Blue Mountains fox control is a problem avoided
Friday, August 10th, 2012 Dead fox found near Braeside Track, Blackheath, Blue Mountains in 2006
There was no sign of it being shot. Was it baited?
Dead fox found near Braeside Track, Blackheath, Blue Mountains in 2006
There was no sign of it being shot. Was it baited?(Photo by Editor, 20060722, free in public domain, click image to enlarge)
.
In June 2012, Gerry from Hazelbrook in the Blue Mountains west of Sydney wrote in the local Blue Mountains Gazette newspaper:
“Our place backs on to bushland. The other morning I was looking out the kitchen window and I saw two foxes just beyond our back fence, ambling along, very relaxed, looking like they owned the place. They were large, and looking extremely well fed.
A few days earlier I had seen a very large feral cat stalking prey in the same area.
Question: whose brief is feral animal control in the Blue Mountains, and what to they actually do about the problem?”
[Source: ‘Who is responsible?’, (letter to the editor), by Gerry Binder, Hazelbrook, Blue Mountains Gazette, 20120627, p.4].
Well, no one from the authorities responded to Gerry in the newspaper.
So who is responsible for fox control across the Blue Mountains? One would be inclined to consider the local Blue Mountains Council, or the regional National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) if the fox is in the National Park.
A phone call to Blue Mountains Council today revealed that the Council does not get involved in feral animal control. It has no policy or strategy to deal with the fox problem, or indeed with feral predation in the Blue Mountains local government area (LGA).
This area comprises two east-west human-settled corridors through the central region of the Blue Mountains: (1) along the Great Western Highway (including Hazelbrook) and (2) along the Bells Line of Road. Both corridors are surrounded and upstream of the UNESCO-listed Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area.
According to the Blue Mountains Council, feral animal control across the Blue Mountains, outside the World Heritage Area, is handled by the New South Wales Government Department, the Livestock Health and Pest Authority. So to answer Gerry’s question above, if anyone has an issue with foxes outside the World Heritage Area, don’t contact Blue Mountains Council, but instead contact the the Livestock Health and Pest Authority (LHPA).
The LHPA has geographically divided the Blue Mountains region into two serviced districts. From Bullaburra east back toward Sydney, the Cumberland Livestock Health and Pest Authority based at Camden takes an interest (Tel: 02-6331 1377). From Wentworth Falls west to Bathurst, the Bathurst Livestock Health and Pest Authority based at Bathurst takes an interest (Tel: 02-4655 9165).
The Livestock Health and Pest Authority (LHPA) is primarily tasked with safeguarding agriculture from threats – such as feral predation, insect control, livestock disease prevention and health. It has sixty offices across NSW and works with rural producers, government and industry to safeguard agriculture in NSW. The LHPA operates under the Rural Lands Protection Act 1998 (NSW) and is ultimately accountable to the NSW Minister for Primary Industries.
Strangely enough, the LHPA has NOT listed foxes as ‘declared pests’ in NSW. It does list wild rabbits, wild dogs, feral pigs and locusts as declared pests. The reason is one of jurisdiction and legal delegation. The LHPA is primarily charged with safeguarding agriculture, not safeguarding native habitat and fauna. It classes foxes and mice merely as ‘nuisance animals’ throughout New South Wales and states that there is no legal obligation for a landholder in NSW to control foxes or mice. LHPA only provides control advice and assistance to rural property owners. So in relation to fox control, the LHPA is more token and lip service. Blue Mountains Council adopts a complete cop out approach to the fox problem across the Blue Mountains.
From its brochure on foxes, the control methods LHPA adopts for fox control are:
- 1080 poison (sodium monofluoroacetate) – a cruel and indiscriminate poison, that kills slowly (carnivores up to 21 hours) causes pain, suffering, trembling, convulsion and vomiting. It is banned in most countries because it is considered inhumane, but still used across Australia. [Read More: ^http://www.wlpa.org/1080_poison.htm]
- Rubber jawed leg hold traps
- Mesh cage traps, which seem the most humane option.
.
This is its public brochure on foxes and note that shooting is not mentioned as an option:
 LHPA Brochure on Foxes
[Source: ^http://www.lhpa.org.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0016/434014/Final-foxes.pdf]
LHPA Brochure on Foxes
[Source: ^http://www.lhpa.org.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0016/434014/Final-foxes.pdf]
.
A week after Gerry’s letter, on the front page of the Blue Mountains Gazette ran the story of a Burns Road resident in nearby Springwood discovering that his cat Sam had been caught in a wild dog trap. Sam’s legs had been broken by the trap and he was euthanised as a result. The article in the paper stated that the Blue Mountains Council and National Parks and Wildlife Service were jointly undertaking a trapping programme in the Blaxland to Springwood area after receiving complaints about wild dogs. Traps has been set along a fire trail to catch the wild dogs. [Source: ‘Sad end for Sam’, by Damien Madigan, Blue Mountains Gazette, 20120704, p.1]
 Rubber Jaw Leg-Hold Trap
Rubber Jaw Leg-Hold Trap
.
That the cat was roaming in the bushland down a fire trail, suggests that it may well have been preying on wildlife as well. What is the difference in wildlife impact between that of a targeted wild dog, and a companion cat that is roaming wild in bushland? That the trap broke the cat’s legs meant that the control method was not humane. It also means that trapping, like poisoning is an indiscriminate form of feral animal control. So herein lies a challenge of feral predator control.
 Native Dingo caught in a rubber jaw leg-hold trap
It confirms that trapping is indiscriminate
Native Dingo caught in a rubber jaw leg-hold trap
It confirms that trapping is indiscriminate
.
In May 2011, Paul from Winmalee in the Blue Mountains, with his stated background in wildlife conservation, wrote in his letter in the Blue Mountains Gazette that shooting feral animals as a conservation measure is a largely inefficient way to control foxes. “The National Parks and Wildlife Service has done studies showing that shooting/hunting feral animals has minimal affect (sic) on their numbers”, he said. [Source: ‘Not conservation’ (letter to the editor), by Paul Bailey, Winmalee, Blue Mountains Gazette, 20110511, p.8]
.
 Recreational shooting of feral animals can attract the wrong mentality
Recreational shooting of feral animals can attract the wrong mentality
.
Back in July 2011, a local Blue Mountains resident, ‘Don’, asked in his email to The Habitat Advocate “would you like to give some coverage to the lack of ongoing fox control around Katoomba?” Don clarified in his email:
“Quite a good effort was made about 3-4 years ago (2007-08) and for about 18 months afterwards there was no sign of foxes but, as happens all too often with the bureaucratic model of pest animal control, there was no ongoing effort and foxes are now back in serious numbers, as can be detected by direct sightings, tracks and scats.
We have noticed huge losses amongst wood duck especially (the ducklings are very vulnerable to fox predation) and the swamp wallaby population is no-where near what it should be. In fact, observable wallaby numbers are down on what they were ten or fifteen years ago.
The cost of control programmes is obviously an issue. Unfortunately, due to the parasitisation of the environmental movement by animal rights folk, self-sustaining control measures such as the commercial exploitation of foxes for their skins is no longer pursued. If that remains the case, can we realistically expect the politicians ever to find the money for ongoing effective fox control, given the competing environmental considerations, not to mention budgetary issues such as mental health, which is sorely languishing?”
 Feral Foxes are healthy across the Blue Mountains
Feral Foxes are healthy across the Blue Mountains
.
Don’s request happened to be our very first request for onground action and so we shall stay by Don and see that his very legitimate request is pursued.
Our understanding is that across the Blue Mountains region, there are three categories of land ownership/control which would be impacted by fox predation:
- The Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area
- Council lands spread across 8 multiple Local Government Areas (LGAs) of:
- Blue Mountains
- Lithgow
- Oberon
- Wollondilly
- Hawkesbury
- Muswellbrook
- Singleton
- Mid-Western Regional (Mudgee)
- Private land including urban, rural, farms and to a small extent, mining leasehold land
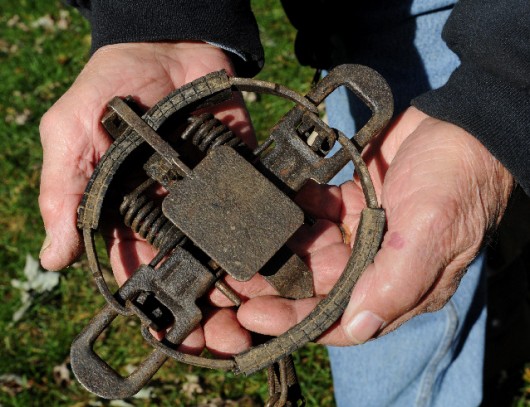
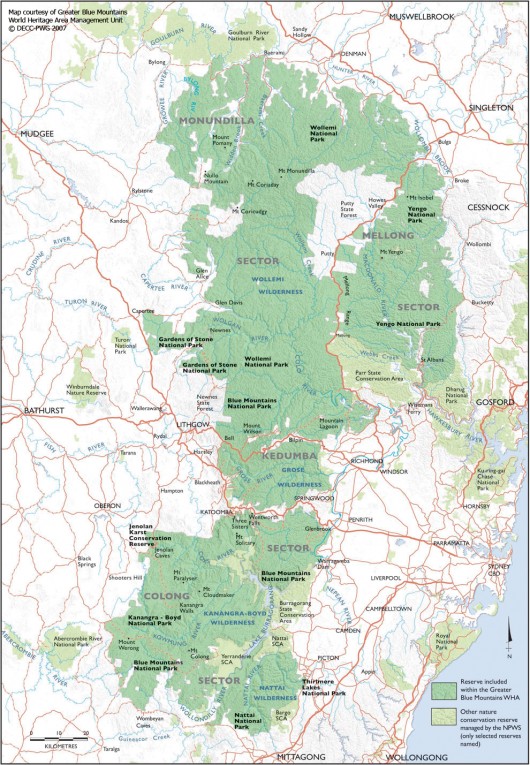 Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area
(Source: New South Wales then Department of Environment and Climate Change, 2007)
(Click image to enlarge)
Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area
(Source: New South Wales then Department of Environment and Climate Change, 2007)
(Click image to enlarge)
.
The custodial responsibility for managing the natural values of the Blue Mountains World Heritage Area is the Australian Government. The area totals roughly 10,000 square kilometres (1.03 million hectares) of sandstone plateaux, escarpments and gorges dominated by temperate eucalypt forest. It comprises eight protected areas:
- Blue Mountains National Park
- Kanangra-Boyd National Park
- Wollemi National Park
- Gardens of Stone National Park
- Yengo National Park
- Nattai National Park
- Thirlmere Lakes National Park
- Jenolan Caves Karst Conservation Reserve
 ‘Blue Mountains World Heritage Area’
Listed by UNESCO in 2000 for its unique and significant natural values
(Photo by the Rural Fire Service)
‘Blue Mountains World Heritage Area’
Listed by UNESCO in 2000 for its unique and significant natural values
(Photo by the Rural Fire Service)
.
Fauna of the Blue Mountains region classified as ‘threatened with extinction’ or ‘rare’ include the Tiger Quoll, the Koala, the Yellow-bellied Glider, the Brush-tailed Rock Wallaby and the Long-nosed Potoroo as well as rare reptiles and endangered amphibians such as the Green and Golden Bell Frog, the Blue Mountain Water Skink and the Broad-headed Snake and endangered birds like the Regent Honeyeater. The largest predator of the region is the Australian Dingo to which its natural prey in the region is the Grey Kangaroo and various subspecies of Wallaby, other macropods, small marsupials and reptiles.
 Tiger Quoll (Dasyurus maculatus)
Also known as the spotted-tail quoll (which we consider a rather naff politically correct name)
An endangered carnivore, native to the Blue Mountains and competing with the Dingo and feral fox as the top order predator of the region
(Photo by OzTrek)
Tiger Quoll (Dasyurus maculatus)
Also known as the spotted-tail quoll (which we consider a rather naff politically correct name)
An endangered carnivore, native to the Blue Mountains and competing with the Dingo and feral fox as the top order predator of the region
(Photo by OzTrek)
.
The feral fox, being carnivorous, poses two types of threats to wildlife across the Blue Mountains region. It preys on small ground dwelling animals and reptiles. It also competes for prey with the Tiger Quoll and Dingo.
.
Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area – significant natural values
.
The Australian Government has outsourced and delegated its custodial responsibility for managing the natural values of the Blue Mountains World Heritage Area to the New South Wales State Government, which has in turn delegated the responsibility to one of its departments, the New South Wales National Parks and Wildlife Service (NSW NPWS).
At the time of writing, the NSW NPWS, is part of the Office of Environment and Heritage (OEH), within the NSW Department of Premier and Cabinet. One has to check every four years or so, because the department changes its name that frequently. This is the current website, but that could change too: ^http://www.nationalparks.nsw.gov.au/about
The regional office of the NSW NPWS is located in Katoomba in the Blue Mountains.
Conservation management of the Blue Mountains World Heritage Area, including feral animal control, is guided by a number of documents. Pertinent to the fox predation threat, the Blue Mountains World Heritage Area listing includes World Heritage natural values worth conserving and protecting under World Heritage Natural Criterion 44 (a)(iv):
“…contains the most important and significant natural habitats for in-situ conservation of biological diversity, including those containing threatened species of outstanding universal value from the point of view of science or conservation…”
.
[Source: ‘The Greater Blue Mountains Area – World Heritage Nomination‘, 1998, prepared by the New South Wales National Parks and Wildlife Service in association with Environment Australia, p 30, referencing World Heritage Operational Guidelines 1998, ^http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/blue-mountains/pubs/gbm-nomination.pdf [>Read Nomination‘ 5.7MB, PDF].
Pertinent to fox predation threat, The Blue Mountains World Heritage Area meets World Heritage Natural Criterion 44 (a)(iv) by it including significant habitats for in situ conservation of biological diversity, taxa of conservation significance, exceptional diversity of habitats providing outstanding representation of the Australian fauna within a single place. These include endemic species, relict species, species with a restricted range, and rare or threatened species (40 vertebrate taxa – including 12 mammal species) and examples of species of global significance such as the Platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus) and the Echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus aculeatus).
[Source: ‘Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Values‘, Australian Government, Department of Environment et al., ^http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/blue-mountains/values.html , accessed August 2012].
 .
.
Threat Abatement Plan – Predation by Foxes
.
In 1999, the Australian Government’s Department of Environment et al. published a threat abatement plan (TAP) which established a national framework to guide and coordinate Australia’s response to the impacts of European red foxes on biodiversity. It sought to comply with Australia’s Endangered Species Protection Act 1992 to promote the recovery of species and ecological communities that are endangered or vulnerable, and to prevent other species and ecological communities from becoming endangered.
In Schedule 3 of the Act, Predation by the European Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes) is listed as a key threatening process. The focus of this plan is on the actions required to reduce the threat posed by foxes to endangered or vulnerable species or ecological communities.
It concluded that ‘eradication of foxes on the mainland is not possible‘ and so settled for methods to reduce fox numbers and predation on wildlife in significant areas. The fox abatement plan aimed to reduce the impact of fox predation on native wildlife over a 5-year period by:
- implementing fox control programs in specific areas of high conservation priority;
- encouraging the development and use of innovative and humane control methods for fox management;
- educating land managers and relevant organisations to improve their knowledge of fox impacts and ensure skilled and effective participation in control activities; and
- collecting and disseminating information to improve our understanding of the ecology of foxes in Australia, their impacts and methods to control them.
The Australian Government’s funding to implement the plan was to be primarily through funding programmes of the Natural Heritage Trust.
The ideal of the Fox Threat Abatement Plan was to eradicate foxes, which seems fair enough. To achieve fox eradication it proposed:
- The mortality rate for foxes must be greater than the replacement rate at all population densities
- There must be no immigration
- Sufficient foxes must be at risk from the control technique so that mortality from all causes results in a negative rate of population increase
- All foxes must be detectable even at low densities
- A discounted benefit-cost analysis must favour eradication over control
- There must be a suitable socio-political environment (Ed: ‘political will’)
[Source: Bomford and O’Brien, 1995]
.
However, because foxes had become so well established across a vast area, the plan pre-concluded that complete removal of foxes from Australia was well beyond the capacity of available techniques and resources. Saunders et al. (1995) reviewed current knowledge on techniques for suppressing fox populations including poison baiting, shooting, trapping, hunting with dogs and fumigating dens. The review concluded that, with the exception of broad-scale baiting, the existing control methods are expensive, labour intensive, require continuing management effort and can be effective in only limited areas.
[Ed: This reads as a self-fulfilling ‘too-hard basket’ prophecy by bureaucrats. Do nothing, and for sure, nothing will happen]
.
Baiting
The fox abatement plan considered that in most situations, poison baiting (using 1080 poison) was the most effective method of reducing fox numbers and impact. However, it acknowledged the negative impact on non-target species. “A major drawback is that it may affect native carnivores and scavengers such as dingoes, quolls, goannas and some scavenging birds, and also domestic dogs.” Whoops.
“Aerial baiting of foxes has been demonstrated to be an effective method of control for covering large areas provided the risk of non-target bait uptake is minimal.”
Sounds the kind of spiel akin to the CIA about its collateral damage in Vietnam with its Agent Orange sorties. Well Western Australia is happy to use aerial baiting of 1080 over large areas (up to three million hectares) and has been shown to dramatically reduce fox numbers. Apparently, it has had minimal impact on populations of rare species because the native fauna somehow have a higher resistance to the naturally occurring 1080 poison found in native plants. Mmm, where is the proof?
..
Biological Control
This was more conceptual a strategy, since no current pathogen yet exists that is virulent, humane and specific to foxes and not transferable to other species. The idea is that by targeting fox fertility, an effective long-term approach to reducing their numbers can be achieved. Fertility control is still at an experimental stage of development. It has not been successfully applied to a free-ranging population of wild vertebrates over a large area nor has it been attempted as a method of reducing the impacts of predation on an endangered or vulnerable species. Methods of fertility control include hormone treatment and sterility (immunocontraceptive technology). However, some scientists and wildlife managers remain sceptical about the likely success and effectiveness of this approach (Carter, 1995). The obstacles to achieving a workable method are formidable and include:
- difficulty of isolating an infectious virus specific to foxes;
- difficulty of developing a contraceptive vaccine;
- difficulty of combining the two into a treatment that causes permanent sterility and no other significant disorders in an infected fox;
- the possibility that in the field, natural selection and elements of fox ecology may overcome or compensate for any attack on the species’ reproductive capacity;
- social concerns that the methods may not be controllable once released; and
- the need to be cost-effective relative to other methods.
.
Barriers to Fox Invasion
Fences have been proposed as a component in conservation management programs to protect endangered species from predators such as foxes and cats. A large range of fence designs has been used to exclude foxes from particular areas but there is little information on the effectiveness of particular designs.
A recent review of predator-proof fencing in Australia (Coman and McCutchan, 1994) found that although fences can be a significant barrier to foxes, even the most elaborate can be breached. Frequent monitoring for the presence of foxes inside the fence is an essential precaution as considerable damage can be caused by a single fox breaching the fence.
Shortcomings of fences include posing a hazard to non-target wildlife, restricting the natural ability of native animals to disperse, the high cost of predator-proof fencing and the necessary maintenance costs for it to be effective. However, recent studies at Shark Bay, Western Australia have found that a combination strategy of fencing, baiting, trapping along with a combination of natural water barriers, can be effective fencing on peninsulas (Department of Conservation and Land Management, 1994).
[Ed: Question is did it adversely affect non-target native species? One could incinerate the entire landscape, defoliate it, concrete it so there may be not foxes left, but then no wildlife as well. This seems consistent with West Australia’s simplistic blanket one-size-fits-all approach to environmental control].
.
Habitat Management
In environments with dense vegetation, steep topography, rocky crevices or extensive wetlands, prey are less likely to be caught by foxes (Saunders et al.et. al. 1995). [Ed: This would seem to describe the Blue Mountains landscape with its many impassable escarpments]
The foraging efficiency of foxes seems to be maximal in open habitats where they are able to range widely and freely. They readily use roads, tracks and other cleared access ways through denser vegetation or complex topography. [Ed: This has been encouraged by the frequent fire regime of the Rural Fires Service and NPWS to remove thick vegetation labelled as ‘fuel’].
Arboreal marsupials become vulnerable when they descend to the ground to move between trees. A continuous canopy and a thick understorey of shrubs enable them to move about in the trees where they are not at risk from fox predation. An important conservation strategy for some situations will be to minimise habitat fragmentation and to investigate options for fire, grazing or other management practices which do not destroy ground habitat.
.
Fox Bounties
Reviews of the history of fox management in particular (Braysher, 1993; Saunders et al.et. al. 1995), concluded that fox bounties have rarely been effective. There is little evidence, except occasionally and in small areas, that hunting of foxes has a significant or lasting impact on fox numbers or the damage they cause. Where private land adjoins or contains important wildlife habitat, assistance or encouragement to landholders and the development of incentives to promote fox control on private land may be appropriate, especially if the property forms part of a buffer zone to protect threatened species populations.
[Ed: This is a scientific lesson for the current NSW OFarrell Government in light of its recent decision to counter legislate for hunting in 79 National Parks across the State for supposed feral animals like foxes]
.
[Source: ‘Threat Abatement Plan for Predation by the European Red Fox‘, Biodiversity Group Environment Australia, 1999, Australian Government’s Department of Environment et al., ^http://www.environment.gov.au/archive/biodiversity/threatened/publications/tap/foxes/index.html].
Blue Mountains Urban Fox Programme (2003)
.
In 2001, the NSW NPWS published its ‘Fox Threat Abatement Plan 2001′.
This is it: >’NSW Threat Abatement Plan – Predation by the red fox (Vulpes vulpes), December 2001‘ (PDF, 930kb)
Then in 2003, the NPWS along with the Blue Mountains Council and other government agencies commissioned a public survey using a questionnaire method to gauge public perception about the impact of foxes across the Blue Mountains. An external consultant as engaged and a committee formed, the Blue Mountains Urban Fox Steering Committee‘.
The survey found that foxes were indeed considered a problem in the Blue Mountains. In January 2004, published in the survey results included was that 64% of those surveyed considered foxes to be a major problem. The impact of foxes was 30% domestic animal impacts, 12% wildlife impacts, and 6% property damage impacts. 53% of respondents felt that not enough was being done to manage foxes in the Blue Mountains townships and surrounding natural areas.
And so the assembled committee prepared a strategy document on the management of ‘urban foxes’ and some education material. But it wasn’t to control foxes…
“The top two priorities of this strategy are for:
- community education
- local research on foxes and their impacts.
.
It was a bureaucratic waste of time so that Blue Mountains NPWS could be politically seen to be thinking about doing something about foxes. The gain was corp0rate-political for NPWS Blue Mountains Senior Ranger, Chris Banffy, to be seen to be doing something on paper, but nothing on the ground, financial gain for the engaged Pest Management Consultant, Nicola Mason.
True to consultant form there was the big survey, survey advertising, data collation, published results in January 2004 and a follow up community workshop on 26th March 2004.
Yes, there was community education published in May 2004. It took the form of another two page A4 brochure. Here it is, as two scanned pages.
.
Community Education Page 1:
 Click image to enlarge and read
Click image to enlarge and read
.
Community Education Page 2:
 Click image to enlarge and read
Click image to enlarge and read
.
And of course, NPWS did nothing about the Blue Mountains confirmed fox problem. It just built a bigger library of reports.
Was it due to lack of funding or lack of direction from Environment ministers. Or perhaps it always just a token public servant ‘look busy’ project to be seen to be thinking about doing something to justify one’s cosy job perpetuation? Certainly to the foxes of the Blue Mountains, it was business-as-usual and they saw nothing from the entire exercise.
 And still the fox threat continues unabated
And still the fox threat continues unabated
.
The whole project was a steaming scat, perhaps one of the better construed abuses of taxpayer and ratepayer funds of the Blue Mountains in living memory.
In 2006, the NPWS then umbrella department called the ‘Department of Environment and Climate Change (DECC) in its ‘State of the Environment Report 2006′, Chapter 6 on Biodiversity, reported on ‘ Terrestrial Invasive Species (Section 6.4). It acknowledged the feral predation problem, combining it with the weed problem:
“Invasive species remain one of the greatest threats to biodiversity in New South Wales. Over half of all the key threatening processes listed relate to invasive species. Once invasive species become widely established, few can ever be eradicated, and controlling them must focus on strategically limiting their impacts on biodiversity. The main vertebrate pests in NSW have been present for the last century, with many widespread across the State.
Predation by foxes and cats is implicated in the decline or extinction of numerous small- to medium-sized animals. Herbivores, particularly rabbits and feral goats, are responsible for overgrazing of native vegetation and land degradation. Some 1350 exotic plant species have become established in NSW, more than 300 of which are significant environmental weeds. New pest species continue to become established in the environment. Combining prevention, early detection and eradication is the most cost-effective way to minimise the impacts of new pests.”
.
DECC listed ‘Introduced Terrestrial Species’ (Ed: a fancy name for feral foxes and cats, etc) as a key bio-indicator of National Park health, with pest animals having a devastating impact on biodiversity. Predation by feral cats and red foxes had contributed to regional declines and the extinction of a range of native species, particularly among small-to medium-sized ground-dwelling and semi-arboreal mammals, ground-nesting birds, and freshwater turtles (Dickman 1996).
DECC recommended better coordination efforts across jurisdictions to target control efforts for species listed as key threatening processes, and research into more effective and target-specific control methods, such as biological control. It prepared a NSW Threat Abatement Plan (TAP). It prioritised feral cat control based on a review of the evidence of cat impacts, and little mention of foxes. The threat abatement strategy was “Research…Develop and trial a cat-specific bait that will ensure non-target species are not impacted.”
[Source: New South Wales Government’s Department of Environment et al., 2006, ^http://www.threatenedspecies.environment.nsw.gov.au/tsprofile/pas_ktp_profile.aspx?id=20008].
Then three years hence in 2007, the NPWS fox survey report was getting a tad stale, so NPWS did another survey and another report. The Katoomba NPWS regional office this time was aggregation feral animals with weeds, and calling the lot ‘pests’. It was drafting its ‘regional pest strategy’ and foxes were now grouped with weeds. It asked for community input, but like most government strategies, they stopped short of funded action to do anything except generate another report confirming a problem that needed to be addressed. This is the report:
[>’Blue Mountains Pest Strategy (NPWS 2007-2011)‘ (PDF, 1.7MB]
In 2008, the Australian Government’s ‘1999 Fox Threat Abatement Plan‘ was superseded by the Australian Government’s ‘2008 Fox Threat Abatement Plan‘.
Read: The ‘2008 Fox Threat Abatement Plan (Background)‘ [PDF 138kb]
Read: The ‘2008 Fox Threat Abatement Plan (Report)‘ [PDF 148kb]
.
In 2010, the NSW NPWS published its ‘Fox Threat Abatement Plan 2010′.
This is it: >’NSW Threat Abatement Plan – Predation by the red fox(Vulpes vulpes), December 2010‘ (PDF, 390kb) ^http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/resources/pestsweeds/110791FoxTAP2010.pdf
Ed: Another year another plan, nothing done, ongoing fox predation, less wildlife.
.
We end here as we began, with a last word from a concerned reader, which succinctly tells it as it is:
.
‘Act now to save native wildlife or it’ll be too late‘
.
“This letter is an appeal on behalf of all our endangered native creatures being destroyed by the ever-increasing numbers of feral animals.
The Federal Government estimates there are 18 million feral cats roaming our countryside killing our unique marsupials and birds in numbers that equate to a massacre. There are also countless numbers of foxes doing their best to wipe out our wildlife. And those are only two of the dreadful “invasive” animals, as the Government calls them. There are also cane toads, carp, pigs and goats.
Unfortunately for our native creatures there is not a politician in Australia who seems to be interested in this matter. They will jump up and down about whales, but ask them to show some interest in our native wildlife and they are struck dumb. If you ask the political parties they will say they have policies to solve these problems but that is empty rhetoric. No one is doing anything constructive to address this problem.
In the case of feral cats, I am advised that governments have access to a number of viruses that could be used with some success but I can only surmise these brave politicians are afraid of a backlash from the “domestic cat lobby”, even though there are vaccines available to protect pet cats.
The only party that I thought might show an interest in this problem, the Greens, hides behinds a screen of policy statements that means absolutely nothing unless implemented with some positive action.
Perhaps someone with some interest in this terrible problem and who has the clout to do something about it might start the ball rolling to protect our native wildlife. Otherwise future generations of Australians may see our brilliant birds and fascinating marsupials only in zoos.
[Source: ‘Act now to save native wildlife or it’ll be too late‘, (letter to the editor) by Neville Ridge, Bowral, Sydney Morning Herald, 20090110, p.24].
…well perhaps not the last word…
 Fox Predation – unequivocal results
Roland Van Zelst, left, Rene Mooejkind and Darren Bain with their night’s haul.
(Photo by Lee Griffith)
Fox Predation – unequivocal results
Roland Van Zelst, left, Rene Mooejkind and Darren Bain with their night’s haul.
(Photo by Lee Griffith)
.
Hundreds of foxes and other feral animals have been culled in agricultural regions across WA to protect livestock and native animals from the destructive pests.
At the weekend, hundreds of farmers and scores of volunteers took part in the annual Red Card for Red Fox drive which encourages rural communities to bait and shoot foxes.
The cull will resume on the March 20-21 weekend.
Now in its eighth year, the Red Fox Drive aims to reduce Australia’s seven million-strong fox population. During the cull weekends, agricultural communities also target feral pigs, cats and rabbits. In the community of Wandering, 120km south-east of Perth, locals culled 140 foxes, nine feral pigs, 12 feral cats and 43 rabbits.
Co-ordinator Lisa Turton said the aim was to keep the fox population at a manageable level.
“We will never be able to eradicate the foxes,” Ms Turton said. “But we need to ensure that their populations are low because they do get to the young lambs and they target the native birds and marsupials.” Foxes eat an average of 136kg of food a year, including lambs, mice, rabbits and many species of native animals.
Ms Turton said those participating in the drive were not “cowboys” with guns but instead followed strict guidelines. “Everybody who takes part must do so on their own land,” she said. “We don’t just go out on the road and start shooting. We do this to protect the native species.”
Last year, 5000 foxes, 230 feral cats and 2500 rabbits were shot over the four weekends throughout WA.
[Source: ‘Shooters take aim at feral foxes to preserve livestock’, by Lee Rondganger, The West Australian, 20100222, ^http://au.news.yahoo.com/thewest/a/-/newshome/6834199/shooters-take-aim-at-feral-foxes-to-preserve-livestock/].
…one more …
 The result of just one cull – the scale of the fox problem is rife!
The result of just one cull – the scale of the fox problem is rife!
.
“They only got one cat.
These animals do have feelings.
However, they don’t belong on this continent.
The native fauna is ill-prepared to deal with their depredations.
And the only way to save many species of native Australian wildlife is to create areas that are free of foxes and cats.
The only way to do that is to kill them.
They shouldn’t be tortured when they are killed. A single killing shot will do.”
.
[Source: ‘Fox and cat cull in Australia’, by ‘Retrieverman’, 20110929, ^http://retrieverman.wordpress.com/2011/09/29/fox-and-cat-cull-in-australia/].
Footnote
.
Response from the Livestock Health and Pest Authority 20120914:
Livestock Health and Pest Authorities (LHPAs) are responsible for administering and enforcing the Rural Lands Protection Act 1998 (RLP Act), which governs the control of declared pest animals in New South Wales (NSW). Animals declared as pests include; feral pigs, wild dogs and European wild rabbits. The declaration of the species as pests requires landholders to control them. Other animals such as foxes, goats and deer are feral and considered pests by many people but the legislation doesn’t require landholders to continually control them.
There are many reasons why these other species of feral animals are not declared pests such as, restricted control options (in the case of fox control), public perception, potential financial value and even recreational value. Therefore the control of these species essentially lies with the landholder to determine whether they need to control them based on impacts caused by the species not because the landholder is legally required to. For example, foxes preying on lambs on an agricultural property, or foxes preying on an endangered species in a National Park.
LHPAs are a statutory authority funded via a rating system whereby landholders with 10 hectares or more pay compulsory rates to the LHPA. LHPAs provide assistance to these landholders in relation to livestock health and pest animal control. LHPAs also provide much greater benefit to the general community through livestock disease surveillance and disease control, and the coordination of pest and feral animal control programs on LHPA rateable and non rateable land.
LHPAs cannot simply declare animal species as pests under the RLP Act. This decision is made by government and LHPAs enforce the legislation set by government. Despite this, LHPAs are involved in coordinating numerous fox control programs around NSW for both agricultural and environmental benefits.
Legal restrictions on pesticide use and restrictions on other control techniques present challenges for landholders in implementing effective fox control. There are restrictions on the distance baits must be laid from houses, a requirement to notify all people who are within 1km of bait sites, and those laying the bait require a training qualification to use and store the pesticide known as 1080. This presents a problem with implementing fox control along the urban and peri-urban corridor along the Great Western Highway in the Blue Mountains.
LHPAs do not set these restrictions. These are set in Pesticide legislation and regulated by the Environment Protection Authority (EPA), and are in place for valid reasons such as reducing the likely impact to animals like domestic dogs which are very susceptible to 1080. LHPAs must however ensure that the restrictions can be observed and applied by the person laying baits to ensure that it is used safely and effectively whilst minimising risks.
1080 is a very effective poison to control carnivores and is very target specific contrary to what many people are led to believe. It is a naturally occurring chemical in Australia and as a result of this many of our native species, particularly birds and reptiles have high natural tolerances to 1080.
Rubber jaw leg hold traps for foxes and wild dogs is effective but generally very labour intensive and require specialised skills. Cage trapping is considered ineffective and only occasionally results in success. Baiting is generally used to reduce populations significantly and trapping is utilised as a secondary technique which aims at maintaining populations at a low level.
The Blue Mountains World Heritage Area (BMWHA) is an enormous area much of which is completely inaccessible. Despite a history of control programs, pest and feral animals are still present, even if in low densities due to the success of control programs. On mainland Australia, despite developments in control techniques, research and understanding of feral and pest animal biology, we are yet to eradicate an introduced vertebrate pest species.
Due to budgetary constraints pest and feral animal control has become much more strategic over the last decade. Pest control is being prioritised based on impacts caused by a particular species whether it is a feral or a declared pest and programs have become highly coordinated to get the most effective results with the available resources. Coordination has involved the establishment of working groups, one such example is the Oberon feral pig and wild dog working group which largely covers most of the BMWHA and includes representatives from various government departments and private landholders who work together to coordinate and implement programs which provide joint benefit to agriculture and the environment.
Pest control can be a sensitive issue and although it may seem little is being achieved, there are a number of programs being implemented particularly in the BMWHA which is a significant conservation area with unique values. The urban corridor through the middle of it adds to its uniqueness but also presents many challenges one of which is pest management. Urban fringe areas generally support higher densities of some pest animals, namely foxes, as we provide them with ideal opportunities to prosper such as food and harbour which are the fundamentals for their survival. We do this without even realising for example, leaving food out for dogs or keeping poultry in our backyards. These are simple examples that are highly attractive to foxes and they can’t resist and won’t refuse them.
Community education and responsible domestic animal keeping is the key to eliminating most of the problem. Pest and feral animal control is a landscape issue and therefore everyone’s problem, not just government. LHPAs will continue to assist landholders and coordinate control programs working within the legislation to ensure that pest control is target specific and effective in providing benefits to agriculture and the environment.’
Steve Parker Ranger Cumberland Livestock Health and Pest Authority