Posts Tagged ‘Sooty Owl’
Saturday, January 7th, 2012
 Cathcart State Forest (NSW) being logged in 2011
[Source: Australian Forests and Climate Alliance ^http://forestsandclimate.net/newsouthwales] Cathcart State Forest (NSW) being logged in 2011
[Source: Australian Forests and Climate Alliance ^http://forestsandclimate.net/newsouthwales]
.
Most of Australia’s native vegetation cover, over 75% of that predating the 1788 Colonial Invasion, has been ‘cleared’ – a euphemism for deforested, logged, destroyed, killed.
Today, as one travels around Australia and sees vasts areas of unproductive, degraded, denuded and abandoned farmlands – one questions why destroy more fragile environment? Yet the exploitative bastards are still hell bent on killing more native forest and bushland, even though they can’t properly manage the ‘already ‘cleared’ lands they’ve got. It is a short sighted insatiability, harking to a 19th Century ‘old blighty’ mindset of taming the land. It is deluded thinking that just because the native vegetation is green and looks fertile that it can be replaced for pasture and cropping and that new cleared land will be any different to that already cleared.
The Liberal-Labor governments and their rural National mates haven’t given a toss throughout the entire 20th Century and still couldn’t give a toss.
 Recent land clearing in the Daly River catchment area
Northern Territory, Australia.
Photo: Environment Centre NT Recent land clearing in the Daly River catchment area
Northern Territory, Australia.
Photo: Environment Centre NT
.
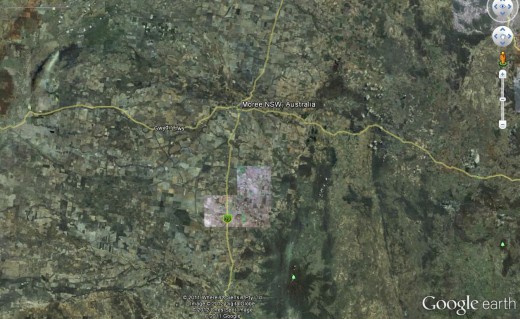 Moree region New South Wales – mainly deforested
Visit Google Earth and zoom into any area of NSW and see that most of it has been deforested
(click image to enlarge) Moree region New South Wales – mainly deforested
Visit Google Earth and zoom into any area of NSW and see that most of it has been deforested
(click image to enlarge)
.
Still across Australia in 2011, thousands of hectares of native forests continue to be deforested – albeit for farming, logging and development, or just bizarre bushfire abandonment. Not only is this occurring on private land, but in State Forests, which most people think are protected. Native forests on land are being cleared branded by State governments as ‘State Forests’ are simply not protected.
The native trees, flora and fauna are not protected from logging, bushfire, State-sanctioned arson (aka ‘hazard reduction‘), State napalming (aka indiscriminate ‘hazard reduction‘), indiscriminate State aerial poisoning with 1080, wildlife poaching, 4WD hooning, trail bike hooning, or even backpacker murdering. The watercourses (and the interconnected groundwater aquifers), that flow through State Forests are not protected from fishing, stormwater run-off, mine tailing contamination, farm pesticide and herbicide, industrial pollution.
.
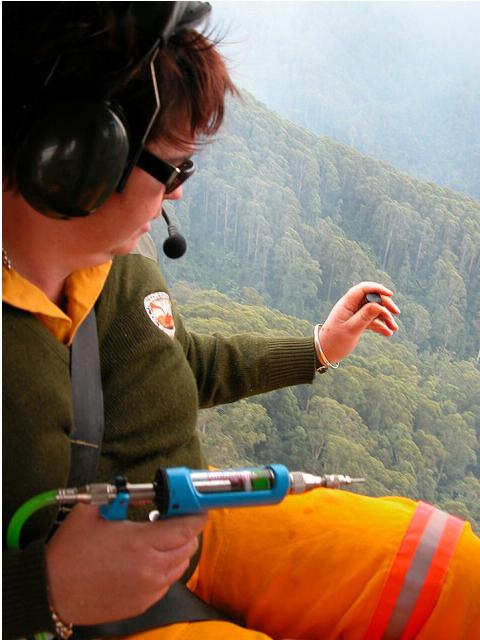 Helicopter Aerial Incendiary
Over Bindarri National Park, 20km south-west of Coffs Harbour, New South Wales
Yes, even our National Parks and Wildlife Service sets indiscriminate fires to National Parks! Helicopter Aerial Incendiary
Over Bindarri National Park, 20km south-west of Coffs Harbour, New South Wales
Yes, even our National Parks and Wildlife Service sets indiscriminate fires to National Parks!
.
For the likes of taxpayer funded government industrial loggers ‘State Forest’ is a euphemism ‘for not logged yet‘. This applies to the likes of Forestry Tasmania, VicForests, Forests NSW, Forestry SA (spot the naming trend), as well as the more aptly Queensland Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries, and likewise the Forest Products Commission of Western Australia.
It seems that doesn’t matter whether there is proof that there is an endangered and protected species such as the Long-Footed Potoroo in the Cann Valley State Forest or Drummer State Forest in Victoria, or protected Koalas in the Murrah/Mumbulla State Forests of New South Wales, or three identified endangered species, the wedge-tailed eagle, the swift parrot and the wielangta stag beetle in Tasmania’s Wielangta State Forests, the Liberal-Labor governments of those States turn a blind eye to deforestation.
It is only when self-funded local communities take the respective government logger to the Supreme Court and win that logging stops momentarily, such as in the recent Victorian Supreme Court case Environment East Gippsland Inc v VicForests [2010] VSC 335. In 2006, the Victorian State Government committed to increasing the conservation parks and reserves within the broader Brown Mountain area. Disregarding its elected master and ignoring any concerns for the ecological Precautionary Principle, State industrial logger VicForests, got stuck in with its mechanical clearfelling of old growth forests in the Brown Mountain area.
Not-for profit group Environment East Gippsland (EEG) self-funded and obtained numerous studies of the area indicated the presence of important threatened and rare species. EEG requested the Minister for Environment and Climate Change, Gavin Jennings, to make an interim conservation order to conserve critical habitat of the endangered Long-footed Potoroo, Spotted-tailed Quoll, Sooty Owl, Powerful Owl and Orbost Spiny Crayfish at Brown Mountain. Even then, the Minister for Environment and Climate Chang did not grant a conservation order, but instead increased the conservation area surrounding Brown Mountain. It took the overriding legal authority of the Supreme Court to stop the Victorian Government and its delinquent logger trashing protected old growth habitat.
 Victorian Labor Minister for Environment (etc), 2007-2010 Victorian Labor Minister for Environment (etc), 2007-2010
.
In March 2010, Forests NSW began controversial logging operations in the Mumbulla State Forest, south of Bermagui on the state’s far south coast. Despite being criticised, after a recent survey identified the forest as a key colony for the region’s remaining koala population, Forests NSW Regional Manager Ian Barnes says the logging must go ahead across 240 hectares of the forest, in order to satisfy a supply agreement with the timber industry.
 Deforestation is all about lining ones pockets out of ecological wanton exploitation
It’s a ‘wam bam thank you mam’ approach no different to what the Vikings did to the British in the eight Century.
Colonial Australians and their descendants are doing the same to Australian ecology in the 19th, 20th and 21st Centuries. Deforestation is all about lining ones pockets out of ecological wanton exploitation
It’s a ‘wam bam thank you mam’ approach no different to what the Vikings did to the British in the eight Century.
Colonial Australians and their descendants are doing the same to Australian ecology in the 19th, 20th and 21st Centuries.
Mr Barnes says the logging will not affect the koala habitat. “We’ve taken quite some effort to avoid any possible conflict there,” he says. “As anybody who reads the recent report will know, the koalas have been found in the eastern side of the forest, and our logging is planned for the western part, as far away as we can get from the koalas.”

Despite assurances, anti-logging campaigners have organised a vigil in the forest in an attempt to stop the logging. Conservationist Prue Acton says the activity will devastate the koala population.
“Why risk the only healthy koala colony left in the far south coast. For what? “ she said. “95% of what is going to be logged is going to end up at the Eden woodchip mill, be shipped to Japan for cheap copy-paper. What a disgrace.”
The Greens MP Lee Rhiannon says the Premier should put the protection of koalas ahead of the interests of logging companies. “The New South Wales Government has refused to end logging in the south east native forest but they should step in and stop the destruction of the koala habitat,” she said.
[Source: ‘Logging begins near key koala habitat‘, ABC, 20100330, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2010/03/30/2859615.htm?site=southeastnsw]
.
‘Loggers are clearing bushland at rising rate‘
[Source: ‘Loggers are clearing bushland at rising rate’, by Ben Cubby, Sydney Morning Herald, 20111221, ^http://www.theherald.com.au/news/national/national/general/loggers-are-clearing-bushland-at-rising-rate/2399764.aspx?storypage=0]

The amount of bushland being cleared by logging in NSW soared last year to the highest level since state-wide records began in 1988. An area equivalent to 138,400 football fields was cleared for crops, forestry or infrastructure, says a government report.
The Office of Environment and Heritage said the rise in logging was probably cancelled out by regrowth, leading to no net loss of trees, though its most recent survey took place in 2008, before the land clearing spike. It said the reasons for the logging increase were unclear.
”[The] most likely factors relate to market demand and favourable climatic conditions and [they] can be expected to fluctuate over time,” a department spokesman said. ”It is also possible that recent changes in forestry methods are more readily detectable by satellite monitoring.”
Environment groups said the annual vegetation report was evidence that logging companies were operating in an unrestrained manner.
Bushfires remain the biggest destroyer of forests in the state, leading to a net loss of 48,300 hectares in 2010, the report said.
.
But logging activities now come a close second, accounting for the removal of 42,700 hectares of trees in 2010. This is up from 31,000 hectares the previous year, and an average of about 21,000 hectares a year since 1988.
About 21,200 hectares of bushland was cleared in 2010 to make new areas for crops and grazing, while 5300 hectares were cut down to make way for roads, factories and housing.
”The NSW government is currently conducting a review of native vegetation controls,” said the chief executive of the Nature Conservation Council of NSW, Pepe Clarke. ”They should take this report as a warning – what is required are stronger land- clearing laws that do more to protect the environment, not weaker ones.”
The Wilderness Society said the government had ”failed in its promises to restrain land clearing, resulting in rapid and accelerating degradation of wildlife habitat and water catchments.”
The most recent State of the Environment report found that there had been no net loss of ”woody cover” across NSW between 2003 and 2008.
”This is because, although clearing has occurred over that period, there has also been an equivalent amount of regrowth including government sponsored environmental and forestry planting programs conducted by private landholders and state forests, within crown forests areas,” the department said.
”Notwithstanding no net loss over the whole state, some regions have experienced net declines in woody cover.”
The report uses the international definition of ”woody cover”, which includes land at least 20% covered by the crowns of trees higher than 2 metres, a description which would include relatively open country.
The introduction of a satellite monitoring system for land clearing last year appears to have increased the level of prosecution for illegal land clearing on private property. On crown lands, the number of prosecutions has increased threefold, from a low base, since 2007.
In 2010, the government received 471 reports of suspected illegal land clearing.
.
‘Landowners sent satellite images identifying land clearing‘
[Source: ‘Landowners sent satellite images identifying land-clearing’, NSW Department of Environment (etc), Media release: 14 May 2010, ^http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/media/DecMedia10051404.htm]
.
NSW Department of Environment Climate Change and Water (DECCW) today began a high tech education campaign to encourage compliance with native vegetation laws by sending letters to landholders including before and after satellite pictures identifying land clearing.
DECCW Director-General Lisa Corbyn said the letters were part of an ongoing education program to encourage compliance with the laws and inform landowners of the proper channels available to them if they want to clear native vegetation.
“We’ve been using satellite technology for some time to identify changes in vegetation cover that may warrant further investigation,” Ms Corbyn said.
“Now we are also using the technology as an education tool. From today, advisory letters will be sent to landowners including before and after satellite pictures showing that vegetation has been cleared on their land.”
Ms Corbyn said the letters aim to inform to the landowner that the satellite imagery has picked up that vegetation had been cleared and highlight the proper channels available to them under the legislation to allow clearing of native vegetation, such as property vegetation plans.
The letters support other tools used by DECCW to encourage compliance with the legislation, including strategic investigations, prosecutions, penalty notices, stop work orders, remedial directions, warning and advisory letters.
The letter also alerts landowners to incentive funding available to restore and protect native vegetation on their properties.
The Native Vegetation Act was introduced in 2003 to bring an end to broadscale land-clearing in NSW. Since then, more than 400,000 hectares of native vegetation has been conserved or rehabilitated on private land through property vegetation plans (PVPs) and 1.6 million hectares has been managed for thinning and invasive native scrub management.
.
Over 60 % of the native vegetation in NSW has been cleared, thinned or substantially disturbed.
.
The impacts of native vegetation clearing have included the extinction of 77 plant and animal species, soil erosion, increased dryland salinity and a decline in water quality.’
.
2003: ‘Clearing rate in NSW 116,000 to 216,000 hectares per year: NSW Govt report’
[Source: ‘Clearing rate in NSW 116,000 to 216,000 hectares per year: NSW Govt report’, by Stephanie Peatling, Environment Reporter, Sydney Morning Herald, 20031117, ^http://www.sydneyalternativemedia.com/id64.html]
.
The equivalent of up to 200,000 football fields may be illegally stripped of native trees and grass each year in NSW, figures suggest.
The first estimates on the extent of the clearings, which the Department of Natural Resources field staff prepared for the Government’s vegetation taskforce, suggest the figure could be as high as 100,000 hectares a year. The figures show between 150,000 hectares and 560,000 hectares were illegally cleared between 1997 and 2002.
The advice is the first official guess at NSW’s illegal clearance levels. The highest rates are in the Barwon, Central West and Far West regions where much of NSW’s remaining native vegetation is located.
The figures have shocked environmentalists, who stress the urgency of making changes to the state’s natural resource management system, which Parliament is debating this week.
A Wilderness Society campaigner, Francesca Andreoni, said: “The new system needs to be fair to everyone, particularly farmers doing the right thing.
“The shocking extent of illegal clearing confirms the urgent need for the Government to implement its decision to end broadscale clearing.”
Figures recording the rate of illegal land clearing each year are almost impossible to compile because it so hard to charge people who breach native vegetation laws. There is also a complicated system of exemptions which allow people to clear land for purposes such as maintaining fire access trails.
Monitoring illegal clearing is potentially dangerous for departmental compliance officers. After reports of illegal clearing earlier this year on a property near Nyngan, in the state’s west, department officers were prevented from entering the property by an angry crowd of up to 150 people.
.
When the amount of land illegally cleared is added to land that is legally approved for clearance, the department estimates between 700,000 hectares and 1.3 million hectares of land were cleared between 1997 and 2002.
.
The figures suggest clearing was faster than the Department of Natural Resources’ previously admitted figure of about 60,000 hectares a year. That figure would give NSW the second-highest clearing rate in the country behind Queensland.

Debate on the Government’s package to overhaul native vegetation laws, based on an election promise to end broad-scale clearing, will take place this week. Last month the Premier, Bob Carr, announced a $406 million deal between farmers and environmentalists to end broad-scale clearing.
Most of the money is expected to go towards such things as tree planting and fencing waterways to help counter salinity and erosion. But local authorities may also compensate farmers for not clearing land. Clearing will still be allowed where it is deemed environmentally necessary.
Under the new system, natural resource management is being overhauled. Thirteen catchment management authorities will replace 19 catchment management boards, 20 regional vegetation committees and 33 water management committees.
Scientists often name land clearing as one of Australia’s most urgent environmental concerns. It contributes to soil salinity, loss of biodiversity and greenhouse gas emissions because carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere when the cleared timber is disposed of, usually through burning.
.
‘Green groups attack logging growth’
[Source: ‘Green groups attack logging growth’, by David Bancroft, My Daily News, 20111229, ^http://www.mydailynews.com.au/story/2011/12/29/green-groups-attack-logging-growth/]
.
Environment groups have banded together to criticise the level of logging occurring in New South Wales. The Nature Conservation Council, The Wilderness Society, National Parks Association, the Northern Inland Council for the Environment and the North Coast Environment Council have issued a joint warning that iconic and endangered species are being threatened by land clearing.
 Illegal deforestation for fire wood, near Taralga, on the western edge of the Blue Mountains
Source: ^http://www.orchidsaustralia.com/article_%20conservation_no3.htm Illegal deforestation for fire wood, near Taralga, on the western edge of the Blue Mountains
Source: ^http://www.orchidsaustralia.com/article_%20conservation_no3.htm
.
In a joint press release, the groups said the NSW annual report on native vegetation released by the Office of Environment and Heritage (Ed. yet another money wasting name change) this month showed 2009/10 was the “worst year on record for clearing of native bushland”.
.
The Wilderness Society campaigns manager Belinda Fairbrother said the report showed that in 2009/10 an area equating to 138,400 football fields was cleared for crops, forestry or infrastructure.
.
“This is higher than any other year since records commenced in 1988 and shows the NSW Government has failed in its promises to restrain land clearing, resulting in rapid and accelerating degradation of wildlife habitat and water catchments,” she said.
North Coast Environment Council president Susie Russell said the report made a sad end to the International Year of Forests.
“The area cleared for forestry in 2009/10 was almost five times greater than it was in 1988/89,” she said.
“It reveals a massive increase in the rate and intensity of logging in NSW, which will be causing untold damage to the extraordinary high diversity forests of north-east NSW.”
Nature Conservation Council chief executive officer Pepe Clarke said land clearing was recognised as the single greatest threat to wildlife in Australia.
“It causes the death of birds and animals, the extinction of species, leads to the poisoning of soils from salinity and makes a major contribution to global warming,” he said.
.
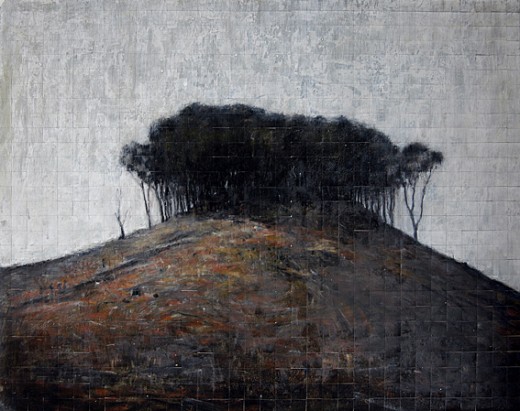 The Liberal-Labor Party ‘Island Vision’ for Australia’s State Forests
‘The Hill’ (Penrose State Forest, NSW) 2007, drawing by James King The Liberal-Labor Party ‘Island Vision’ for Australia’s State Forests
‘The Hill’ (Penrose State Forest, NSW) 2007, drawing by James King
^http://www.jamesking.com.au/drawings.html
.
Tags: 1788 Colonial Invasion, Cathcart State Forest, deforestation, Eden woodchip mill, fire wood, Forests NSW, Google Earth, hazard reduction, Helicopter Aerial Incendiary, Island Vision for Australian State Forests, koala habitat, land clearing, Logging, Long-footed Potoroo, Murrah/Mumbulla State Forests, not logged yet, Orbost Spiny Crayfish, Powerful Owl, precautionary principle, Sooty Owl, spotted-tailed quoll, State-sanctioned Arson, VicForests, Wielangta State Forests
Posted in Koalas, Owls, Quolls, Threats from Bushfire, Threats from Deforestation, Threats from Farming | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Friday, November 18th, 2011
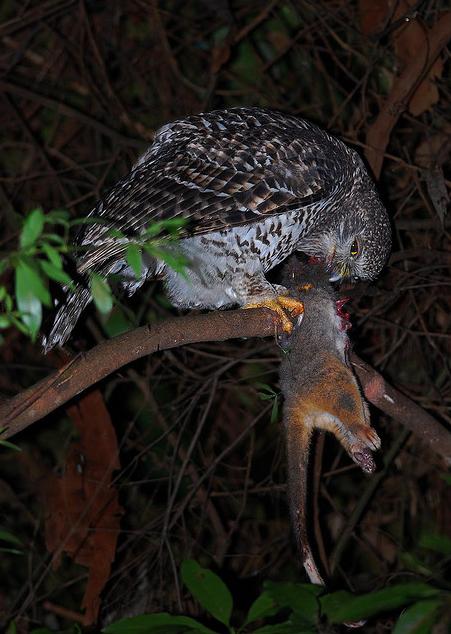
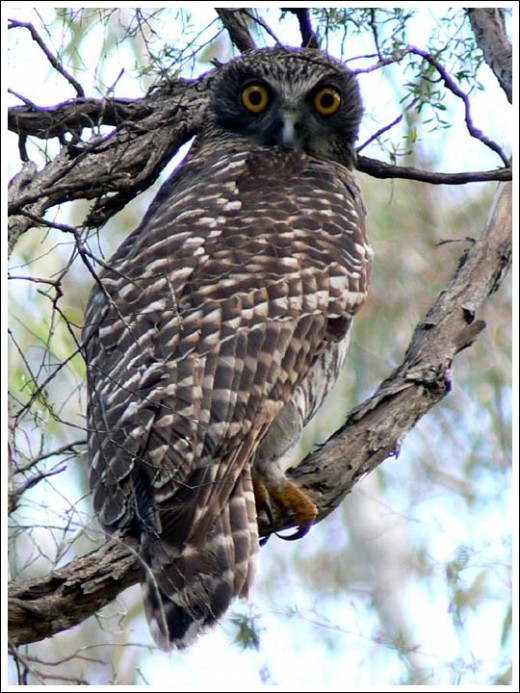 Powerful Owl (Ninox strenua)
(© Photo by Duncan Fraser, ^http://bencruachan.org/blog/?p=170) Powerful Owl (Ninox strenua)
(© Photo by Duncan Fraser, ^http://bencruachan.org/blog/?p=170)
.
The Powerful Owl (Ninox strenua) is Australia’s largest owl, yet in Victoria it has become a threatened species due to human destruction of old growth forest habitat; particularly the destruction of hollow-bearing trees used by this owl for nesting, roosting and home for its natural prey – possums. ‘Powerful Owls are adversely affected by the clearfelling of forests and the consequent conversion of those forests into open landscapes, but the species may persist in forests that have been lightly or selectively logged.’
[Source: ^http://www.birdsaustralia.com.au/our-projects/powerful-owl-wbc.html]
.
Since European settlement, 65% of Victoria’s forest cover has been cleared (Woodgate & Black 1988). Only 5% of freehold land remains forested. This past permanent loss of habitat has likely led to an overall reduction in owl numbers and fragmentation of the original continuous population into a series of small residual populations, each of which is at risk of becoming locally extinct.

‘It is estimated that hollows suitable for owls do not form, even in the fastest-growing eucalypts, until they are at least 150-200 years of age (Parnaby 1995). Of 21 nest trees observed by McNabb (1996) in southern Victoria, about 50% were senescent and all ranged between 350-500 years of age, based on data collected by Ambrose (1982).
Over much of its range, the lack of suitably large hollows is considered to be a limiting factor to successful breeding and population recruitment. The Powerful Owl is, therefore, vulnerable to land management practices that reduce the availability of these tree hollows now or in the future. The loss of hollow-bearing trees has been listed as a potentially threatening process under the Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act (SAC 1991).
In addition, prey density may be an important determinant in territory size and breeding success, particularly considering that only the male hunts during the breeding season. Seebeck (1976) estimated that about 250 possums (or their equivalent) would be required per year by a family group and recent studies have estimated around 300 prey items for a breeding pair rearing two young (Webster unpubl. data.). Key prey are also dependent on hollow trees.’

In its final recommendation the Scientific Advisory Committee (SAC 1994) has determined that:
‘the Powerful Owl is significantly prone to future threats which are likely to result in extinction, and very rare in terms of abundance or distribution.’
.
The short-term conservation objective is to prevent further decline by ensuring that good quality habitat for at least a population target of 500 breeding pairs of Powerful Owl is maintained on public land in Victoria.
[Source: ‘Powerful Owl Action Statement‘, Victorian Government’ s Department of Natural Resources and Environment (or whatever its latest incarnation is), ^http://www.oren.org.au/issues/endspp/powerfulowlAS.htm]
.
.
‘Impact of Bushfire on Sooty Owls and Powerful Owls’
[Source: Rohan Bilney, Report on Sooty Owls and Powerful Owls for the Supreme Court proceeding number 8547 of 2009 – Environment East Gippsland v VicForests, pp.12-13]
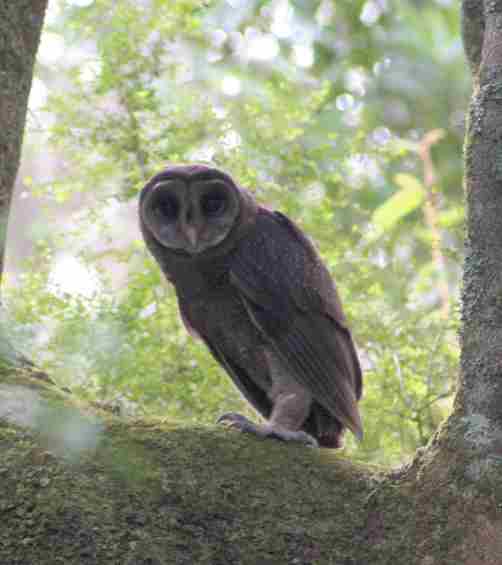

Greater Sooty Owl (Tyto tenebricosa)
.
‘Fire is likely to kill individual owls and small mammals, and remove potential habitat in the short-term, potentially resulting in long-term impacts.
‘How owl populations adapt or respond to fire is largely unknown’
.
‘Fire can consume hollow-bearing trees, while also stimulating hollow formation, but as hollow formation can take decades, frequent fires are likely to result in a net loss of hollow-bearing trees from the landscape (Gibbons and Lindenmayer 2002). This is likely to cause detrimental effects to all hollow-dependant fauna (Catling 1991; Gibbons and Lindenmayer 2002; Garnett et al. 2003).

‘Sooty Owls typically occupy habitats subject to infrequent fire regimes such as wetter forest types, possibly due to higher densities of hollow-bearing trees in such landscapes. Frequent fire regimes also simplify habitat structure, which can cause deleterious impacts on terrestrial mammals (Catling 1991; SAC 2001), which includes increased predation rates by feral predators due to the loss of habitat refuge (Wilson and Friend 1999). Overall, it therefore seems likely that owls and small mammals will be negatively impacted by frequent fire regimes. It is likely, however, that it will be the impacts of fire on prey densities that dictate how the owls respond to fire.
 Brown Mountain ancient old growth logged, incinerated, razed by VicForests
(Photo by Environment East Gippsland) Brown Mountain ancient old growth logged, incinerated, razed by VicForests
(Photo by Environment East Gippsland)
.
‘Most species are not adapted to fire per se, but adapted to a particular fire regime, which include fire aspects such as intensity, frequency, seasonality and scale (Bradstock et al. 2002). Due to variations in the life history requirements of species and their ability to survive fire, particular fire regimes can advantage some species, while being deleterious to others (Bradstock et al. 2002; Gill and Catling 2002; Keith et al. 2002). Due to the varying ecological responses to fire, it is important for biodiversity conservation that we not only understand species responses to particular fire regimes, but to ensure that appropriate fire regimes are maintained across the landscape. As prescribed fire is used as a management tool for reducing fuel load to minimise fire risk, it is important that its effects on biodiversity are well understood.
‘Unfortunately, knowledge on how native species respond to particular fire regimes is poorly understood, especially for fauna (SAC 2001, 2003; Clarke 2008). So, in the absence of this crucial ecological information it is virtually impossible to implement appropriate fire regimes which will result in minimal negative ecological impacts, let alone enhance biodiversity. Fire, both prescribed burning and wildfire, can present a threat to owls if conducted at inappropriate seasons, frequency, intensity or scales. It is therefore difficult to quantify the threat. The threat of inappropriate burning at high fire frequencies is likely to be mainly concentrated around human assets and populations, while fires in more remote forested areas will be subject to less frequent fires (DSE 2004). Fire also affects the entire owl population because all habitats occupied by owls is flammable.
‘Victoria has experienced three catastrophic fire events in the past 7 years, and combined with prescribed burning, approximately three million hectares have been burnt in this time.‘
‘This equates to approximately 2/3 of potential Sooty Owl habitat in Victoria. How populations of Sooty Owls and many other forest dependant fauna have been affected by these fires remains poorly understood or unknown. The ability for forest fauna to recover is therefore being hampered by further prescribed burning, and recovery is also hampered by reduced fecundity caused by a decade of drought, and for the owls, low prey population densities.’

.
.
The ‘Bushfire Fighting Principle’ corrupted by blinkered economic rationalism
.
The traditional principle of bushfire management is to put out bushfires…one would think. Yet this simple concept has been hijacked, bastardised and corrupted by successive governments as a consequence of systemic under-resourcing. Government under-resourcing has contributed to the deadly human toll in recent years.
The corrupting of this core bushfire management principle has morphed into a blanket one-size-fits-all defeatist policy of broadscale prescribed burning – burning the bush before it burns. The bushfire management tradition of ‘suppression‘ has been economically rationalised and politically supplanted by the proactively sounding notion of ‘prevention‘.
In Victoria, the fundamental job of putting out bushfires has bureaucratically morphed into a ‘Code of Practice for Fire Management on Public Land’, with its two general principles…
.Fire management planning on public land must address the threat of wildfire, guide the use of prescribed burning, and provide for the achievement of integrated land management objectives such as human safety and environmental management.’ (Clause 50)
‘Fire management activities must be undertaken in a participative manner where the responsibility for reducing the likelihood and consequence of wildfire is appropriately shared between public and private land holders and managers.’ (Clause 51)
.
What happened to the fundamental principle of bush fire fighting?
To put out bushfires!
Instead, vast areas of remaining native bushland and forests across Australia are being deliberately burnt to the point where critical faunal habitat is sterilised – only the trees remain, while the rich underlying vegetation, demonised as ‘hazardous fuel‘ is incinerated and repeatedly prevented from regrowth. Wildlife habitat has become a fuel hazard targeted for burning by the very custodians charged with wildlife conservation. And out of the Victorian Royal Commission into the Black Saturday bushfires, the anticipated kneejerk response by bushfire agencies to commence Prescribed Burning Armageddon against the bush has started as many genuine conservationists have feared.
And what has been the full realised cost of the 2009 Victorian Bushfires – valuing human lives, human injuries, ongoing trauma, livelihoods, wildlives, livestock, private property, natural assets, on top of the direct operational response cost, the indirect costs of contribiting agencies, the donations raised, capital costs, the opportunity costs, the investigation costs, the Royal Commission costs? No one has come up with a figure. These values were outside the Victorian Royal Commission’s terms of reference – so what real value was it? Economic rationalising of emergency management is costing lives and contributing to species extinctions.
.
.
Victorian Government Policy of Bushfire Lighting
.
The Victorian Government’s delegated custodian on natural areas across the State is the infamous Department of Sustainability and Environment (DSE), with a reputation for lighting most of the bushfires it euphemistically labels as ‘prescribed burning’ wherein it finds unburnt bushland and prescribes its own burning regimes. When such custodial agencies restore the word ‘conservation‘ back into their title, some respect may return.
DSE’s ‘Code of Practice for Fire Management on Public Land‘ was revised in 2006. It relies upon background premises that since “much of the Australian continent is fire-prone”, that “fire occurs naturally”, that “many species of vegetation and wildlife have adapted to living within the natural fire regime” and that “Victoria’s Indigenous people used fire as a land management tool for thousands of years”. The Code justifies that “Victoria’s flora, fauna and the ecosystems they form are adapted to fire of varying frequencies, intensities and seasonality.” Victoria’s Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act 1988 has objectives to ensure “Victoria’s native flora and fauna can survive, flourish, and retain their potential for evolutionary development”. Now the integrity of this Act is under threat. Perversely DSE’s Code of Practice argues that deliberate burning of bushland and forest habitat will help Victoria’s native flora and fauna to survive, flourish, and retain their potential for evolutionary development.
Crap!
DSE stretches its rationalising propaganda further, claiming that excluding bushfire can have “negative consequences for Victoria’s flora and fauna“. And this is where the hijacking, bastardisation and corrupting turns from mythology into unsubstantiated falsehood and misinformation. No document exists to zoologically prove that native fauna will suffer such negative consequences if it does not have a bushfire range through its habitat. As a result, the Code of Practice implies that bushfire is ok for all Victorian bushland and forests – DSE conveniently convinces itself that the urgent moral imperative for DSE to suppress bushfires is extinguished. So now it lights more fires than it puts out.
The Code also premises that “often these wildfires can be difficult to suppress”. Well no wonder with an grossly under-resourced, firetruck-centric volunteer force.
 . .
.
‘DSE holds fire management workshop in Bendigo’
.
On 22nd June 2011, DSE staged a workshop of stakeholders to discuss some recommendations of the Royal Commission into Victoria’s February 20o9 bushfire tragedy. According to the website ‘Friends of Box-Ironbark Forests’, in attendance were representatives from the CFA, local government, The Wilderness Society, Bendigo Field Naturalists Club, Friends of Kalimna Park, North Central Victoria Combined Environment Groups [NCVCEG], Apiarists Association and DSE attended a workshop on June 10 to learn about the process for implementing the findings of the Victorian Bushfires Royal Commission. Though Friends of Box-Ironbark Forests (FOBIF) was not invited to this workshop, we were represented by members of some of the other groups.
Once again DSE’s Code of Practice for Fire Management on Public Land (COP) is to again be reviewed and updated, except its premises have not changed, so what’s the point? The following notes taken on the issue of Fire management Zones/Prescriptions is telling of how disconnected DSE is from wildlife habitat conservation:
.
‘Fire Management Zones (FMZ) have been reviewed recently. An interim zoning is to be released soon. With little time left the group briefly discussed the merits of fire management zones, and how they might relate to the risk model. It was highlighted that the residual fuel load is an important aspect, but further detail as to how was not provided.
NCVCEG made the point that the current diagram used by DSE to represent the relationship between ecological outcomes and fire management outcomes across the four FMZ is misleading, encourages poor planning, discourages biodiversity management in zones 1 and 2, and neglects to recognise that fire management outcomes may be achieved in all zones, especially where integrated planning and alternative practices (to prescribed burning) are established.
In relation to FMZ the Apiarists pointed out that Box Ironbark forests generally have very low fuel levels in comparison to heavily forested regions where many lives were lost during the fires in 2009. The merit of burning areas used for honey production was questioned and the long term impacts of severe burning on Box Ironbark forest ecology was raised.’
.
[Source: Friends of Box-Ironbark Forests, 20110622, ^http://www.fobif.org.au/2011/06/dse-holds-fire-management-workshop-in-bendigo/]
.
.
Yet at the same time DSE points out that… ‘biodiversity is in decline‘
.
In its ‘Victoria’s Biodiversity Strategy 2010–2015: Consultation Draft‘ DSE reminds us that two hundred years of (immigrant deforestation), severe droughts, major bushfires and the impact of climate change, has severely affected Victoria’s species and ecosystems. DSE professes:
- Victoria is the most cleared and densely populated state in Australia. Victoria has the highest proportion (48%) of sub-bioregions in Australia in poor condition, with four out of Australia’s five most cleared bioregions found in western Victoria (CES 2008).
- Approximately half of Victoria’s native vegetation has been cleared for agricultural and urban development, including 80% of the original cover on private land. Victoria is losing native vegetation at a rate of some 4,000 hectares per year, mostly from endangered grasslands (DSE 2008).
- Victorian landscapes are the most stressed in the country (NLWRA 2001). One third of Victoria’s major streams are in poor or very poor condition. Two thirds of wetlands have been either lost or degraded and nearly half of our major estuaries are significantly modified. Flows at the Murray mouth are estimated to be a quarter of what would naturally occur (VCMC 2007).
- 44% of our native plants and more than 30% of our animals are either extinct or threatened (CSIRO 2004). The highest number of threatened species in any one region in Australia occurs in north western Victoria.
- Exotic species represent about 30% of the Victorian flora with 1,282 species considered naturalised and a further 214 species considered incipiently naturalised in Victoria. This has increased from 878 naturalised species in 1984. It is estimated that an average of 7.3 new plant species establish in Victoria per year, and this number is increasing by a rate of 0.25 plants per year. Approximately 90% of the native vegetation in Melbourne is impacted by weeds, with more than 50% considered severely degraded. There are 584 serious or potentially serious environmental weeds in Victoria with 129 very serious (CES 2008).
- Over 100 marine species have been introduced to Port Phillip Bay.’
.
[Source: Victorian Government’s Department of Sustainability and Environment, ^http://www.dse.vic.gov.au/conservation-and-environment/biodiversity/victorias-biodiversity-strategy/biodiversity-strategy-renewal/draft-victorian-biodiversity-strategy-2010-2015/current-state, Clause 2.2 ‘Biodiversity is in decline‘]
.
.
State aware but doesn’t care
.
The Victorian landscape has undergone massive changes in the past 150 years. As a consequence of environmental degredation and destruction of indigenous flora and fauna:
- Over 60% of the state has been cleared, and much of what is left is seriously degraded by weed invasion;
- Of the two thirds of the state which is privately owned, only 5% retains its natural cover;
- Soil erosion and salination have become serious problems;
- Over 35% of our wetlands have been drained;
- Close to 80% of rivers and wetlands have been substantially modified;
- Almost all native grasslands have been eliminated or modified;
- Many other vegetation communities are almost extinct, or critically endangered;
- Over 900 exotic plant species have been established in Victoria, many of which are weeds, and scores of noxious exotic animal species are now widespread;
- 23 native mammal species have become extinct in Victoria.
.
[Source: The Southern Peninsula Indigenous Flora & Fauna Association Inc., ^ http://www.spiffa.org/victorias-biodiversity-crisis.html]
.
And the Victorian Government is well aware.
DSE acknowledges that the ‘clearing of native vegetation (across Victoria) and habitat has also led to the loss or decline in wildlife species. Habitat fragmentation has meant that wildlife are more at risk from predators, harsh environmental conditions, and human influences (e.g. roads) as they move between remnant patches. Isolated patches support fewer and lower densities of wildlife, increasing the chances of population extinction in individual patches as a result of the impacts of chance events upon genetically simplified populations. Habitat loss and degradation also increases the susceptibility of wildlife to severe environmental conditions, such as fire and drought, and broader processes, such as climate change and changing rainfall patterns.’
DSE acknowledges that ‘while maintaining or restoring ecosystem function will help to reduce the rate at which species decline, we already have a legacy of species that are at risk due to past ecological disruption, and a latent ‘extinction debt’. Victoria’s past land management actions have resulted in the loss of species and created and ongoing risk of future losses. Many existing threatened species occur in remnant or fragmented landscapes where the work required to recover them is intensive, expensive and long-term. In extreme cases it is necessary to remove part of the remnant population to captivity until critical threats have been mitigated.
DSE acknowledges that ‘effective threatened species recovery requires:
- Effectively dealing with threats to reduce the rate at which species become threatened;
- Conducting recovery efforts in situ by managing the processes that degrade their habitat or directly threaten them, including, where required, support from ex situ conservation programs;
- The best available knowledge and an adaptive management approach, including adoption of the precautionary principle when required;
- Co-operative approaches to recovery, with an effective and efficient mix of incentives and regulations; and
- Planning and regulatory frameworks to provide clear and consistent policy, process and outcomes.’
.
Yet in the same breath DSE goes on to reinforce its ‘fire is good for wildlife‘ propaganda – ‘a substantial proportion of Australia’s unique biota is dependent, to varying degrees, on fire and the variety of fire regimes for its continued existence and development.‘
[Source: DSE’s ‘Code of Practice for Fire Management on Public Land‘, Clause 2.3.8 ‘Challenges relating to fire management’]

.
.
‘Fuel reduction burns threaten species’ – or Black Saturday incompetence an excuse for broadscale State Arson
[Source: Peter Vaughan, Monash University, Melbourne, 20100531,^http://www.reportage-enviro.com/2010/05/fuel-reduction-burns-threaten-endangered-species/]
.
‘Conservationists are concerned that fuel reduction burns in East Gippsland will threaten endangered species and reduce biodiversity.
On March 16, fire managers from the Department of Sustainability and Environment (DSE) ignited a fuel reduction burn in the Dinner Creek catchment of Waygara state forest, approximately 14 km West of Orbost. The fire quickly gained intensity, aided by a temperature of 30 degrees Celsius. It burnt most of the environmentally sensitive vegetation within the fire zone along four kilometres of the Dinner Creek.
DSE Fire Manager for the Orbost Region, Steve de Voogd, said that the Dinner Creek fuel reduction burn grew hotter than intended. The fire was meant to burn 2206 hectare of coastal forest and leave a mosaic of burnt and un-burnt areas within the fire’s containment lines.
.
According to Mr de Voogd, the DSE is now under community pressure to reduce the risk of wildfire through fuel reduction burning, and that must take precedent over ecological considerations.
.
“Although there is probably room for more fire ecology planning, it is incumbent on the DSE to take action because the consequences of doing nothing may be worse,” Mr de Voogd said.
Most of the hollow bearing trees in the burn zone, which were home to a number of endangered species protected under state and federal law, were destroyed.
Dr Rohan Bilney, an expert on Australian forest owls and spokesperson for the Gippsland Environment Group, said that the program intended to burn large areas of coastal forest without adequate ecological planning, monitoring or research, which threatened crucial habitat and food sources for the forest’s owls species.
.
“The coastal forests of East Gippsland are the strong hold of the Masked Owl, a species listed as threatened under two laws: the Victorian Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act and the Federal Environmental Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act. Most of East Gippsland’s Masked Owls live in the coastal forests now being subjected to intense broad area fuel reduction burns by the DSE,” said Dr Bilney.

Masked Owl (Tyto novaehollandiae)
.
The Masked Owl Action Statement, prepared under the Victorian Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act, estimates only 150 pairs of Masked Owl exist in Victoria. Of that total, 100 pairs are found in East Gippsland and most are concentrated in the coastal forest.
DSE Manager of Biodiversity in East Gippsland, Dr Steve Henry, said that the current DSE fuel reduction fire strategy allows for large fires but burning on such a scale leaves few options for the protection of important ecological values.
“If there are some areas that contain specific environmental attributes that we want to protect, we could exclude them from fire with a bulldozer line. However that is expensive and often very destructive on most of these large burns. The main management technique used is the way in which the lighting pattern of the fire is done, sometimes that is not as effective as we would hope,” he said.
Mr Henry said that funding constraints have not permitted the DSE to conduct detailed ecological studies of the coastal forests, including the effect of fire on the environment.
A post-fire ecological survey is currently being conducted by the DSE in selected fuel reduction areas.
The Dinner Creek fire was just one of 48 fuel reduction burns planned by the DSE for the region during 2009-2010. Like other fuel reduction burns, the DSE must comply with the Victorian Code of Practice for Fire Management on Public Land.
The primary objective of the Code is to protect of life and property, while minimising negative impacts on natural and cultural values, and abiding by threatened species legislation, are also included.
The Code of Practice also states that the DSE must prepare a Fire Ecology Strategy that includes input from ecological experts and full consideration of all available scientific research.
If little ecological research exists, fuel reduction burning can be conducted under the rational that it may reduce the future risk of wildfire.
.
In the absence of scientific data, the DSE will continue to plan fuel reduction burns from computer desktops, utilising the ad hoc data collected as part of the Environmental Vegetation Class mapping projects of the late 1990s.
While political pressure continues to increase, the DSE fire policy will remain focused on protecting the community against the spectre of Black Saturday.’
 Burn it in case it burns, because we don’t have the resources for wildfire suppression Burn it in case it burns, because we don’t have the resources for wildfire suppression
.
.
‘Climate change, fires and logging -the deadly combination for Victoria’s species’
[Source: Environment East Gippsland, ^http://www.eastgippsland.net.au/?q=node/446]
.
‘Two hundred years ago the Sooty owl was abundant and fed on about 18 species of ground prey in Gippsland. Today they have only two or three to chose from. Other species are under similar pressure.
Many of our native animals have become sparser in numbers and their range has shrunk. Some, like the Southern Brown Bandicoot (Federally listed but not State listed), are now isolated in small “island” populations which are dangerously close to extinction mainly due to threats of fire and predation. Fires destroy understorey cover, making it easy for foxes and dogs to wipe out small populations of ground dwelling animals.
The 2003 fires and the recent December ’06 fires have destroyed the habitat and ground cover over about 2 million hectares of Victoria’s forested country. This has had a horrifying impact on ground mammals, birds and hollow dependent species.
.
Scientist and Quoll expert, Dr Chris Belcher, has calculated that this species’ Victorian numbers were reduced by 33 – 45% as a result of the ’03 fires. The December ’06 fires would have reduced this again to even more precarious numbers.
The isolated colony of Long Footed Potoroos discovered around Wonangatta (or Wongongara?) will most likely have been killed as a result of the recent fires.
The Helmeted Honeyeaters had five small and isolated populations left but the 1983 fires wiped out four of them. Yellingbo is still likely to burn and our faunal emblem will be extinct on this planet.
Bandicoots are very fire sensitive. There are small and vulnerable populations scattered in Gippsland. In 1994, fires burnt 97% of the Royal National Park and Bandicoots no longer survive in this area. The safety of thick ground cover does not return for years, meaning foxes and dogs heavily predate any survivors.
.
East Gippsland is the last stronghold for many of our rare and endangered fauna. It is a wetter environment and has much higher floristic diversity and therefore animals.
Climate change will now make fires more frequent and intense in SE Australia (CSIRO). Governments must adapt management of natural areas to account for this reality as it is for agriculture, water and energy.
The greatest pressure on Eastern Victorian species has been in the Critical Weight Range from 35 gms to 5 kg. Many ground dwelling animals are extremely susceptible to fire. Potoroos, Quolls, Bandicoots, native rodents (the rare New Holland Mouse, Smokey Mouse etc).
The predation rate after a fire is huge and patches of unburnt forest within the fire zones are absolutely essential to help populations survive predation, recover and disperse in time. These areas are critical to protect from further disturbance.
The recovery of species after a fire is now very different from 200 yrs ago. Populations are more isolated, salvage logging further destroys their chances, there is less diversity of prey species for the higher order predators like owls and quolls to turn to if gliders and possums are impacted by fires (or logging the hollow-rich forests).
Logging ecologically diverse forests favours the return of biologically poor tree communities such as silvertop and stringybark. The forests with mixed gum and box throughout can have 20-50 times higher animal densities. Significant vegetation changes due to massive landscape disturbance such as clearfelling, makes endangered species recovery from fire even more unlikely.
In the 1990s, East Gippsland supported seven times more threatened species than other areas in Victoria. This made the region seven times more important for our endangered species’ survival. Since the fires of 03 and 06, it is not unreasonable to suggest that East Gippsland is the last refuge and last chance for these species to survive extinction. Extinction can happen very quickly.
Species which are fairly general in their roosting, nesting and feeding needs can often survive (as they have in other areas of the state) but the many specialist species which rely on large areas of diverse and thick forest are highly likely to vanish forever.
This is why the hasty and unscientifically mapped areas of newly reserved forest require careful refinements. The needs of the state’s threatened species must be made the priority. Independent biologists and on-ground local knowledge (not VicForests) must be used to finalise the new reserve boundaries, with the long-term impact of the recent fires as a major guiding factor.
The Bracks Government suggested there be no net loss of resource as an adjunct to the mapped reserve areas. This is an impossible and irrational qualification as fires can take out large percent of the forest and therefore wood resources in one season. Commercial use of forest should be allocated only after biologically essential considerations have been adequately addressed.
Another point made in pre-election promises was to make sure the new areas are mapped and industry changes are resourced so as to adhere to the terms and spirit of the RFA. This then should see the government honour its long overdue commitment to carry out research into the impact of clearfelling on threatened species, to identify sustainability indicators, carry out five yearly reviews and ensure threatened species are protected. None have been honoured in the last 10 years!
The recent court ruling regarding the EPBC Act should also give the state government substantial opportunity to begin to alter protection measures for Federally listed species in East Gippsland.
The conscience of this government cannot put the very limited future of several sawmills ahead of a large number of entire species. Continued logging of intact original forests must not be the overriding priority. The ability for species to cope with the escalating impacts of climate change and fires from 2007 onwards has to now be put ahead of politics and union threats. These species survived well in Australia for over 40,000 years. The clearfell logging industry has been around for less than 40 years. Political priorities have an even shorter lifespan.’

.
.
Further Reading:
.
[1] ^ http://eastgippsland.net.au/files/Sooty_Owl_%20Powerful_Owl_Bilney_December_2009.pdf , [ Read Report]
[2] Environment East Gippsland website, ^ http://www.eastgippsland.net.au/
[3] ‘ Sooty Owl Action Statement‘, Victorian Department of Sustainability and Environment (DSE), [ Read Statement]
[4] ‘ Powerful Owl Action Statement‘, (DSE) ^ http://www.dse.vic.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0019/103177/092_powerful_owl_1999.pdf , [ Read Statement]
[5] ‘ Masked Owl Action Statement‘, (DSE), ^ http://www.dse.vic.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0015/103173/124_Masked_Owl_2001.pdf , [Read Statement]
[6] Victorian Rainforest Network website, ^ http://www.vicrainforest.org/
[7] The Southern Peninsula Indigenous Flora & Fauna Association Inc., ^ http://www.spiffa.org/victorias-biodiversity-crisis.html
[8] ‘Protecting Victoria’s Powerful Owls’, ^ http://www.dse.vic.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0012/102144/PowerfulOwls.pdf , [ Read Report]
[9] ‘ Fire Protection Plan Gippsland Region‘, 2011, ^ http://www.dse.vic.gov.au/fire-and-other-emergencies/fire-management/fire-protection-plans/fire-protection-plan-gippsland-region , [ Read Plan]
[10] ‘ North East Victoria: Biodiversity‘, Australian Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry, ^http://www.daff.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0007/63583/Environmental_Values.pdf , [ Read Report]
[11] ‘ Submission to East Gippsland Forest Management Zone Amendments September 2010‘, ^ http://vnpa.org.au/admin/library/attachments/Submissions/EG%20Zoning%20Review%20Joint%20Submission%20ENGO%20Groups.pdf , [ Read Report]
[12] ‘ Ecology and conservation of owls‘ by Ian Newton, ^ http://www.publish.csiro.au/pid/3152.htm
.
Tags: DSE, Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act, fuel reduction program, habitat trees, hazard reduction, hollow trees, hollow-dependant fauna, Masked Owl, Powerful Owl, prescribed burning, Sooty Owl, State Arson, State Logging, VicForests, Victoria's old growth forests, Victorian Bushfires Royal Commission, Victorian Department of Sustainability and Environment
Posted in Gippsland (AU), Owls, Threats from Bushfire, Threats from Deforestation | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Saturday, September 3rd, 2011
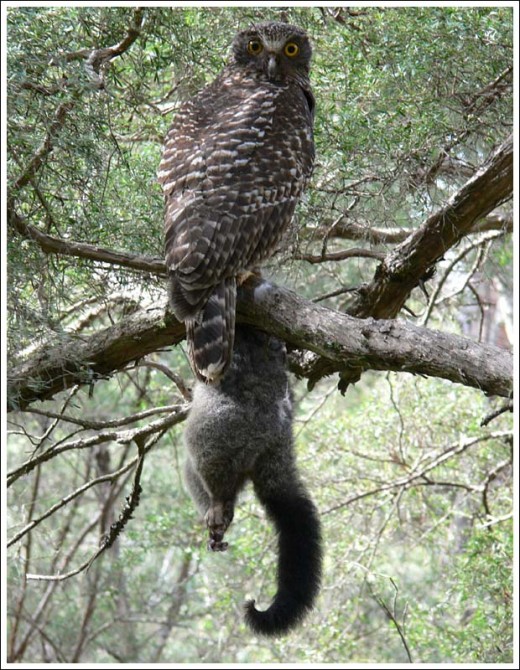 Australia’s native Powerful Owl with native prey – a juvenile Brushtail Possum (2kg?) Australia’s native Powerful Owl with native prey – a juvenile Brushtail Possum (2kg?)
© Photo by Duncan Fraser
^http://www.natureofgippsland.org/
.
Powerful Owl Call
(turn on your computer volume)

.
.
Drought, bushfires…it’ll take years to find out what’s happened to Victoria’s Forest Owls
.
[Source: ‘Something is knocking the states owls off their perches‘, by John Elder, The Age newspaper (Victoria, Australia), 20100613, ^http://www.theage.com.au/victoria/something-is-knocking-the-states-owls-off-their-perches-20100612-y4s0.html]
.
‘What’s happened to Victoria’s carnivorous owls? A significant number have vanished, and the (Victorian) Department of Sustainability and Environment (DSE) isn’t sure what’s going on.
It’s assumed the top end of the woodland food chain is either starving to death because its food source has been killed off by the drought and fires, or it is relocating to parts unknown, but it will take years to find an answer.
The DSE has been monitoring the owl populations – including that of the Powerful Owl, Australia’s largest owl – since 2000. Since then, detection rates in South Gippsland and the Bunyip State Park have dropped by half.
In some areas of the Bunyip State Park – half of which was lost to the Black Saturday fires – detections of the Sooty Owl have dropped to a third.
DSE owl specialist Ed McNabb says: ”We don’t know what’s happened to them. We can only assume that drought has played a major role. We noticed the downward trend before the fires. They’re very mobile birds, but the fires would have had an impact on their prey.”
Powerful and sooty owls, both officially listed as vulnerable, mainly eat sugar gliders and ringtail possums. The possums in particular are known to have little resistance to chronic hot weather, and their failure to thrive in the drought is the main reason why owl numbers have dropped.
While owls may have escaped (Victoria’s) Black Saturday fires, many possums would have been incinerated.
.
McNabb says the smaller carnivorous birds, such as the barking owl, are able to sustain themselves on insects. Powerful and sooty owls can also eat rabbits and birds such as magpies and kookaburras, but they need to make the change in their diet before energy loss reduces their ability to effectively hunt.
”They’ll either starve or take something else,” said McNabb.
Equally disastrous for the owls was the loss of old trees with large hollows that they require for nesting. They might have shifted elsewhere to recolonise, but this would mean taking over an already occupied territory. ”And there tends to be a home-ground advantage in these battles,” said Mr McNabb. The occupying bird has inside knowledge of the territory and a greater capacity to defend its patch, because it’s energy store will be higher. Flying great distances in search of food saps the strength from large birds and even causes them to starve.
The DSE’s biodiversity team leader for West Gippsland, Dr Rolf Willig, said:
The top order carnivores were ”an indicator species as to the well-being of the ecosystem.
Theoretically, if they’re happy, the rest are happy.”
.
For five years Dr Willig has been running a playback monitoring program in South Gippsland, where recordings of owl calls are played into the dark and answering calls are recorded. The number of birds answering calls have dropped significantly this year.
”The results indicate we may be having a delayed reaction from the fires,” he said. ”The possums not actually killed in the fires might have been exposed afterward, and the owls picked them off, eating all the food that was left.”
It will take years to find out what’s happened. ”And not just three or five years. We’ll be out here for a long time,” said Dr Willig.’
.
.
‘Conservation through Knowledge’ – a motto of leadership

The Royal Australasian Ornithologists Union is Australia’s largest non-government, non-profit, bird conservation organisation. It has sensibly branded itself as ‘Birds Australia‘, which in just two words says all that it is about, and the Emu family graphic is uniquely representative of Australia ~ the Emu being Australia’s largest bird.
Similarly sensible is its motto ‘Conservation through knowledge‘ which provides inspiration for conservation leadership, beyond Ornithology. The organisation was founded way back in 1901 to promote the study and conservation of the native bird species of Australia and adjacent regions, making it Australia’s oldest national birding association.
The Powerful Owl call above is sourced courtesy of Birds Australia.
.
.
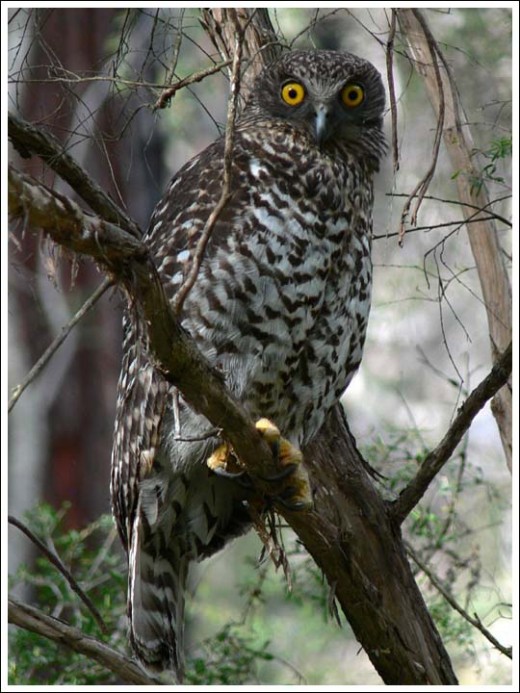
Powerful Owl (Ninox strenua)
http://www.birdsaustralia.com.au/our-projects/powerful-owl-wbc.html
 Powerful Owl (weighs under 1.5 kg) Powerful Owl (weighs under 1.5 kg)
© Photo by Duncan Fraser
^http://www.natureofgippsland.org/
.
A noctural top-order predator of tall old forests, the Powerful Owl is territorial, sedentary and monogamous ~ it calls one place home and mates for life (a lifestyle model for many humans).
.
HABITAT
Throughout most of its range this species typically inhabits open and tall wet sclerophyll forest, mainly in sheltered, densely vegetated gullies containing old-growth forest (where they breed in hollows in large trees) with a dense understorey, often near permanent streams. Such habitats are often dominated by Mountain Grey Gum, Mountain Ash, Manna Gum or Narrow-leafed Peppermint. They occasionally also occur in rainforest in gullies surrounded by sclerophyll forest or woodland. Powerful Owls also occur in adjacent open dry sclerophyll forests and woodlands, such as those dominated by box–ironbark eucalypts, Candlebark, Messmate or riparian River Red Gums; they sometimes also occur in open casuarina and cypress-pine forests.
The main food source for these owl species is hollow-dependant mammals (e.g. greater gliders, sugar gliders). Natural processes that create tree hollows typically take hundreds of years to form.
Human disturbed forests, through logging/burning/fragmentation/euphemistic ‘clearing’, destroy these vital yet rare hollow-bearing trees, and this considerably disadvantages owls.
DISTRIBUTION
- Endemic (found nowhere else on the planet, except for…) to eastern and south-eastern mainland Australia, mainly on the seaward side of the Great Divide.
.
CONSERVATION STATUS
- Vulnerable in Queensland
- Vulnerable in New South Wales
- Vulnerable in Victoria
- Endangered in South Australia
.
SURVIVAL THREATS
- Powerful Owls are adversely affected by the clearfelling of forests and the consequent conversion of those forests into open landscapes. [Deforestation]
.
When in flight, the silhouette of the Powerful Owl is distinctive, combining long, broad, rounded and deeply fingered wings with a large, sturdy body and a longish tail, gently rounded at the tip when spread. The flight is rather slow, with deep laboured wing-beats interspersed with glides.

.
.
References and Further Reading:
.
[1] The Nature of Gippsland (photographic website), ‘A photo gallery featuring the natural world of Gippsland, Victoria, Australia’, Photographs by Duncan Fraser, ^ http://www.natureofgippsland.org/
[2] Birds Australia, (Special survey on Powerful Owl distribution around Sydney, 2011), ^ http://birdsinbackyards.net/surveys/powerful-owl.cfm
[3] ‘ Powerful Owl (Conservation) Action Statement, Victorian Government, Department of Sustainability and Environment, (1999), ^ http://www.dse.vic.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0019/103177/092_powerful_owl_1999.pdf [ Read More]
[4] ‘ Protecting Victoria’s Powerful Owls‘, Victorian Government, Department of Sustainability and Environment, (2001), ^ http://www.dse.vic.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0012/102144/PowerfulOwls.pdf [ Read More]
.
– end of article –
Tags: Birds Australia, Conservation through Knowledge, Forest Owls, hollow-bearing trees, old growth, Otway Ranges, Powerful Owl, Sooty Owl, South Gippsland
Posted in 07 Habitat Conservation!, Gippsland (AU), Otway Ranges (AU), Owls, Threats from Bushfire, Threats from Deforestation | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Friday, August 26th, 2011
 Who does one believe?… Who does one believe?…
Greenwash Tick
.
.
.
Tuesday 23-Aug-2011:
‘Paper manufacturer loses green credentials’
by Liz Hobday, ABC News, 20110823, ^http://www.abc.net.au/news/2011-08-23/paper-manufacturer-loses-green-credentials/2851982/?site=melbourne, accessed 20110825]
.
The Wilderness Society says Australian Paper cannot meet environmental standards. The manufacturer of Reflex paper has lost part of its international environmental certification, after withdrawing from an audit of its wood supplies.

The Forest Stewardship Council was auditing Australian Paper, to check that the wood used to make Reflex paper is not sourced from high conservation value forests.
Luke Chamberlain from the Wilderness Society says the company withdrew from the process, because it cannot meet environmental standards.
“The makers of Reflex paper get their wood from the Victorian State Government native forest logging arm VicForests,” he said.
 “VicForests log in endangered species habitat. They log old growth forests in East Gippsland and the central highlands” “VicForests log in endangered species habitat. They log old growth forests in East Gippsland and the central highlands”

Australian Paper says its products are not sourced from high conservations value forests threatened by logging.
Shaun Scallan from Australian Paper says they withdrew because the audit process changed while it was underway.
“We pulled out because of a change in the definition of part of the standard late in the piece, which did not allow us enough time to then satisfy that changed definition,” he said.
.
.
Meanwhile the same Shaun Scallan of Australian Paper just the day prior on Monday 22 August 2011 posts his media release:
.
‘Australian Paper retains FSC Chain of Custody Certification’…?
by Shaun Scallan, Australian Paper, 20110822, ^http://australianpaper.com.au/media/2478/AP%20FSC%20audit%20release%20FINAL%20Aug%2022_2011.pdf, accessed 20110825
.
‘Australian Paper has successfully retained Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) Chain of Custody certification (FSC-C002059) in its latest audit. Auditor Rainforest Alliance confirmed that under the certification Australian Paper may continue to produce FSC-certified product based on sourcing of material from FSC-certified operations and recycled content, as allowed under the FSC rules for Mixed and Recycled product.
.
“We are pleased to have retained our FSC Chain of Custody certification,” Australian Paper CEO Mr Jim Henneberry said.
“Australian Paper has held Chain of Custody certification since 2006. However, we have decided to remove the Controlled Wood component from our certification at this time as there has been uncertainty around the interpretation of key elements of the standards.”
.
“Advice received by Rainforest Alliance from FSC International around the interpretation of the Standard was received after the physical audit had been completed. This left insufficient time for us to address and so we elected to withdraw Controlled Wood from our certification.” Mr Henneberry said.
.
Australian Paper remains committed to ensuring that fibre supplies come from internationally recognised, third party certified sources and also regards the Australian Forestry Standard and PEFC as benchmark certifications under this policy. The majority of wood supplied to Australian Paper is certified to the Australian Forestry Standard.
.
“We are also continuing to consult with a wide range of stakeholders as part of our Future Fibre Strategy review,” Mr Henneberry said.
“It is vital that we achieve the best balance between the environment, the health of regional communities and our ongoing competitiveness. We look forward to sharing outcomes from this review in due course.”
.
.
Meanwhile, we have the boss of Nippon Paper (the Japanese company that owns the misnomer ‘Australian Paper’) declaring Nippon Paper is going gang-busters to become a top global pulp and paper company…(at any cost?)
 ‘Since I was appointed president of Nippon Paper Group, Inc. in 2008, I have been pursuing “growth-oriented management.” This means exploring every possibility with a consistently positive stance, actively seizing opportunities, achieving the growth needed to become one of the top pulp and paper companies worldwide, as set out in the Group Vision 2015, and developing corporate value that meets the expectations of all stakeholders.’ ~ President of Nippon Paper Group, Yoshio Haga. [Source: ^http://www.np-g.com/e/about/president.html] ‘Since I was appointed president of Nippon Paper Group, Inc. in 2008, I have been pursuing “growth-oriented management.” This means exploring every possibility with a consistently positive stance, actively seizing opportunities, achieving the growth needed to become one of the top pulp and paper companies worldwide, as set out in the Group Vision 2015, and developing corporate value that meets the expectations of all stakeholders.’ ~ President of Nippon Paper Group, Yoshio Haga. [Source: ^http://www.np-g.com/e/about/president.html]
 . .
.
Meanwhile, the stated Charter of Nippon Paper Group includes:
.
‘6. Active involvement with environmental issues assures that…’
.
- ‘We shall promote afforestation projects, to create and make effective use of sustainable forest resources.’
- ‘We shall promote energy conservation, the use of wastepaper and other measures to effectively use resources that are limited in quantity.’
- ‘We shall manage and reduce all types of discharge and waste generated in the course of corporate activities.’
- ‘We shall research and develop manufacturing technologies, and products and services that are in harmony with the environment.’
.
[Source: ^http://www.np-g.com/e/about/charter.html#shead2]

Editor: It is suspicious when a Japanese company is more than content to log and irrevocably destroy another country’s old growth forests, while Japan’s own old growth forests around Mt Fuji remain sacrosanct.
‘In spite of the abundant natural resources, logging is not commonly practiced in the forests of Japan. Japan Forests are venerated and protected since they provide essential soil cover and help in water conservation. All Species are encouraged to grow in the Forests in Japan , from the broad-leaved deciduous to the evergreen coniferous types. There are also many forests which grow near volcanic areas, destroyed and then rejuvenated every time an eruption occurs. The Aokigahara Forest at the base of Mount Fuji is one such forest. Locals as well as tourist camp, trek and hike through these dense forests of Japan to explore their unusual natural beauty.
‘Some Japan Forests are designated as Sacred Forests . These forests generally contain an ancient religious Shrine, usually worshiping the Shinto religion and are protected from trespassing and destruction. These forest shrines are still venerated as national treasures.
.
Some of the sacred forests in Japan are-
- The Forest of the Yahiko Jinja has many trees like the Cedar, Cypress and Oaks. The Shrine has a sacred Chinquapin tree as well.
- The Forest of Atsuta Jinja is an important Shinto Shrine, housing one the three important Shinto relics – the holy sword of Kusanagi-no-tsurugi. The forest has evergreens like the Japanese Camellia Sakaki, camphor trees, Ilex and Japanese Honeysuckle.
- The Forest of Kashima Jingu has over 800 species of trees like varieties of Cedar, Fir and Oak. The Kashima Jingu is an important shrine of the Kanto Area. The forest has been designated as a Wildlife Protection area for the rare birds in the region.
- The Forest of Shimogamo Jinja covers over 495 hectares and has many different species of deciduous trees like the Zelkova, the Elm and the Hackberry. The Shrine itself has 53 buildings which have been designated as National Heritage Architecture.
- The Forest of the Kirishima Jingu covers and area of 887 hectares. Located near the Mount Kirishima Volcano, the forest has been destroyed and then recovered for over 60 times.
- The Forest of the Kasuga Taisha is home to the beautiful podocarpus Nagi. The forest also contains many species of evergreens and shrubs. Trees like the Kasuga, the Andromeda and the Ichii also grow there. People from all over Japan visit the venerated shrine in the quarterly pilgrimages.‘
[Source: ^http://www.mapsofworld.com/japan/japan-tourism/forests-in-japan.html]
 Japan’s sacred Aokigahara Forest Japan’s sacred Aokigahara Forest
.
Ethics question for Yoshio Haga (President of Nippon Paper Group):
What moral right do the Japanese have to consider their own native old growth Aokigahara Forest more sacred than Australia’s sacred native old growth forests such as those across East Gippland?
 Stump of Brown Mountain’s sacred 600 year old Mountain Ash old growth tree.
It was logged by VicForests in November 2008 for Nippon Paper’s Reflex Paper. Stump of Brown Mountain’s sacred 600 year old Mountain Ash old growth tree.
It was logged by VicForests in November 2008 for Nippon Paper’s Reflex Paper.
.
.
In light of VicForests recent civil prosecution in the Victorian Supreme Court, Nippon Paper Group’s association with VicForests calls into question the reputation of Nippon Paper Group and its brand Reflex Paper:
.
‘VicForests has been stopped from harvesting certain coupes in the Brown Mountain forest in East Gippsland containing old growth forest
– habitat for rare and threatened species – until the completion of steps implementing the precautionary principle.’
.
.
.
‘Environment East Gippsland Inc v VicForests – The precautionary principle in action’
22 November 2010:
[Source: Blake Dawson (Lawyers), ‘Environment Matters’, 20111122, ^http://www.blakedawson.com/Templates/Publications/x_article_content_page.aspx?id=60457, accessed 20110825]
.
.
In Brief:.
- ‘The Victorian Supreme Court decision in Environment East Gippsland Inc v VicForests firmly embeds the approach to the precautionary principle laid down in Telstra Corporation Limited v Hornsby Shire Council (2006).’
- ‘The case makes it clear that the precautionary principle can be the subject of an enforceable obligation.’
- ‘The case also makes it clear that the precautionary principle applies both at the strategic and operational stages of a project or undertaking.’
- ‘The fact that VicForests complied with its forestry approvals was not enough to satisfy the Court that it had met its obligations with regard to the precautionary principle.’
.
‘In Environment East Gippsland Inc v VicForests [2010] VSC 335 conservation group Environment East Gippsland (EEG) won a landmark injunction against VicForests, a state-owned timber business with responsibility for commercial timber harvesting in Victoria’s state forests.
VicForests has been stopped from harvesting certain coupes in the Brown Mountain forest in East Gippsland containing old growth forest – habitat for rare and threatened species – until the completion of steps implementing the precautionary principle.
In this case, Justice Osborn of the Supreme Court of Victoria undertook a thorough analysis of the application of the precautionary principle in the context of a detailed legislative regime aimed at balancing biodiversity protection and commercial timber harvesting. The case embeds the approach to the precautionary principle laid down by Chief Justice Preston of the Land and Environment Court of New South Wales, in Telstra Corporation Limited v Hornsby Shire Council (2006) 67 NSWLR 256.’
.
The lead-up to the litigation
.
‘The Brown Mountain forests in Victoria’s East Gippsland contain old growth forests and provide habitat for rare and threatened species such as the Powerful Owl, the Spotted-tailed Quoll (mainland Australia’s largest marsupial carnivore) and the Long-footed Potoroo. However, these areas are also amongst the most productive timber harvesting forests in Victoria and play a crucial role in Victoria’s sustainable timber industry.
In 2006, the Victorian State Government committed to increasing the conservation parks and reserves within the broader Brown Mountain area. Nevertheless, in 2008 commercial logging in the Brown Mountain area began.
After numerous studies of the area indicated the presence of important threatened and rare species, EEG requested the Minister for Environment and Climate Change, Gavin Jennings, to make an interim conservation order to conserve critical habitat of the endangered Long-footed Potoroo, Spot-tailed Quoll, Sooty Owl, Powerful Owl and Orbost Spiny Crayfish at Brown Mountain. The Minister did not grant a conservation order, but instead increased the conservation area surrounding Brown Mountain.
Having failed to obtain undertakings from VicForests that it would not proceed to log the Brown Mountain coupes, EEG sought interlocutory injunctive relief. An interlocutory injunction restraining logging was granted by Justice Forrest on 14 September 2009 (see our article Environmental litigation heats up with some significant wins for public interest litigants in our 2 October 2010 edition of Environment Matters ), pending the outcome of the full proceedings before Justice Osborn in the Supreme Court of Victoria.’
.
The legislative regime
.
‘Logging of state forests in Victoria is regulated by a complex scheme of legislation, codes of practice, management plans and procedures, described by Osborn J as “labyrinthine”. The principal legislation includes the Forests Act 1958 (Vic) (Forests Act), Sustainable Forests (Timber) Act 2004 (Vic) (SFT Act), Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act 1988 (Vic) and Conservation, Forests and Lands Act 1987 (Vic).’
.
Responsibilities for timber harvesting and forestry management
.
‘VicForests is a state-owned corporation, established in 2004 to undertake the harvesting of timber in Victoria’s state forests. The Secretary to the Department of Sustainability and Environment (DSE) has overarching responsibility for managing state forests and timber harvesting within forests under the Forests Act.’
.
Legal challenge
.
‘EEG sought an injunction restraining VicForests from harvesting four coupes at Brown Mountain containing old growth forest. It also sought declarations that timber harvesting within the coupes by VicForests in accordance with the current forestry regime would be unlawful.
EEG argued that the current conservation measures for the Brown Mountain coupes did not meet the requirements of the regulatory system, which addresses the preservation of conservation values and in particular the protection of endangered species. EEG also argued that VicForests had failed to implement the precautionary principle.
VicForests took issue with EEG’s standing to sue. Further, it denied the presence of a number of endangered species and argued that the logging of the Brown Mountain coupes would take place under a legislative framework that adequately protects endangered species and would, therefore, be lawful. It also argued that it was DSE’s responsibility to stipulate any further requirements for habitat protection in accordance with the regulatory regime.’
.
EEG’s standing
.
‘Following the settled High Court authority that standing to bring such proceedings depends on the plaintiff’s “special interest” in the subject matter of the litigation (Australian Conservation Foundation v Commonwealth (2000) 200 CLR 591), Osborn J was satisfied that EEG had a relevant “special interest” because:
- EEG uses the coupes to a greater degree than the general public (for example, the group has a “Valley of the Giants Old Growth Forests Walk” through the affected coupes);
- EEG’s predecessor was involved in the consultative process for the formulation of the applicable forest management plan; and
- the government has previously recognised EEG’s status as a body representing this sector of the public interest.’
.
The precautionary principle [Ed: once again]
.
‘The VicForests case firmly embeds in Australian environmental jurisprudence the approach to the precautionary principle laid down by Chief Justice Preston of the Land and Environment Court of New South Wales, in Telstra Corporation Limited v Hornsby Shire Council (2006) 67 NSWLR 256 (Telstra). Justice Osborn’s decision in VicForests is the first Supreme Court application of the Telstra principles.
The precautionary principle is integrated throughout the Victorian forestry regime’s many instruments.
Following Preston CJ’s two-fold test in Telstra, Osborn J stressed that the precautionary principle is a test of common sense. There must be:
- a threat of serious or irreversible environmental damage; and
- scientific uncertainty as to the environmental damage.
Justice Osborn stated:
Once both of these conditions or thresholds are satisfied, a precautionary measure may be taken to avert the anticipated threat of environmental damage, but it should be proportionate … [The] degree of precaution appropriate will depend on the combined effect of the seriousness of the threat and the degree of uncertainty.
It is a “wherever practicable” test.
In practice, this meant that once the two-fold test was satisfied by EEG, VicForests had the onus of proving that the threat posed by logging the coupes did not exist or was negligible. Because it could not do this, the question then became:
- whether the threat was able to be addressed by adaptive management measures (in this case the requirement for surveys and management zone reviews); and
- whether the measure alleged to be required (here the permanent injunction against logging the coupes) was proportionate to the threat in issue.
Justice Osborn carefully examined the legislative regime and held that it is not intended that VicForests only apply the precautionary principle at the strategic planning stage:
VicForests is specifically required to apply it [the precautionary principle] having regard to the results of monitoring and research as they come to light during operations. … The requirements of the precautionary principle fall to be considered in the light of the whole of the evidence bearing on these matters as it now is and not as it was at the time VicForests completed planning.
Justice Osborn stressed, however, that the precautionary principle sits within a wider statutory regime that takes into account principles of sustainable development.
He held that unless VicForests complied with the requirements of the applicable Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act Statements and with conditions stated in the relevant allocation order (under the Forests Act) and the Timber Release Plan (under the SFT Act), logging at Brown Mountain would be unlawful.
This meant that VicForests could not rely on its current approvals to log the coupes because DSE had not, for example, changed zonings in the coupes to reflect the presence of threatened species. VicForests had an ongoing, active duty to apply the precautionary principle, which included responding to new information as it became available.
Importantly, Osborn J stressed that the precautionary principle can be the subject of an enforceable obligation.’
.
Outcome
.
‘Justice Osborn ordered that VicForests stop harvesting until various measures had been completed to respond to the detection of endangered species and to implement a precautionary approach with respect to their potential extinction. The required measures included:
- creating or amending special management zones, special protection zones and retained habitat areas to protect the Long-footed Potoroo, Greater Gliders and Yellow-bellied Gliders (as relevant);
- undertaking further surveys for the Giant Burrowing Frog, Large Brown Tree Frog and Spotted-tailed Quoll; and
- completing a current review of the Powerful Owl and Sooty Owl Management Areas,
to the satisfaction of the Director, Biodiversity Policy and Programs, DSE.
The difficulty for the Court in formulating its orders was that the power to act on the evidence of rare and endangered species and implement the required legislative and policy changes lies not with VicForests, against whom the injunction was sought, but with DSE.
Justice Osborn overcame this difficulty by stopping VicForests from logging until certain actions are undertaken, these actions being DSE responsibilities. VicForests had maintained throughout proceedings that it would comply with any changes to the regulatory regime made by DSE, and this was accepted by the Court.
.
Significance of the decision
.
This case firmly embeds the approach to the precautionary principle laid down by Chief Justice Preston in Telstra Corporation Limited v Hornsby Shire Council (2006) 67 NSWLR 256.
Justice Osborn’s decision makes it clear that:
- The precautionary principle can be the subject of an enforceable obligation.
- Parties having an obligation to apply the precautionary principle cannot demonstrate compliance with the principle solely through departmental approval of their actions or relevant approvals under the regulatory regime; the precautionary principle is an active obligation that applies throughout operations, requiring parties to respond to new information as it arises.
- The precautionary principle applies throughout all stages of operation, not just the strategic planning (or approvals) stage.
The decision has broader implications because:
- The precautionary principle is embedded in many other statutory regimes in Victoria and around Australia, apart from the Victorian legislative regime for forestry and the protection of endangered species. The decision has implications for any statutory regime in which the principle is enshrined.
- Although VicForest is a state-owned enterprise operating within a highly regulated environment, there is scope for the decision to be applied to other types of entities operating within industries where the precautionary principle is relevant.
Furthermore, a decision of the Supreme Court of Victoria has strong precedent value, and is likely to be adopted by the Supreme Courts of other States, and perhaps even higher courts or courts with federal jurisdiction.
.
Action points
.
Parties under an obligation to apply the precautionary principle need to be aware that:
- to implement the precautionary principle as per the principles laid down in Telstra, parties need to ask:
- is there a real threat of serious or irreversible damage to the environment?
- if yes, is it attended by a lack of full scientific certainty (in the sense of material uncertainty)?
- if yes, is the threat non-existent or negligible?
- if no, is the threat able to be addressed by adaptive management and is the measure alleged to be required proportionate to the threat in issue?
- the principle must be applied at both the strategic decision making stage of a project, and throughout the operational stage; and
- it may not be sufficient to simply obtain and comply with project approvals – parties need to proactively respond to new information as it arises throughout the operational stage.’
.
..
.
Further Reading:
.
[1] >Vicforests’ Ecological Genocide
.
[2] ‘Nippon buys Maryvale mill‘, by Ian McIlwraith, The Age newspaper, 20090217, ^http://www.theage.com.au/business/nippon-buys-maryvale-mill-20090216-89bu.html, accessed 20110826]
.
‘Paperlinx will take a $600 million hit on its half year results and the future of its Tasmanian operations is under review after last night unveiling the partial sale of its Australian papermaking business.
Japan’s Nippon Paper Group will buy most of Australian Paper, which includes the Maryvale pulp mill in Gippsland, for more than $700 million, including taking on attached debt and a three-year profit share agreement.
Money from the sale, expected to be completed in June, will go to reducing PaperlinX’s debt burden to about $340 million…’
[Editor: So Paperlinx was in debt to the Australian Tax Office by over a billion dollars? How can Australia’s pulp industry be profitable then?]
.
[3] Australian Paper Watch website (providing information about the logging of Victoria’s forests to make paper products such as Reflex by Nippon Paper and their ‘subsidiary’ Australian Paper), ^http://www.australianpaper.forests.org.au/
.
[4] Nippon Paper’s Maryvale Mill Upgrade, ^http://www.reflex.com.au/2008-Maryvale-Mill-Upgrade/
‘Australian Paper has a long history in the La Trobe Valley in Gippsland, Victoria, dating back to 1937 when established. Today, the Mill is Australia’s largest integrated pulp and paper operation. In response to global paper trends and changing consumer expectations for our products, Australian Paper (Nippon Paper subsidiary) embarked on a major upgrade of the Maryvale Pulp Mill in 2006 which was completed in December 2008. With an investment of $350 million, the upgrade significantly expanded the Mill’s production of bleached pulp capacity and delivered a range of safety, health and environmental benefits.’
.
[5] ‘Loggers, activists clash over forest‘, by Adam Morton, The Age newspaper, 20110817, August 17, 2011, ^http://www.theage.com.au/victoria/loggers-activists-clash-over-forest-20110816-1iwew.html
.
‘Conservationists have held up timber workers in a fiercely contested area of native forest on Melbourne’s fringe for nearly a month, chaining themselves to bulldozers and climbing trees scheduled for logging.
The protest, which has led to at least 10 arrests, is expected to reach a climax today as activists and local residents march into the logging coupe outside Toolangi in Victoria’s central highlands.
Protest organisers claim they have evidence the coupe is home to the endangered Leadbeaters Possum, which scientists say is under threat after Black Saturday bushfires wiped out up to half its habitat. But the Department of Sustainability and Environment says there has been no sign of live possums. Department spokeswoman Kim Payne said one tree in the coupe had hollows that showed evidence of possum use. That tree would be left standing, but the coupe did not meet the legal criteria of prime possum habitat and could otherwise be logged.
Sarah Rees, director of Healesville-based group My Environment, said it was cruel to think a possum could be protected by retaining a single tree while taking away the forest around it. She said logging was hurting central highlands communities.
.
”Tourism based on the state forest is far more important to the local economy than forestry and the two cannot co-exist,” she said.
The conflict over the Toolangi State Forest was the focus of a public meeting in the area late last week when logging opponents verbally clashed with forestry workers, who accused the activists of restraint of trade. One contractor said he had lost about $80,000 due to the protests.

David Walsh, spokesman for state commercial timber agency VicForests, said the Toolangi protests had cost forest workers significant time. Only about a quarter of the 19-hectare coupe had been harvested. He said gates raised to ensure public safety had been damaged. ”VicForests believes these are legal harvesting operations which comply with the detailed legislative framework governing native timber harvesting in Victoria,” he said.‘
.
Editor: The legal doctrine of ‘restraint of trade’ sought to be applied in the commercial exploitation and destruction of old growth forests, is an invalid excuse. It is a contemptible euphemism for a ‘right to rape’ old growth ecology that is being contrived by commercial lawyers profiting from the exploiters ~ a case of the morally bankrupt collaborating with the damned.
[6] Ethical Paper website, ^http://www.ethicalpaper.com.au/
.
[7] My Environment website, ^http://www.myenvironment.net.au/

.
– end of article –
Tags: Aokigahara Forest, Atsuta Jinja, Australian Forestry Standard, Australian Paper, Chain of Custody certification, deforestation, East Gippsland, EEG, endangered species habitat, Environment East Gippsland, Environment East Gippsland Inc v VicForests, Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act, Forest Stewardship Council, Forestry Standard Certification, FSC, FSC audit process, FSC Chain of Custody Certification, FSC International, FSC-C002059, Future Fibre Strategy, Giant Burrowing Frog, Greater Glider, Greenwash Tick, Kashima Jingu, Kasuga Taisha, Kirishima Jingu, Large Brown Tree Frog, Leadbeaters Possum, Logging, Long-footed Potoroo, Maryvale Pulp Mil, My Environment, Nippon Paper Group, PEFC, Powerful Owl, precautionary principle, pulp and paper, Rainforest Alliance, Reflex Paper, restraint of trade, right to rape, sacred forest, Shimogamo Jinja, Shinto religion, Sooty Owl, The Wilderness Society, Timber Release Plan, Toolangi State Forest, TWS, VicForests, Yahiko Jinja, Yellow-bellied Glider
Posted in Gippsland (AU), Owls, Potoroos, Quolls, Reptiles, Threats from Deforestation | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Saturday, July 23rd, 2011
 Posted by Tigerquoll: Posted by Tigerquoll:
The VicMolesters are at it again.
Chainsaw-wielding loggers of VicForests are set to target old growth Mountain Ash near Sylvia Creek in the Central Highlands, to Melbourne’s north, east of Kinglake. That an inferno that was Black Saturday in February 2009 ripped through forests in the area around Narbethong, Toolangi and Kinglake matters squat to these woodchip mercenaries.
 The Burned Area Emergency Response Report (BAER) commissioned by the Brumby Government after the 2009 bushfires recommended preserving refuge areas such as those in Toolangi for biodiversity recovery. The Burned Area Emergency Response Report (BAER) commissioned by the Brumby Government after the 2009 bushfires recommended preserving refuge areas such as those in Toolangi for biodiversity recovery.
That the targeted forests have become isolated islands of habitat to rare wildlife matters squat to them. That the forests are home to Victoria’s endangered and disappearing Leadbeater’s possum, the Spotted-Tail Quoll, the Sooty Owl, and Baw Baw frog are but collateral damage to these bastards. “Over half the Leadbeater’s Possum’s forest habitat was destroyed in the Black Saturday bushfires, so every last bit that survives is incredibly precious, and essential to this tiny animals’ survival,” said spokesperson for local group ‘My Environment’ Sarah Rees.

“The criteria the government is using to identify Leadbeater’s Possum habitat are too conservative. We’re talking about Victoria’s wildlife emblem, we should be making sure they multiply and flourish, not simply cling on to the edge of survival.”
VicForests old growth logging is all for a quick buck from woodchip sales to make Reflex Paper. They would sell their daughters for less.

“DSE has confirmed the logging coupe contains old growth trees, even though VicForests and Government Minister Louise Asher insisted last week that it was not old growth forest,” said Wilderness Society forest campaigner Luke Chamberlain.

Tigerquoll
Suggan Buggan
Snowy River Region
Victoria 3885
Australia
Tags: Baw Baw Frog, Black Saturday, Burned Area Emergency Response Report, DSE, Eucalyptus regnans, Leadbeaters Possum, old growth granny killers, Sooty Owl, Spotted-Tail Quoll, Sylvia Creek, The Wilderness Society, Toolangi, VicForests, VicMolesters
Posted in Owls, Possums and Gliders, Quolls, Reptiles, Threats from Bushfire, Threats from Deforestation | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
|
|
 Cathcart State Forest (NSW) being logged in 2011
[Source: Australian Forests and Climate Alliance ^http://forestsandclimate.net/newsouthwales]
Cathcart State Forest (NSW) being logged in 2011
[Source: Australian Forests and Climate Alliance ^http://forestsandclimate.net/newsouthwales]
 Recent land clearing in the Daly River catchment area
Northern Territory, Australia.
Photo: Environment Centre NT
Recent land clearing in the Daly River catchment area
Northern Territory, Australia.
Photo: Environment Centre NT
 Moree region New South Wales – mainly deforested
Visit Google Earth and zoom into any area of NSW and see that most of it has been deforested
(click image to enlarge)
Moree region New South Wales – mainly deforested
Visit Google Earth and zoom into any area of NSW and see that most of it has been deforested
(click image to enlarge)
 Helicopter Aerial Incendiary
Over Bindarri National Park, 20km south-west of Coffs Harbour, New South Wales
Yes, even our National Parks and Wildlife Service sets indiscriminate fires to National Parks!
Helicopter Aerial Incendiary
Over Bindarri National Park, 20km south-west of Coffs Harbour, New South Wales
Yes, even our National Parks and Wildlife Service sets indiscriminate fires to National Parks!
 Victorian Labor Minister for Environment (etc), 2007-2010
Victorian Labor Minister for Environment (etc), 2007-2010
 Deforestation is all about lining ones pockets out of ecological wanton exploitation
It’s a ‘wam bam thank you mam’ approach no different to what the Vikings did to the British in the eight Century.
Colonial Australians and their descendants are doing the same to Australian ecology in the 19th, 20th and 21st Centuries.
Deforestation is all about lining ones pockets out of ecological wanton exploitation
It’s a ‘wam bam thank you mam’ approach no different to what the Vikings did to the British in the eight Century.
Colonial Australians and their descendants are doing the same to Australian ecology in the 19th, 20th and 21st Centuries.

 Illegal deforestation for fire wood, near Taralga, on the western edge of the Blue Mountains
Source: ^http://www.orchidsaustralia.com/article_%20conservation_no3.htm
Illegal deforestation for fire wood, near Taralga, on the western edge of the Blue Mountains
Source: ^http://www.orchidsaustralia.com/article_%20conservation_no3.htm
 The Liberal-Labor Party ‘Island Vision’ for Australia’s State Forests
‘The Hill’ (Penrose State Forest, NSW) 2007, drawing by James King
The Liberal-Labor Party ‘Island Vision’ for Australia’s State Forests
‘The Hill’ (Penrose State Forest, NSW) 2007, drawing by James King