‘State Arson’, ‘State Logging’ wiping out owls
Friday, November 18th, 2011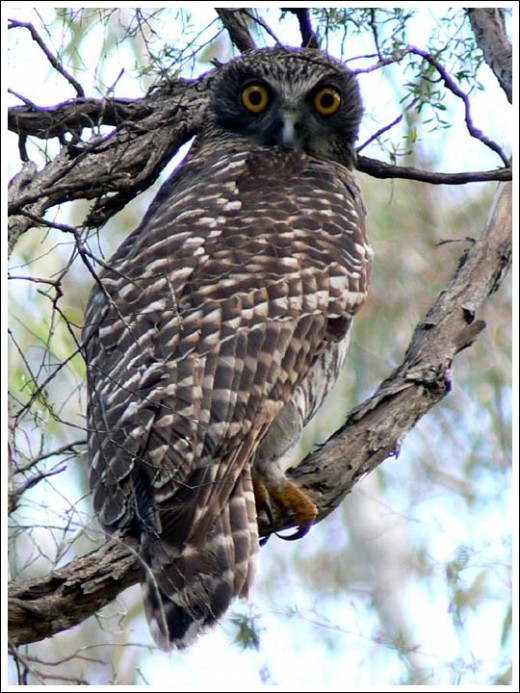 Powerful Owl (Ninox strenua)
(© Photo by Duncan Fraser, ^http://bencruachan.org/blog/?p=170)
Powerful Owl (Ninox strenua)
(© Photo by Duncan Fraser, ^http://bencruachan.org/blog/?p=170)
.
The Powerful Owl (Ninox strenua) is Australia’s largest owl, yet in Victoria it has become a threatened species due to human destruction of old growth forest habitat; particularly the destruction of hollow-bearing trees used by this owl for nesting, roosting and home for its natural prey – possums. ‘Powerful Owls are adversely affected by the clearfelling of forests and the consequent conversion of those forests into open landscapes, but the species may persist in forests that have been lightly or selectively logged.’
[Source: ^http://www.birdsaustralia.com.au/our-projects/powerful-owl-wbc.html] .Since European settlement, 65% of Victoria’s forest cover has been cleared (Woodgate & Black 1988). Only 5% of freehold land remains forested. This past permanent loss of habitat has likely led to an overall reduction in owl numbers and fragmentation of the original continuous population into a series of small residual populations, each of which is at risk of becoming locally extinct.
‘It is estimated that hollows suitable for owls do not form, even in the fastest-growing eucalypts, until they are at least 150-200 years of age (Parnaby 1995). Of 21 nest trees observed by McNabb (1996) in southern Victoria, about 50% were senescent and all ranged between 350-500 years of age, based on data collected by Ambrose (1982).
Over much of its range, the lack of suitably large hollows is considered to be a limiting factor to successful breeding and population recruitment. The Powerful Owl is, therefore, vulnerable to land management practices that reduce the availability of these tree hollows now or in the future. The loss of hollow-bearing trees has been listed as a potentially threatening process under the Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act (SAC 1991).
In addition, prey density may be an important determinant in territory size and breeding success, particularly considering that only the male hunts during the breeding season. Seebeck (1976) estimated that about 250 possums (or their equivalent) would be required per year by a family group and recent studies have estimated around 300 prey items for a breeding pair rearing two young (Webster unpubl. data.). Key prey are also dependent on hollow trees.’
In its final recommendation the Scientific Advisory Committee (SAC 1994) has determined that:
‘the Powerful Owl is significantly prone to future threats which are likely to result in extinction, and very rare in terms of abundance or distribution.’
.
The short-term conservation objective is to prevent further decline by ensuring that good quality habitat for at least a population target of 500 breeding pairs of Powerful Owl is maintained on public land in Victoria.
[Source: ‘Powerful Owl Action Statement‘, Victorian Government’ s Department of Natural Resources and Environment (or whatever its latest incarnation is), ^http://www.oren.org.au/issues/endspp/powerfulowlAS.htm].
.
‘Impact of Bushfire on Sooty Owls and Powerful Owls’
[Source: Rohan Bilney, Report on Sooty Owls and Powerful Owls for the Supreme Court proceeding number 8547 of 2009 – Environment East Gippsland v VicForests, pp.12-13]Greater Sooty Owl (Tyto tenebricosa)
.
‘Fire is likely to kill individual owls and small mammals, and remove potential habitat in the short-term, potentially resulting in long-term impacts.
‘How owl populations adapt or respond to fire is largely unknown’
.
‘Fire can consume hollow-bearing trees, while also stimulating hollow formation, but as hollow formation can take decades, frequent fires are likely to result in a net loss of hollow-bearing trees from the landscape (Gibbons and Lindenmayer 2002). This is likely to cause detrimental effects to all hollow-dependant fauna (Catling 1991; Gibbons and Lindenmayer 2002; Garnett et al. 2003).
‘Sooty Owls typically occupy habitats subject to infrequent fire regimes such as wetter forest types, possibly due to higher densities of hollow-bearing trees in such landscapes. Frequent fire regimes also simplify habitat structure, which can cause deleterious impacts on terrestrial mammals (Catling 1991; SAC 2001), which includes increased predation rates by feral predators due to the loss of habitat refuge (Wilson and Friend 1999). Overall, it therefore seems likely that owls and small mammals will be negatively impacted by frequent fire regimes. It is likely, however, that it will be the impacts of fire on prey densities that dictate how the owls respond to fire.
 Brown Mountain ancient old growth logged, incinerated, razed by VicForests
(Photo by Environment East Gippsland)
Brown Mountain ancient old growth logged, incinerated, razed by VicForests
(Photo by Environment East Gippsland)
.
‘Most species are not adapted to fire per se, but adapted to a particular fire regime, which include fire aspects such as intensity, frequency, seasonality and scale (Bradstock et al. 2002). Due to variations in the life history requirements of species and their ability to survive fire, particular fire regimes can advantage some species, while being deleterious to others (Bradstock et al. 2002; Gill and Catling 2002; Keith et al. 2002). Due to the varying ecological responses to fire, it is important for biodiversity conservation that we not only understand species responses to particular fire regimes, but to ensure that appropriate fire regimes are maintained across the landscape. As prescribed fire is used as a management tool for reducing fuel load to minimise fire risk, it is important that its effects on biodiversity are well understood.
‘Unfortunately, knowledge on how native species respond to particular fire regimes is poorly understood, especially for fauna (SAC 2001, 2003; Clarke 2008). So, in the absence of this crucial ecological information it is virtually impossible to implement appropriate fire regimes which will result in minimal negative ecological impacts, let alone enhance biodiversity. Fire, both prescribed burning and wildfire, can present a threat to owls if conducted at inappropriate seasons, frequency, intensity or scales. It is therefore difficult to quantify the threat. The threat of inappropriate burning at high fire frequencies is likely to be mainly concentrated around human assets and populations, while fires in more remote forested areas will be subject to less frequent fires (DSE 2004). Fire also affects the entire owl population because all habitats occupied by owls is flammable.
‘Victoria has experienced three catastrophic fire events in the past 7 years, and combined with prescribed burning, approximately three million hectares have been burnt in this time.‘
‘This equates to approximately 2/3 of potential Sooty Owl habitat in Victoria. How populations of Sooty Owls and many other forest dependant fauna have been affected by these fires remains poorly understood or unknown. The ability for forest fauna to recover is therefore being hampered by further prescribed burning, and recovery is also hampered by reduced fecundity caused by a decade of drought, and for the owls, low prey population densities.’
.
.
The ‘Bushfire Fighting Principle’ corrupted by blinkered economic rationalism
.
The traditional principle of bushfire management is to put out bushfires…one would think. Yet this simple concept has been hijacked, bastardised and corrupted by successive governments as a consequence of systemic under-resourcing. Government under-resourcing has contributed to the deadly human toll in recent years.
The corrupting of this core bushfire management principle has morphed into a blanket one-size-fits-all defeatist policy of broadscale prescribed burning – burning the bush before it burns. The bushfire management tradition of ‘suppression‘ has been economically rationalised and politically supplanted by the proactively sounding notion of ‘prevention‘.
In Victoria, the fundamental job of putting out bushfires has bureaucratically morphed into a ‘Code of Practice for Fire Management on Public Land’, with its two general principles…
.Fire management planning on public land must address the threat of wildfire, guide the use of prescribed burning, and provide for the achievement of integrated land management objectives such as human safety and environmental management.’ (Clause 50)
‘Fire management activities must be undertaken in a participative manner where the responsibility for reducing the likelihood and consequence of wildfire is appropriately shared between public and private land holders and managers.’ (Clause 51)
.
What happened to the fundamental principle of bush fire fighting?
To put out bushfires!
Instead, vast areas of remaining native bushland and forests across Australia are being deliberately burnt to the point where critical faunal habitat is sterilised – only the trees remain, while the rich underlying vegetation, demonised as ‘hazardous fuel‘ is incinerated and repeatedly prevented from regrowth. Wildlife habitat has become a fuel hazard targeted for burning by the very custodians charged with wildlife conservation. And out of the Victorian Royal Commission into the Black Saturday bushfires, the anticipated kneejerk response by bushfire agencies to commence Prescribed Burning Armageddon against the bush has started as many genuine conservationists have feared.
And what has been the full realised cost of the 2009 Victorian Bushfires – valuing human lives, human injuries, ongoing trauma, livelihoods, wildlives, livestock, private property, natural assets, on top of the direct operational response cost, the indirect costs of contribiting agencies, the donations raised, capital costs, the opportunity costs, the investigation costs, the Royal Commission costs? No one has come up with a figure. These values were outside the Victorian Royal Commission’s terms of reference – so what real value was it? Economic rationalising of emergency management is costing lives and contributing to species extinctions.
.
.
Victorian Government Policy of Bushfire Lighting
.
The Victorian Government’s delegated custodian on natural areas across the State is the infamous Department of Sustainability and Environment (DSE), with a reputation for lighting most of the bushfires it euphemistically labels as ‘prescribed burning’ wherein it finds unburnt bushland and prescribes its own burning regimes. When such custodial agencies restore the word ‘conservation‘ back into their title, some respect may return.
DSE’s ‘Code of Practice for Fire Management on Public Land‘ was revised in 2006. It relies upon background premises that since “much of the Australian continent is fire-prone”, that “fire occurs naturally”, that “many species of vegetation and wildlife have adapted to living within the natural fire regime” and that “Victoria’s Indigenous people used fire as a land management tool for thousands of years”. The Code justifies that “Victoria’s flora, fauna and the ecosystems they form are adapted to fire of varying frequencies, intensities and seasonality.” Victoria’s Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act 1988 has objectives to ensure “Victoria’s native flora and fauna can survive, flourish, and retain their potential for evolutionary development”. Now the integrity of this Act is under threat. Perversely DSE’s Code of Practice argues that deliberate burning of bushland and forest habitat will help Victoria’s native flora and fauna to survive, flourish, and retain their potential for evolutionary development.
Crap!
DSE stretches its rationalising propaganda further, claiming that excluding bushfire can have “negative consequences for Victoria’s flora and fauna“. And this is where the hijacking, bastardisation and corrupting turns from mythology into unsubstantiated falsehood and misinformation. No document exists to zoologically prove that native fauna will suffer such negative consequences if it does not have a bushfire range through its habitat. As a result, the Code of Practice implies that bushfire is ok for all Victorian bushland and forests – DSE conveniently convinces itself that the urgent moral imperative for DSE to suppress bushfires is extinguished. So now it lights more fires than it puts out.
The Code also premises that “often these wildfires can be difficult to suppress”. Well no wonder with an grossly under-resourced, firetruck-centric volunteer force.
.
‘DSE holds fire management workshop in Bendigo’
.
On 22nd June 2011, DSE staged a workshop of stakeholders to discuss some recommendations of the Royal Commission into Victoria’s February 20o9 bushfire tragedy. According to the website ‘Friends of Box-Ironbark Forests’, in attendance were representatives from the CFA, local government, The Wilderness Society, Bendigo Field Naturalists Club, Friends of Kalimna Park, North Central Victoria Combined Environment Groups [NCVCEG], Apiarists Association and DSE attended a workshop on June 10 to learn about the process for implementing the findings of the Victorian Bushfires Royal Commission. Though Friends of Box-Ironbark Forests (FOBIF) was not invited to this workshop, we were represented by members of some of the other groups.
Once again DSE’s Code of Practice for Fire Management on Public Land (COP) is to again be reviewed and updated, except its premises have not changed, so what’s the point? The following notes taken on the issue of Fire management Zones/Prescriptions is telling of how disconnected DSE is from wildlife habitat conservation:
.
‘Fire Management Zones (FMZ) have been reviewed recently. An interim zoning is to be released soon. With little time left the group briefly discussed the merits of fire management zones, and how they might relate to the risk model. It was highlighted that the residual fuel load is an important aspect, but further detail as to how was not provided.
NCVCEG made the point that the current diagram used by DSE to represent the relationship between ecological outcomes and fire management outcomes across the four FMZ is misleading, encourages poor planning, discourages biodiversity management in zones 1 and 2, and neglects to recognise that fire management outcomes may be achieved in all zones, especially where integrated planning and alternative practices (to prescribed burning) are established.
In relation to FMZ the Apiarists pointed out that Box Ironbark forests generally have very low fuel levels in comparison to heavily forested regions where many lives were lost during the fires in 2009. The merit of burning areas used for honey production was questioned and the long term impacts of severe burning on Box Ironbark forest ecology was raised.’
.
[Source: Friends of Box-Ironbark Forests, 20110622, ^http://www.fobif.org.au/2011/06/dse-holds-fire-management-workshop-in-bendigo/].
.
Yet at the same time DSE points out that… ‘biodiversity is in decline‘
.
In its ‘Victoria’s Biodiversity Strategy 2010–2015: Consultation Draft‘ DSE reminds us that two hundred years of (immigrant deforestation), severe droughts, major bushfires and the impact of climate change, has severely affected Victoria’s species and ecosystems. DSE professes:
- Victoria is the most cleared and densely populated state in Australia. Victoria has the highest proportion (48%) of sub-bioregions in Australia in poor condition, with four out of Australia’s five most cleared bioregions found in western Victoria (CES 2008).
- Approximately half of Victoria’s native vegetation has been cleared for agricultural and urban development, including 80% of the original cover on private land. Victoria is losing native vegetation at a rate of some 4,000 hectares per year, mostly from endangered grasslands (DSE 2008).
- Victorian landscapes are the most stressed in the country (NLWRA 2001). One third of Victoria’s major streams are in poor or very poor condition. Two thirds of wetlands have been either lost or degraded and nearly half of our major estuaries are significantly modified. Flows at the Murray mouth are estimated to be a quarter of what would naturally occur (VCMC 2007).
- 44% of our native plants and more than 30% of our animals are either extinct or threatened (CSIRO 2004). The highest number of threatened species in any one region in Australia occurs in north western Victoria.
- Exotic species represent about 30% of the Victorian flora with 1,282 species considered naturalised and a further 214 species considered incipiently naturalised in Victoria. This has increased from 878 naturalised species in 1984. It is estimated that an average of 7.3 new plant species establish in Victoria per year, and this number is increasing by a rate of 0.25 plants per year. Approximately 90% of the native vegetation in Melbourne is impacted by weeds, with more than 50% considered severely degraded. There are 584 serious or potentially serious environmental weeds in Victoria with 129 very serious (CES 2008).
- Over 100 marine species have been introduced to Port Phillip Bay.’
.
[Source: Victorian Government’s Department of Sustainability and Environment, ^http://www.dse.vic.gov.au/conservation-and-environment/biodiversity/victorias-biodiversity-strategy/biodiversity-strategy-renewal/draft-victorian-biodiversity-strategy-2010-2015/current-state, Clause 2.2 ‘Biodiversity is in decline‘].
.
State aware but doesn’t care
.
The Victorian landscape has undergone massive changes in the past 150 years. As a consequence of environmental degredation and destruction of indigenous flora and fauna:
- Over 60% of the state has been cleared, and much of what is left is seriously degraded by weed invasion;
- Of the two thirds of the state which is privately owned, only 5% retains its natural cover;
- Soil erosion and salination have become serious problems;
- Over 35% of our wetlands have been drained;
- Close to 80% of rivers and wetlands have been substantially modified;
- Almost all native grasslands have been eliminated or modified;
- Many other vegetation communities are almost extinct, or critically endangered;
- Over 900 exotic plant species have been established in Victoria, many of which are weeds, and scores of noxious exotic animal species are now widespread;
- 23 native mammal species have become extinct in Victoria.
.
[Source: The Southern Peninsula Indigenous Flora & Fauna Association Inc., ^http://www.spiffa.org/victorias-biodiversity-crisis.html].
And the Victorian Government is well aware.
DSE acknowledges that the ‘clearing of native vegetation (across Victoria) and habitat has also led to the loss or decline in wildlife species. Habitat fragmentation has meant that wildlife are more at risk from predators, harsh environmental conditions, and human influences (e.g. roads) as they move between remnant patches. Isolated patches support fewer and lower densities of wildlife, increasing the chances of population extinction in individual patches as a result of the impacts of chance events upon genetically simplified populations. Habitat loss and degradation also increases the susceptibility of wildlife to severe environmental conditions, such as fire and drought, and broader processes, such as climate change and changing rainfall patterns.’
DSE acknowledges that ‘while maintaining or restoring ecosystem function will help to reduce the rate at which species decline, we already have a legacy of species that are at risk due to past ecological disruption, and a latent ‘extinction debt’. Victoria’s past land management actions have resulted in the loss of species and created and ongoing risk of future losses. Many existing threatened species occur in remnant or fragmented landscapes where the work required to recover them is intensive, expensive and long-term. In extreme cases it is necessary to remove part of the remnant population to captivity until critical threats have been mitigated.
DSE acknowledges that ‘effective threatened species recovery requires:
- Effectively dealing with threats to reduce the rate at which species become threatened;
- Conducting recovery efforts in situ by managing the processes that degrade their habitat or directly threaten them, including, where required, support from ex situ conservation programs;
- The best available knowledge and an adaptive management approach, including adoption of the precautionary principle when required;
- Co-operative approaches to recovery, with an effective and efficient mix of incentives and regulations; and
- Planning and regulatory frameworks to provide clear and consistent policy, process and outcomes.’
.
Yet in the same breath DSE goes on to reinforce its ‘fire is good for wildlife‘ propaganda – ‘a substantial proportion of Australia’s unique biota is dependent, to varying degrees, on fire and the variety of fire regimes for its continued existence and development.‘
[Source: DSE’s ‘Code of Practice for Fire Management on Public Land‘, Clause 2.3.8 ‘Challenges relating to fire management’]
.
.
‘Fuel reduction burns threaten species’ – or Black Saturday incompetence an excuse for broadscale State Arson
[Source: Peter Vaughan, Monash University, Melbourne, 20100531,^http://www.reportage-enviro.com/2010/05/fuel-reduction-burns-threaten-endangered-species/]
.
‘Conservationists are concerned that fuel reduction burns in East Gippsland will threaten endangered species and reduce biodiversity.
On March 16, fire managers from the Department of Sustainability and Environment (DSE) ignited a fuel reduction burn in the Dinner Creek catchment of Waygara state forest, approximately 14 km West of Orbost. The fire quickly gained intensity, aided by a temperature of 30 degrees Celsius. It burnt most of the environmentally sensitive vegetation within the fire zone along four kilometres of the Dinner Creek.
DSE Fire Manager for the Orbost Region, Steve de Voogd, said that the Dinner Creek fuel reduction burn grew hotter than intended. The fire was meant to burn 2206 hectare of coastal forest and leave a mosaic of burnt and un-burnt areas within the fire’s containment lines.
.
According to Mr de Voogd, the DSE is now under community pressure to reduce the risk of wildfire through fuel reduction burning, and that must take precedent over ecological considerations.
.
“Although there is probably room for more fire ecology planning, it is incumbent on the DSE to take action because the consequences of doing nothing may be worse,” Mr de Voogd said.
Most of the hollow bearing trees in the burn zone, which were home to a number of endangered species protected under state and federal law, were destroyed.
Dr Rohan Bilney, an expert on Australian forest owls and spokesperson for the Gippsland Environment Group, said that the program intended to burn large areas of coastal forest without adequate ecological planning, monitoring or research, which threatened crucial habitat and food sources for the forest’s owls species.
.
“The coastal forests of East Gippsland are the strong hold of the Masked Owl, a species listed as threatened under two laws: the Victorian Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act and the Federal Environmental Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act. Most of East Gippsland’s Masked Owls live in the coastal forests now being subjected to intense broad area fuel reduction burns by the DSE,” said Dr Bilney.
Masked Owl (Tyto novaehollandiae).
The Masked Owl Action Statement, prepared under the Victorian Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act, estimates only 150 pairs of Masked Owl exist in Victoria. Of that total, 100 pairs are found in East Gippsland and most are concentrated in the coastal forest.
DSE Manager of Biodiversity in East Gippsland, Dr Steve Henry, said that the current DSE fuel reduction fire strategy allows for large fires but burning on such a scale leaves few options for the protection of important ecological values.
“If there are some areas that contain specific environmental attributes that we want to protect, we could exclude them from fire with a bulldozer line. However that is expensive and often very destructive on most of these large burns. The main management technique used is the way in which the lighting pattern of the fire is done, sometimes that is not as effective as we would hope,” he said.
Mr Henry said that funding constraints have not permitted the DSE to conduct detailed ecological studies of the coastal forests, including the effect of fire on the environment.
A post-fire ecological survey is currently being conducted by the DSE in selected fuel reduction areas.
The Dinner Creek fire was just one of 48 fuel reduction burns planned by the DSE for the region during 2009-2010. Like other fuel reduction burns, the DSE must comply with the Victorian Code of Practice for Fire Management on Public Land.
The primary objective of the Code is to protect of life and property, while minimising negative impacts on natural and cultural values, and abiding by threatened species legislation, are also included.
The Code of Practice also states that the DSE must prepare a Fire Ecology Strategy that includes input from ecological experts and full consideration of all available scientific research.
If little ecological research exists, fuel reduction burning can be conducted under the rational that it may reduce the future risk of wildfire.
.
In the absence of scientific data, the DSE will continue to plan fuel reduction burns from computer desktops, utilising the ad hoc data collected as part of the Environmental Vegetation Class mapping projects of the late 1990s.
While political pressure continues to increase, the DSE fire policy will remain focused on protecting the community against the spectre of Black Saturday.’
 Burn it in case it burns, because we don’t have the resources for wildfire suppression
Burn it in case it burns, because we don’t have the resources for wildfire suppression
.
.
‘Climate change, fires and logging -the deadly combination for Victoria’s species’
.
‘Two hundred years ago the Sooty owl was abundant and fed on about 18 species of ground prey in Gippsland. Today they have only two or three to chose from. Other species are under similar pressure.
Many of our native animals have become sparser in numbers and their range has shrunk. Some, like the Southern Brown Bandicoot (Federally listed but not State listed), are now isolated in small “island” populations which are dangerously close to extinction mainly due to threats of fire and predation. Fires destroy understorey cover, making it easy for foxes and dogs to wipe out small populations of ground dwelling animals.
The 2003 fires and the recent December ’06 fires have destroyed the habitat and ground cover over about 2 million hectares of Victoria’s forested country. This has had a horrifying impact on ground mammals, birds and hollow dependent species.
.
Scientist and Quoll expert, Dr Chris Belcher, has calculated that this species’ Victorian numbers were reduced by 33 – 45% as a result of the ’03 fires. The December ’06 fires would have reduced this again to even more precarious numbers.
The isolated colony of Long Footed Potoroos discovered around Wonangatta (or Wongongara?) will most likely have been killed as a result of the recent fires.
The Helmeted Honeyeaters had five small and isolated populations left but the 1983 fires wiped out four of them. Yellingbo is still likely to burn and our faunal emblem will be extinct on this planet.
Bandicoots are very fire sensitive. There are small and vulnerable populations scattered in Gippsland. In 1994, fires burnt 97% of the Royal National Park and Bandicoots no longer survive in this area. The safety of thick ground cover does not return for years, meaning foxes and dogs heavily predate any survivors.
.
East Gippsland is the last stronghold for many of our rare and endangered fauna. It is a wetter environment and has much higher floristic diversity and therefore animals.
Climate change will now make fires more frequent and intense in SE Australia (CSIRO). Governments must adapt management of natural areas to account for this reality as it is for agriculture, water and energy.
The greatest pressure on Eastern Victorian species has been in the Critical Weight Range from 35 gms to 5 kg. Many ground dwelling animals are extremely susceptible to fire. Potoroos, Quolls, Bandicoots, native rodents (the rare New Holland Mouse, Smokey Mouse etc).
The predation rate after a fire is huge and patches of unburnt forest within the fire zones are absolutely essential to help populations survive predation, recover and disperse in time. These areas are critical to protect from further disturbance.
The recovery of species after a fire is now very different from 200 yrs ago. Populations are more isolated, salvage logging further destroys their chances, there is less diversity of prey species for the higher order predators like owls and quolls to turn to if gliders and possums are impacted by fires (or logging the hollow-rich forests).
Logging ecologically diverse forests favours the return of biologically poor tree communities such as silvertop and stringybark. The forests with mixed gum and box throughout can have 20-50 times higher animal densities. Significant vegetation changes due to massive landscape disturbance such as clearfelling, makes endangered species recovery from fire even more unlikely.
In the 1990s, East Gippsland supported seven times more threatened species than other areas in Victoria. This made the region seven times more important for our endangered species’ survival. Since the fires of 03 and 06, it is not unreasonable to suggest that East Gippsland is the last refuge and last chance for these species to survive extinction. Extinction can happen very quickly.
Species which are fairly general in their roosting, nesting and feeding needs can often survive (as they have in other areas of the state) but the many specialist species which rely on large areas of diverse and thick forest are highly likely to vanish forever.
This is why the hasty and unscientifically mapped areas of newly reserved forest require careful refinements. The needs of the state’s threatened species must be made the priority. Independent biologists and on-ground local knowledge (not VicForests) must be used to finalise the new reserve boundaries, with the long-term impact of the recent fires as a major guiding factor.
The Bracks Government suggested there be no net loss of resource as an adjunct to the mapped reserve areas. This is an impossible and irrational qualification as fires can take out large percent of the forest and therefore wood resources in one season. Commercial use of forest should be allocated only after biologically essential considerations have been adequately addressed.
Another point made in pre-election promises was to make sure the new areas are mapped and industry changes are resourced so as to adhere to the terms and spirit of the RFA. This then should see the government honour its long overdue commitment to carry out research into the impact of clearfelling on threatened species, to identify sustainability indicators, carry out five yearly reviews and ensure threatened species are protected. None have been honoured in the last 10 years!
The recent court ruling regarding the EPBC Act should also give the state government substantial opportunity to begin to alter protection measures for Federally listed species in East Gippsland.
The conscience of this government cannot put the very limited future of several sawmills ahead of a large number of entire species. Continued logging of intact original forests must not be the overriding priority. The ability for species to cope with the escalating impacts of climate change and fires from 2007 onwards has to now be put ahead of politics and union threats. These species survived well in Australia for over 40,000 years. The clearfell logging industry has been around for less than 40 years. Political priorities have an even shorter lifespan.’