also common for hunters to poach tigers to eliminate competition for ungulates and for locals to kill tigers in retaliation for depredations on domestic animals such as dogs and cows.
.
Habitat Loss
.
In Russia, human population growth does not threaten habitat as it does in many other tiger-range countries. However, activities such as logging, grazing, various development projects and uncontrolled fires are all resulting in direct habitat loss in the Russian Far East. Habitat is increasingly being divided into isolated patches, particularly at the southern edge of Amur tiger range.
Logging takes place in most of Amur tiger habitat. Although existing guidelines for timber harvest are actually quite sufficient, significant illegal logging and overharvest still occur. Selective logging, rather than clear cutting, is most common in tiger habitat, and does not seriously impact the quality of the habitat, if access to the extensive road system is controlled (thereby limiting poaching).
Fires are another important form of habitat loss. Many local residents consider fires to be the main cause of loss of forest habitat in parts of Primorsky Krai, and Amur tigers avoid areas that have burned, as they provide neither adequate cover for hunting, nor the habitat needed for prey.
.
Illegal Hunting of Ungulates
.
Illegal hunting of ungulates such as deer and wild boar significantly reduce prey availability for tigers. While official estimates continue to report stable numbers of ungulates, many hunters and wildlife biologists believe that abundance of ungulates in the Russian Far East has decreased considerably over past 15 years. Analyses from WCS’s Amur Tiger Monitoring Program clearly demonstrate that ungulate numbers are often 2-3 times higher inside protected areas, which are nonetheless impacted by poaching, though to a lesser extent.
Low ungulate numbers also foster a sense of competition between hunters and tigers. When ungulates numbers are low, it is easy to blame tigers, even when the root cause of population declines is over-harvest by humans. When there is little prey available in the forest, tigers sometimes enter villages and prey on domestic animals, including dogs and livestock, which creates tiger-human conflict situations.
.
Roads
.
The number of roads in Amur tiger habitat is increasing steadily as logging activities and development push into even the most remote regions. Besides allowing greater access for poachers, roads increase tiger mortality from vehicle collision, and increase the probability of accidental encounters between tigers and people, leading to tigers being shot out of fear or opportunity.
Roads also provide poachers greater access to ungulate habitat, which reduces tiger prey abundance. Roads can be divided into two categories: primary roads, which are maintained year-round and provide access between villages and towns; and secondary roads, which are not regularly maintained but nonetheless allow access.
From 1992 to 2000 the Wildlife Conservation Society studied the fates of radio-collared Siberian tigers living in areas with no roads, secondary roads and primary roads. Our findings:
- 100% survival rate for adult tigers living in areas with no roads
- 89% survival rate for adult tigers living in areas with secondary roads
- 55% survival rate for adult tigers living in areas with primary roads
.
These results clearly demonstrate that the presence of both secondary and primary roads both greatly increase the odds of tigers being poached, and indicate the need for road closures and access control. (Ed. Main roads contribute to tiger road kill reducing tiger populations by about a half).
.
‘World tiger population shrinking fast’
.
..
[Source: ‘World tiger population shrinking fast‘, IOL, 20080312, ^http://www.iol.co.za/scitech/technology/world-tiger-population-shrinking-fast-1.392813]
.
The number of tigers in the world has diminished at an alarming speed in recent years, global conservation group WWF cautioned on Wednesday, blaming poaching for much of the decline. “We are left with roughly 3,500 tigers (2008) all around the world now,” Bivash Pandav, a tiger specialist at the World Wildlife Fund, said, pointing out that “five years back, the estimate was around 5,500 to 6,000.” [Ed: In 2010 total world population was 3,200, and in 2011?, 2012?]
.
In India, which is home to nearly half of the world’s tigers, or 1,400 animals,
the number of the big cats has shrunk by 60% over the past three to four years!
…Pandav said during a visit to Sweden.
A century ago, some 40,000 tigers roamed the Indian subcontinent, according to the WWF, which singles out poaching, widespread destruction of the tigers’ natural habitat and human hunting of their prey as the main causes of today’s dire situation.
“Poaching is primarily to meet the demand for tiger bones in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)… That’s the immediate reason behind the decline of tigers,” Pandav explained.
“The situation is pretty bad in the sense that they (the tigers) are rapidly being wiped out from many parts of their range,” he added.
.
According to the WWF:
- On the Chinese market, a dead tiger can be worth “tens of thousands of dollars”
- The United States is the world’s second largest market for tiger products.
.
Despite the daunting challenge of preserving tiger populations, Pandav insisted that “there is definitely hope,” pointing out that big cats “are prolific breeders (and) produce large numbers of offspring.”
“Despite all the problems, there are a couple of places in India (where tigers) are doing pretty well,” he said.
To rectify the overall situation however, the animals need access to forests, food and undisturbed habitats, Pandav said, insisting that the main priority was to protect the tigers from poachers and put “pressure on China to stop the farming of tigers.”
“The Chinese government is actively planning to legalise the trade (of tiger products) and if they legalise this trade then the demand for wild tigers is going to increase many fold,” he said, pointing out that people preferred products from wild tigers over farmed animals. That is going to be the death blow for the tigers in the wild,” he said.
.
‘Plight Tiger’
.
[Source: ‘Plight Tiger‘, by Neha Sinha, India Express, 20090101, ^http://www.indianexpress.com/news/plight-tiger/405197/]
..
‘At the beginning of this year, a ground-breaking, new, and scientific tiger census, which took two years to complete, announced that there were 1,411 wild tigers left in India. By November, the Government had admitted that of that number, 14 tigers had been poached this year. The figure actually may be nearly double.
The poaching cases registered and seizures of body parts of tigers this year show that around 27 of the big cats have been killed in 2008, making the number of wild tigers in India less than even 1,400, and showing that government efforts have failed so far to deter poachers.
“On an average, 25 tigers are poached every year”
.
…says an official from the NTCA. Data compiled by the WPSI shows an equal number, 27 tigers, were killed in 2007.
In January, a tiger survey commissioned by the Government indicated that there were only five-seven tigers left in Panna. Now, tiger experts fear the number may actually be just two. Kanha, also in Madhya Pradesh, lost a tiger to poaching by electrocution, using an 11,000-volt current, this November.
According to data compiled by the Wildlife Protection Society of India (WPSI), there have been 27 instances of tiger skins and parts being found in different parts of the country in 2008. The Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB), which came into existence this year, recovered a tiger skeleton from Gurgaon and two tiger skins from Himachal Pradesh, a case that involved a Tibetan national.
“Tiger killing may be higher than what recorded numbers tell us,” admits National Tiger Conservation Authority Member Secretary Rajesh Gopal. “Poachers are very clandestine and at times even a tiger carcass may not be found.”
A WCCB official said their main problem was that the trade in tiger parts was trans-country and inter-state, necessitating strong intervention from the Centre.
“Day before, we managed to get a case registered in Bihar for Dariya, a tiger poacher, who was arrested in December in Katni, Madhya Pradesh. A case had to be registered in Bihar where he is suspected to have poached tigers from the Valmiki tiger reserve. We have to expedite history-sheeting quickly to facilitate arrest of poachers who travel and escape extensively,” he added.
“The fact that tiger numbers are going down but poaching remains constant is a huge cause for concern. The number of tigers as per the Census is very low. If we don’t improve protection, India may well lose its tigers,” says Belinda Wright, Executive Director, WPSI.
The tiger census also shows another trend: that India’s tigers are now found only in areas with a high degree of protection, which is sanctuaries or existing tiger reserves. Recognising this, the NTCA has given approval to as many as 12 new tiger reserves this year, of which four — Pilibhit (Uttar Pradesh), Sunabeda (Orissa), Rapa Pani (MP) and Sahyadri (Madhya Pradesh) — have got in-principle approval.’
.
Videos on the plight of the Bengal Tiger
.
Videos in 2010 on the Bengal Tiger by big cat expert Dr. Alan Rabinowitz i, hosted by the BBC on its Lost Land of the Tiger series.
Click the following link then scroll down to watch the four episode extracts:
- Episode 1: ‘Fragmented Isolation‘
- Episode 1: ‘Tantalizing Tigers‘
- Episode 2: ‘Nowhere To Go‘
- Episode 2: ‘Population Patterns‘
.
.
.
What if tigers did become extinct?
.
[Source: ‘What if tigers did become extinct?’, World Wildlife Fund, ^http://wwf.panda.org/what_we_do/endangered_species/tigers/last_of_the_tigers/what_if_tigers_did_become_extinct_/]
.
.
Coextinction of other species
.
The tiger is at the top of the food chain in all the ecosystems it lives in. If one species in a food chain becomes extinct there is a knock-on effect on other species. The loss of a main predator can actually cause the extinction of a prey species as greater competition presents a threat to a species.
When the Bali and Javan tigers became extinct in the 20th century, poachers turned their attention to the Sumatran tiger. Which animal will be exploited into extinction once all the tigers are gone?
If tigers were to go, the forests which are currently protected as key habitat would be more likely to fall victim to illegal logging, conversion to agriculture and development. This leads to greater CO2 emissions and climate change. Deforestation currently accounts for 15% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Which species live alongside the tiger?
Many of the species which could be affected by the disappearance of tigers are also endangered and already fighting for their own survival. The 5 sub-species of tigers live in some of the most spectacular parts of the world which provide a home for some other amazing species, including:
- Brown bear
- Sloth bear
- Sun bear
- Dhole
- Elephant
- Clouded leopard
- Amur leopard
- Lion tailed macaque
- Musk deer
- Orangutan
- Rhino
- Saola
.
Tiger Reserves
.
Huangnihe River Nature Reserve
^http://www.ancientsites.com/aw/Places/District/1138640
.
India’s Panna Tiger Reserve
^http://www.pannatigerreserve.in/
.
Sundarbans Tiger Project
^http://www.sunderbansnationalpark.com/
.
Palamau Tiger Reserve
^http://projecttiger.nic.in/palamau.htm
.
Kanha Tiger Reserve
^http://projecttiger.nic.in/kanha.htm
.
Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve
^http://www.tadobatiger.com/
.
Hukawng Valley Wildlife Sanctuary
^http://www.wcs.org/news-and-features-main/a-valley-of-tigers.aspx
.
.
Read More About the Campaigns to Save Tigers from Extinction
.
^http://www.panthera.org/species/tiger/subspecies
.
^http://www.savetigersnow.org/
.
^http://www.internatyearofthetiger.org/plight.htm
.
^http://www.forevertigers.com/plight.htm
.
^http://www.bbc.co.uk/nature/life/Tiger
.
Chinese unethical handing of Tigers…
.
A herd of Siberian tigers chased and devoured live chicken flung at them from a tourist safari bus at the Siberian Tiger Forest Park in Harbin, north-west China, on Tuesday.

Siberian Tigers Grab at Live Chickens Tossed at Them to Tourists’ Delight in China
20111227 (two days ago)
Photo by Sheng Li
.
[Source: ‘Siberian Tigers Grab at Live Chickens Tossed at Them to Tourists’ Delight in China‘, by By Sanskrity Sinha, IBTimes, 20111228, ^http://www.ibtimes.com/articles/273353/20111228/siberian-tigers-grab-live-chickens-tossed-tourists.htm]
.
 Tiger Parts used in backward TCM Wine Tiger Parts used in backward TCM Wine
.
In China, only about 20 tigers are thought to be left in the wild!
.
“The existence of tiger ‘farms’ and increasing illegal trade in tiger products is seriously threatening this precious species.”
~ Ge Rui, Asian Regional Director of the International Fund for Animal Welfare.
.
[Source: ‘Thirst is building for tiger bone wine’, by Yang Wanli (China Daily), 20100301, ^http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/metro/2010-03/01/content_9516414.htm]
.
Tags: Amur Tiger, Amur Tiger Monitoring Program, Bangladesh, Bengal Tiger, China, fires, habitat loss, India, National Tiger Conservation Authority, Russian Far East, Siberian Tiger, Siberian Tiger Project, Sundarbans Delta, TCM, tiger, tiger census, Tiger Plight, tiger poaching, Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wildlife Conservation Society, Wildlife Crime Control Bureau, Wildlife Protection Society of India, World Wildlife Fund
Posted in Threats from Bushfire, Threats from Deforestation, Threats from Poaching and Poisoning, Threats from Road Making, Tigers | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
|
|
 ANZ Bank’s new brand represents a bank “for the people”
For the people or for its executives?
ANZ Bank’s new brand represents a bank “for the people”
For the people or for its executives?
 A Gunns Woodchip Mill at Longreach, Tasmania
A Gunns Woodchip Mill at Longreach, Tasmania
 .
. Gunns Clearfell of Tasmanian Heritage
© Photo by Alex Wise
Source: ^http://www.alexwisephotography.net/blog/2008/11/08/tasmania-clearfelling/
Gunns Clearfell of Tasmanian Heritage
© Photo by Alex Wise
Source: ^http://www.alexwisephotography.net/blog/2008/11/08/tasmania-clearfelling/
 Pulp Mill protest, Launceston Tasmania
A pulp mill for the people?
Pulp Mill protest, Launceston Tasmania
A pulp mill for the people?
 Gunns’ pulp mill site on the Tamar River, Tasmania
Gunns’ pulp mill site on the Tamar River, Tasmania .
.