Posts Tagged ‘RFS’
Thursday, November 8th, 2012
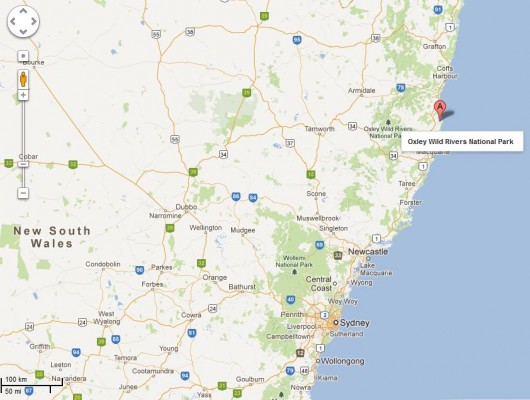
 Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Click image to enlarge
Inscribed on the asset register of World Heritage sites in 1994…but how much has been wiped out by October’s bushfires?
[Photo Source: New South Wales Government,
^http://www.nationalparks.nsw.gov.au/oxley-wild-rivers-national-park/travel-info] Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Click image to enlarge
Inscribed on the asset register of World Heritage sites in 1994…but how much has been wiped out by October’s bushfires?
[Photo Source: New South Wales Government,
^http://www.nationalparks.nsw.gov.au/oxley-wild-rivers-national-park/travel-info]
.
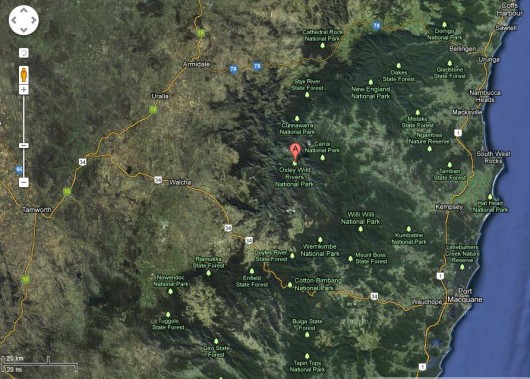 Location of Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Click image to enlarge – note the patchy dark green of remnant forests Location of Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Click image to enlarge – note the patchy dark green of remnant forests
[Source: Satellite Map – Google Maps]
.
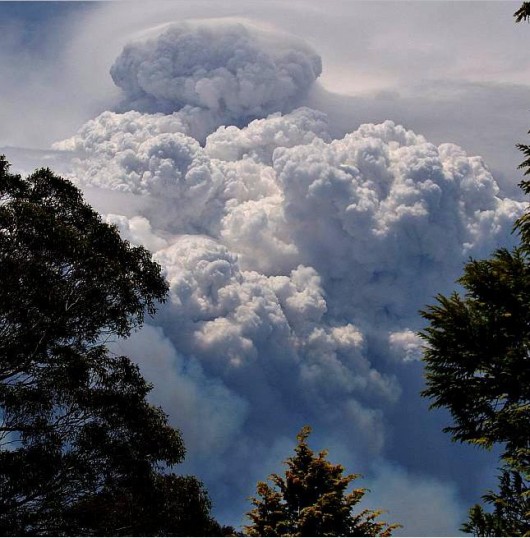
The ‘Macleay River’ Bushfire (Oct 2012)
.
 Macleay River Bushfire October 2012
– left to burn for a week from 12th Oct 2012 because not a threat to private property
..then the wind picked up…unbelievable! Macleay River Bushfire October 2012
– left to burn for a week from 12th Oct 2012 because not a threat to private property
..then the wind picked up…unbelievable!
.
Over the past month, a single contiguous area covering some 60,000 hectares of vegetation has been left to burn by bushfire. That equates to 600 km2 or roughly 25km x 25km.
Much of what has been burned is/was of World Heritage values within the included Oxley Wild Rivers National Park. This is unacceptable custodial neglect.
If this was Sydney, this is the black boxed area that would have been incinerated: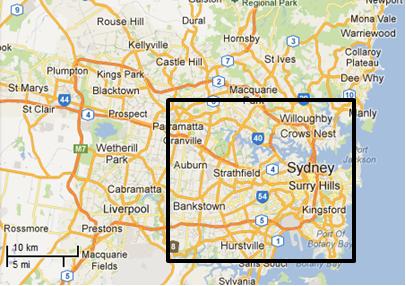 Putting this 60,000ha bushfire into a Sydney urban perspective
Professional urban fire fighting would not allow 60,000 hectares of private property and human lives to burn
– such would historically dwarf the Great Fire of London. Putting this 60,000ha bushfire into a Sydney urban perspective
Professional urban fire fighting would not allow 60,000 hectares of private property and human lives to burn
– such would historically dwarf the Great Fire of London.
.
The Rural Fire Service has labelled the bushfire the ‘Macleay River Fire‘. But it began as two separate bushfires on or before 12 October, nearly a month prior. One was then labelled ‘Georges Junction Fire‘ and the other ‘Freds Creek Fire‘, both purportedly ignited by bush arsonist(s). Seven days later, the Georges Junction Fire has burnt an estimated 8,931 ha, while the then much smaller Freds Creek Fire had burnt 1,688 ha. By the time the combined bushfire was extinguished 60,000 hectares had been burned, much within the World Heritage Area..
This is yet another classic case of bushfire neglect primarily by the delegated custodians of the National Park and World Heritage Area – the New South Wales National Parks and Wildlife Service. Is this due to chronic lack of resourcing; and/or symptomatic of a disturbing rationalist culture that believes that burning Australian vegetation, even ancient rainforest, could be somehow beneficial to biodiversity.
Remote ignitions go undetected, then unsuppressed, until many days later, bushfire weather conditions worsen and the fires get out of control, combine and destroy vast areas of important Nationl Park and World Heritage.
This 2012 Macleay River Fire is like the ‘2006 Grose Valley Fires‘ of the Blue Mountains repeated to script.
.
.
The Australian Government continues to be ultimately culpable for gross neglect in failing to protect its custodial listed natural heritage.
The Rural Fire Service has learnt to avoid accusatioins of incompetence by routinely removing timely records on its websites about the operational response in the days at the start of the ignitions. Details about the timings of ignition detection and initial suppression are deliberately withheld from the public.
The following bushfire updates are mainly from second-hand news media. A notable recurring theme across these news reports is that the media interest and the target of the fire fighting effort, just like in urban fire fighting, is to save humans lives and property. This is not a bad thing, but the glaring omission is the lack of interest in suppressing the bushfire in the National Park and World Heritage.
The Rural Fire Service policy and operational strategy is such that if human lives and properrty are not directly threatened by bushfire, then a bushfire is allowed to continue burning, irrespective of whether it is burning through National Park or World Heritage. Since the Rural Fire Service has the same terms of reference as the professionaly paid New South Wales Fire Brigade, then they are essentially doing the same urban job.
The only reason the Rural Fire Service exists in less populated rural areas instead of the professionaly paid New South Wales Fire Brigade, is traditionally so that the Australian Government and New South Wales Government can save money by relying on unpaid, under-resourced volunteers. Yet the environment in rural fire fighters work in is inherently more dangerous, demanding and in need of sophisticated resources for military-speed detection and suppressions of bushfires.
.
21 Oct: Bushfire Update
.
‘Blazes burn out of control: Permits suspended as hot, dry weather hits North West’
[Source: ”Blazes burn out of control: Permits suspended as hot, dry weather hits North West”, by Wendy Spooner, Northern Leader (regional newspaper), 20121021, ^http://www.northerndailyleader.com.au/story/411057/blazes-burn-out-of-control-permits-suspended-as-hot-dry-weather-hits-north-west/]
.
 Satellite infrared image of the fire called Georges Junction inside the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Having already burnt out a massive 14,000 hectares and is likely to join up with the Freds Creek fire.
The active edge of the fire shows up bright yellow; the red areas are the burnt areas.
(Photo by New England RFS) Satellite infrared image of the fire called Georges Junction inside the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Having already burnt out a massive 14,000 hectares and is likely to join up with the Freds Creek fire.
The active edge of the fire shows up bright yellow; the red areas are the burnt areas.
(Photo by New England RFS)
.
<<Two massive bushfires in the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park were basically running unchecked yesterday because of adverse firefighting conditions, incident controller for the New England bushfire emergency, Allyn Purkiss, said.
Mr Purkiss said the two Section 44-declared fires one named Freds Creek and the other Georges Junction were likely to join up yesterday and burn out a total of 30,000 hectares in the coming weeks.
“They took a big run under strong winds (on Saturday)..The fires had started after landholder burns had got away”, Mr Purkiss said.
..The fire named Freds Creek, which started on October 12, had burnt out 3,189 hectares and was crowning at 4am yesterday, with flames jumping from treetop to treetop.
“It means it’s very uncontrollable very dangerous conditions,” Mr Purkiss said yesterday.
The RFS had been unable to aerial-bomb the fires because of gusty winds. Mr Purkiss described it as “nigh-on impossible” to water-bomb in those conditions.
Instead, RFS volunteers had concentrated on saving property. He said it was hard to tell how many homes and remote-area shacks might be affected.
“We’re still trying to come to terms with that. We could have up to 50 in the area: there are shacks all through this country,” he said.
Mr Purkiss said the other fire, Georges Junction, had already burnt out 14,000 hectares. (Ed: Same as the 2006 Grose Valley Fires).
He said conditions in the New England RFS zone were “fairly similar” to strong, gusty winds on Saturday. “The forecast is for 50km/h winds by late afternoon,” Mr Purkiss said.
No homes had been lost in either fire yet. “None that we know of,” he said. The RFS was doing a “fairly extensive reconnaissance of the area”, he said.
Three other fires one about 40km east of Guyra, one near Walcha and one near Ebor had also started since Friday.
The Guyra fire, which started on Saturday, was located in the Mt Mulligan/Wards Mistake area.
Locals had alerted the RFS to the fire, which was in “very remote country … it’s difficult to get to no roads, no trails”, Mr Purkiss said.
“I’ve tasked an aircraft to get out there today and map it and give us some intel (intelligence),” he said..
“No properties were under threat: it was burning in scrub.“
.
Mr Purkiss said he was “not sure” how much land had been burnt out he would have to wait for information provided by the aircraft crew.
The Walcha fire, called Panhandle and in the Enfield State Forest, had burnt out five hectares by the time it was contained by mid-afternoon on Saturday.
The Ebor-area fire was located “in an area we can’t get to”, Mr Purkiss said. “We’re flying to map it today,” he said yesterday.
It had also burnt out five hectares.
“Local landholders and Ebor RFS assisted in containing it,” he said.
Mr Purkiss said the New England RFS zone was unlikely to lift its suspension of fire permits today.
“While ever we have a bushfire emergency like this going, all permits are suspended we’re already dealing with enough fires, so we don’t need any more mistakes giving us grief than we already have,” he said.
Mr Purkiss said this season had already started to play out differently compared to the past three years.
In the past three fire seasons, rain had usually come along and helped extinguish any fires but this season was different, with many more periods of extended dry weather.
“In talking to the local staff, they say that this (Georges Junction) is the largest fire they have had since 2009,” Mr Purkiss said. “We’re working hard to get it done. We thank the volunteers and employers for allowing us to fight these very large fires.”>>
.
22 Oct: Bushfire Update
.
‘Macleay River fire threatens homes’
[Source: ‘Macleay River fire threatens homes’, by Victoria Nugent, The Armidale Express (regional newspaper), 20121022, ^http://www.armidaleexpress.com.au/story/410559/macleay-river-fire-threatens-homes/?cs=469]
. Properties between Georges Junction and Five Day Creek were at threat from fire yesterday
(Photo: The Armidale Express) Properties between Georges Junction and Five Day Creek were at threat from fire yesterday
(Photo: The Armidale Express)
.
<<Fire continues to threaten properties near Oxley Wild Rivers National Park after two blazes combined yesterday.
The Macleay River bushfire had already burnt about 20,000 hectares early yesterday afternoon as more than 30 firefighters battled the out of control blaze, NSW Rural Fire Service spokeswoman Bridie O’Connor said.
The inferno may have posed a threat to properties between Georges Junction and Five Day Creek, particularly on the Carrai and Fitzroy Tablelands and on the Macleay River in the vicinity of Lower Creek and Comara, Ms O’Connor said early yesterday afternoon.
“We’re looking at a minimum of six hours before some properties might be affected,” she said. “People should expect to see smoke and fire and be alert.”
Hot and windy conditions over the weekend (20th and 21st) saw the fires at Georges Junction and Freds Creek combine.
The Georges Junction fire, near Cochrane State Forest, which started on October 12 had burnt more than 14,859 hectares and was still burning out of control when it met with the Freds Creek fire early yesterday afternoon. The fire at Freds Creek was being controlled yesterday afternoon after three State Forest groups joined the NSW Rural Fire Service to use bulldozers to create fire breaks earlier in the week.
Meanwhile, the Armidale to Kempsey Road between Waterfall Way and Bellbrook was closed on Saturday and Sunday because of the fires.
The Rural Fire Service was concentrating its efforts on establishing containment lines.
People on properties near Georges Junction and on the Macleay were urged to be alert for fire warnings.>>
.
23 Oct: Bushfire Update
.
‘Total fire bans expected back in place by Thursday’
[Source: ‘Total fire bans expected back in place by Thursday’, by Campbell Walker, Namoi Valley Independent (newspaper), 20121023, ^http://www.nvi.com.au/story/415687/total-fire-bans-expected-back-in-place-by-thursday/]
.
<<…Adverse weather conditions on Sunday hindered attempts to subdue two massive bushfires in the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park. Fire crews were reduced to protecting property on the ground and the two fires merged late on Sunday as fire crews battled from the ground to protect property, unable to water bomb due to gusty winds across the region.
The fire, now named the Macleay River Fire had burnt out 28,733 hectares as of last night, Inspector Brett Loughlin, public liaison officer for Armidale Section 44 with the NSW Rural Fire Service, said.
Mr Loughlin was expecting the fire to burn out more land.
“We’re doing some mapping now and expect it to be around that 30,000-hectare mark,” he said. He said 52 firefighters were on the ground creating firebreaks, doing backburning and helping protect the property of landholders living within a few kilometres of the fire front.
“There are properties in close proximity,” Mr Loughlin said. “The fire has flared up a little this afternoon and some embers are falling around properties in the Lower Creek area.
“No property is under threat at the moment … the fire’s not doing anything like it was doing on Saturday (when it was out of control – a day of hot, gusty westerly winds).”
Five helicopters are currently tasked to water bombing the Macleay River Fire.
Oxley Wild Rivers National Park is still shut to the public…>>
.

.
25 Oct: Bushfire Update
.
‘Arson suspected in Macleay River fire‘
[Source: ‘Arson suspected in Macleay River fire’, by Kitty Hill, Northern Daily Leader (local print newspaper), 20121025, ^http://www.northerndailyleader.com.au/story/420443/arson-suspected-in-macleay-river-fire/]
.
<<Rural Fire Service forensic investigators have interviewed a ‘person of interest’ as the battle to contain the Macleay River fire enters its 15th day.
RFS investigators from Kempsey and Coffs Harbour arrived yesterday to investigate the possible cause of the blaze in the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park which has since burnt out 33,160 hectares of bush and pasture land.
RFS Public Liason Officer Inspector Brett Loughlin said all major fires were investigated as a matter of cause and investigations were ongoing.
Around 80 firefighters from the NSW RFS, FRNSW and NPWS, supported by five aircraft and four bulldozers are fighting the fire, which has a 247 kilometre perimeter.
Ember attack on properties around the Lower Creek area were reported yesterday but Inspector Loughlin said that firefighters were working with local landholders to protect at-risk homes.
Inspector Loughlin said that good containment lines had been established by fire crews in the last 24 hours and today “aerial incendiary” work by helicopter would be carried out on the south western side of the blaze. “It’s still an active fire but we’re starting to get a handle on it,” Inspector Loughlin said.
The Macleay River Fire is the culmination of the ‘Freds Creek Bushfire‘ and ‘Georges Junction Bushfire‘ that had merged last weekend. The fire is burning in the vicinity of the Comara, Georges Junction, Five Day Creek, Lower Creek, Blanches Creek and Smith Creek areas.
Another fire burning near Guyra, has been contained. The ‘Mulligans Bushfire‘, which has burnt out 3207 hectares near the Guy Fawkes National Park has been burning since Saturday.>>
 Macleay River Bushfire
(Photo by Sean Bremmer) Macleay River Bushfire
(Photo by Sean Bremmer)
.
1 Nov: Bushfire Update
.
Rural Fire Service Reported Operational Statistics:
[Source: New South Wales Government, Rural Fire Service, ^ http://www.rfs.nsw.gov.au/]
‘MACLEAY RIVER FIRE‘
ALERT LEVEL: Advice
LOCATION: 50 kms east of Armidale, 75 kms west of Kempsey, 65kms east of Walcha
COUNCIL AREA: Armidale Dumaresq
STATUS: Being Controlled (Ed: glass half-full spin)
TYPE: Bush fire
FIRE: Yes
SIZE: 51,405 ha
RESPONSIBLE AGENCY: Rural Fire Service
UPDATED: 1 Nov 2012 15:25
.
5 Nov: Bushfire Update
.
‘NSW fires declared natural disaster zones’
.
[Source: ‘NSW fires declared natural disaster zones’, by AAP, 20121105, ^ http://www.heraldsun.com.au/news/breaking-news/nsw-fires-declared-natural-disaster-zones/story-e6frf7kf-1226510654741]
.
<<Three local government areas have been declared natural disaster zones in the wake of a major fire that has been raging in northern NSW for two weeks.
The massive front formed on October 21 when the Freds Creek and Georges Junction fires combined at the Macleay River. It has damaged over 51,000 hectares of:
- National Parks
- State Forests
- Private Land
.
across three shires:
- Armidale Dumaresq shire‘
- Walcha shire
- Kempsey shire
.
“These fires have been burning in the area for a number of days and due to the conditions, they merged into one large fire, jumped containment lines and threatened numerous properties,” Emergency Services Minister Michael Gallacher said in a statement on Monday.
“This declaration triggers a number of disaster assistance schemes to assist with the cost of disaster relief and recovery.”
Over the last two weeks, bushfires have raged across the New England and Mid North Coast regions. Other fires under this declaration include the Clay fire in Armidale Dumaresq, the Panhandle fire in Walcha and the Mulligans fire in Guyra on the western side of Guy Fawkes National Park, which has burnt over 3,400 hectares of National Park and private land.
Mr Gallacher said the Macleay River fire had damaged significant portions of the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park, which is part of the Gondwana Rainforests of Australia World Heritage Area, a series of protected areas which were first inscribed on the World Heritage List in 1986 and extended in 1994.
.
5 Nov: Bushfire Update
.
<<Three separate fires burning out of control south-west of Casino since the weekend have been contained, the Clarence Valley Rural Fire District reports.
The ‘Dubadar Creek Bushfire‘, which was believed to have been started by arsonists before blowing out from 50ha to 300ha on Saturday, was contained on Sunday and was extinguished at midday today, the district’s incident controller Stuart Watts said.
Two separate blazes, also deliberately lit, at Mt Pickabooba 4km from the Dubadar Creek fire were expected to be contained by this afternoon following back-burning, Mr Watts said. The Rural Fire Service had 10 fire trucks, 19 personnel and two bulldozers working to bring the fires under control on the weekend. The Northern Star has approached the police for comment.
The battle with the blazes come as NSW Police and Emergency Services Minister Michael Gallacher declared natural disasters for the Mid North Coast – parts of which only a year ago were receiving the same declaration for floods – and New England areas.
“The main focus of this declaration is the Macleay River Fire, which developed on 21 October 2012 as the culmination of the Fred’s Creek and Georges Junction Fires,” Mr Gallacher said in a written statement.
“These fires have been burning in the area for a number of days and due to the conditions, they merged into one large fire, jumped containment lines and threatened numerous properties…Firefighters have been working hard to create containment lines around the Macleay River Fire to protect properties as the fire approaches.
“As of 1 November 2012, the Macleay River Fire continues to burn and is estimated to have damaged over 51,000 hectares of National Parks, State Forests and private land across the three LGA’s of Armidale Dumaresq, Walcha and Kempsey.
“The Macleay River Fire has damaged significant portions of the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park, which is part of the Gondwana Rainforests of Australia World Heritage Area, a series of protected areas which were first inscribed on the World Heritage List in 1986 and extended in 1994.“>>
.
Reader Comment:
by ‘coco50’ from Ballina 20111105:
<<When is our judicial system going to get serious about arsonists? It is difficult enough to catch them. Think about what they do. They destroy natural bushland and animal habitat. They put the lives of people at risk or even cause deaths. They destroy property which causes hardship and suffering and years to rebuild. This pushes up everyone’s insurance premiums. They out emergency services personnel at risk.
But when we get an arsonist in court, the defence counsel makes an argument like: “My client had a difficult childhood – his parents and peers didn’t understand him. He is remorseful”
The Judge almost cries while handing out a “slap on the wrist” sentence. It is much harder to start a fire in jail while you are doing 20 years time. Lock them up!>>
.
[Source: ‘Fires contained as disaster declared’ , 20121105, Northern Star (local print newspaper), ^http://www.northernstar.com.au/news/fires-contained/1609219/]
.
6 Nov: Bushfire Update
.
Rural Fire Service Reported Operational Statistics:
.
[Source: New South Wales Government, Rural Fire Service, ^ http://www.rfs.nsw.gov.au/]
.
‘MACLEAY RIVER BUSHFIRE’
ALERT LEVEL: Advice
LOCATION: 65km East of Walcha
COUNCIL AREA: Armidale Dumaresq
STATUS: Being Controlled
TYPE: Bush fire
FIRE: Yes
SIZE: 59, 663 ha
RESPONSIBLE AGENCY: Rural Fire Service
UPDATED: 6 Nov 2012 09:10
.
Oxley Wild Rivers National Park is World Heritage ‘protected‘
.

1986: Gondwana Rainforests of Australia inscribed on the World Heritage List.
.
 World Heritage Listing because local people thought it was so important to save before it was gone World Heritage Listing because local people thought it was so important to save before it was gone
.
Over twenty-five years ago, in 1986 the Gondwana Rainforests of Australia, then called the Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves of Australia (CERRA), were inscribed on the World Heritage List for their outstanding natural universal values.
Theses rainforest comprise the Great Escarpment of eastern New South Wales, then known as the Australian East Coast Sub-tropical and Temperate Rainforest Parks, were inscribed on the World Heritage list meeting the following three World Heritage Natural Criteria:
- Outstanding example representing significant ongoing geological processes and biological evolution (World Heritage Natural Criterion viii)
- Outstanding example representing major stages of the earth’s evolutionary history (World Heritage Natural Criterion ix)
- Containing important and significant habitats for the in situ conservation of biological diversity (World Heritage Natural Criterion x)
.
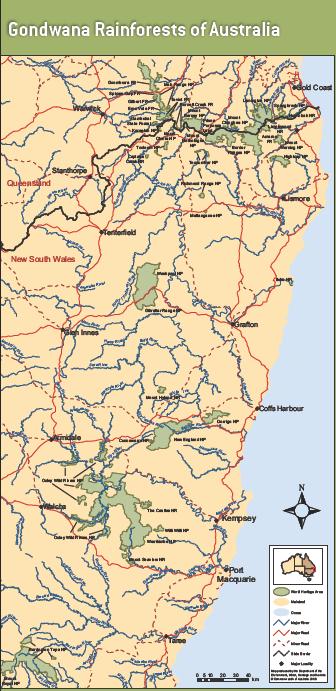 Trying to save the surviving remnant patches of Gondwana Rainforest ecosystems
(Ed: These few green shades are emblematic of Australian ransacking)
Read: >Large Map
[Source: ^http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/gondwana/pubs/gondwana-map.pdf] Trying to save the surviving remnant patches of Gondwana Rainforest ecosystems
(Ed: These few green shades are emblematic of Australian ransacking)
Read: >Large Map
[Source: ^http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/gondwana/pubs/gondwana-map.pdf]
.
The Gondwana Rainforests contains the largest and most significant remaining stands of subtropical rainforest and Antarctic Beech (Nothofagus moorei) cool temperate rainforests in the world, the largest and most significant areas of warm temperate rainforest and one of only two remaining large areas of Araucarian rainforest in Australia.
 Enormous Antarctic Beech (Nothofagus moorei)
At Cobark Park, Barrington Tops, 50 metres tall Enormous Antarctic Beech (Nothofagus moorei)
At Cobark Park, Barrington Tops, 50 metres tall
.
The Gondwana Rainforests of Australia is a serial property comprising the major remaining areas of rainforest in southeast Queensland and northeast New South Wales. They include the most extensive areas of subtropical rainforest in the world, large areas of warm temperate rainforest and nearly all of the Antarctic beech cool temperate rainforest. Some of the oldest elements of the world’s ferns and conifers are found here and there is a concentration of primitive plant families that are direct links with the birth and spread of flowering plants over 100 million years ago.
A wide range of plant and animal lineages and communities with ancient origins in Gondwana, many of which are restricted largely or entirely to the Gondwana Rainforests, survive in this collection of reserves. The Gondwana Rainforests also provides the principal habitat for many threatened species of plants and animals.
The area is one of the best places on earth to see ancient ferns and Araucaria such as Hoop Pines.
 Hoop Pine
(Araucaria cunninghamii)
Found naturally in the dry rainforests of New South Wales and Queensland and in Papua New Guinea.
The trees can live up to 450 years and grow to a height of 60 m. Hoop Pine
(Araucaria cunninghamii)
Found naturally in the dry rainforests of New South Wales and Queensland and in Papua New Guinea.
The trees can live up to 450 years and grow to a height of 60 m.
.
Rainforest once covered most of the ancient southern supercontinent Gondwana and remains the most ancient type of vegetation in Australia. The Gondwana Rainforests provide an interesting living link with the evolution of Australia. Few places on earth contain so many plants and animals which remain relatively unchanged from their ancestors in the fossil record.
Due to two centuries of colonial deforestation across New South Wales and Queensland – timbergetting, ‘land clearing’ for agriculture and housing – the reserves of rainforest that comprise The Gondwana Rainforests in discontinuous patches, surrounded by fireprone eucalypt forest and cleared agricultural lands.
These patches range in size from tiny gully stands to lush forests covering large valleys and ranges. Collectively, these ‘serial sites’ despite their small size and scattered fragments, provide proximity and interconnection by corridors of semi-natural habitats and buffers. Their natural asset value is fragile and demands intensive management and protection in order to preserve their ecological integrity.
.
[Source: Australian Government, ^http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/gondwana/resources.html]
.
The ecosystems of the Gondwana Rainforests contain significant and important natural habitats for species of conservation significance (World Heritage Natural Criterion x).
The Gondwana Rainforests provides the principal habitat for many species of plants and animals of outstanding universal value, including more than 270 threatened species as well as relict and primitive taxa. Many of the rare and threatened flora and fauna species are rainforest specialists, and their vulnerability to extinction is due to a variety of factors including the rarity of their rainforest habitat.
The Gondwana Rainforests also protects large areas of other vegetation including a diverse range of heaths, rocky outcrop communities, forests and woodlands. These communities have a high diversity of plants and animals that add greatly to the value of the Gondwana Rainforests as habitat for rare, threatened and endemic species. The complex dynamics between rainforests and tall open forest particularly demonstrates the close evolutionary and ecological links between these communities.
Species continue to be discovered in the property including the re-discovery of two mammal species previously thought to have been extinct:
- The Hastings River Mouse (Pseudomys oralis)
- Parma Wallaby (Macropus parma)
 Parma Wallaby (Macropus parma)
Endemic to rainforests and sclerophyll forests in New South Wales from the Watagan Mountains in the South to the Gibraltar Range in the North.
Parma wallabies were thought to have become extinct a century ago until being discovered again in the 1970s. Parma Wallaby (Macropus parma)
Endemic to rainforests and sclerophyll forests in New South Wales from the Watagan Mountains in the South to the Gibraltar Range in the North.
Parma wallabies were thought to have become extinct a century ago until being discovered again in the 1970s.
.
1994: Oxley Wild Rivers NP added to World Heritage
.
In 1994, large extensions of rainforests across south-east Queensland and New South Wales including the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park were added to the World Heritage listed Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves of Australia (CERRA), now entitled The Gondwana Rainforests of Australia (since 2007).
 OxleyWild Rivers National Park – location map
[Source: Google Maps]
. OxleyWild Rivers National Park – location map
[Source: Google Maps]
.
These reserves comprise almost 50 separate remnant reserves of unspoilt rainforest wilderness stretching from north-east New South Wales (the Oxley Rivers region) up through south-east Queensland. Each of these reserves contains important nature conservation values in its own right, however the full significance of the property becomes evident only when viewed as a whole, and collectively CERRA provides a significant network of habitats for many of Australia’s rare and endangered species.
Since 1994, the Australian Government in co-operation with both the New South Wales and Queensland Governments have recognised the need for coordinated, consistent and cooperative management, to ensure that the integrity of CERRA‘s values is protected. At the time, the World Heritage Committee requested the Australian Government complete management plans of individual sites. Six years later in 2000, the Australian Government published its ‘Strategic Overview for Management for the Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves of Australia to guide co-operative management by the three Governments in relation to the identification, protection, conservation, rehabilitation and presentation of the Gondwana Rainforests. In 2002, a Technical and Scientific Advisory Committee and a Community Advisory Committee were established.
The Gondwana Rainforests of Australia are managed principally by the New South Wales National Parks and Wildlife Service (part of the New South Wales Department of Environment and Climate Change) and the Queensland Environmental Protection Agency.
.
[Source: Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves of Australia – Strategic Overview for Management’, November 2000, Australian Government, ^http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/publications/strategy/pubs/mgtoverview.pdf]
.
Later 1,850 ha of Winterbourne State Forest, also known at the Big Lease, was added to the reserves wilderness. Currently (2012), the remaining 1,560 ha of Winterbourne and 1,075 ha of Enmore State Forests are to be added to the National Park. Further inclusions include Green Gully headwaters and 1,439 ha of leasehold land in the lower Chandlers River gorge.
The Macleay Gorges Wilderness Area, covering 50,000 hectares, was declared World Heritage in 1996 and further extended in 1997.
In 2007, Macleay Gorges Wilderness Area and Oxley Wild Rivers National Park, along with the 50 separate Crown Land reserves of remnant ancient rainforest were collectively renamed under the umbrella term Gondwana Rainforests of Australia to better reflect their World Heritage values. These include important rainforested areas between Newcastle and Brisbane from Mount Royal National Park and Banrrington Tops National Park to Lamington National Park inland of Queensland’s Gold Coast.
.
[Source: Australian Government, ^http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/invasive/publications/pubs/mainland-islands-oxley-wild-rivers-national-park.pdf]
.
 Aspley Falls in flood
Oxley Wild Rivers National Park Aspley Falls in flood
Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
.
High waterfalls crashing into steep gorges are spectacular examples of an important ongoing natural process – erosion. Erosion by coastal rivers created the Great Escarpment and the steep-sided caldera of the Tweed Valley surrounding Mount Warning. This towering mountain was once the buried plug of an ancient vast volcano. Today, rainforest grows on the fertile, well watered soils that remain.
The Macleay River on the Mid North Coast of New South Wales, Australia, has the world’s second-fastest flowing currents during flooding, when it can hold over 200,000 gigalitres.
Its headwaters flows from the Gara River on the eastern side of the Northern Tablelands near the tonwships of Armidale and Walcha. Key tributaries are the Chandler River, Styx River and Apsley River as well as the Tia River, Dyke River and Yarrowitch River, which pass through a number of spectacular gorges and waterfalls in the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park.
The Macleay River flows 400km south-east through Kempsey and into the Pacific Ocean at South West Rocks. Upon colonial discovery in the 1820s; the ancient, tall native Red Cedar (Toona ciliata) forests were completely deforested.
 Australian Red Cedar Forest
Tamborine National Park, Gold Coast Hinterland, Queensland
(such trees have long been logged through the Oxley Rivers region) Australian Red Cedar Forest
Tamborine National Park, Gold Coast Hinterland, Queensland
(such trees have long been logged through the Oxley Rivers region)
.
In 1976, the Apsley Macleay Gorges were identified as being of ‘true wilderness quality‘.
At that stage the public protection offered to the area was limited to two small reserves in the south, and a few local council run recreation areas at popular sites such as Wollomombi Falls, Dangars and Apsley Falls. With future land-use undecided, the NSW Electricity Commission began surveying the Apsley Valley for a hydro-electric scheme in the late 1970s. The Apsley Gorge National Park of 6,718 hectares was gazetted followed by the 3,456 hectare Yarrowitch Gorge National Park soon after.
In 1989 East Kunderang Station of 30,400 hectares passed to the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) and was proclaimed the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park.
.
Rich Wildlife through Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
.
Oxley Wild Rivers National Park is rich in fauna, with over 350 species recorded, including 55 mammals.
It is a major refuge for the Brush-tailed Rock-wallaby (Petrogale pencillata), with the largest confirmed population in the Green Gully area of Yarrowitch.
.
 Brush-tailed Rock Wallaby (Petrogale penicillata) in Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
This species is listed in New South Wales as ‘Vulnerable to extinction’, but that was by the NSW Scientific Committee in 2003, nine years ago
There have been two major bushfires through since then – one in 2009 and now in 2012
How many viable individuals have been lost to the Macleay River Bushfire – does the NSW NPWS know or care? Brush-tailed Rock Wallaby (Petrogale penicillata) in Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
This species is listed in New South Wales as ‘Vulnerable to extinction’, but that was by the NSW Scientific Committee in 2003, nine years ago
There have been two major bushfires through since then – one in 2009 and now in 2012
How many viable individuals have been lost to the Macleay River Bushfire – does the NSW NPWS know or care?
.
<<Oxley Wild Rivers National Park, including Green Gully Track, is closed until further notice due to wildfire.>>
[Source: ^http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkFireClosure.aspx?id=N0043]
.
Other species found in the park include:
- Dingoes
- Bandicoots
- Bats
- Koalas
- Wombats
- Quolls
- Brushtail Possums
- Sugar gliders
- Platypus
- Echidnas
- Numerous small ground mammals
- Wedge-tailed Eagles
- Peregrine falcons
Over 173 bird species, 38 reptile and 19 amphibian species have been recorded in Oxley Wild Rivers National Park.
Skinks, goannas, tortoises, lizards, snakes, frogs and fish occur in the park, particularly on the river flats. A number of fish species have been recorded. Notable, is the speckled longfin eel (Anguilla reinhardtii), which breeds in the ocean with the juveniles eventually returning to the Apsley–Macleay River system.
There are fourteen known threatened species within the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park:
Six mammal species:
- Brush-tailed Phascogale (tuan) (Phascogale tapoatafa)
- Brush-tailed Rock Wallaby (Petrogale penicillata)
- Koala (Phascolarctos cinereus)
- Squirrel Glider (Petaurus norfolcensis)
- Tiger Quoll (Dasyurus maculatus)
- Hastings River Mouse (Pseudomys oralis)
.
Four bird species:
- Glossy Black Cockatoo (Calyptorhynchus lathami)
- Greater Sooty Owl (Tyto tenebricosa)
- Superb Fruit-dove (Ptilinopus superbus),
- Turquoise Parrot (Neophema pulchella)
One amphibian subspecies:
- Macleay River Turtle (Emydura macquarii dharra)
.
One reptile species:
- Carpet Python (Morelia spilota variegata)
.
Two frog species:
- Peppered Tree Frog (Litoria piperata)
-
The Glandular Frog or New England Tree Frog (Litoria subglandulosa)
.
 Brush-tailed Phascogale
[Source: Animal Hospital, ^http://www.chidlowmarsupialhospital.org.au/page-17-1-identification.html] Brush-tailed Phascogale
[Source: Animal Hospital, ^http://www.chidlowmarsupialhospital.org.au/page-17-1-identification.html]
.
All these wildlife were previously widespread, but now are vulnerable to extinction or worse; which has become an Australian cliché, but at the same time an indictment on Australians.
But how much of this protected wilderness region is left after last fortnight’s bushfire catastrophe?
How can it be deemed to be protected, when bushfire is allowed to ravage it and its vitally recognised flora and fauna? Was the World Heritage Area allowed to burn as a convenient bushfire management operational defacto Hazard Reduction? There were no human assets at risk. It was wilderness and so out of sight out of mind…such is the dominant bushphobic culture of the Australian and State Governments, so accused of neglect and incompetence after the 2009 Victorian Bushfires that killed 173 people.
To current anthropocentric (20th C babyboomer) governments, this ‘Macleay River Fire’, irrespective of its World Heritage ecological protection, is blanketly and culturally dismissed as just another hazardous fuel region to target within Australia’s continent-wide Government Arson strategy. Successive generations will revisit this prevailing cultural mindset of ‘hazard reduction‘ and cast it alongside 19th C ‘timbergetting‘ and 20th C ‘clearfelling‘.
In the Blue Mountains, some 40,000 hectares of native vegetation is currently approved by the same Australian and New South Wales Governments for deliberate burning.
If deliberately setting fire to the native vegetation is committed privately it is deemed bush arson and so attracts a poultry 14 years gaol or less even less, despite people having been burned to death as a direct consequence.
But if deliberately setting fire to the native vegetation is previously prescribed by Government, then participants are artificially deemed legally immune and impune from criminal liability, even if the prescribed bushfires they light get out of control, which is all too frequently.
The Australian Government’s official public relations message reads:
Institutional arrangements for the protection and management of Gondwana Rainforests are strong. The property is made up of 41 reserves, almost all of which are within the protected area estate, and primarily managed by the Queensland Parks and Wildlife Service and the New South Wales National Parks and Wildlife Service. Both States have legislation relating to protected areas and native flora and fauna that provide protection for the values of the Gondwana Rainforests.
All World Heritage properties in Australia are ‘matters of national environmental significance’ protected and managed under national legislation, the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999. This Act is the statutory instrument for implementing Australia’s obligations under a number of multilateral environmental agreements including the World Heritage Convention. By law, any action that has, will have or is likely to have a significant impact on the World Heritage values of a World Heritage property must be referred to the responsible Minister for consideration. Substantial penalties apply for taking such an action without approval. Once a heritage place is listed, the Act provides for the preparation of management plans which set out the significant heritage aspects of the place and how the values of the site will be managed.
National Heritage is also a matter of national environmental significance under the EPBC Act.
Importantly, this Act also aims to protect matters of national environmental significance, such as World Heritage properties, from impacts even if they originate outside the property or if the values of the property are mobile (as in fauna). It thus forms an additional layer of protection designed to protect values of World Heritage properties from external impacts.
The impacts of climate change and high levels of visitation, undertaking effective fire management, and mitigating the effects of invasion by pest species and pathogens present the greatest challenges for the protection and management of Gondwana Rainforests.
Climate change will impact particularly on those relict species in restricted habitats at higher altitudes, where particular microclimatic conditions have enabled these species to survive.
Management responses include improving the resilience of the property by addressing other threats such as inappropriate fire regimes and invasion by pest species, and trying to increase habitat connectivity across the landscape.
[Source: Australian Government, ^http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/gondwana/values.html]
.
Recall 2009: 9,500 hectares of Oxley Wild Rivers left to burn
.
In December 2009, a lightning strike started a bushfire in the Youdales Hut area of the Oxley Wild Rivers region. The hut was unaffected (human property?), but 1,500 hectares of inaccessible steep country was burnt out before it was brought under control.
Another lightning strike started a large bushfire in the Reedy Creek region of the park. This fire has burnt out over 8,000 hectares of rough country.
.
[Ed: Yes, steep wilderness terrain without convenient fire trails carved through it, is naturally inaccessible to lumbering urban fire trucks – so RFS/NPWS where were the waterbombing aircraft on 12th Oct 2012, when the fires were tiny and manageable?]
.
Tags: Antarctic Beech, Australian East Coast Sub-tropical and Temperate Rainforest Parks, Australian Red Cedar Forest, Brush-tailed Phascogale, Brush-tailed Rock-wallaby, bush arsonists, bushfire out of control, Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves of Australia, Freds Creek Fire, Georges Junction Fire, Gondwana Rainforests of Australia, Green Gully Track, Hoop Pine, Macleay Gorges Wilderness Area, Macleay River Fire, Oxley Wild Rivers National Park, RFS, Rural Fire Service, wildfire, World Heritage
Posted in Kangaroos and Macropods, Threats from Bushfire | 3 Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Saturday, August 18th, 2012
 Six Foot Track being bulldozed into a two-laned RFS Fire Trail
(Photo by Daniel Kelton, 20120802) Six Foot Track being bulldozed into a two-laned RFS Fire Trail
(Photo by Daniel Kelton, 20120802)
.
News is filtering out that a large section of the iconic Six Foot Track has been bulldozed and vast swathes of forest destroyed.
The Six Foot Track starts from the Blue Mountains west of Sydney near the famous Explorers’ Marked Tree on the Great Western Highway near Katoomba and traces through wild gorges, forests and over ridges to the famous Jenolan Caves, some 42km to the south-west.
‘The Track descends via Nellies Glen to the Coxs River and then climbs Blacks Range before descending again to the Jenolan River by way of Binomea Ridge. In traversing The Track walkers cross a number of distinct cultural and physical landscapes.
 . .
 [Source: ^http://www.adventure.com.au/SixFootTrack.asp] [Source: ^http://www.adventure.com.au/SixFootTrack.asp]
.
William Cooper was instructed in 1884 to undertake a survey of a bridle track between Katoomba and Jenolan Caves. Cooper also supervised the construction of a track which had a width of six feet following approval by the New South Wales Parliament.’ [Source: ‘Six Foot Track Conservation and Management Plan’, 1997, Foreword, prepared by Integrated Site Design Pty Ltd in association with Jim Smith for the Six Foot Track Heritage Trust].
 The 19th Century Heritage of the Six Foot Track
(An old photo at the information shelter at the start of The Track) The 19th Century Heritage of the Six Foot Track
(An old photo at the information shelter at the start of The Track)
.
Aug 2012: Track Bulldozed
.
Two weeks ago, on Thursday 2nd August 2012, an Outdoor Recreation Lecturer leading a group of students along the Six Foot Track happened across a crew of construction workers driving bulldozers and in the process of destroying the Six Foot Track. The section of the track affected is situated between Allum Creek and the Black Range Campsite.
When challenged, the construction workers said that the work had been approved by Oberon Council and Kanangra Boyd National Parks Office. They were calling it “road maintenance“.
So much for the Six Foot Track and its 19th Century heritage. It is now a six metre wide road so that fire trucks can hoon along ringing their fire bells in the middle of the forest. In some places the Track has been bulldozed it to 30 metres wide!
 Six Foot Track bulldozed beyond recognition
(Photo by Daniel Kelton, 20120802) Six Foot Track bulldozed beyond recognition
(Photo by Daniel Kelton, 20120802)
.
Daniel Kelton, an Outdoor Recreation Lecturer at TAFE and a Bush Walking Guide for a regional commercial company leads regular walks along the Six Foot Track more than twenty times a year.
“I saw numerous earth moving machines blocking the iconic track, doubling the width of the original fire trail in places, I saw many old growth trees bulldozed and pushed into the bush in piles, I saw water drains driven excessively into the vegetation on each side of the track. I witnessed stunned native birds walking amongst the newly felled trees. The impact is over a 15km section of the 6ft Track and has impacted up to 30 metres each side of the original fire trail”, Mr Kelton said.
 . .
Initial investigation has revealed that the earth works were given the go ahead by Oberon Council Engineering Service’s works manager, Ian Tucker, and the Oberon Area Manager with the New South Wales National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS), Kim De Govrik, apparently without any environmental, hydrological, or cultural heritage assessments or supervision.
After initial complaints being made to National Parks and Wildlife Service office and Oberon Shire Council from Friday 27th July, road works where substantially decreased, yet Aboriginal sites were damaged after these concerns where raised.
 NPWS Oberon Area Manager, Kim De Govrik, in mock bandage leading a protest rally last June NPWS Oberon Area Manager, Kim De Govrik, in mock bandage leading a protest rally last June
[Source: Western Advocate newspaper, Photo by Chris Seabrook,
^http://www.westernadvocate.com.au/story/96608/riled-rangers-target-national-park-hunts/]
.
Wanton Destruction of Habitat and Cultural Sites
.
Initial onsite investigation has confirmed the following damage caused along the Six Foot Track:
.
- Aboriginal Sites have been destroyed at Mini Mini Saddle, Kyangatha Station and Alum Creek along the Track
- Road works have been bulldozed to within less than a metre of watercourses along Little River (large piles of dirt waiting to be washed into the river in the next rain)
- Counted 213 mature native trees pushed over with a 300 mm or more Diameter at Breast Height (DBH)
- At least 23 hollow forming (habitat) trees pushed over
- Heritage listed fence post and gate from the old Kyangatha Station knocked down and has disappeared.
- The Six Foot Track has been widened, up to double its original width, “For fire trucks to pass” as explained by NPWS Oberon Office
- Water mitre drains have been pushed into the bush up to 50 metres in length
- Considerable destruction of native vegetation and top soil removal through wetland areas, which may fall under the ecosystem classification of a Montane Peatlands (Temperate Highland Swamps on Sandstone?)
- Water drains have been created in inappropriate or unnecessary locations
- Piles of soil have been graded into Spring Gully at Grid Reference 2234450E 62603500N, with no silt trap to prevent siltation of the watercourse
- Vast areas of exposed soil left will inevitably attract weeds
- Large amounts of non-road or safety related impact on vegetation stretching up 50 square in some areas.
- There appears to have been no consultation with land owners, or the Aboriginal Land Council, or Gundungurra people of the region
- The damage will cause serious adverse impact on tourism appeal of The Six Foot Track
- Since the Six Foot Track is now no longer a walking track, vehicles will use it and present a hazard to bush walkers walking along the new road.
 . .
The Aboriginal site destruction and massive Native Flora impact was which committed by a contract road works gang, who where engaged to undertake the works without any impact statements, by Ian Tucker of Oberon Shire Council. The destruction has occurred between Grid Reference 2236590E 6262500N at old Kayangatha Station Ruins and Grid Reference 2269000E 6260600N at the edge of the Pine Forest.
Aboriginal Sites that have been destroyed by machinery are at the following grid references:
.
- Kyangatha Station: 2236590E 6262500N on the right edge of the road 50m North of the cattle grid. Two chert flakes, and one quartz flake
- Mini Mini Saddle: 2235850E 6261700N on the flat cleared ground opposite the un-used cattle grid. Six chert flakes, a direct impact break in one of the flakes from a heavy machine rolling over it
- Alum Creek: 2234900E 6260500N on the Little River side of the road opposite Tree of Heaven cluster. One white chert flake.
.
All sites are comprised of small chert and quartz flake material of varying colours and sizes. The size of the materials vary from 10mm to 50mm. I was led to believe that the site in which heavy rolling machines have rolled over, and broken some of the chert flake pieces, at Mini Mini Saddle was a pre-recorded camp site. This directly breaches Section 90 of the National Parks and Wildlife Act 1974, whether the sites where identified prior to the works or not.
In an undated Archaeological assessment of the Six Foot Track by Hooper and Marloo, which ran numerous predicted modelling of Archaeological significant areas it was interesting to note that the Black Range was mentioned as a possible route to the West from the Megalong and Kanimbla Valleys. The significance of the ridge as a travel path remained un-assessed, although it was noted as a highly likely area for Aboriginal sites. It is also interesting to note that the only two site areas in the West of the Six foot track that where impacted by the recent works, were listed in the article.
.
Why?
.
The unsupervised construction workers called it “routine maintenance”. Crap! Clearly, this is illegal land use development. It is wanton irreverible vandalism of important New South Wales natural and cultural heritage.
 Oberon Man? Oberon Man?
.
It appears the Oberon Council was in a hurry to spend “a big payout from flood relief money” according to one of the construction workers, and that they fast tracked the earth works. They told National Parks and the Six Foot Track Heritage Trust that the works where only minor and would fall under the banner of “routine maintenance“.
But how can flood relief money be connected to converting The Six Foot Track into a two-laned fire trail? Has the funding been misappropriated by Oberon Council?
 In the past two weeks, many of the so called ‘improvement areas’ have subsequently
returned to their original boggy state even after little to no rain.
This begs the question: Why the works where carried out in the first place? In the past two weeks, many of the so called ‘improvement areas’ have subsequently
returned to their original boggy state even after little to no rain.
This begs the question: Why the works where carried out in the first place?
.
National Parks seem to have agreed with the works, so that they can now drive two fire trucks along it – hooning along a nice wide speedway two abreast.
 You reckon? You reckon?
.
“I feel very hurt, and disheartened by the damage to the Track, and I have many unanswered questions”, says Mr Kelton:
- ‘How can Oberon Council claim that the large amount of impact was only routine maintenance?’
- ‘Why where local Aboriginal Land Council Members not consulted about the impact on potential sites?’
- ‘Why was there no member from National Parks or Aboriginal Lands Council on the ground during the works to assess (supervise) damage?’
- ‘Why where local businesses and tour operators not consulted or informed?’
- ‘Why does National Parks need to drive two fire trucks along the track, as there are no residential properties along the Black Range Road, and fire trucks could not pass each other on any of the long hill sections anyway?’
- ‘Would a more thoughtful, ongoing fire control regimes negate the necessity for emergency fire truck access?’
- ‘Was the impact to local tourism even considered?’
- ‘What will be the safety and aesthetic impact of the widened road for bushwalkers, who share the track?’
.
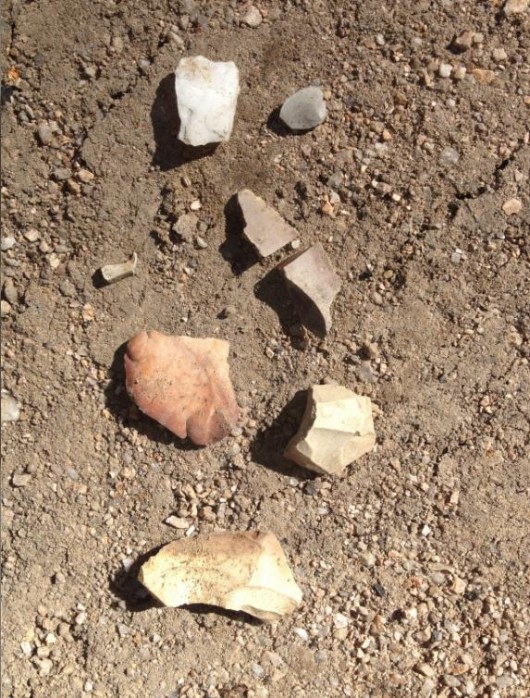 Aboriginal rock implements found along the bulldozed section of the Six Foot Track
Aboriginal cultural sites have been reportedly destroyed
at Mini Mini Saddle, Kyangatha Station and Alum Creek.
. Aboriginal rock implements found along the bulldozed section of the Six Foot Track
Aboriginal cultural sites have been reportedly destroyed
at Mini Mini Saddle, Kyangatha Station and Alum Creek.
.
 Oberon Man’s Day Off? Oberon Man’s Day Off?
.
History of Government Vandalism to Six Foot Track
.
Destruction to The Six Foot Track is not new. Back in June 2005, the Blue Mountains Bushfire Co-ordination Committee, under the chairmanship of Blue Mountains Councillor Chris Van Der Kley, subcontracted a similar bulldozing of the Nellies Glen section of the Six Foot Track. Again the earth works were unsupervised. Again the earth works caused considerable ecological and riparian damage and again they involved reckless bulldozing through documented Aboriginal sites and cultural heritage – as in the case now, numerous ancient stone implements were discovered disturbed by the trail making works.
 In August 2005, recent bulldozing of the Six Foot Track was inspected
by local Indigenous people and members of the Blue Mountains Conservation Society In August 2005, recent bulldozing of the Six Foot Track was inspected
by local Indigenous people and members of the Blue Mountains Conservation Society
(Photo by Liz Mitchell, 20050814)
.
Subsequent remediation of the works involved a number of stakeholder meetings and the responsibility for environmental remediation was passed from the BM Bushfire Co-ordination Committee to the Blue Mountains Council to fix. The earth works had resulted in significant disturbance of the road verge in several sections along the road. Ultimately the remediation was carried out by a soil remediation consultant through the New South Wales Department of Lands Soil Conservation Service costing $27,000.
The Soil Conservation Service inspected the damage and created a rehabilitation plan and specification for a section of Crown Road and Crown Reserve (Nellies Glen Road and along the Six Foot Track) where fire trail maintenance works were implemented by the Blue Mountains Rural Fire Service.
The majority of the mitre drains installed typically exceeded the recommended amount of fall. Many of the mitre drains have been extended into drainage lines and were already actively eroding. There were several sections of track where mitre drains had been installed and there was insufficient drainage / fall causing water to build up and likely to erode the table drains and / or mitre drains down slope. Several small culverts had been graded over limiting their capacity. There were several sections of track where water flow would likely increase due to the slope and lack of drainage measures. Several creek crossings had been graded over, potentially exposing the creek bed to scour. There was also noted significant clearing and disturbance along the length of the roadside/track.
All sound familiar? Read More: >’Report and Specification for Restoration Works on Nellies Glen Road and the Six Foot Track (Aug 2005) (PDF, 730kb).
The Department of Lands Soil Conservation Service is the New South Wales Government agency to which the custodial Six Foot Track Heritage Trust reports.

Back in 2005, a local Blue Mountains resident, Liz Mitchell, reported her similar shock discovery of recent bulldozing along the Nellies Glen section of The Six Foot Track to this Editor. At the time, this Editor was acting in the capacity as Honorary Director of Colong Foundation for Wilderness. Subsequent investigations were initiated including a walk down The Track to inspect the damage first hand. This Editor wrote the following two articles in the Local Blue Mountains Gazette in the weeks following:
.
Letter #1: ‘RFS Bulldozes Six Foot Track’
.
This is what a bulldozer can do midweek when nobody’s watching. (Ed: See photo above)
The Six Foot (Bridle) Track is a State icon, first negotiated on horseback in 1887 as a shortcut from Katoomba to Jenolan Caves. The track is ‘protected’ under the Central Tablelands Heritage Trust by the Department of Land and Water Conservation. The area holds important Aboriginal cultural value. The Track passes through a significant River Oak Forest vegetation community and the topsoils along this river valley are particularly sandy, and once exposed are highly susceptible to erosion and weed infestation.
RFS choice of contractor has bulldozed the heritage Six Foot Track out to a 66 foot speedway and fresh mitre drains to channel the new runoff problem into Megalong Creek. Once the rains come and the exposed topsoil’s washed into the creek, flat chance the bush’ll come back.
This is not fire trail ‘maintenance’. This is road making. How ‘strategic’ anyway is a track deep in a bush valley over two kilometres from Katoomba? Strategic for arsonists perhaps. Anyone else would need development consent to bulldoze bush – and probably would be rightly rejected. The privileged exemption status granted to the RFS is for times of emergency. It is not a carte blanche for cowboy contractors.
This sad muddy bog left at the Corral Creek crossing is testament to the loose procedural controls of the bushfire committee. Such actions cannot help the RFS’ otherwise high community standing.’
[Source: ‘RFS Under Fire’ (title changed by newspaper), Blue Mountains Gazette, 20050727, Read previous article on The Habitat Advocate: >’RFS Bulldozes Six Foot Track‘]
.
Letter #2: ‘Six Foot Track Abused’
.
‘The June bulldozing or grading of the Six Foot Track near Megalong Creek was not only wrong, unnecessary and excessive; it breached the statutory provisions of the Crown Lands Act 1989 under Crown Lands (General Reserves) Bylaw 2001, which prescribes rules for the Track’s environmental protection, heritage and public recreation.
For instance, By-law 23 (2) (n) prohibits conduct in the reserve involving defacing or removing or disturbing any rock, sand, soil, stone or similar substance. It appears no written consent was provided by the Trustee of the Six Foot Track Heritage Trust to the RFS.
The bulldozing also breached the Six Foot Track Conservation and Management Plan of 1997 (two volumes totalling 279 pages). Section 2.1.1 prescribes the need for ecologically sustainable development principles to be followed for all management and planning associated with the Track. Bulldozing or grading is not ecologically sustainable. Policy Statement (7.2) (d) states that the physical elements of the Track including examples of the original alignment, works and sites of Aboriginal and European significance and remnant stands of vegetation should be retained and conserved wherever possible. Numerous threatened species of flora and fauna are recorded as likely present in the Six Foot Tack environs and are listed in Volume I of the Plan. The Plan also states at Section 8.2.5 that “Where development consent is not required an environmental impact statement should be undertaken where there is likely to be an adverse impact on the environment.”
The Plan proposes the following general management objectives for the Six Foot Track:
- To ensure that all management decisions fully recognise the considerable cultural and heritage significance of the Six Foot Track
- To seek to recover and retain the Track’s original character by the preservation and restoration of identified sites and Track features.’
[Source: ‘Six Foot Track abused’, by Editor, (letter to the editor), Blue Mountains Gazette, 20050831, p.12]
.
 Oberon Man after a big night out? Oberon Man after a big night out?
.
Letter #3: ‘RFS Strategy Misguided’
.
It has been revealed that the June bulldozing or grading of the Six Foot Track near Megalong Creek was a mere drop in the RFS Bushfire Mitigation Programme. Across the Blue Mountains, some twenty natural reserves including the Six Foot Track were targeted under the RFS 2004-05 fire trail strategy – Edith Falls, McMahons Point, Back Creek, Cripple Creek, plus some 95 hectares inside our National Park. According to the federal Department of Transport and Regional Services (DOTARS) website, $151,195 was granted to the RFS in the Blue Mountains alone, bulldozing 144 hectares of bush in the name of “addressing bushfire mitigation risk priorities.”
The Six Foot Track Conservation and Management Plan 1997, Vol II lists numerous vulnerable species of fauna recorded near Megalong Creek – the Glossy Black-Cockatoo (Clyptorhynchus lathami), Giant Burrowing Frog (Heleioporus australiacus) and the Tiger Quoll (Dasyurus maculatus). The RFS contractors wouldn’t have had a clue if they were within 100 metres or 1 metre of rare, vulnerable or threatened species.
The RFS is not exempt from destroying important ecological habitat; rather it is required to have regard to the principles of Ecologically Sustainable Development (ESD). Yet the RFS policy on hazard reduction is woefully loose on the ‘Bushfire Co-ordinating Committee Policy 2/03’ on ESD – advocating protection of environmental values and ensuring that ESD commitments are adopted and adhered to by contractors. Experience now confirms this policy is nothing more than ‘green-washing’.
The critical value of dedicated RFS volunteer fire-fighters fighting fires is without question. What deserves questioning is the unsustainable response of the RFS ‘old guard’ to fire trails and hazard reduction with token regard for sensitive habitat. Repeated bushfire research confirms that bushfires are mostly now caused by arson and that the prevalence of property damage is a result of more residential communities encroaching upon bushland.’
[Source: ‘RFS Strategy Misguided’ by Editor, (letter to the editor), Blue Mountains Gazette, 20051005]
.
Recommendations:
.
The management and conservation of The Six Foot Track is guided by the aptly named ‘Six Foot Track Conservation and Management Plan‘ 1997, which comprises two volumes of a total of 279 pages.
However, on at least two occasions now this plan has been ignored and The Six Foot Track and its surrounding natural habitat and cultural heritage fabric have been extensively vandalised by government contractors. This is unacceptable. Enough is enough. Some organisations are just either slow at learning, or more likely think they are above the law and somehow beyond community accountability.
We make the following recommendations:
- All earth works to be immediately halted along The Six Foot Track
- An immediate inspection of the damage to be made by Department of Lands and stakeholders including local indigenous peoples to be invited to inspect and comment
- Since the NPWS, the Oberon Council or the Trustee of The Six Foot Track can’t be trusted with environmental heritage, the Premier of New South Wales, Mr Barry O’Farrell, should order the Legislative Assembly Committee on Environment and Regulation to conduct a Parliamentary Enquiry with terms of reference to investigate: (1) The extent of the damage to environmental and cultural values caused by the earth works, (2) The extent to which the damage has breached The Six Foot Track Conservation and Management Plan, (3) The custodial failings by the trustee, (4) Whether government flood relief funds have been misused by the Oberon Council, and (5) Make findings and recommendations as to appropriate actions including environmental remediation and appropriate future governance of The Six Foot Track conservation, management and reporting framework and the delegation of its execution.
- Disciplinary action should be taken against NPWS Oberon Area Manager, Kim De Govrik; Oberon Council Engineering Service’s works manager, Ian Tucker; and against the Trustee of the Six Foot Track Heritage Trust, Jon Guyver, or whoever is currently in the role. If they are found responsible for the damage, then they should each be immediately dismissed from their positions and from their respective government employers.
.
Is this the image of Oberon Tourism?
 . .
Tags: Aboriginal Sites, Alum Creek, Blue Mountains Rural Fire Service, Bulldozing Six Foot Track, bushwalking, Fire Trail, fire trucks, Kanangra Boyd National Parks Office, Kyangatha Station, Mini Mini Saddle, Montane Peatlands, New South Wales National Parks and Wildlife Service, NPWS, Oberon Council, RFS, Six Foot Track, Spring Gully
Posted in Blue Mountains (AU), Threats from Bushfire, Threats from Road Making | 4 Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Saturday, July 7th, 2012
 The fire tragedy afflicted Australia’s legendary ‘Conservation Cradle’
A scorched Grose Valley from Evan’s Lookout, looking north up Govett’s Gorge
(Photo by Editor taken 20061209, free in public domain. Free Large Image) The fire tragedy afflicted Australia’s legendary ‘Conservation Cradle’
A scorched Grose Valley from Evan’s Lookout, looking north up Govett’s Gorge
(Photo by Editor taken 20061209, free in public domain. Free Large Image)
.
A heritage tragedy unfolds
.
A simple lighting stike ignited remote bushland in rugged terrain within the Blue Mountains National Park, over 5km north of the township of Blackheath on 20061113.
 Innocuously, the ignition started off on hilly Burra Korain Ridge,
It was far from settlement but during relatively calm weather and low temperature, so it was not suppressed but ‘monitored’
..then the wind picked up. Innocuously, the ignition started off on hilly Burra Korain Ridge,
It was far from settlement but during relatively calm weather and low temperature, so it was not suppressed but ‘monitored’
..then the wind picked up.
.
It and a second ignition west were allowed to continue burning for days until they eventually coalesced with compounded backburning into a firestorm some ten days later down in the Grose Valley. On 20061122, the prized Grose Valley and its iconic and precious Blue Gum Forest were incinerated under a pyrocumulus cloud of towering wood smoke that could be seen from the Sydney coast a hundred kilometres away. Some 14,070 hectares of National Park habitat was burnt. The tragedy did not so much as ‘strike‘ from the lighting itself, but as Blue Mountains residents we saw it ‘unfold‘ over many days and nights under the trusteeship of Bushfire Management.
.
..ten days later
 The pyrocumulus cloud of a screaming, dying Grose Valley precious to many, including wildlife The pyrocumulus cloud of a screaming, dying Grose Valley precious to many, including wildlife
The Grose Valley and its Blue Gum Forest and wildlife burning to death on 20061122
A greenhouse gas estimate was not taken.
.
Community shock, sadness and overwhelming sense of loss
.
How was this allowed to happen?
In the days that followed, many Blue Mountains residents and especially the many conservationists familiar with the Grose Valley and Blue Gum Forest over many years became deeply shocked at learning about the loss of this magnificent sacred preserved forest – its tall 300+ year old rare Blue Gums (Eucalytus deanii).
Without knowledge of personal accounts, one respects that the dramatic scenes of the smoke and fire inflicted personal trauma with many, given so many people’s long and established personal knowledge, affinity, love, awe and respect for..
‘The Blue Gum‘
.
The Habitat Advocate reaches out to these people (doesn’t matter the fact that years have passed) and we choose to express the view of a need to tell truths and to seek some sense of learned maturity from it all. For the Grose Valley contained many tracks, many walks and many special places if one knew where to look. Popes Glen and from Govetts Leap down under Bridal Veil following the popular Rodriguez Pass to Junction Rock then Acacia Flat and the Blue Gum Forest in the heart of the Grose. Many special places includes Beauchamp Falls, Docker Buttress, Pulpit Rock, Lockley Pylon, Anvil Rock lookout, Perrys Lookdown, Hanging Rock, Pierces Pass, Asgard Swamp, and the inaccessible Henson Glen and David Crevasse gorge.
To this editor, the return in 2007 to a previously sacred special, but incinerated Neates Glen was emptying in spirit. There was heartfelt shock and dismay by many local conservationists familiar with the iconic Blue Gum Forest who became deeply saddened by the tragedy.
 Neates Glen, as it was Neates Glen, as it was
But since incinerated, not by the wildife, but by deliberately lit ‘backburning’
.
Phone calls and emails were exchanged with many locals wanting to know the extent of the damage and whether ‘the Blue Gum‘ could recover. The original fire had been fanned westward from Burra Korain Head spotting along the Blackheath Walls escarpment, but then decended and burnt through Perrys Lookdown, Docker Buttress and down and through the Blue Gum. Deliberately lit backburns had descended and burnt out Pierces Pass (Hungerfords Track) through rainforest into the Grose and everyone had seen the pyrocumulus mushroom cloud towering 6000 feet above the Grose on the 22nd.
There was an immense sense of loss. The relatively small Blue Gum Forest, perhaps just several hectares, was unique by its ecological location, by its grand age and by its irreplaceability. The sense of loss was perhaps more pronounced amongst the more mature conservationists, now lesser in number, who knew its original saviours of the 1930s – Alan Rigby, Myles Dunphy and other dedicated bushwalkers who had championed to save it from logging 81 years ago.
 The conservation heritage of The Blue Gum Forest dates back to Australia’s earliest conservation campaign from 1931
For this reason ‘The Blue Gum Forest’ has been passionately respected as
Australia’s ‘Cradle of Conservation’ The conservation heritage of The Blue Gum Forest dates back to Australia’s earliest conservation campaign from 1931
For this reason ‘The Blue Gum Forest’ has been passionately respected as
Australia’s ‘Cradle of Conservation’
.
The region is home to threatened or rare species of conservation significance living within the rugged gorges and tablelands, like the spotted-tailed quoll, the koala, the yellow-bellied glider, the long-nosed potoroo, the green and golden bell frog and the Blue Mountains water skink. Many would have perished in the inferno, unable to escape. The Grose is a very quiet and sterile place now, with only birds. But to the firefighters, these were not human lives or property.
.
Deafening silence from the ‘Firies’ naturally attracted community enquiry and suspicion
.
The day after the firestorm that enveloped the Grose Valley, the wind subsided and from 20061123 through to the final mopping up date of 20061203, the 2006 Grose Bushfire and its many ember spotfires came under bushfire management control and were ultimately extinguished or else considered to be ‘benign‘.
It is important to note that during the entire bushfire event from 20061113 through to 20061203, only NSW Rural Fire Service ‘Major Fire Updates’ on its website and headline journalism appeared in the local Blue Mountains Gazette newspaper. Initially, the community, conservationists and ‘firies’ were respectfully passive. In the immediate aftermath of the fire from 20061204 through to the weekly issue of the Blue Mountains Gazette on 20061129, the local community, conservationists and ‘firies’ were letter silent in the paper. It was a combination of shock, preoccupation with the emergency and respectful anticipation of communication from the bushfire authorities.
One can assume here that given the scale of the tragedy, many in the Blue Mountains community were respectfully patient in anticipation of an assured announcement from Bushfire Management or some communication process. But none eventuated.
.
Injustice
.
The following weekly issue of the Gazette was published on 20061129, but no communication from Bushfire Management. Only dismissive bureaucratic statements came from Parks and Wildlife’s Regional Director Geoff Luscombe with a tone suggesting minimal damage and business-as-usual.
This was the article:

6th Dec: ‘Park managers take stock as smoke clears’
[Source: ‘Park managers take stock as smoke clears’, by journalist Jacqui Knox, Blue Mountains Gazette, 20061206, ^http://www.bluemountainsgazette.com.au/news/local/news/general/park-managers-take-stock-as-smoke-clears/487936.aspx?storypage=0]
 Ed: This RFS propaganda photo was included in the media article.
Govetts Leap Track (shown here) was deliberately lit by Bushfire Management Ed: This RFS propaganda photo was included in the media article.
Govetts Leap Track (shown here) was deliberately lit by Bushfire Management
.
‘Hundreds of fire-fighters are celebrating a return to normality this week after cooler weather and an intense two-week campaign by volunteers and professionals brought a fire in the Grose Valley under control.
According to the Rural Fire Service this good weather, combined with a thorough mop-up operation and ongoing infra-red monitoring, means flare-ups are unlikely. However the 15,000 hectare burnt area – including the iconic Blue Gum Forest – is likely to remain closed for the “foreseeable future” due to safety concerns and regeneration.
Geoff Luscombe, regional manager of the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS), said the fact that only part of the Grose Valley burnt meant many animals had been able to seek refuge.
“Many of the Australian plants and animal species have learnt not only to survive fire but to exploit it,” he said. However he confirmed fears that the fire had burnt Blue Gum Forest – a Mecca for bushwalkers and conservationists in the heart of the Grose Valley.
“Blue gums aren’t a particularly fire-tolerant species,” he said. “Fire last burnt through Blue Gum in 1994. The effects of this fire we don’t know yet and we may not know for many months to come.”
A botanist has been sent to inspect the area and there could be ongoing monitoring. Mr Luscombe did not wish to comment on how the fire was handled due to a lengthy absence, but Inspector Jack Tolhurst from the Blue Mountains District Rural Fire Service has warded off any potential criticism.
“I think at the moment we should be looking at the positive,” said Inspector Tolhurst. “The fire is contained . . . It’s been a very long campaign but at the end of the day we haven’t lost any property or lives and half the Grose Valley at least remains intact.”
A fire that broke out near Zig-Zag Railway last week has also been contained. [Ed. According to inside reports, Zig Zag Railway Station was accidentally firebombed by an aerial helicopter attempting backburning].
“We’ve had a lot of help from a wide range of people. We’ve had wonderful support from the community . . . it was a wonderful effort from everyone.”
Meanwhile the hard work has only just begun for another group of dedicated volunteers. Blue Mountains WIRES are expecting to rescue a number of fire-affected native animals in coming months as they wander into residential areas for food and water.
“The arboreal animals – possums and gliders – they come to grief,” said chairperson Greg Keightly. “Birds suffer heat stress and smoke inhalation. They’re going to be flying around bewildered.”
He said residents who see native wildlife in urban areas should keep pets inside, provide water off the ground in a place safe from predators, and avoid the temptation to feed wildlife.
“Things come up for months after fires,” said Mr Keightley. “Do ring us (4754-2946) if you thing something is injured or doing it tough,” he said.
The national park south of the Great Western Highway, and the lookout at Govetts Leap, are open to visitors. For information on closures call 4787-8877 or visit www.nationalparks.nsw.gov.au’
.
.
Mismanagement?
.
So the silence from the firies, from Bushfire Management and from the New South Wales Government ultimately responsible and accountable, was deafening. It was as if the entire Firie fraternity had gone to ground in a code of silence behind closed doors.
So naturally the community response was that something smelt fishy. This communication intransigence was a public relations blunder by Bushfire Management, to its detriment.
Then filtered out accounts of crazy operational mismanagement during the bushfire and of bush arson by the firies behind the roadblocks beyond the public gaze.

- Rumours circulated that the initial ignition had been left for burn in the critical first few days of 13th November and 14th November up on Burra Korrain Ridge because it wasn’t right next to a road so that fire trucks could get to it. The fire had even been abandonned. Then the wind picked up and it spread. Airborne firefighting was not called in until a Section 44 incident declaration was effected on 15th November.
- A second fire nearby to the west near Hartley Vale, purported also lit by dry lightning on 14th Nov, had attracted broadscale backburning from the Hartley Vale Road. But the backburn got out of control, ripped up the valley fanned by winds and crossed over the Darling Causeway on to the Blackheath Escarpment and the Upper Grose to join up with the first blaze. The onground evidence shows that this was a hazard reduction burn starting from alongside the Hartley Vale Road just east of the village of Hartley Vale.
- Then came the account of senior bushfire management at the Rural Fire Service headquarters at Homebush ordering a ‘headburning’ a new 10km fire front along the south of the Bells Line of Road into the Grose Valley. Perhaps the NSW Government had stepped in demanding action. Perhaps RFS headquarters response was a series of overreactions, albeit too late and to be seen to be now ‘acting’ was only compounding the fire risk to the Grose . Apparently, the RFS Commissioner had even touted imposing a massive defacto hazard reduction north of the Bells Line of Road right though the vast wilderness of the Wollemi National Park, to somehow head off another fire on 20th November some 80km away north of Wiseman’s Ferry, but that strategy was rejected in a heated operational debate. [“The Wollemi National Park is part of the World Heritage Area and covers 488,620 hectares. Important values of the park include the spectacular wild and rugged scenery, its geological heritage values, its diversity of natural environments, the occurrence of many threatened or restricted native plant and animal species including the Wollemi pine and the broad-headed snake, significant plant communities, the presence of a range of important Aboriginal sites and the park’s historic places which are recognised for their regional and national significance.” – Wollemi NP Plan of Management, April 2001]
- Even the Zig Zag tourist railway station was apparently accidently firebombed by an overzealous airborne firefighter starting backburning en mass
- Then came the account of Blackheath residents who had their houses subjected to the risk of a deliberately lit backburn during the course of the bushfire. Despite the out of control wildfire being many miles to the north west of Blackheath, a broadscale backburn (some say is was really a ‘defacto hazard reduction‘) was lit along the fire trail below the electricity transmission line near Govetts Leap lookout. But it got out of control briefly and threatened to burn houses in Connaught Road. Indeed the entire Blackheath Escarpment fire from Hat Hill Road south through Govetts Leap Lookout and Ebans Head was started deliberately as a ‘strategic’ backburn.
 Blackheath Escarpment completely burnt (top) for hectares, looking south from Hat Hill Road
(Photo by editor 20061209, free in public domain, click image to enlarge) Blackheath Escarpment completely burnt (top) for hectares, looking south from Hat Hill Road
(Photo by editor 20061209, free in public domain, click image to enlarge)
.
 The rural property east of Hartley Vale where on 20070207 there was clear evidence of hazard reduction (HR)
commencing only from the south side Hartley Vale Road, opposite.
Eucalypts were burned only at the base, but further up the hill the tree crowns had been burned.
The HR had quickly got out of control and then crossed over the Darling Causeway.
(Photo by editor 20070207, free in public domain, click image to enlarge) The rural property east of Hartley Vale where on 20070207 there was clear evidence of hazard reduction (HR)
commencing only from the south side Hartley Vale Road, opposite.
Eucalypts were burned only at the base, but further up the hill the tree crowns had been burned.
The HR had quickly got out of control and then crossed over the Darling Causeway.
(Photo by editor 20070207, free in public domain, click image to enlarge)
.
Once two weeks had passed since the dramatic firestorm and with only silence emanating from Bushfire Management and the NSW Government, local people had had enough and they wanted answers.
Some 143 local yet disparate conservationists via ‘jungle drums’ met up, discussed the issue, united informally and agreed to go public. They informally formed the ‘Grose Fire Group‘ and contributed to a fighting fund some $1700 odd and became vocal. Two weeks after the Grose Valley Firestorm the Grose Fire Group managed a full page open letter in the local Blue Mountains Gazette on 20061206 on page 13. It was directed to the ultimate authority responsible and accountable for the Grose Fire Tragedy, the NSW Government. The Premier at the time was Labor’s Morris Iemma MP. The NSW Member for the NSW Seat of Blue Mountains as well as NSW Minister for Environment at the time was Bob Debus MP.
Those who valued the Blue Gum Forest challenged those responsible for its protection. The tragedy certainly stirred and polarised the Blue Mountains community. Conservationists naturally wanted answers, an enquiry, a review of bushfire prevention and management from:
- NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service under the direction of Regional Director Geoff Luscombe
- NSW Rural Fire Service under the direction of Commissioner Phil Koperberg
- Blue Mountains Bushfire Management Committee aligned with Blue Mountains City Council and chaired by Councillor Chris Van Der Kley.
.
‘Grose Valley Fire – World Heritage takes a hit’
“The Blue Gum Forest, birth-place of the modern conservation movement, was badly damaged by the Grose fire on Wednesday the 22nd of November. If this precious forest was a row of houses, then there would automatically be a major investigation into how the fire was fought. The fact that this major loss of our natural heritage is only now becoming known is testimony to the prevailing attitudes of those controlled the media spin during this recent fire event,” said Keith Muir director of the Colong Foundation for Wilderness.
“Until today the overall perception from the media was that this fire was a good one. No houses or lives lost”, Mr Muir said.
“There where no media updates on the struggle to save Blue Gum. No the reports of success in saving fire sensitive rare plants and rainforests along the escarpment edge. All the media reports spoke of bushland burnt; not on the success of any strategy to minimise the impact on the World Heritage listed national park, while saving lives and property”, he said.
“The Blue Mountains National Park Fire Management Strategy 2004 sets out all the necessary actions to protect the natural environment, as well as life and property. Yet for some reason it appears at this stage that the fire was not fought according to that agreed Strategy, as far as its provisions on natural heritage were concerned”, said Mr Muir.
“Increased fire is a major threat to World Heritage values of the Greater Blue Mountains national parks. Unless we develop and implement better strategies to defend the bush, as well as lives and property, then climate change will make this threat much worse,” Mr Muir said.
“The fire management strategies and techniques undertaken during the fire need to be re-examined to ensure the diversity of the Blue Mountains forests is protected into the future,” he said.
“Future fire management requires the feedback that only an inquiry into the Grose Valley Fire can achieve. Such an inquiry should not be taken as a criticism of those involved in fighting fire. It is an opportunity to ensure that everyone stays on fully board with future efforts to minimise fire damages,” Mr Muir said.’
[Source: Colong Foundation for Wilderness, ^http://www.colongwilderness.org.au/media-releases/2006/12/grose-valley-fire-%E2%80%93-world-heritage-takes-hit]. The magnificent rich carpeted Gross Valley, as it was
(compare with the lead photo at the start of this article, click image to enlarge) The magnificent rich carpeted Gross Valley, as it was
(compare with the lead photo at the start of this article, click image to enlarge)
.
What exacerbated the conflict was not some much that the bushfire had got out of control and had raged through the precious Grose Valley per se, but it was more the defensive, aloof reaction by ‘Firies’ which escalated into a barrage of defensive and vocal acrimony against any form of criticism of the firefighters.
In the face of such palatable denial by the Firies,of any accountability the initial shock and sadness within the local community within days quickly manifested into outrage and anger, and even to blame and accusations.
 
Most conservationists however felt a right to question and seek specific answers from Bushfire Management about the Grose Fires, for lessons to be learned, for fundamental changes to be made to bushfire management policy, bushfire fighting resourcing and practices, all simply so that such a tragedy should not be repeated.
But the key problem was that the ‘Firies‘ adopted an ‘in denial’ approach to a community suffering loss. Many Firies denied that they had done anything wrong and rejected any criticism by conservationists. Some Firies vented their anger in the local media attacking anyone who dared criticise. Clearly, Bushfiore Management’s debriefing and review of the bushfire in its immediate aftermath was poorly managed.
Underlying the conflict was the Firies urban fire fighting mandate to ‘protect lives and property” – that is human ones, not forests, not wildlife. Whereas what emerged with many in the Blue Mountains community was the implicit expectation that the World Heritage Area is an important natural asset to be protected, including from devastating bushfire.
 The Grose Valley
Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area The Grose Valley
Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area
.
Hence, it was a conflict between differing cultural value systems. It was about recognition of the value of the natural assets of the Blue Gum Forest and the Grose Valley within the Bue Mountains National Park within the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area.
 The iconic Blue Gum Forest
(Acacia Flat, before the pyrocumulus firestorm of 22nd November 2006) The iconic Blue Gum Forest
(Acacia Flat, before the pyrocumulus firestorm of 22nd November 2006)
.
 The iconic Blue Gum Forest
(The aftermath) The iconic Blue Gum Forest
(The aftermath)
.
20 Sep: (2 months prior)…‘Fire crews prepare’
[Source: ‘Fire crews prepare’, Blue Mountains Gazette, 20060926]
.
‘With warmer days just around the corner and continuing dry weather the Blue Mountains Region National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) is again undertaking rigorous preparation for the coming fire season.
“Every year around this time the NPWS run a number of fire preparedness days to ensure staff and fire-fighting equipment are fully prepared for the season ahead,” said Minister for Environment Mr Bob Debus.
 NSW Labor Minister for Environment
Mr Bob Debus MP NSW Labor Minister for Environment
Mr Bob Debus MP
.
“Fire preparedness days require fire-fighting staff to check their personal protective equipment, inspect fire-fighting pumps and vehicles and ensure that communication equipment and procedures are in place and working before the fire season begins.”
Mr Debus said a number of exercises, including four-wheel drive and tanker driving, first aid scenarios, entrapment and burnovers, were also employed to re-familiarise staff with all aspects of fighting fires.
“Burnovers, where fire-fighters are trapped in a vehicle as fire passes over it, is one of the worst case scenarios a fire-fighter can face so pre-season practice is critical to ensure that their response is second nature”, he said. “Local fire-fighters have also undergone stringent fitness assessments to make sure they are prepared for the physical demands of fire-fighting – like being winched from a helicopter into remote areas with heavy equipment, to work long hours under very hot and dry conditions wearing considerable layers of protective clothing”, Mr Debus explained.
Mr Debus said that fire preparedness and fitness assessment days worked in conjunction with a number of other initiatives as part of a year-long readiness campaign for the approaching summer.
“Over the past 12 months, NPWS officers have conducted more than 150 hazard reduction burns on national park land across NSW.”
.
“Nineteen hazard reduction burns have been conducted in the Blue Mountains region covering nmore than 4500 ha” ~Bob Debus MP
.
Mr Debus said that while fire-fighting authorities are preparing themselves to be as ready as possible for flare ups and major fires, home-owners in fire prone areas of teh Blue Mountains should also be readying themselves for the approaching season. “Now is the time to start cleaning gutters, ember proof houses and sheds, prepare fire breaks and clear grass and fuel away from structures”, he said.’
.
20 Nov: ‘Bushfires rage closer’
[Source: ‘Bushfires rage closer’, by Dylan Welch and Edmund Tadros, Sydney Morning Herald (with Les Kennedy and AAP), 20061120, ^http://www.smh.com.au/articles/2006/11/21/1163871368365.html?from=top5]
.
Wisemans Ferry:
‘Residents in the historic Hawkesbury River village of St Albans prepared for the worst as raging bushfires neared. Their predicament came with a fresh fire outbreak in a remote corner of Wollemi National Park, 73 kilometres north of Windsor about 2pm. A Rural Fire Service spokesman said the blaze had destroyed 450 hectares by 3pm. It was being fanned by a string of north-westerly winds and had jumped Putty Road, causing its closure to traffic between Singeleton and Richmond. Winds of up to 80kmh forecast for the early hours of tomorrow are expected to drive the fire towards St Albans. About 45 Rural Fire Service volunteers with 10 tankers have been deployed to protect the small community as residents tried to safeguard their homes from floating embers. At least two helicopters were in the air to assist the operation.
 Wildfire, spot fires and back burning across the Blackheath plateau
(Photo by Rural Fire Service) Wildfire, spot fires and back burning across the Blackheath plateau
(Photo by Rural Fire Service)
.
Blue Mountains:
‘Meanwhile a spokesman for the RFS, Andrew Shade, told (the Sydney Morning Herald) firefighters were waiting to see if changing winds would affect the Blue Mountains fires, which jumped containment lines overnight. “The fire is across about 7000 hectares; we’ve got 18 aircraft working the fire, including two sky cranes, [and] 400 personnel at the fire on about 60 trucks.”
..Other fires continue to burn across the state, with a number of fires across 7000 hectares in the Hunter Valley burning in remote and inaccessible areas. Two other fires, near Forbes and Bathurst respectively, are both contained but the RFS has expressed concerns over the weather and its ability to cause a change in the nature of the the two blazes. Firefighters set up a containment line to protect the outskirts of Blackheath in the Blue Mountains.
Rural Fire Service Commissioner Phil Koperberg said today winds gusting up to 80kmh were predicted for about 3am tomorrow – a time when firefighting planes are unable to fly. At a news conference in Katoomba, Mr Koperberg described the present threat to Blue Mountain towns as “fairly serious … not grave”. However, he urged residents to clean fuel away from their homes as a precaution. This afternoon the most intense efforts were along a containment line at the northern end of Hat Hill Road at Anvil Rock. If that line was breached, the outskirts of Blackheath could be under threat, he said. Firefighters expected wind changes in the area between 4pm and 6pm today. The Bells Line of Road remains closed and the Blue Mountains National Park will remain closed until further notice.
The Great Western Highway and the Darling Causeway were open but drivers were advised to proceed with caution, with smoke likely to affect the roads. A total fire ban now applies in all but the north-east corner of the state as temperatures in the high 30s (Celsius), the strong winds and low humidity combine to produce potentially savage conditions…’
.
22 Nov: ‘Firefighters standing strong’
[Source: Firefighters Standng Strong’, by Shane Desiatnik, Blue Mountains Gazette, Wednesday, 20061122, pages 1 and 3,^ http://www.bluemountainsgazette.com.au/news/local/news/general/standing-strong/439486.aspx?storypage=0, Ed: Note this is quoted from the paper edition, which was different to the online edition]
.
‘Thick smoke continues to drift across the Blue Mountains as the largest firefighting and backburning operation in the region since January 2003 enters its second week.
Hundreds of RFS volunteers, NSW Fire Brigades, SES and NPWS personnel, a number of remote firefighting units and 16 waterbombing aircraft are enlisted under a Section 44 declaration with a mission of containing and then attacking bushfires burning in the Grose Valley. The fires are believed to have been ignited by lightning on Monday, November 13 and at the time of going to press had burnt out 3800 hectares of bushland and private parkland in the valley below Blackheath, Mt Victoria, Bell and Mt Tomah.
No homes were under threat on Tuesday morning, but the RFS almost doubled its resources in the Blue Mountains on Monday night following unfavourable weather conditions.
The NSW FireBrigades also deployed extra fire engines and firefighters ot the Blue Mountains on Tuesday.
The large Blue Mountains bushfire broke its containment lines at Anvil Rock about 11 pm on Monday. Earlier, a comprehensive backburning operation involving 300 firefighters commenced on Saturday night between Blackheath and Mt Victoria to protect the townships if conditions worsened. A second phase began along Bells Line of Road between the Darling Causeway and Mt Tomah on Monday morning, continuing to Pierces Pass picnic area to the south.
The backburning activities can cause heavy smoke to linger in residential areas and residents are advised to close windows and doors. An emergency operations centre is active in Katoomba under the control of Local Emergency Operating Controller and Blue Mountains Police Local Area Commander Patrick Paroz, with the RFS as the lead combat agency.
Blue Mountains RFS community safety officer Eric Berry said remote area firefighting units will continue to attack the fire at the fringe and a fleet of 16 aircraft based in Medlow Bath airfield will operate to contain the fire.
“14 medium to heavy capacity helicopters have been operating 24/7 since last Tuesday [Ed: This contradicts the official RFS Section 44 Incident Controllers Report – Wednesday 15th not Tuesday 14th] and we now have three air crane helicopters on the job,” Inspector Eric Berry said. “This is a massive operation, certainly the biggest in the last three years. “It involves up to 300 RFS, NSW Fire Brigades, NPWS, police and SES personnel and volunteers at any one time, sourced from all over eastern NSW as well as every Blue Mountains RFS brigade. “Then there are the support services chipping in like the Salvation Army, who have been supplying breakfast at 5.30 am on a daily basis for the firefighters.”
Inspector Berry said RFS community information meetings last weekend were very successful in seven upper Mountains towns. “More than 200 residents attended one of the meetings held at Blackheath Golf Club, giving us an opportunity to explain what is going on in plain English. “More meetings may occur, but in the meantime residents should phone the RFS information line for updates. “We are getting nearly 6000 hits on our website per day and are updating the site at regular intervals.”
The Gazette visited the Medlow Bath Airfield last Friday, which continues to be a hive of activity. Six helicopters, including a giant sky crane chopper, took off and landed several times inside an hour, collecting water loads from nearby dams and dropping them into and ahead of the flames. Kev Adams, an RFS volunteer from Gloucester, described the conditions the pilots had to deal with early last week as wild.
“I came down from Gloucester last Wednesday and we went up in a chopper and the wind was blowing at about 41 knots. “We hit a pocket of turbulence and I hit my head on the ceiling even though I was strapped in, that’s how wild the wind was. “Hopefully we’ll be able to head home soon.”
Inspector Eric Berry said good progress has been made, but the weather ahead could test the containment lines.’
.
Ed: Additional reporting in the online version of this article:
‘Severe weather is expected for the Blue Mountains this afternoon between 2.00pm and 5.00pm. A Total Fire Ban has been declared for a number of areas across the state today, including the Blue Mountains. Temperatures in the Blue Mountains are expected to reach 31 degrees with west-north-west winds gusting up to 45km/h.
Fire behaviour yesterday was subdued due to mild conditions and the main front extinguishing in very low fuel levels. Advantage was taken of these conditions to consolidate containment lines. The fire has now been burning for fourteen days and burnt nearly 15,000 hectares.
The amount of smoke is likely to increase today. Aircraft and ground crews will be actively patrolling the fire for reactivation of fire edges. Infrared hot spot technology is being used in an attempt to identify stumps and roots that are still smouldering near the edges. Crews can then locate the hotspots and extinguish them.
The Bells Line of Road between the Darling Causeway and Mount Tomah has been re-opened but may be closed intermittently. Mount Banks and Pierces Pass trails and tracks are closed to the public. Residents in the Blue Mountains and Hawkesbury should remain vigilant.’
.
22 Nov: ‘Bushfire breaks lines again’
[Source: ‘Bushfire breaks lines again’, 20061122, Sydney Morning Herald, (AAP), ^http://www.smh.com.au/news/national/bushfire-breaks-lines-again/2006/11/22/1163871435049.html]
.
 Volunteers back burn along Bells Line of Road as smoke from the fire front can be seen overhead
(Photo by Wade Laube) Volunteers back burn along Bells Line of Road as smoke from the fire front can be seen overhead
(Photo by Wade Laube)
.
‘A major bushfire burning out of control in the Blue Mountains again broke containment lines overnight ahead of forecast rugged day for fire fighters. Two separate blazes have blackened more than 8,000 hectares of the Blue Mountains, west of Sydney, with the larger of the two burning on a massive front about four kilometres north of the township of Blackheath.
Wind gusts of up to 70kph are forecast to push through that area, around Grose Valley, about 4am (AEDT) today. Blustery conditions expected for most of the day with temperatures in the low 30s (Celsius).
Rural Fire Service (RFS) Commissioner Phil Koperberg has said the towns of Mt Tomah and Mt Wilson would be vulnerable to a wind change. An RFS spokesman said crews had been working on a 35km containment line through the night but the bigger fire had now broken its eastern containment lines. He said crews were prepared for the “tricky” conditions expected early today, with wind gusts expected to pick up as the day gets warmer. Waterbombing aircraft cannot take off until first light but no property is currently under direct threat.
Meanwhile, a new bushfire burning in the Wiseman’s Ferry area is not posing any immediate threat to the village of St Albans, 90km north-west of Sydney. However, the RFS spokesman said that could also change depending on today’s winds. A total fire ban has been declared for much of the state today, including the Greater Sydney and Greater Hunter areas, the Illawarra and far south coast, southern and central ranges, the upper and lower central west plains and the eastern Riverina.’
.
23 Nov: “Massive fire back-burn effort’
[Source: ‘Massive fire back-burn effort’, Mx (free Sydney commuter newspaper), by Matt Sun, 20061123, page 1]
.
‘Hundreds of firefighters are today hoping a massive 30km containment line will stop the Blue Mountains bushfire in its tracks. [Ed: Bit late, this is the day after that pyrocumulus firestorm]
About 200 Rural Fire Service and NSW Fire Brigade firefighters worked overnight on a back-burn between Blackheath and Wentworth Falls. Firefighters were on standby until temperatures dropped and winds died. They were sent in to light the back-burn as soon as conditions calmed down. Crews spent this morning back burning on the Bells Line of Road and hoping to create containment lines near the village of (Mt) Tomah if winds subside.
The RFS said 400 firefighters started work on the blaze this morning. The weather bureau forecast a maximum temperature of 27C, 45kph gusting winds and 17% humidity this afternoon.
Two fires, both ignited by lightning 10 days ago, joined up this week and have now destroyed 14,500 ha. An RFS spokeswoman said the fire was burning 2.5 km south of Mt Tomah and 7km north of Wentworth Falls…Crews and 15 aircraft will remain on standby to extinguish any spot fires that pass over teh containment line. Fire-bombing helicopters Elvis and Shania were likely to be sent to other fires burning across NSW.
The RFS today said Blue Mountains townships were not in immediate danger but should remain alert. But experts warned the extreme weather conditions would return next week, with the mercury reaching the mid 30s.’
.
29 Nov: “Firefighters gain upper hand”
[Source: ‘Firefighters gain upper hand’, by Shane Desiatnik, 20061129, ^http://www.bluemountainsgazette.com.au/news/local/news/general/firefighters-gain-upper-hand/348587.aspx]
 RFS propaganda photo for a sympathetic media
These two RFS firies are at the Evan’s Lookout backburn that was deliberatly lit by the RFS
(Photo by Blue Mountains Gazette journalist, Shane Desiatnik, 20061124) RFS propaganda photo for a sympathetic media
These two RFS firies are at the Evan’s Lookout backburn that was deliberatly lit by the RFS
(Photo by Blue Mountains Gazette journalist, Shane Desiatnik, 20061124)
.
The above photo shot taken by the local Blue Mountains Gazette newspaper’s lead journalist, achieved front page on 20061129. The caption read: “Assessing the aftermath: Medlow Bath RFS crew member Noah Taylor and team leader Michael Anderson near Evans Lookout last Friday.”
This same photo was re-used by the Blue Mountains Gazette a year later on 20071024 (page 7) to support an article by the Rural Fire Service incident controller in charge of co-ordinating the fire-fighting of the 2006 Grose Fire, Mal Cronstedt, who responded to an article in the paper on this subject by The Habitat Advocate dated 20071010.
.
‘Hundreds of weary but determined firefighters are steadily gaining the upper hand over a Grose Valley bushfire that has burned about 15,000 hectares since November 13.
Daylight waterbombing by a fleet of choppers based at Medlow Bath airfield, increasing access by remote area firefighting units, successful backburns along the northern and southern escarpments and milder than predicted weather conditions since Saturday have limited the spread of the fire.
At the time of going to press, 130 RFS, NSW Fire Brigades and NPWS firefighters and nine helicopters were conducting backburns, mopping up buffer zones and cutting in access trails to the fire’s fringes. The active front of the fire was within containment lines yesterday morning, allowing the Bells Line of Road and Mt Tomah Botanical Gardens to re-open.
A small fire that started at Mitchells Lookout in Mt Victoria on November 23 is extinguished and investigations are continuing into its cause.
Blue Mountains RFS is warning residents to remain vigilant by continuing to prepare their homes for fire if conditions worsen and to immediately report any suspicious activity to CrimeStoppers by calling 1800-333-000.
The milder conditions are a welcome relief from the heat and 100 km/h wind gusts that put residents of Hazelbrook, Linden, Faulconbridge and Winmalee on high alert last Wednesday afternoon.
An explosion within the fire, which witnesses described as causing a mushroom-like cloud to develop, ignited spotfires four kilometres north of Lake Woodford and five kilometres north of Hazelbrook. Many residents headed home early from work to clear gutters and roofs and two Winmalee schools opted to close for 24 hours as a precaution. Eighteen water-bombing aircraft attacked the spotfires, extinguishing one within hours and the second by Thursday evening.
For daily fire updates and advice, go to www.bluemountains.rfs.nsw.gov.au, phone a dedicated 24-hour hotline manned by local volunteers on 1800-264-525 or visit your local RFS station, staffed by volunteer station officers.
“These people are the unsung heroes of the RFS,” Blue Mountains RFS public liaison and education officer Paul McGrath said.
.
Overwhelming grief shunned by government hush, galvanised an immense sense of environmental injustice :
It was time to challenge (with due civility) the unaccountable bastards in authority…the NSW Government:
 An extract of a full page letter in the Blue Mountains Gazette 20061206 on page 13 An extract of a full page letter in the Blue Mountains Gazette 20061206 on page 13
It was commissioned by 143 concerned Blue Mountains residents
It was addressed not to the ‘firies’, but to the NSW Government.
.
 Pulpit Rock on the left of the Grose Valley, before the firestorm
It is easy to see why the Blue Mountains, with their Eucalytus tree oil suspended in the atmosphere, get their famous name.
(Photo by Chris Ellis) Pulpit Rock on the left of the Grose Valley, before the firestorm
It is easy to see why the Blue Mountains, with their Eucalytus tree oil suspended in the atmosphere, get their famous name.
(Photo by Chris Ellis)
.
Tags: 2006 Grose Fires, Blackheath Escarpment, Blue Gum Forest, Blue Mountains, Blue Mountains Council, Blue Mountains Gazette, Blue Mountains National Park, Blue Mountains World Heritage Area, Bob Debus MP, Burra Korain Ridge, bushfire management, Cradle of Conservation, defacto hazard reduction, Firies, Geoff Luscombe, Grose Fire Group, Grose Valley Fires 2006, Gross Valley, Hartley Vale, hazard reduction, Neates Glen, NPWS, NSW Government, NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service, Premier Morris Iemma, pyrocumulus cloud, RFS, RFS Commissioner Phil Koperberg, RFS Section 44 Report, Rural Fire Service
Posted in Blue Mountains (AU), Threats from Bushfire | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Friday, March 30th, 2012
This article was initially written by this editor and published in the Blue Mountains Gazette newspaper on 20051005 as a letter to the editor, entitled ‘RFS strategy misguided‘.
.
 19th Century heritage-listed ‘Six Foot Track’
..bulldozed by the Rural Fire Service in July 2005, widened into a convenient Fire Trail for its fire truck crews. 19th Century heritage-listed ‘Six Foot Track’
..bulldozed by the Rural Fire Service in July 2005, widened into a convenient Fire Trail for its fire truck crews.
.
It has been revealed that the June bulldozing or grading of the Six Foot Track near Megalong Creek (Blue Mountains, New South Wales) was a mere drop in the Rural Fire Service (RFS) Bushfire Mitigation Programme.
Across the Blue Mountains, some twenty natural reserves including the Six Foot Track were targeted under the RFS 2004-05 Fire Trail Strategy:
- Edith Falls
- McMahons Point
- Back Creek
- Cripple Creek
- Plus some 95 hectares inside the Blue Mountains National Park.
.
Read: [>RFS Fire Trail Policy]
Read: [>RFS Fire Trail Classification Guidelines]
.
According to the Australian Government’s (then) Department of Transport and Regional Services (DOTARS) website, some $151,195 was granted to the RFS in the Blue Mountains alone, for it to bulldoze and burn 144 hectares of native bushland under the euphemism of “addressing bushfire mitigation risk priorities” (Ed: Read ‘bush arson‘)
‘The Six Foot Track Conservation and Management Plan 1997, Vol II’ lists numerous vulnerable species of fauna recorded near Megalong Creek – the Glossy Black-Cockatoo (Clyptorhynchus lathami), Giant Burrowing Frog (Heleioporus australiacus), Spotted-tailed Quoll (Dasyurus maculatus).
 Glossy Black-Cockatoo
[Source: Dubbo Field Naturalist & Conservation Society Glossy Black-Cockatoo
[Source: Dubbo Field Naturalist & Conservation Society
http://www.speednet.com.au/~abarca/black-cockatoo.htm]
.
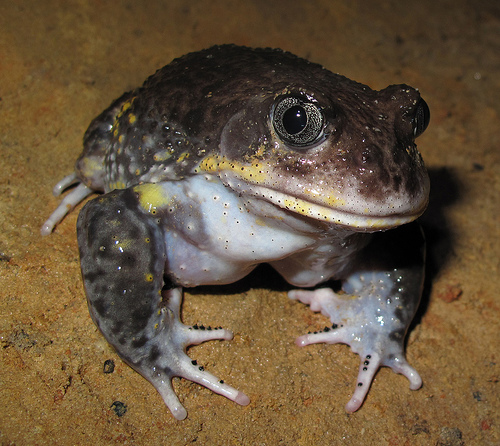 Giant Burrowing Frog
[Source: Frogs.org.au, ^http://frogs.org.au/community/viewtopic.php?t=4876&sid=0dc45ef08e12cd5e1d27524bca2269f9] Giant Burrowing Frog
[Source: Frogs.org.au, ^http://frogs.org.au/community/viewtopic.php?t=4876&sid=0dc45ef08e12cd5e1d27524bca2269f9]
.
 Spotted-tailed Quoll
(Dasyurus maculatus)
Blue Mountains top order predator, competing with the Dingo Spotted-tailed Quoll
(Dasyurus maculatus)
Blue Mountains top order predator, competing with the Dingo
.
The RFS contractors wouldn’t have had a clue if they were within 100 metres or 1 metre of rare, vulnerable or threatened species.
The RFS is not exempt from destroying important ecological habitat; rather it is required to have regard to the principles of Ecologically Sustainable Development (ESD).
Read: >RFS Policy 2-03 Ecologically Sustainable Development
.
The ‘Rationale‘ of this RFS ESD policy states at Clause 1.2:
‘The Bush Fire Coordinating Committee, under the Rural Fires Act 1997 Sec 3 (d), is required to have regard to ESD as outlined in the Protection of the Environment Administration Act 1991, which sets out the following principles:
a) The precautionary principle namely, that if there are threats of serious or irreversible environmental damage, lack of full scientific certainty should not be used as a reason for postponing measures to prevent environmental degradation. In the application of the precautionary principle, public and private decisions should be guided by:
i. careful evaluation to avoid, wherever practicable, serious or irreversible damage to the environment, and
ii. an assessment of the risk-weighted consequences of various options.
.

b) Inter-generational equity namely, that the present generation should ensure that the health, diversity and productivity of the environment are maintained or enhanced for the benefit of future generations
.
.

c) Conservation of biological diversity and ecological integrity should be a fundamental consideration in all decisions.
.

d) Recognising the economic values that the natural environment provides. The natural environment has values that are often hard to quantify but provide a benefit to the entire community. By recognising that the natural environment does have significant economic and social values we can improve decision making for the present and future generations.’
.
 . .
Yet the RFS policy on hazard reduction is woefully loose in the ‘Bushfire Co-ordinating Committee Policy 2 /03 on ESD‘ – which (on paper) advocates protecting environmental values and ensuring that ESD commitments are adopted and adhered to by contractors.
Experience now confirms this policy is nothing more than ‘greenwashing’. The RFS wouldn’t know what environmental values were if they drove their fire truck into a Blkue Mountains upland swamp. There is not one ecologist among them.
While the critical value of dedicated RFS volunteer fire-fighters fighting fires is without question, what deserves questioning is the unsustainable response of the RFS ‘old guard’ to fire trails and hazard reduction with token regard for sensitive habitat. Repeated bushfire research confirms that bushfires are mostly now caused by:
- Bush arson (hazard reduction included, escaped or otherwise)
- More residential communities encroaching upon bushland.
.
Under the ‘Blue Mountains Bushfire Management Committee Bushfire Risk Management Plan’ (Ed: their bureaucratic name), key objectives are patently ignored:
- ‘Ensure that public and private land owners and occupiers understand their bushfire management responsibilities’
- ‘Ensure that the community is well informed about bushfire protection measures and prepared for bushfire events through Community Fireguard programs’
- ‘Manage bushfires for the protection and conservation of the natural, cultural, scenic and recreational features , including tourism values, of the area’.
.
Instead, the Rural Fire Service is content to look busy by burning and bulldozing native bushland. The RFS actively demonises native vegetation as a ‘fuel hazard‘, in the much the same way that ignorant colonists of the 18th and 19th centuries demonised Australia’s unique wildlife as ‘vermin‘ and ‘game‘.
.
Further Reading:
.
[1] Previous article on The Habitat Advocate: ‘ RFS Bulldozes Six Foot Track‘ (published 20101220): [> Read Article]
.
[2] Tip of the Bush-Arson Iceberg
What these government funded and State-sanctioned bush-arsonists get up to, deliberately setting fire to wildlife habitat, is an ecological disgrace.
The following list is from just 2005 of the vast areas of native vegetation deliberately burnt across New South Wales in just this one year. [Source: DOTARS].
Not surprisingly, this State-sanctioned bush-arson information is no longer published by government each year for obvious clandestine reasons, as the bush-arson continues out of the public eye.
The hazard reduction cult is similarly perpetuated across other Australian states – Victoria, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, West Australia as well as Northern Territory and the ACT. No wonder Australia’s record of wildlife extinctions tragically leads the world! There is little precious rich wildlife habitat left.
.
National Park and Wildlife Service (NSW) Bush Arson:
(Note: ‘NR’ = Nature Reserve, ‘NP’ = National Park, ‘SCA’ = State Conservation Area… as if these bastards care)
| Reserve / Activity Name |
Treatment Area (km2) |
| Baalingen NR |
5 |
| Baalingen NR |
6 |
| Bald Rock NP |
7 |
| Banyabba NR |
0.5 |
| BANYABBA NR |
3 |
| BANYABBA NR |
24 |
| BANYABBA NR |
8 |
| Barakee NP |
6 |
| Barool NP |
20 |
| Barool NP |
6 |
| Barool NP |
5 |
| Barool NP |
4 |
| Barool NP |
2 |
| Barool NP |
5 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
2.5 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
2 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
6 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
18 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
6 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
16 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
11 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
1 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
4 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
2 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
1 |
| Barrington Tops NP |
3 |
| Basket Swamp NP |
1 |
| Basket Swamp NP |
12 |
| Basket Swamp NP |
2 |
| Basket Swamp NP |
4 |
| Bellinger River NP |
1 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
0.8 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
3 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
0.9 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
0.9 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
5 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
13 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
5 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
0.4 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
1 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
2 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
3 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
5 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
3.6 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
1.9 |
| Ben Boyd NP |
1.6 |
| Ben Halls Gap NP |
3 |
| Bindarri NP |
2 |
| Black Bulga SCA |
8 |
| Black Bulga SCA |
12 |
| Black Bulga SCA |
21 |
| Blue Mountains NP |
42 |
| Blue Mountains NP |
8.3 |
| Blue Mountains NP |
23 |
| Blue Mountains NP |
10 |
| Blue Mountains NP |
12 |
| Bogendyra NR |
|
| Bolivia NR |
1 |
| BOLLONOLLA NR |
2 |
| Bondi Gulf NR |
8 |
| Bondi Gulf NR |
6 |
| Bondi Gulf NR |
10 |
| BONGIL BONGIL NP |
0.3 |
| BONGIL BONGIL NP |
0.5 |
| Boonoo Boonoo NP |
9 |
| Boonoo Boonoo NP |
10 |
| Booti Booti NP |
0.5 |
| Booti Booti NP |
0.3 |
| Booti Booti NP |
3 |
| Booti Booti NP |
0.3 |
| Booti Booti NP |
3 |
| Border Range NP |
6 |
| Border Ranges NP |
4 |
| Border Ranges NP |
3 |
| Border Ranges NP |
4 |
| Border Ranges NP |
2.8 |
| Bouddi NP |
0.5 |
| Bouddi NP |
0.3 |
| Bouddi NP |
0.9 |
| Bouddi NP |
0.9 |
| Bouddi NP |
0.5 |
| Bouddi NP |
1.1 |
| Bouddi NP |
0.5 |
| Bouddi NP |
1.9 |
| Bouddi NP |
1.1 |
| Bouddi NP |
0.6 |
| Bouddi NP |
2.3 |
| Bournda NR |
10 |
| Bournda NR |
5 |
| Bournda NR |
0.5 |
| Bournda NR |
0.5 |
| Bournda NR |
0.5 |
| Brindabella NP |
20 |
| Brisbane Water NP |
4.4 |
| Brisbane Water NP |
2.4 |
| Brisbane Water NP |
3.7 |
| Brisbane Water NP |
3.6 |
| Brisbane Water NP |
0.3 |
| Brisbane Water NP |
3.1 |
| Brisbane Water NP |
0.6 |
| Budawang NP |
4.8 |
| Budderoo NP |
10 |
| Bugong NP |
3.1 |
| Bundgalung NP |
2 |
| BUNDJALUNG NP |
7 |
| BUNDJALUNG NP |
4.5 |
| BUNDJALUNG NP |
8 |
| BUNDJALUNG NP |
1.5 |
| BUNDJALUNG NP |
0.5 |
| BUNDJALUNG NP |
6 |
| BUNDJALUNG NP |
3 |
| BUNDJALUNG NP |
3 |
| BUNDJALUNG NP |
4 |
| BUNDJALUNG NP |
2 |
| BUNDJALUNG NP |
1 |
| Bundundah Reserve |
1.94 |
| Bundundah Reserve/Morton NP |
4.7 |
| Bungawalbyn NP |
2 |
| Bungawalbyn NP |
2.25 |
| Bungawalbyn NP |
4 |
| Bungawalbyn NP |
5 |
| Bungawalbyn NP |
3 |
| Bungawalbyn NP |
4.5 |
| Bungawalbyn NP |
6.5 |
| Bungawalbyn NP |
5 |
| Bungawalbyn NP |
1.65 |
| Bungawalbyn NP |
1.5 |
| Burnt Down Scrub NR |
2 |
| Burnt School NR |
2 |
| Burrinjuck NR |
8 |
| Burrinjuck NR |
15 |
| Burrinjuck NR |
3 |
| Butterleaf NP |
|
| Butterleaf NP |
3 |
| Butterleaf NP |
3.2 |
| Butterleaf NP |
1.2 |
| Butterleaf NP |
1.6 |
| Butterleaf NP |
1.2 |
| Butterleaf NP |
2 |
| Butterleaf NP |
1.8 |
| Butterleaf NP |
1.4 |
| Butterleaf NP |
0.5 |
| Butterleaf NP |
2.3 |
| Butterleaf NP |
3.3 |
| Butterleaf NP |
3.9 |
| Butterleaf NP |
5.3 |
| Butterleaf NP |
0.4 |
| Butterleaf NP |
0.5 |
| Butterleaf NP |
1.5 |
| Butterleaf NP |
2.9 |
| Butterleaf NP |
5.3 |
| Butterleaf NP |
4 |
| Butterleaf NP |
3.3 |
| Butterleaf NP |
3.6 |
| Butterleaf NP |
1.5 |
| Butterleaf NP |
8.8 |
| Butterleaf NP |
0.5 |
| Capoompeta NP |
10 |
| Cataract NP |
|
| Cataract NP |
1.5 |
| Cataract NP |
2 |
| Cataract NP |
2 |
| Cataract NP |
1.5 |
| Cataract NP |
2 |
| Cataract NP |
1 |
| Clayton Chase |
5 |
| Clayton Chase |
10 |
| Clayton Chase |
3.5 |
| Clayton Chase |
4 |
| Clayton Chase |
3 |
| Clayton Chase |
3 |
| Clayton Chase |
4 |
| Conjola NP |
5.7 |
| Conjola NP |
1.8 |
| Conjola NP |
8.3 |
| Conjola NP |
4.8 |
| Conjola NP |
2.9 |
| Conjola NP |
4.5 |
| Conjola NP |
6.5 |
| Coolah Tops NR |
28 |
| Coolah Tops NR |
1 |
| Coolah Tops NR |
6 |
| Copeland Tops SCA |
3 |
| Copeland Tops SCA |
3.5 |
| Corramy SCA |
0.7 |
| Cottan-bimbang NP |
6 |
| Cottan-bimbang NP |
16 |
| Cottan-bimbang NP |
15 |
| Culgoa NP |
30 |
| Curramore NP |
|
| Curramore NP |
8 |
| Curramore NP |
8.9 |
| Curramore NP |
11 |
| Curramore NP |
5.5 |
| Dapper NR |
10 |
| Deua NP |
15.2 |
| Deua NP |
1.4 |
| Deua NP |
1 |
| Deua NP |
4 |
| Deua NP |
21.5 |
| Deua NP |
2.1 |
| Deua NP |
1.4 |
| Deua NP |
3.3 |
| Deua NP |
8.5 |
| Deua NP |
20.8 |
| Deua NP |
5.3 |
| Deua NP |
6.6 |
| Deua NP |
28.2 |
| Deua NP |
5.65 |
| DUNGGIR NP |
4 |
| Eurobodalla NP |
0.8 |
| Eurobodalla NP |
2.5 |
| Eurobodalla NP |
0.8 |
| Eurobodalla NP |
2.4 |
| Eurobodalla NP |
2 |
| Flaggy creek NR |
3 |
| Flaggy creek NR |
1.8 |
| GANAY NR |
2 |
| GANAY NR |
2 |
| Garawarra SCA |
|
| Garby NR |
2 |
| Gardens of Stone NP |
18 |
| Gibraltar NP |
14 |
| Goobang NP |
5 |
| Goobang NP |
25 |
| GUMBAYNGIR SCA |
12 |
| GUMBAYNGIR SCA |
7 |
| GUMBAYNGIR SCA |
6 |
| Ironbark NR |
13.5 |
| Jerrawangala NP |
6.83 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
2.37 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
5.42 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.56 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.82 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
1.45 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
1.72 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.21 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.32 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.7 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.4 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.35 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.35 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.48 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
1.03 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.65 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
1.91 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.34 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.95 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
1.46 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
0.71 |
| Jervis Bay NP |
1.07 |
| Jingellic NR |
20 |
| Karuah NR |
10 |
| Karuah NR |
28 |
| Karuah NR |
10 |
| Karuah NR |
12 |
| Karuah NR |
1 |
| Kings Plains NP |
7 |
| Kings Plains NP |
0 |
| Kings Plains NP |
4 |
| Koreelah NP |
6 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
30 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
9.5 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
22 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
22 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
33 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
33 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
33 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
12 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
12 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
17 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
5 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
28 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
9 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
6 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
6 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
26 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
8.9 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
15 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
15 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
2.5 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
8.9 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
10 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
11 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
4.8 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
18 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
19 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
7.2 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
7.2 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
13 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
18 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
33 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
33 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
18 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
18 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
15 |
| Kosciuszko NP |
12 |
| Kwiambal NP |
7 |
| Kwiambal NP |
3 |
| Kwiambal NP |
2 |
| Kwiambal NP |
2.25 |
| Lake Macquarie SCA |
0.3 |
| Lake Macquarie SCA |
0.4 |
| Lake Macquarie SCA |
0.4 |
| Lake Macquarie SCA |
0.4 |
| Ledknapper NR |
15 |
| Linton NR |
12.5 |
| Meroo NP |
2.4 |
| Meroo NP |
0.9 |
| Meroo NP |
0.6 |
| Meroo NP |
3.3 |
| Meroo NP |
3.9 |
| Meroo NP |
3.5 |
| Meroo NP |
0.5 |
| Morton NP |
5.9 |
| Morton NP |
8.3 |
| Morton NP |
3.8 |
| Morton NP |
6 |
| Morton NP |
13 |
| Morton NP |
0.4 |
| Morton NP |
4.5 |
| Morton NP |
5 |
| Morton NP |
2.7 |
| Morton NP |
0.7 |
| Morton NP |
2.1 |
| Morton NP |
1 |
| Morton NP |
6 |
| Mt Canobolas SCA |
1 |
| Mt Clunnie NP |
6.5 |
| Mt Dowling NR |
2 |
| MT NEVILLE NR |
11 |
| MT NEVILLE NR |
1 |
| MT NEVILLE NR |
1.5 |
| MT NEVILLE NR |
11 |
| MT NEVILLE NR |
1.5 |
| MT NEVILLE NR |
3.5 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
2 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
4 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
2.5 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
1.5 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
1.5 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
4 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
7 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
2 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
2.5 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
6 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
3 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
0.5 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
0.5 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
2.5 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
2 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
1 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
2.5 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
6 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
2 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
1 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
2.5 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
2 |
| MT PIKAPENE NP |
1.5 |
| Mummell Gulf NP |
3 |
| Mummell Gulf NP |
7 |
| Mummell Gulf NP |
5 |
| Munmorah SRA |
0.7 |
| Munmorah SRA |
0.8 |
| Munmorah SRA |
0.45 |
| Munmorah SRA |
1 |
| Munmorah SRA |
2 |
| Munmorah SRA |
0.9 |
| Munmorah SRA |
1.6 |
| Muogamarra NR |
1 |
| Murramarang NP |
0.9 |
| Murramarang NP |
8 |
| Murramarang NP |
1 |
| Murramarang NP |
5.1 |
| Murramarang NP |
8.2 |
| Murramarang NP |
3.1 |
| Murramarang NP |
6.8 |
| Murramarang NP |
16 |
| Murramarang NP |
4.3 |
| Murramarang NP |
4 |
| Myall Lakes NP |
5 |
| Myall Lakes NP |
5 |
| Myall Lakes NP |
1.5 |
| Myall Lakes NP |
2 |
| Myall Lakes NP |
1 |
| Myall Lakes NP |
5 |
| NGAMBAA NR |
2 |
| NGAMBAA NR |
5 |
| Nombinnie NR |
10 |
| Nymboida NP |
6 |
| Nymboida NP |
12 |
| Nymboida NP |
3 |
| Nymboida NP |
4 |
| Nymboida NP |
1 |
| Nymboida NP |
4 |
| Nymboida NP |
4 |
| Nymboida NP |
3.2 |
| Nymboida NP |
4.5 |
| Nymboida NP |
2 |
| Nymboida NP |
4 |
| Nymboida NP |
2.8 |
| Nymboida NP |
4.2 |
| Nymboida NP |
4.2 |
| Nymboida NP |
4.2 |
| Nymboida NP |
4.2 |
| Nymboida NP |
4.2 |
| Nymboida NP |
4.2 |
| Nymboida NP |
4.2 |
| Nymboida NP |
4.2 |
| Nymboida NP |
7 |
| Nymboida NP |
6 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
10.7 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
19.1 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
13.4 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
18 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
18 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
15 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
33 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
33 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
5 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
5 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
4 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
3 |
| Oxley Wild Rivers NP |
7 |
| Parma Creek NR |
0.21 |
| Parma Creek NR |
0.07 |
| Parma Creek NR |
0.3 |
| Parma Creek NR |
0.01 |
| Parma Creek NR |
0.29 |
| Parma Creek NR |
5 |
| Paroo Darling NP |
60 |
| Policemans Cap |
10 |
| Razorback NR |
17 |
| Richmond Range NP |
3.9 |
| Richmond Range NP |
6.5 |
| Richmond Range NP |
3.8 |
| Richmond Range NP |
4.5 |
| Richmond Range NP |
5.5 |
| Richmond Range NP |
9 |
| Royal NP |
1 |
| Seven Mile Beach NP |
1.09 |
| Seven Mile Beach NP |
1.79 |
| Seven Mile Beach NP |
2.24 |
| Seven Mile Beach NP |
0.74 |
| Seven Mile Beach NP |
2.03 |
| Severn River NR |
6 |
| Single NP |
21 |
| South East Forest NP |
5 |
| South East Forest NP |
1.2 |
| South East Forest NP |
1.2 |
| South East Forest NP |
2.6 |
| South East Forest NP |
3 |
| South East Forest NP |
10.9 |
| South East Forest NP |
1.3 |
| South East Forest NP |
1 |
| South East Forest NP |
1.2 |
| South East Forest NP |
2.8 |
| South East Forest NP |
2 |
| South East Forest NP |
1.2 |
| South East Forest NP |
2 |
| South East Forest NP |
5.1 |
| South East Forest NP |
3.5 |
| South East Forest NP |
0.5 |
| South East Forest NP |
6 |
| South East Forest NP |
3 |
| South East Forest NP |
1 |
| South East Forest NP |
5.5 |
| South East Forest NP |
0.8 |
| Stoney Batter NR |
6 |
| Tapitallee NR |
0.52 |
| Tapitallee NR |
0.33 |
| Tapitallee NR |
0.36 |
| Tapitallee NR |
0.32 |
| Tarlo River NP |
3.8 |
| Tarlo River NP |
2.1 |
| Tarlo River NP |
2.9 |
| Tarlo River NP |
5.9 |
| Tarlo River NP |
6.5 |
| Tarlo River NP |
2.7 |
| Tarlo River NP |
2.1 |
| Tarlo River NP |
6 |
| Tollingo NR |
150 |
| Tomaree NP |
1.8 |
| Tooloom NP |
3 |
| Toonumbar NP |
31.9 |
| Toonumbar NP |
8.5 |
| Toonumbar NP |
17 |
| Toonumbar NP |
21.5 |
| Triplarina NR |
0.71 |
| Triplarina NR |
0.32 |
| Triplarina NR |
0.66 |
| Triplarina NR |
0.75 |
| Triplarina NR |
1.34 |
| Triplarina NR |
0.31 |
| Triplarina NR |
1.24 |
| Triplarina NR |
1.35 |
| Ungazetted (Kalyarr NP) |
48 |
| Ungazetted (Kalyarr NP) |
26 |
| Unknown |
7 |
| Wa Hou NR |
10 |
| Wa Hou NR |
1 |
| Wa Hou NR |
7 |
| Wa Hou NR |
1 |
| Wa Hou NR |
11 |
| Wa Hou NR |
1 |
| Wa Hou NR |
7 |
| Wa Hou NR |
1 |
| Wa Hou NR |
1 |
| Wa Hou NR |
1 |
| Wa Hou NR |
1 |
| Wallaroo NR |
3 |
| Wallaroo NR |
1.5 |
| Wallaroo NR |
8 |
| Wallaroo NR |
5 |
| Wallaroo NR |
11 |
| Wallaroo NR |
7 |
| Wallaroo NR |
7 |
| Wallaroo NR |
16 |
| Wallaroo NR |
6 |
| Wallingat NP |
2 |
| Wallingat NP |
1.3 |
| Wallingat NP |
3.6 |
| Wallingat NP |
3.3 |
| Washpool Np |
18 |
| Washpool NP |
5.3 |
| Washpool NP |
5.6 |
| Washpool NP |
7.1 |
| Washpool NP |
6.4 |
| Washpool NP |
1.6 |
| Washpool NP |
7 |
| Washpool NP |
2.8 |
| Watson’s Creek NR |
5 |
| Wereboldera SCA |
9 |
| Woggoon NR |
144 |
| Wollemi NP |
21 |
| Wollemi NP |
12 |
| Wollemi NP |
10 |
| Wollemi NP |
30 |
| Wollemi NP |
7 |
| Wollemi NP |
11 |
| Wollemi NP |
7 |
| Wollemi NP |
16 |
| Wollemi NP |
2 |
| Wollemi NP |
8 |
| Wollemi NP |
5 |
| Woodford Island NR |
1.5 |
| Woodford Island NR |
2 |
| Woodford Island NR |
3 |
| Woodford Island NR |
3 |
| Woollamia NR |
1.51 |
| Woollamia NR |
0.77 |
| Woollamia NR |
1.95 |
| Woollamia NR |
1.88 |
| Woollamia NR |
0.74 |
| Woomargama NP |
15 |
| Yabbra NP |
8 |
| Yabbra NP |
45 |
| Yango NP |
0.45 |
| Yanununbeyan NP |
11 |
| YARRIABINNI NP |
2 |
| YARRIABINNI NP |
3 |
| YARRIABINNI NP |
5 |
| YARRIABINNI NP |
6 |
| YARRIABINNI NP |
4 |
| Yuraygir NP |
4 |
| Yuraygir NP |
3.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1 |
| YURAYGIR NP |
0.03 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1 |
| Yuraygir NP |
3.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1.5 |
| Yuraygir NP |
28 |
| Yuraygir NP |
10 |
| Yuraygir NP |
12 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1 |
| Yuraygir NP |
1 |
| Yuraygir NP |
4 |
| Yuraygir NP |
3.5 |
|
3,785.10 Ha |
i.e. An area 6km x 6km
.
NSW Local Government Areas (LGAs)
| Bush Fire Management Committee / LGA |
Reserve / Activity Name |
Treatment Area (km2) |
| Blue Mountains |
Northern Strategic Line -Primary |
8 |
| Blue Mountains |
De Faurs Trail – Mt Wilson -Primary |
2.8 |
| Blue Mountains |
Mitchell’s Creek Fire Trail – Primary |
3.5 |
| Blue Mountains |
Nellies Glen Fire Trail |
2.8 |
| Blue Mountains |
Back Creek Fire Trail – Primary |
3.2 |
| Blue Mountains |
Mt Piddington Trail – Hornes Point |
N/A |
| Bombala |
Gibraltar Ridge Fire Trail (2) (PT) |
20 |
| Bombala |
Mt Rixs Fire Trail (PT) |
6 |
| Bombala |
Roaring Camp Fire Trail (PT) |
12 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Brest Fire Trail (2) (PT) |
15 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Calabash Fire Trail (2) (PT) |
22 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Murrumbucca Fire Trail (2) (ST) |
15 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Bridge Fire Trail (2) (PT) |
6 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Log In Hole Fire Trail (2) (PT) |
5 |
| Gloucester |
Upper Avon Fire Trail |
11 |
| Greater Argyle |
Mountain Ash Fire Trail |
10 |
| Greater Argyle |
Mootwingee Fire Trail |
6 |
| Greater Hume |
Murphy’s Fire Trail |
0.2 |
| Greater Hume |
Mandaring Fire Trail |
1 |
| Greater Queanbeyan City |
Queanbeyan River Fire Trail |
5.5 |
| Greater Queanbeyan City |
Gourock Fire Trail |
5.8 |
| Hawkesbury District |
Jacks Trail |
1.6 |
| Hawkesbury District |
Duffys Trail (2) ?tenure |
3 |
| Mallee |
Various Fire Trails |
N/A |
| Mallee |
No 21 Fire Trail |
20 |
| Namoi/Gwydir |
Warialda State Forest |
6.5 |
| Namoi/Gwydir |
Zaba-Kaiwarra-Kiora Fire Trail (check) |
10 |
| Namoi/Gwydr |
Blue Nobby Fire Trail (check) |
8 |
| Namoi/Gwydr |
Araluen Fire Trail (check) |
6 |
| Snowy River |
Snowy Plain Fire Trail (2) (PT) |
18 |
| Snowy River |
Crackenback Fire Trail (PT) |
10 |
| Snowy River |
Devils Hole Fire Trail (PT) |
18 |
| Snowy River |
Golden Age Fire Trail (2) (PT) |
8 |
| Sutherland |
Sabugal Pass Fire Trail |
N/A |
| SW Mallee |
Various Fire Trails |
N/A |
| SW Mallee |
Oberwells Fire Trail |
28 |
| SW Mallee |
Mandleman Fire Trail |
40 |
| Upper Lachlan |
Johnsons Creek Fire Trail |
15 |
| Warringah/Pittwater |
Lovett Bay Trail (2) |
2.5 |
| Warringah/Pittwater |
Elvina Bay Trail (2) |
1.5 |
| Yass Valley |
Nelanglo Fire Trail |
21 |
| Yass Valley |
Hayshed Fire Trail 1 |
7 |
| Yass Valley |
Hayshed Fire Trail 2 |
7 |
|
|
391.90 km2 |
i.e. An area 20km x 20km
.
Forests NSW (government’s industrial logger of NSW remnant forests).
(Forests NSW did not publish the area burnt, only the cost. As a rule of thumb use $3000/square km)
| Bush Fire Management Committee |
Reserve / Activity Name |
NSW
Allocation |
| Clarence Zone |
Dalmorton SF |
$30,000 |
| Future Forests |
Swan |
$20,050 |
| Future Forests |
Tindall |
$10,680 |
| Future Forests |
Tooloom |
$10,425 |
| Future Forests |
Mazzer |
$7,341 |
| Future Forests |
Kungurrabah |
$4,435 |
| Future Forests |
Morpeth Park |
$3,773 |
| Future Forests |
Loughnan |
$3,155 |
| Future Forests |
Inglebar |
$3,000 |
| Future Forests |
Lattimore |
$2,604 |
| Future Forests |
Byrne |
$1,755 |
| Future Forests |
Ziull 4 |
$1,677 |
| Future Forests |
Lejag |
$1,670 |
| Future Forests |
Ziull 2 |
$1,600 |
| Future Forests |
Bates |
$1,563 |
| Future Forests |
Ziull 3 |
$1,454 |
| Future Forests |
Envirocom |
$1,410 |
| Future Forests |
Morgan |
$1,361 |
| Future Forests |
McNamara |
$1,279 |
| Future Forests |
Neaves |
$967 |
| Future Forests |
Zuill |
$872 |
| Future Forests |
Boyle |
$807 |
| Future Forests |
Fitzpatrick |
$791 |
| Future Forests |
Morrow |
$785 |
| Future Forests |
Morrow |
$785 |
| Future Forests |
Morrow |
$785 |
| Future Forests |
Wallwork |
$665 |
| Future Forests |
Smith |
$665 |
| Future Forests |
Wilson |
$622 |
| Future Forests |
Jarramarumba |
$600 |
| Future Forests |
Hession |
$597 |
| Future Forests |
Edwards |
$563 |
| Future Forests |
Maunder |
$558 |
| Future Forests |
Kuantan |
$515 |
| Future Forests |
Billins |
$484 |
| Future Forests |
Cox |
$475 |
| Future Forests |
Paterson |
$461 |
| Future Forests |
Gladys |
$415 |
| Future Forests |
O’Keefe |
$371 |
| Future Forests |
Woodcock |
$369 |
| Future Forests |
Pratten |
$346 |
| Future Forests |
Truswell |
$323 |
| Future Forests |
Divine |
$323 |
| Future Forests |
Hastings |
$323 |
| Future Forests |
White |
$300 |
| Future Forests |
Miller |
$300 |
| Future Forests |
Koop |
$300 |
| Future Forests |
Lacy |
$277 |
| Future Forests |
Nosrac |
$277 |
| Future Forests |
Tully |
$277 |
| Future Forests |
Baker |
$277 |
| Future Forests |
Yaganegi |
$277 |
| Future Forests |
Siezowski |
$254 |
| Future Forests |
Zuill |
$254 |
| Future Forests |
Atcheson |
$254 |
| Future Forests |
Dissevelt |
$254 |
| Future Forests |
Hoy |
$254 |
| Future Forests |
Woods |
$254 |
| Future Forests |
Dawson |
$254 |
| Future Forests |
Hagan |
$254 |
| Future Forests |
Skelly |
$231 |
| Future Forests |
Robards |
$231 |
| Future Forests |
Maunder |
$231 |
| Future Forests |
Day |
$231 |
| Future Forests |
O’Connell |
$231 |
| Future Forests |
Kompara |
$231 |
| Future Forests |
Carmen |
$231 |
| Future Forests |
Maurer |
$231 |
| Future Forests |
Cunin |
$208 |
| Future Forests |
GCC |
$208 |
| Future Forests |
White |
$208 |
| Future Forests |
Hayer |
$208 |
| Future Forests |
Southgate |
$208 |
| Future Forests |
Peck |
$208 |
| Greater Taree |
Kiwarrak SF |
$40,000 |
| Hastings |
Cowarra SF |
$30,000 |
| Hastings |
Caincross SF |
$4,000 |
| Hume |
Clearing fire trails |
$100,000 |
| Hume |
New FT |
$6,000 |
| Hunter |
Pokolbin SF |
$13,600 |
| Hunter |
Myall River SF |
$12,800 |
| Hunter |
Myall River SF |
$12,800 |
| Hunter |
Heaton SF |
$12,400 |
| Hunter |
Bulahdelah SF |
$6,100 |
| Hunter |
Watagan SF |
$3,200 |
| Hunter |
Awaba SF |
$3,200 |
| Hunter |
Myall River SF |
$3,100 |
| Macquarie |
Warrengong |
$16,250 |
| Macquarie |
Vulcan & Gurnang |
$11,519 |
| Macquarie |
Kinross SF |
$8,800 |
| Macquarie |
Mount David |
$6,101 |
| Macquarie |
Newnes SF |
$5,199 |
| Macquarie |
Printing 25 fire atlas’ |
$2,048 |
| Macquarie |
Black Rock Ridge |
$447 |
| Mid-Nth Coast – Taree |
Knorrit SF |
$36,000 |
| Mid-Nth Coast – Taree |
Yarratt SF |
$16,000 |
| Mid-Nth Coast – Wauchope |
Boonanghi SF |
$37,000 |
| Mid-Nth Coast – Wauchope |
Northern Break |
$9,000 |
| Mid-Nth Coast – Wauchope |
Caincross SF |
$3,000 |
| Mid-Nth Coast – Wauchope |
Western Break |
$2,000 |
| Monaro |
Clearing fire trails |
$114,685 |
| North East |
Thumb Creek SF |
$46,000 |
| North East |
Candole SF |
$29,535 |
| North East |
Various State Forests |
$20,000 |
| North East |
Mt Belmore SF |
$12,115 |
| North East |
Candole SF |
$8,900 |
| North East |
Lower Bucca SF |
$5,500 |
| North East |
All North Region |
$3,300 |
| North East |
Wild Cattle SF |
$3,000 |
| North East |
Orara East SF |
$1,900 |
| Northern -Casino |
Barragunda |
$11,522 |
| Northern -Casino |
Yaraldi 2003 |
$8,847 |
| Northern -Casino |
Yaraldi 2004 |
$3,207 |
| Richmond Valley |
Bates |
$20,000 |
| Richmond Valley |
Whiporie SF |
$13,154 |
| Richmond Valley |
Swanson |
$12,000 |
| Richmond Valley |
McNamara |
$10,180 |
| Richmond Valley |
Whiporie SF |
$9,582 |
| Southern |
Pollwombra FT |
$6,360 |
| Southern-Eden |
Various – whole district |
$112,019 |
| Tamworth |
Nundle SF |
$40,000 |
| Walcha |
Nowendoc SF |
$30,000 |
| Walcha |
Styx River SF |
$20,000 |
|
|
$1,073,482 |
i.e. Approximately an area 20km x 20km
.
NSW Department of Lands (what native vegetation’s left).
| Bush Fire Management Committee |
Reserve / Activity Name |
Treatment Area Ha / Other |
Treatment Area (km2) |
| Baulkham Hills |
Porters Rd / Cranstons Rd |
|
5 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Porters Rd / Cranstons Rd (2) |
|
4 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Pauls Road Trail |
|
5 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Mount View Trail |
|
1 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Idlewild |
|
2 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Maroota Tracks Trail |
|
7 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Yoothamurra Trail |
|
1 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Kellys Arm Trail |
|
3 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Dargle Ridge Trail |
|
5 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Dargle Trail |
|
3 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Days Road Trail |
|
3 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Dickinsons Trail |
|
6 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Fingerboard Trail |
|
3 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Floyds Road Trail |
|
8 |
| Baulkham Hills |
Neichs Road Trail |
|
4 |
| Bega |
Eden Strategic Fire Trail |
|
3 |
| Bega |
Illawambera Fire Trail |
|
1 |
| Bega |
Merimbula/Turu Beach Strategic Protection |
|
2 |
| Bega |
Yankees Gap |
|
2 |
| Bega |
Millingandi Special Protection (Trail) |
|
1 |
| Bega |
Wallagoot Strategic Protection (Trail) |
|
1.2 |
| Bega |
South Eden Strategic Protection (Trail) |
|
1 |
| Bega |
Merimbula/Pambula Strategic Protection (APZ) |
|
1 |
| Bega |
Pacific St Tathra |
|
0.5 |
| Bland |
Bland Villages (FTM) |
|
2 |
| Bland |
Water Tower Reserve FTM |
|
3 |
| Blue Mountains |
Cripple Creek Fire Trail Stage 2 |
|
5 |
| Blue Mountains |
Cripple Creek Fire Trail Complex |
|
5 |
| Blue Mountains |
Caves Creek Trail |
|
0.4 |
| Blue Mountains |
Edith Falls Trail |
|
2 |
| Blue Mountains |
Boronia Rd – Albert Rd Trails |
|
1 |
| Blue Mountains |
Perimeter Trail – North Hazelbrook |
|
1.5 |
| Blue Mountains |
McMahons Point Trail – Kings Tableland |
|
7 |
| Blue Mountains |
Back Creek Fire Trail |
|
3.2 |
| Blue Mountains |
Mitchell’s Creek Fire Trail |
|
3.5 |
| Bombala |
Gibraltar Ridge Fire Trail |
|
11 |
| Bombala |
Burnt Hut Fire Trail |
|
5 |
| Bombala |
Merriangah East Fire Trail |
|
12 |
| Bombala |
Bombala Towns & Villages (Trails) |
|
10 |
| Campbelltown |
St Helens Park – Wedderburn Rd (Barriers) |
|
0.3 |
| Campbelltown |
Barrier / Gate |
|
|
| Campbelltown |
Riverview Rd Fire Trail |
|
0.65 |
| Canobolas |
Calula Range FTM |
|
|
| Canobolas |
Spring Glen Estate FTM |
|
|
| Cessnock |
Neath South West Fire Trail |
|
2 |
| Cessnock |
Neath South East Fire Trail |
|
1.5 |
| Cessnock |
Neath North Fire Trail (2) |
|
1 |
| Cessnock |
Gates – Asset Protection Zones |
|
|
| Cessnock |
Signs – Asset Protection Zones |
|
|
| Cessnock |
Signs – Fire Trails |
|
|
| Cessnock |
Kearsley Fire Trail |
|
0.5 |
| Cessnock |
Neath – South (Trail) |
|
4 |
| Cessnock |
Neath – North (Trail) |
|
2 |
| Clarence Valley |
Bowling Club Fire Trail |
|
1 |
| Clarence Valley |
Brooms Head Fire Trail |
|
0.2 |
| Clarence Valley |
Ilarwill Village |
|
0.3 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Chakola Fire Trail |
|
21 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Good Good Fire Trail |
|
12 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Inaloy Fire Trail |
|
19 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Cowra Creek Fire Trail |
|
4 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
David’s Fire Trail |
|
2.1 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Clear Hills Fire Trail |
|
5 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Mt Dowling Fire Trail |
|
16 |
| Cooma-Monaro |
Towneys Ridge Fire Trail |
|
6 |
| Cunningham |
Warialda Periphery 2 |
|
20 |
| Cunningham |
Upper Bingara Fire Trail |
|
|
| Dungog |
Dungog Fire Trail Signs |
|
|
| Far North Coast |
Byrangary Fire Trail |
|
1 |
| Far North Coast |
Main Arm Fire Trail (NC67) |
|
2 |
| Far North Coast |
Burringbar Fire Trail (NC69) |
|
1 |
| Far North Coast |
Mill Rd Fire Trail (NC95) |
|
1 |
| Far North Coast |
Broken Head Fire Trail (NC68) |
|
0.5 |
| Far North Coast |
New Brighton Fire Trail (NC44) |
|
0.5 |
| Far North Coast |
Mooball Spur Fire Trail |
|
1 |
| Far North Coast |
Palmwoods Fire Trail (NC06) |
|
0.5 |
| Gloucester |
Coneac Trail |
|
6 |
| Gloucester |
Moores Trail |
|
6 |
| Gloucester |
Mt Mooney Fire Trail |
|
6 |
| Gosford District |
Signs – Fire Trails |
|
|
| Great Lakes |
Ebsworth Fire Trail |
|
1 |
| Great Lakes |
Tuncurry High Fire Trail |
|
0.6 |
| Great Lakes |
Monterra Ave Trail – Hawks Nest |
|
0.7 |
| Greater Argyle |
Browns Rd Komungla |
|
12 |
| Greater Argyle |
Greater Argyle Fire Trail Maintenance |
|
|
| Greater Argyle |
Cookbundoon Fire Trail |
|
2 |
| Greater Taree District |
Tinonee St Road Reserve |
|
0.25 |
| Greater Taree District |
Beach St SFAZ – Wallabi Point |
|
0.35 |
| Greater Taree District |
Sth Woodlands Dr – SFAZ |
|
1.3 |
| Greater Taree District |
Cedar Party Rd – Taree |
|
2 |
| Hawkesbury District |
Sargents Road (2) ?tenure |
|
0.75 |
| Hawkesbury District |
Parallel Trail (2) |
|
2.5 |
| Hawkesbury District |
Parallel Trail (1) |
|
1.1 |
| Hornsby/Ku-ring-gai |
Tunks Ridge, Dural |
|
1 |
| Hornsby/Ku-ring-gai |
Radnor & Cairnes Fire Trail |
|
0.5 |
| Hornsby/Ku-ring-gai |
Binya Cl, Hornsby Heights |
|
1.5 |
| Shellharbour District |
Saddleback – Hoddles Trail |
|
3 |
| Shellharbour District |
Rough Range Trail |
|
1 |
| Lake Macquarie District |
Kilaben Bay Fire Trail |
|
1.5 |
| Lake Macquarie District |
Gates – Access Management |
|
|
| Lake Macquarie District |
Signs – APZ |
|
|
| Lake Macquarie District |
Signs – Fire Trails |
|
|
| Lithgow |
Wilsons Glen Trail |
|
6.1 |
| Lithgow |
Kanimbla Fire Trail No 314 |
|
7.8 |
| Lithgow |
Camels Back Trail No 312 |
|
4.5 |
| Lithgow |
Crown Creek Trail No 206 |
|
7 |
| Lithgow |
Capertee Common Trail No 203 |
|
3 |
| Lower Hunter Zone |
Access Infrastructure – All Districts |
|
|
| Lower North Coast |
Cabbage Tree Lane Fire Trail, Kempsey |
|
1.5 |
| Lower North Coast |
Bullocks Quarry Fire Trail |
|
0.66 |
| Lower North Coast |
Perimeter Protection, Main St, Eungai Creek, Nambucca |
|
0.6 |
| Mid North Coast |
Urunga Lagoon, Bellingen |
|
4 |
| Mid North Coast |
Wenonah Head, Bellingen |
|
4 |
| Mudgee |
Munro’s Fire Trail |
|
24 |
| Mudgee |
Munro’s Fire Trail |
|
5.25 |
| Penrith |
Londonderry/Castlereagh |
|
6 |
| Port Stephens |
Bobs Farm Fire Trails |
|
4 |
| Port Stephens |
Salamander Way Fire Trail |
|
1.5 |
| Port Stephens |
Gan Gan Hill West Fire Trail |
|
1.2 |
| Port Stephens |
Nelson Bay – Gan Gan Hill (Trail) |
|
1.5 |
| Port Stephens |
Taylors Beach Fire Trail |
|
1 |
| Port Stephens |
Nelson Bay – Wallawa Rd (SFAZ) |
|
0.7 |
| Port Stephens |
Taylors Beach East Fire Trail |
|
3.5 |
| Port Stephens |
Nelson Bay – Wallawa Rd (Gates) |
|
|
| Port Stephens |
Port Stephens Fire Trail Signs |
|
|
| Port Stephens |
Corlette – Salamander Way (Trail) |
|
1 |
| Shoalhaven |
APZ Access Works |
|
|
| Snowy River |
Southern Boundary Fire Trail |
|
3 |
| Snowy River |
Somme Valley Fire Trail |
|
5 |
| Sutherland District |
Forbes Creek North Trail |
|
1.3 |
| Sutherland District |
Still Creek Complex (Trail) |
|
3.8 |
| Sutherland District |
Mannikin Trail |
|
1.5 |
| Sutherland District |
Viburnum Trail |
|
0.8 |
| Sutherland District |
Mill Creek Complex |
|
2.6 |
| Sutherland District |
Loftus Creek Complex |
|
1.9 |
| Sutherland District |
Cranberry Trail |
|
0.8 |
| Sutherland District |
Turella Trail |
|
0.8 |
| Sutherland District |
Freemantle Trail |
|
0.4 |
| Sutherland District |
Illaroo Trail |
|
0.7 |
| Sutherland District |
Yala East Trail |
|
0.9 |
| Sutherland District |
Bunyan Fire Trail |
|
1.2 |
| Sutherland District |
Rosewell Service Trail |
|
0.5 |
| Sutherland District |
Belarada Service Trail |
|
0.3 |
| Sutherland District |
Belbowrie Service Trail |
|
0.3 |
| Sutherland District |
Leawarra Fire Trail |
|
0.9 |
| Sutherland District |
McKenzie Service Trail |
|
0.7 |
| Sutherland District |
Walsh Close Trail |
|
0.7 |
| Sutherland District |
Yala West Trail |
|
0.7 |
| Sutherland District |
Barnes Cres Service Trail |
|
0.6 |
| Sutherland District |
Illumba Trail |
|
0.5 |
| Sutherland District |
Penrose Trail |
|
0.5 |
| Sutherland District |
Tatler Place Trail |
|
0.5 |
| Sutherland District |
Torumba Service Trail |
|
0.5 |
| Sutherland District |
Friendship Trail |
|
0.4 |
| Sutherland District |
Kippax – Rosewall Trail |
|
0.4 |
| Sutherland District |
Tallarook Service Trail |
|
0.4 |
| Sutherland District |
Billa Service Trail |
|
0.3 |
| Sutherland District |
Chestnut Trail |
|
0.2 |
| Sutherland District |
Croston Rd Trail |
|
0.3 |
| Sutherland District |
Kingswood Rd Trail |
|
0.3 |
| Sutherland District |
Roebourne Trail |
|
0.3 |
| Sutherland District |
Whimbrel Service Trail |
|
0.3 |
| Sutherland District |
Shearwater Trail |
|
0.1 |
| Tamworth |
Moore Creek Dam Reserve |
|
3.5 |
| Tamworth |
Moore Creek Dam Reserve |
|
1 |
| Tumut |
Bundarbo Fire Trail (Stage 1) |
|
30 |
| Tumut |
Yammatree Reserve |
|
2 |
| Tumut |
Thomas Boyd Track Head |
|
2 |
| Tumut |
Tumut Bush Common |
|
5 |
| Tumut |
Batlow Hill |
|
2 |
| Tumut |
Rimmers Ridge – Adelong |
|
|
| Tumut |
Bangadang |
|
7 |
| Upper Lachlan |
Upper Lachlan Fire Trail Maintenance |
|
|
| Upper Lachlan |
Isabella Fire Trail |
|
10 |
| Wagga Wagga |
Silvatite Reserve (Trails) |
|
5 |
| Wagga Wagga |
Wagga Wagga Towns & Villages (Trails) |
|
10 |
| Wagga Wagga |
Kyeamba Gap |
|
4 |
| Wagga Wagga |
San Isadore |
|
3 |
| Warringah/Pittwater |
Sandy Trail |
|
0.1 |
| Warringah/Pittwater |
Lovett Bay Trail |
|
2.5 |
| Warringah/Pittwater |
Elvina Bay Trail |
|
1.5 |
| Warringah/Pittwater |
Aumuna Cooyong Trail |
|
0.2 |
| Wingecarribee |
P3 Fire Trail |
|
6 |
| Wingecarribee |
Weir Fire trail |
|
3.8 |
| Wingecarribee |
Lukes Fire trail |
|
0.1 |
| Wollondilly |
Bargo Weir Fire Trail |
|
10 |
| Wyong District |
YMCA North / South Link Fire Trail |
|
2 |
| Wyong District |
YMCA South / Kanangra Dr Fire Trail |
|
2 |
| Wyong District |
Lake Munmorah Fire Trails |
|
3.25 |
| Wyong District |
Hyles St Fire Trail, Chittaway Pt |
|
0.1 |
| Wyong District |
Big “T” and YMCA Link Fire Trails |
|
1.5 |
| Wyong District |
Lake Road Fire Trail, Chittaway Point |
|
0.1 |
| Wyong District |
Big “T” Fire Trail – Crangan Bay |
|
1.1 |
| Wyong District |
Wyong APZ Signs |
|
|
| Wyong District |
Lake Road Fire Trail, Tuggerah |
|
1 |
| Wyong District |
Doyalson North, 219-225 Pacific Hway (Trail) |
|
0.8 |
| Yass Valley |
Yass Valley Fire Trail Maintenance |
|
|
|
|
|
565.16 |
i.e. Approximately an area 24km x 24km
. .
Tags: Blue Mountains National Park, Bulldozing Six Foot Track, bush arson, Bush Fire Coordinating Committee, Bushfire Mitigation Programme, controlled burning, Department of Transport and Regional Services, DOTARS, Ecologically Sustainable Development, Fire Trail Strategy, Giant Burrowing Frog, Glossy Black-Cockatoo, hazard reduction, Megalong Creek, prescribed burning, RFS, Rural Fire Service, Six Foot Track, spotted-tailed quoll
Posted in Birds (Australian), Blue Mountains (AU), Quolls, Reptiles, Threats from Bushfire, Threats from Greenwashing | 1 Comment »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Friday, March 16th, 2012
In November 2006, two separate bushfires that were allowed to burn out of control for a week as well extensive deliberate backburning, ended up causing some 14,070 hectares of the Blue Mountains National Park to be burnt.
This wiped out a significant area of the Grose Valley and burnt through the iconic Blue Gum Forest in the upper Blue Mountains of the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area (GBMWHA).
In the mind of Rural Fire Service (RFS) and the National Parks and Wildlife Service of New South Wales (NPWS), National Parks and World Heritage do not figure as a natural asset worth protecting from bushfire, but rather as an expendable liability, a ‘fuel’ hazard, when it comes to bushfire fighting.
.
This massive firestorm has since been branded the ‘Grose Valley Fires of 2006‘.
To learn more about the background to this bushfire read article: >’2006 Grose Valley Fires – any lessons learnt?‘
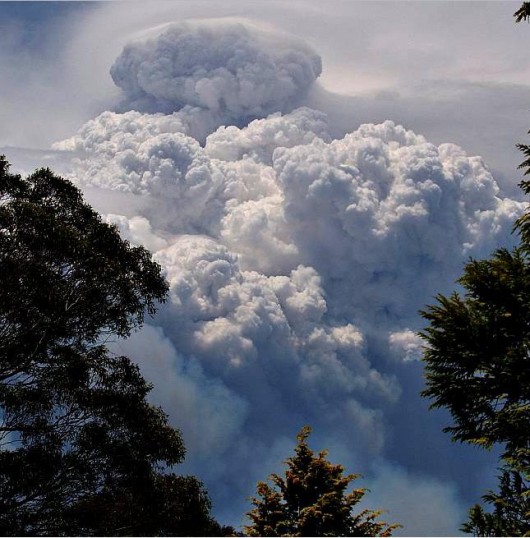 Pyrocumulous ‘carbon’ smoke cloud
above the firestorm engulfing the Grose Valley 20061123 Pyrocumulous ‘carbon’ smoke cloud
above the firestorm engulfing the Grose Valley 20061123
.
About a month after the fire, on Tuesday 19th December 2006 there was apparently an ‘Inter-Agency Review‘ which took place at Katoomba behind closed doors by members of bushfire management and operating personnel involved in the fire fighting. Despite requests by this Editor, no minutes or reports of that meeting were ever forthcoming. The meeting was internal and secret.
Immediate local community outrage called for explanations and accountability from the Rural Fire Service (RFS) (the government agency responsible for rural fire fighting throughout the State of New South Wales) in charge of fighting the bushfires and for a review of bushfire management practices with a view to ensuring that the highly valued Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area and iconic Blue Gum Forest in particular is protected from bushfire in future. Many members of the local community called for an independent and public review or enquiry.
One local resident wrote in the local Blue Mountains Gazette newspaper:
.
‘Questioning the RFS’
by Dr Jackie Janosi, Katoomba, 20061204
.
‘To start, this is directed at the upper levels of the RFS and not to the wonderful local volunteers – many of whom are loved and respected friends and colleagues.
To stop the loud community Chinese whispers and restore faith with the local community, could someone please respond with factual answers about the recent Grose Valley fire that are not reinterpreted with a political spin.
- How many hectares of bush was burnt by the Grose Valley wildfire and how many was burnt by the RFS mitigation efforts?
- How many houses and lives were at risk from the wildfire as versus to the RFS fire?
- How many millions of dollars were spent on water bombing the RFS fire?
- How many litres of precious water were used to put out the RFS fire?
- Is it true that soil-holding rainforest was burnt and that the real reason for the Mt Tomah road block was erosion from the RFS removal of this natural fire-break?
- Was local advice and expertise sought and followed or simply ignored?
- If mistakes were made, what measures will be taken to ensure that this does not happen again?
.
I sincerely hope that if mistakes were made then the upper levels of the RFS can show the humility and good future planning that is now required to restore it’s good reputation. I hope that the RFS can show that it is still a community group that cares for the safety of our Blue Mountains residents, is able to respect and respond to our very special local environment and is able to make sound decisions about valuable resources.’
.
Ed: Her questions were never answered. With the RFS rejecting calls for a public or independent review, there was a general sense amongst many in the local community of a cover up and of gross incompetence going unaccounted for.
 One of two ignitions that got out of control
– this one in ‘Lawson’s Long Alley‘, north of Mount Victoria
(Photo: Eric Berry, Rural Fire Service, 2006) One of two ignitions that got out of control
– this one in ‘Lawson’s Long Alley‘, north of Mount Victoria
(Photo: Eric Berry, Rural Fire Service, 2006)
A week later, a front page article was published in the Sydney Morning Herald 20061211 by journalist Gregg Borschmann entitled ‘The ghosts of an enchanted forest demand answers‘ ^http://www.smh.com.au/news/national/the-ghosts-of-an-enchanted-forest-demand-answers/2006/12/10/1165685553891.html [>Read article]. A second in depth article by Borschmann was also run on page 10 ‘The burning question‘, ^http://www.smh.com.au/news/national/the-burning-question/2006/12/10/1165685553945.html?page=fullpage#contentSwap1, [>Read article – scroll down].
.
Community activists form ‘Grose Fire Group’ in protest
.
Within days of the Grose Valley Fires finally coming under control, some 143 Blue Mountains concerned residents informally formed the ‘Grose Fire Group’ and collectively funded a full page letter in the local Blue Mountains Gazette 20061206 asking of the RFS a different set of questions:
.
‘We call on the New South Wales government to:
1. Undertake a thorough, independent review of the Grose Valley fire, involving all stakeholders, with particular attention to the following questions:
- Were fire detection and initial suppression timely and adequate?
- Were resources adequate, appropriate and supported?
- Were the adopted strategies the best available under the circumstances?
- Could other strategies of closer containment have offered lower risk to the community, better firefighter safety, higher probabilities of success, lower costs and less impact on the environment?
- Was existing knowledge and planning adequately utilised?
- Is fire management funded in the most effective way?
2. Ensure adequate funding is available for post-fire restoration, including the rehabilitation of environmental damage.
3. Pay for more research to improve understanding of fire in the Blue Mountains landscape and methods for fire mitigation and suppression.
4. Improve training in strategies for controlling fires in large bushland areas.
5. Improve pre-fire planning to support decision-making during incidents.
6. Improve systems to ensure that local fire planning and expertise is fully utilised during incidents, and that the protection of the natural and cultural values of World Heritage areas and other bushland are fully considered.’
.
On 20061220, my letter was published in the Blue Mountains Gazette on page 12:
.
‘Blue Gum Lessons’
.
‘One of our most precious natural heritage assets, the Blue Gum Forest, has been allowed to be scorched by bushfire. This demands an independent enquiry into current fire fighting practices to ensure such a tragedy is not repeated.
Not a witch hunt, but what is needed is a constructive revision into improving bushfire fighting methods incorporating current research into the issue. The intensity and frequency of bushfires have become more prevalent due to disturbances by man, including climate change.
An enquiry should consider the assets worth saving; not just lives, homes and property but natural assets of the World Heritage Area. Fire fighting methods should seek to protect all these values. It seems back-burning, however well-intentioned, burnt out the Blue Gum. This is unacceptable. What went wrong? The future survival of our forests depends on how we manage fire.’

Blue Gum Forest shortly after the firestorm
(Photo: Nick Moir, Sydney Morning Herald 20061210)
.
Ed: The above community questions and demands were ignored by the RFS and the New South Wales Government. Many within the ranks of the RFS came to its defence, as the following letters to the Blue Mountains Gazette reveal.
 . .
 . .

[>Read PDF version]
As letters to the editor continued over the Christmas holiday break, by January 2007, Local Member for the Blue Mountains and Minister for the Environment, Bob Debus MP finally responded by proposing that community members be given an opportunity to discuss their concerns with fire authorities and be encouraged to contribute to the development of revised fire management strategies, policies and procedures which may arise from the routine internal reviews of the 2006-07 fire season, and particularly the Grose Valley fire.
The ‘Grose Valley Fire Forum‘ was scheduled for Saturday 17th February 2007, but it was invitation only. I requested permission to attend, but by was rejected.
 The incinerated remains of the Grose Valley
– now devoid of wildlife, also incinerated The incinerated remains of the Grose Valley
– now devoid of wildlife, also incinerated
.
Grose Valley Fire Forum
.
The following is an edited account of the official ‘Report on (the) Grose Valley Fire Forum‘, which was arranged and co-ordinated by the Blue Mountains World Heritage Institute (BMWHI) and which took place at Blue Mountains Botanic Garden, Mount Tomah on Saturday 17th February 2007. The Report is dated 16 March 2007. ‘The content of this report reflects the Forum discussion and outcomes and does not necessarily reflect the views of the Blue Mountains World Heritage Institute‘ – BMWHI.
.

.
The Grose Valley Fire Forum and report were undertaken by the Blue Mountains World Heritage Institute at the request of the NSW Minister for the Environment, the Honourable Bob Debus MP.
.
Forum Participants
.
- Associate Professor Sandy Booth – Forum Chairman and Facilitator (BMWH Institute)
- Professor Ross Bradstock Centre for Environmental Risk Management of Bushfires, University of Wollongong
- Mr Ian Brown BM Conservation Society
- Mr Don Cameron BM Conservation Society
- Mr Matthew Chambers Environmental Scientist, Blue Mountains City Council (Observer)
- Dr Rosalie Chapple Forum Co-Facilitator, BMWH Institute
- Mr Bob Conroy Director Central, Parks and Wildlife Division, DEC
- Ms Carol Cooper Darug and Gundungurra Nations (Observer)
- Superintendent Mal Cronstedt Blue Mountains District, Rural Fire Service
- Mr Grahame Douglas Acting Chair, BM Regional Advisory Committee
- Group Captain John Fitzgerald Blue Mountains District, Rural Fire Service
- Mr Shane Fitzsimmons Executive Director Operations, Rural Fire Service (Observer)
- Mr Richard Kingswood Area Manager Blue Mountains, Parks and Wildlife Division, DEC
- Mr Geoff Luscombe Regional Manager Blue Mountains, Parks and Wildlife Division, DEC
- Dr Brian Marshall President, BM Conservation Society (Observer)
- Mr Hugh Paterson BM Conservation Society & NSW Nature Conservation Council
- Dr Judy Smith GBMWH Advisory Committee Member
- Inspector Jack Tolhurst Blue Mountains District, Rural Fire Service
- Mr Haydn Washington GBMWH Advisory Committee Member
- Mr Pat Westwood Bushfire Program Coordinator, Nature Conservation Council
- Members of the general public were not permitted to attend, including this Editor, who had requested permission to attend
.
List of Acronyms used in this Report
.
AFAC Australasian Fire Authorities Control
ARC Australian Research Council
BFCC Bush Fire Coordinating Committee
BM Blue Mountains
BMCC Blue Mountains City Council
BMWHI Blue Mountains World Heritage Institute
BFMC Blue Mountains District Bush Fire Management Committee
BMCS Blue Mountains Conservation Society
CERMB Centre for Environmental Risk Management of Bushfires, Faculty of Science, University of Wollongong
CRC Co-operative Research Centre
DEC NSW Department of Environment & Conservation
GBMWHA Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area
GIS Geographic Information System
NCC NSW Nature Conservation Council
NPWS NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service, Department of Environment & Conservation
RAFT Remote Area Fire-fighting Team
CRAFT Catchment Remote Area Fire-fighting Team
RFS NSW Rural Fire Service
 The Grose Valley from Govetts Leap, Blackheath
(Photo by Editor 20061209, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge) The Grose Valley from Govetts Leap, Blackheath
(Photo by Editor 20061209, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge)
.
Forum Agenda
.
10.00 Welcome to Country – Carol Cooper
Introduction by the Forum Chair -Sandy Booth:
- Purpose
- Process
- Agreements
- Outcomes
- Reporting
.
10.10 Introduction and opening statement by each participant without comment
.
10.30 Presentations (10 mins each) by:
- Mal Cronstedt (RFS) – report on agency debrief Dec 19
- Richard Kingswood (NPWS) – national parks and fire management
- Dr Brian Marshall President, Blue Mountains Conservation Society – local community perspective
- Ross Bradstock (Wollongong University) – gaps and priorities in bushfire research for the BM
.
11.10 Points of Clarification
.
11.20 Grose Valley Fire Management
- Issues not covered in RFS official Section 44 Debrief Report
.
11.40 Fire Management and the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area (WHA) (Ed: the region affected by the fire)
- Longer term and landscape scale management issues relating including climate change implications
.
12.00 Grose Valley Fire Management
.
1.00-2.00 Lunch
.
Grose Valley Fire Management and the WHA (continued)
- Identification of agreed list of actions, with nominated organisations and recommended timeframes
.
Close & Afternoon Tea (Ed: no specific time set. 5pm?)
Ed: Assuming that the forum concluded at around 5pm, the duration allocated for discussing and devising the ‘Actions’, including each Action’s Goal, Trends, Causes and Conditions, Delegation and Timeframe was just 3 hours, presuming the forum ended at 5pm.
.
Since there are and remain some 50 listed Actions out of this forum within a 3 hour allocated period (2pm to 5pm), just 3.6 minutes was allowed for discussing and devising the details of each Action. It is highly implausible that this could have been completed at the forum. So the question remains: were many of the Forum’s 50 Actions in fact devised outside the forum either by the Blue Mountains World Heritage Institute on its own or in consultation with some of the forum attendees?
.
In any case none of the Actions has been undertaken. There has been no follow up report on the performance of the Actions.
.
This Grose Valley Forum of 2007 was just a politically contrived token talk-fest behind closed doors. Its glossy motherhood report was designed to appease critics of the RFS management of this devastating fire.
.
The forum was not open to the general public, nor was it independent of bushfire management’s selective bias.
.
The only benefit was that bushfire management would appease the critics of its handling of the fire fighting by producing a report and that most would forget. Well the purpose of this article is, out of respect for the ecology and wildlife of the Grose Valley, to reveal that report and to help ensure people do not forget.

Forum Introduction
In November 2006, fire caused by lightning strikes burnt a significant area of the Grose Valley in the upper Blue Mountains of the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area (GBMWHA). Like many areas throughout the GBMWHA, the Grose Valley is an area of high natural and cultural value, including the iconic Blue Gum Forest. The two original ignitions were designated as the Burrakorain Fire and the Lawson’s Long Alley Fire, and they came jointly under the jurisdiction of an emergency declaration under Section 44 of the Rural Fires Act.
Community members called on the State Government to undertake a thorough and independent review of the management of this fire, involving all stakeholders. Principal among the issues raised by the concerned residents were backburning, impacts of frequent fires, under-utilisation of local expertise, and economic costs. The community members also called for adequate funding for rehabilitation and environmental restoration works, to conduct more research and training in certain areas of fire management, to improve pre-fire planning
and to develop management systems to better capture and utilise local knowledge.
Local Member for the Blue Mountains and Minister for the Environment, Hon. Bob Debus responded to these concerns by proposing that community members be given an opportunity to discuss their concerns with fire authorities and be encouraged to contribute to the development of revised fire management strategies, policies and procedures which may arise from the routine internal reviews of the 2006-07 fire season, and particularly the Grose Valley fire. The Minister also noted the opportunity for the community to be informed of, and
contribute to, the development of future research projects concerning climate change and fire regimes.
The Minister invited the Blue Mountains World Heritage Institute (BMWHI) to organise and chair a forum of representative community members and fire authorities. The Institute is an independent non-profit organisation that supports the conservation of the natural and cultural heritage of the GBMWHA, with a key objective to “support the integration of science, management and policy within and adjoining the GBMWHA properties.
The purpose of the forum was to:
- Brief the community on the management of the Grose Valley fire and the framework and context for the management of fire generally within the World Heritage Area
- Identify any issues that relate specifically to the management of the Grose Valley fire, and that haven’t already been captured and/or responded to within the s.44 debrief report
- Identify longer term and landscape scale issues relating to the management of fire in the Greater Blue Mountains WHA, particularly in this time of climate change
- Develop an action plan, which responds to any unresolved issues identified above.
.
In accordance with the Minister’s brief (Ed: Bob Debus), the following organisations were represented at the forum:
- NSW Dept of Environment and Conservation;
- NSW Rural Fire Service
- Blue Mountains Conservation Society
- Nature Conservation Council of NSW
- Blue Mountains City Council
- NPWS Regional Advisory Committee
- GBMWHA Advisory Committee.
In addition to senior representatives of the agencies involved, representatives also came from the principal community-based organisations that had expressed concern and called for a review process. It should be noted that one of the main public calls for a review was made by an informal coalition of residents that was not formally represented at the forum, but a number of these residents were members of those organisations represented.
.
(Ed: the general public were not permitted to attend, there was no public notice of the forum in advance, and this Editor was specifically excluded from attending.)
.
Forum Process
An open invitation was given to the community organisations to identify the issues of community interest and concern to be discussed at the Forum.
From these issues, a consolidated list of 22 issues (Table 1.2) was prepared by the Institute, and then circulated to all participants prior to the forum. To facilitate the workshop discussions and the detailed consideration of the identified issues, the ‘5R Risk Management Framework‘ was used to group the issues.
Following a Gundungurra and Darug ‘Welcome to Country’ by Carol Cooper, and an introduction by the Forum Chair, self-introductions and personal opening statements were made by each participant without comment. These were followed by a series of briefins on management of the Grose Valley Fire and fire management generally within the World Heritage Area. The Forum began by acknowledging that fire management in the Blue Mountains is close to best practice in many ways.
It was unfortunate that copies of the Section 44 debrief report were not available for the forum as anticipated (Ed: a copy is provided in the ‘Further Reading‘ appendix below).
While this was partly overcome through verbal presentation and comment, it limited the ability to reach consensus on the factual basis of what happened on the fire ground and to move forward productively from this point of consensus. Community representatives expressed their dissatisfaction with this situation, and it must be noted that the forum was therefore not able to engage effectively on specific issues of the control strategies used on the Grose Valley Fires.
After a brief session on points of clarification, the issues presented to the forum were explored in detail by working through a problem orientation process that asked a series of questions about each issue, to reach consensus on the exact nature of the problem. As this work progressed, a series of agreed actions were identified to effectively address key aspects of the issues as these unfolded. It is noted that the issues addressed toward the end of the day were examined in less detail due to time constraints, but warrant further attention (e.g. the issue about remote area fire-fighting teams). The original list of 22 issues was consolidated into 11 goal statements, with 50 associated actions.
The main body of this report presents the goals and actions along with documentation of the discussion that took place on the day. It utilises the structured approach to systematically work through the issues, and identify the actions required to bring about more sustainable bushfire management for the Blue Mountains. Within a week of the Forum, the Institute circulated a copy of the forum proceedings to all participants for comment and clarification. The Institute also sought identification of responsibilities for the 50 Actions identified by the Fire Forum.
It is strongly recommended that implementation of the Action Plan be reviewed annually by the representative organisations, to assess progress and effectiveness of actions. It is proposed that the BMWH Institute co-ordinate this review process in partnership with the Nature Conservation Council, with a workshop held after the 2007/08 fire season, to re-address the issues and their progress. (Ed: This was never done)
.
Forum Overview
.
A big challenge in bushfire management is how to better integrate valid community interests with those of fire management agencies. Over recent years, the public has come to demand and expect a greater say in decision-making processes that impact upon their local environment. The Grose Valley Fire Forum represents a step forward in this process of better integrating community knowledge and interests into local natural resource management.
The Forum also illustrated that the Blue Mountains community is both a great supporter of fire authorities, and of the role of volunteer firefighters for the outstanding effort that they are prepared to undertake on behalf of the community.
.
The concerns and questions addressed at the forum included:
- Identifying weaknesses and gaps in fire management plans and processes
- How well are plans being implemented and what are the barriers to implementation e.g. financial, institutional, political?
- How should fire authorities and land managers respond to climate change impacts?
.
- Integrating scientific knowledge into fire management plans
- How can bushfire management policy allow for the incomplete knowledge of complex ecological systems?
- What roles should science and other research play in decision processes, given the uncertainty arising from incomplete understanding of ecosystem dynamics and insufficient scientific information?
.
- The role of fire as an ecological process
- How do we resolve the conflict between rapid fire suppression to reduce risk versus the fire-dependency of the ecosystem?
- What does it take to more effectively mitigate against the risk?
.
- Concern that fire control strategies do not compromise the significant natural and cultural heritage values of the Greater Blue Mountains region.
- How can bushfire management policy better account for protection of World Heritage values?
- How adaptive is bushfire management and policy to the specific circumstances of the Blue Mountains?
.
The Forum recommended actions in relation to:
- Better interpretation of ecological data into decision-making and practical fire-fighting procedures
- Improvements in bushfire risk management planning
- Better translation of legislated objectives for protection of natural and cultural values into operational guidelines
- Improved information flow between fire authorities and the community during and after major fires, including more transparency and public involvement in the review processes
- Increasing funding for fire-related research, planning, risk mitigation, and post-fire ecological rehabilitation
- Enhancing the preparedness, detection and rapid fire response capacity of fire authorities in response to fire ignitions
- Modelling the effects of different control strategies and suppression.
.
The Forum acknowledged the increasing and serious challenges arising from risks associated with liabilities and litigation. These trends are of principal concern to fire management agencies and the fire fighters themselves, and many in the general community share these concerns.
Bushfire management is a cultural phenomenon, inextricably bound up between nature and culture. It involves the interaction of multiple, complex systems, including:
- organisational/institutional behaviour and decision-making
- fire fighting strategies and technologies
- science, research and ecosystem behaviour
- variable fire behaviour and weather, including climate change
- politics; and
- personal values and attitudes.
.
The complexity is increasing, especially with climate change, along with pressure for bushfire management to be more adaptive and responsive to the needs of the present and the future.
Facilitating the necessary changes in the behaviour of any of these systems is highly challenging for both government and the community. These systems often have severe constraints including limited resources, threats of litigation, and limited data on which sound decisions can be confidently made. Where these systems are not continuing to learn and adapt, is where attention is needed, not on individual accountabilities. Sound decision-making at the time of a fire event is crucial and the process by which these decisions are made requires careful
analysis. The system should be able to support open reflection after a fire, without blame or litigation. This is where a process of scientific analysis should come into its own: what the fire did, what was done to control it, what worked, what didn’t, why or why not, and what can be done to make things better. How can the system be changed and improved to make success more likely?
Research and adaptive management are essential in helping to address both current challenges and the issues arising from climate change. But alone, these will not bring about the required changes as neither of these domains explicitly addresses the overall policy process or the political realm in which bushfire management happens. Conflict and uncertainty are becoming increasingly common, as evidenced by the Four Corners Program “Firestorm” broadcast on Monday 12th March. The program featured the 2004 Canberra Bushfires and also
raised the Grose Valley fire and resulting Fire Forum.
To overcome the key problems identified by the Grose Valley Fire Forum and achieve real and lasting triple bottom line outcomes, change and innovation need to take place in the realm of governance. This is particularly the case in the areas of science, policy and decision-making.
The Grose Valley Fire Forum has brought fire management agencies and interested representatives of the community together in a spirit of co-operation to consider issues critical to the management of bushfires. Driven by the high conservation values of the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area, the implications of the issues raised at this Forum have obvious relevance to other regions and states. Protecting people as well as the environment should not be mutually exclusive. Our efforts to address this challenge in the Blue Mountains will increasingly come in for close scrutiny.
Notwithstanding the existing mechanisms of review and community consultation surrounding bushfire management, the Institute recommends to the Minister that the issues and actions identified herein by the Grose Valley Fire Forum warrant special consideration and support.
Properly pursued with senior political and agency commitment and support, they offer key insights and potential pathways for the continued adaptive development and implementation of state of the art fire fighting for which NSW, and in particular, the Blue Mountains are justifiably renowned.
.
Issues of Community Interest and Concern
.
A. Research, information and analysis
.
1. Commitment in fire management to conservation of natural and cultural values of World Heritage Area as well as human life and property.
2. Understanding and consideration (including on-ground knowledge) both by those involved in pre-fire planning and those required to make operational decisions during fire events -of the WH values for which the GBMWHA was inscribed on the world heritage list, and of other values, such as geodiversity, cultural values and beauty, which have the potential to be nominated for World Heritage listing in the future.
3. Biodiversity impacts of frequent fires in Grose Valley for last 40 years, including impacts of the recent fire on World Heritage values.
4. The ecological basis for fire policy (knowledge base for response of local biota to fire regimes) e.g. biodiversity loss associated both with high fire frequency and intensity, and with fire exclusion.
5. Translation of NPWS Blue Mountains Fire Management Plan (e.g. risks to natural heritage particularly World Heritage values) to S.52 operational plans during Grose Valley fire.
6. Effectiveness of review processes in generating real improvements for the future; current debriefing process performed by BFMCs [i.e. BFCC Policy 2/2006].
7. Assessment of community values – protection of property versus protection of the natural environment.
8. Implications of climate change for increased fire frequency and intensity.
9. Adequate funds for fire suppression versus inadequate funds for research, planning and fire mitigation.
.
B. Risk modification
.
10. Effectiveness of current risk strategies in managing fire regimes for biodiversity and community/asset protection (e.g. upper Grose Valley).
11. Implications of climate change for risk modification (e.g. fuel reduction).
.
C. Readiness
.
12. Skills in implementing fire control strategies for large bushland areas e.g. back-burning.
13. Ecological sustainability of current responses to fire (both suppression & bushfire risk management) e.g. knowledge and skill of plant operators in sensitive environments (environmental damage from machine work e.g. bulldozer lines).
14. Community understanding of control strategies used.
15. RAFT capacity (e.g. for night-time work).
16. Efficiency of fire detection technologies.
.
D. Response
.
17. Back-burn control strategy from “Northern Strategic Line” and Bell’s Line of Road in large bushland area: overriding consideration for asset protection versus lack of consideration and recognition of impacts on ecological values.
18. Application of planning, guidelines, procedures & local information & expertise during fire suppression.
19. Rapid containment of lightning strike or arson fires.
20. Aerial attack efficiency and effectiveness.
21. Media – inaccurate and misleading use of language and presentation of information.
.
E. Recovery
.
22. Funding for post-fire assessment, strategy review and ecological restoration including addressing activation of weed seed banks.
.
Problem Orientation Process
(Problem Solving Methodology applied by the BMWHI to the Forum)
.
1. Clarify goals in relation to the issue
- What goals or ends do we want?
- Are people’s values clear? (there may be an over-riding goal and then more specific goals to operationalise the over-riding goal)
.
2. Describe trends
- Looking back at the history of the issue, what are the key trends?
- Have events moved toward or away from the specified goals? Describe both past and current trends.
.
3. Analyse causes and conditions
- What factors, relationships, and conditions created these trends, including the complex interplay of factors that affected prior decisions? (e.g. environmental, social, political factors) i.e. what explanations are there for the trends?
- What management activities have affected the trends?
- What are the conflicts about different approaches to address the issue?
.
4. Projection of developments (e.g. if no action is taken to address the issue)
- Based on trends and conditions, what is likely to happen in the future (e.g. if nothing is done differently).
- If past trends continue, what can we expect?
- Is the likely future the one that will achieve the goals?
- What future possible developments are there (e.g. politically, environmentally e.g. how will climate change affect the problem)?
5. Decide on any Actions to address the problem
- If trends are not moving toward the goal, then a problem exists and actions need to be considered.
- What other policies, institutional structures, and procedures might move toward the goal?
- What research, analysis, or public education may be needed?
* Adapted from Clark, T.W. 2002. “The Policy Process: a practical guide for natural resource professionals.” Yale University Press. U.S.
 Vast hectares of the Blue Mountains’ native vegetation was either left to burn uncontrolled
or else deliberately burned by the RFS and NPWS Vast hectares of the Blue Mountains’ native vegetation was either left to burn uncontrolled
or else deliberately burned by the RFS and NPWS
.
Action Plan
~ a consolidated list of goals and actions [organisations delegated for executing ‘Actions’ are shown in brackets […]
.
1. Protection of Natural and Cultural Values
.
GOAL:
.
To protect natural and cultural heritage values, consistent with the protection of human life and property, by ensuring that bushfire management strategies:
• take a risk management approach toward protection of these values
• improve access to and interpretation of natural and cultural heritage values when deciding on fire suppression strategies and tactics
• ensure that these natural and cultural heritage guidelines for fire management are integrated throughout the entire planning framework for short, medium and long-term bushfire management and operational strategies.
.
ACTIONS:
.
1. Data collected within the “Managing ecosystem change in the GBMWHA” project, including the new GIS, to be effectively interpreted into decision-making and practical fire-fighting terms. [Responsibility for action: BMWHI & CERMB – ARC Linkage project, NPWS, BMCC, BMCS]
2. Monitor impacts of fires on Aboriginal cultural heritage values, and undertake opportunistic mapping of these values post-fire. Translate findings into decision-making and practical fire fighting terms. As a priority, undertake an opportunistic survey of Aboriginal cultural heritage post-Grose fire. [Aboriginal communities, BMWHI, NPWS]
3. Greater effort in general to be made in translating and interpreting research and other relevant information on the protection of ecological and cultural values to better inform decision-making and into practical fire-fighting terms wherever required. [CERMB, BMWHI, NPWS, BMCC, BMCS]
4. Consider further developments in environmental risk management planning by the BFCC for inclusion in the Bush Fire Risk Management Plan model template. [BFMC]
5. Effectively integrate the strategic hazard reduction plan being developed by BMCC, into the risk management plan and the operations plans. [BMCC, BFMC]
6. Translate the NPWS Fire Management Strategies objectives for protection of natural and cultural values into operational guidelines across the entire planning framework at all levels, using a risk management approach. [NPWS, BFMC]
7. Continue to identify the best mix of treatments i.e. prevention, mitigation, suppression and recovery, to achieve both fire management and land management objectives. [NPWS, RFS, BFMC]
8. Review risk management and operational plans to include relevant reserve fire management plan information, including aspects of mitigation and appropriate fire management guidelines from the RFS Environmental Code [BFMC].
9. Develop a single map-based approach for interagency use that depicts all relevant information in a user-friendly way and enables optimal use and consideration of this information under operational conditions. [NPWS, RFS, BMCC, BFCC, BFMC, BMCS]
10. Provide the outcomes of this forum to the BFCC for consideration in developing and reviewing policies and procedures such as for the Bush Fire Risk Management Policy and Bush Fire Risk Management Plan Model template. [NPWS, RFS]
11. Develop a quantitative framework for risk management: undertake research to evaluate the effectiveness of current strategies to inform the resources and strategies required to achieve integrated life, property, cultural and natural value protection outcomes. The research should identify what is the return on current ‘investment’ and the results then linked back to budgeting systems [BMWHI].
12. Undertake and improve community liaison and surveys to better capture community values within fire management plans [BFMC].
.
2. The Role of Fire as an ‘Ecological Process’
.
GOAL:
(2?) To better understand the role of fire as an ecological process, including the long-term ecological effects of fire regimes on fauna and flora, as a basis for identifying fire regimes that sustain the ecology both locally and across the landscape.
.
ACTIONS:
13. Undertake a research project using the Grose Valley fire as a case study, to ascertain and explore the opportunities to improve fire management for protection of ecological impacts [NPWS, BMCC, CERMB, BMWHI].
14. Development of a threat abatement plan for the ecological consequences of high frequency fires. [DEC]
15. Use the Blue Mountains as a case study for modelling different control strategies and suppression (e.g. analysis of suppression operations) utilising historical raw data for retrospective mapping. [RBradstock/CERMB]
16. Source external funds for priority research and investigation projects [NPWS, RFS, BMCC].
17. Undertake ecological research into the impacts of fire regimes including intervals between fires, ensuring an appropriate focus on large-scale transformation [NPWS, BMCC, CERMB, BMWHI].
18. Undertake the necessary ground-truthing investigations to ascertain whether ecological predictions are being played out. That is, are observed trends in ecosystems matching the predictions from the models? Other research and investigation priorities include:
a. Threatened species and communities, including mapping of successional processes (e.g. woodland to heathland shifts and changes to hanging swamp boundaries) and wet sclerophyll forest (e.g. Blue Gum Forest, E. oreades) and warm temperate rainforest regeneration;
b. Species composition and structure comparison of those areas burnt in 2002;
c. Species composition and structure comparison of those fires burnt with high frequency;
d. Document / map / audit weed plumes that have occurred after past fires, and similarly for the weed plumes that will already be occurring after the 2006 Grose Valley fire;
e. Build upon current research results to further elucidate how the Grose Valley responded to the ‘94 fire. [CERMB, NPWS, BMCC & BMWHI via ARC Linkage Grant]
19. Initiate appropriate involvement of the broader community in research and particularly Aboriginal people for Aboriginal cultural heritage research, in all relevant research projects. [BMWHI, NPWS, BMCC]
20. Develop mechanisms to effectively and promptly communicate research outcomes to agencies, fire-fighters and communities, and for application of these to risk management planning and human resource planning and assessment during fires. [BFMC]
.
3. Review Processes and Public Communication
.
GOAL:
.
To ensure effectiveness of fire review and debriefing processes and their communication to the public by:
- Communicating to the community the results of interagency review processesincluding an analysis of fire strategies and environmental impacts within major debriefs and review
- Enabling greater community participation in major fire debriefs and fire reviews.
.
ACTIONS:
.
21 Urgent distribution of the section 44 debrief report to all participants in the forum. [RFS]
22 Greater provision for earlier feedback to and from the community after a major fire, regarding fire control strategies, prior to release of formal report. Also address what the barriers are to increasing community knowledge and what approaches are most effective. [RFS, BFMC]
23 Request the Coordinating Committee to revisit the s44 debrief policy and procedures and/or other appropriate mechanisms to develop an appropriate means for getting feedback from the community via a system that enables issues to be raised and feedback to be provided. The development of a policy and procedural framework for Incident Controllers may assist here. [NCC/NPWS, BMCS]
24 Undertake promotion and community education programs to familiarise the community with the framework that exists for debriefing processes and the arising information flows and decision-making processes. Incorporate this into existing Firewise program. [BFMC, RFS]
25 Encourage a culture of openness, learning and evidence-based decision-making, including understanding by volunteer fire fighters that criticism is of the process not of the implementer. [All organisations represented at forum]
26. Continue to undertake interpretation / education / media and fire-related Discovery activities. [NPWS]
.
4. Climate Change and Risk Mitigation
.
GOAL:
To prepare for the more extreme conditions associated with climate change, by addressing the policy and management implications for control strategies and landscape management.
.
ACTIONS:
27. Research priorities include:
- Investigate efficacy of current risk mitigation in the Blue Mountains. [NPWS, CERMB]
- Climate change impacts on hanging swamps.
- Build understanding of underlying shifts in environmental conditions and their effects on fire occurrence and fire behaviour.
- Implications of climate change for fire behaviour and invasive species. [CERMB, BMWHI & ARC Linkage project]
- Investigate plant dispersal in relation to climate change, quantifying ecological processes and habitat requirements critical to species persistence and their ability to move to new habitats given climate change. [CERMB, BMWHI & ARC Linkage project]
28. The results of this Forum should be used to advocate and lead improved dialogue and action to address the key issues pertaining to climate change and start to influence policy change. [NCC, BMWHI, CERMB, BMCS, NPWS, RFS, BMCC]
29. Investigate opportunities for increased resourcing for risk mitigation and for bushfire behaviour research. [NPWS, RFS, CERMB, BMWHI]
30. Enhance the preparedness, detection and rapid fire response capacity of fire authorities in response to fire ignitions. [Fire authorities]
31. Deliver a presentation about this forum, at the May 2007 conference of the Nature Conservation Council of NSW on bushfire and climate change. [DEC, BMWHI, NCC; 31 May-1 June 2007]
.
5. Resourcing and Investment
.
GOAL:
Increase the availability of resources for fire-related research, planning and fire mitigation.
.
ACTIONS:
32. Formally approach the Environmental Trust to consider the allocation of Environmental Trust funds for use in fire related research including investigation of fire impacts. [NPWS]
33. Raise the needs and investigate the opportunities for increased commitment to rehabilitation following fire with the Catchment Management Authorities. [BFMC]
34. Allocation of additional resources for the BFMC to implement the recommendations in this document, particularly for actions resulting in strengthening risk management objectives. [BFMC members]
.
6. Risk Management Strategies for Multiple Outcomes
.
GOAL:
.
To develop effective fire risk management strategies for mitigation and suppression in large bushland areas through:
- Evidence-based plans and strategies;
- Ensuring that fire fighters in wilderness and other remote areas have adequate support and training for safe and effective implementation of fire control strategies.
.
ACTIONS:
.
35. Address the issue of risk management planning, including investigating use of corridors for hazard reductions as part of an integrated approach that allows for ecological considerations. [Land managers/NPWS]
36. Seek more funding for community involvement in Local Government Area fire management (i.e. liaison officer position for community engagement prior to release of plan), which will assist administration/enforcement of regulatory processes. [BMCC]
37. Workshops held to provide further information regarding fire suppression in remote/wilderness areas, and BFMC to list potential contractors that could be eligible for such ecologically sound, operational training in fire control strategies for remote/wilderness areas including back-burning and bulldozer lines. [BFMC, NPWS]
.
7. RAFT Capacity
.
GOAL:
.
To improve RAFT (Remote Area Firefigfting Team) capacity to deal effectively with most remote ignitions.
.
ACTIONS:
.
38. Facilitate and support more RFS people to participate in RAFT [RFS]
39. Review and combine NPWS and RFS RAFT policy and procedures, including consideration for nighttime RAFT deployment [NPWS, RFS].
40. Address pre-deployment capacity in context of return on investment i.e. economically model across landscape to see how it meets needs and model against suppression costs [NPWS, RFS].
.
8. Fire Detection Technologies
.
GOAL:
.
To explore the potential of emerging technologies for higher efficiency in fire detection.
.
ACTIONS:
.
41. Consider the new technologies where appropriate and consider the benefits of Blue Mountains piloting new technologies for broad-scale remote surveillance, and evaluate cost effectiveness. [BF Coordinating Committee and NPWS]
.
9. Aerial Attack
.
GOAL:
.
Continue to optimise effectiveness of aerial attack strategies and operations.
.
ACTIONS:
.
42. Practically strengthen record keeping during operations to assist analysis by identifying a system that is capable of catching data in real-time. [DBFMA, BFCC]
43. Identify and use some simple decision rules for aircraft deployment to maximise aircraft cost-effectiveness. [BFMC]
.
10. Role of the Media
.
GOAL:
.
To have better processes in place to ensure accurate presentation of fire incident information through the media.
.
ACTIONS:
.
44. Work with the tourism industry to develop their risk management strategy. [BFMC]
45. Before/during a fire, convey explanations of what control strategies and why, to inform community. [BFMC]
46. Undertake pre-season briefs to journalists; discourage use of sensitised language (e.g. National Parks destroyed, trashed, destruction and horror, fire hell etc). [District Committee, RFS, NPWS, BFMC]
47. Engage local media in communicating exactly which areas are out of bounds, so they people don’t stop coming to remaining open areas. [BFMC]
.
11. Post Fire Recovery
.
GOAL:
.
To adequately fund ecological restoration after a large wildfire.
.
ACTIONS:
.
48. Approach the Environmental Trust regarding the establishment of a delineated fund (possibly from Trust Funds) to support ecological restoration which could be needed for several years post-fire and ensure initiative is appropriately linked to Section 44 state level response and also the SCA for post fire ecological funding to protect catchment values. [NPWS]
49. Ensure a strategic approach to site rehabilitation e.g. by placing an emphasis on rehabilitation of weedy sites that are a threat to natural values downstream. [Land managers]
50. NPWS to consider establishing a new dedicated staff position to coordinate and manage volunteers undertaking rehabilitation projects and activities within the Blue Mountains region of DEC. [NPWS]
.
This Forum was a Farce
.
None of these 50 Actions has been acted upon nor implemented since 2007; now five years ago.
.
The entire forum process was a farce from the outset. It only served to allow those responsible to escape accountability and responsibility for incompetence and mass bush arson without reputational blemish.
.
RFS Incident Controller, Mal Cronstedt, relocated himself back to West Australia (Fire & Emergency Services Authority), where he was from. NPWS Blue Mountains Manager, Richard Kindswood, went on extended leave. RFS Commissioner, Phil Koperberg, was seconded by the NSW Labor Party to become Minister for Blue Mountains (i.e. promoted). Bob Debus was seconded by the Federal Labor Party to become Federal Member for Macquarie (i.e. promoted). Blue Mountains Councillor Chris van der Kley stayed on as Chair of the Blue Mountains Bushfire Management Committee.
.
Blue Mountains Bushfire Fighting practice, strategy, management, culture remains ‘RFS Business-as-usual’ status and similarly ill-equipped for the next bushfire catastrophe.
.
No lessons were learnt. More tragically, no lessons want to be learnt.
.
RFS: …’we know what we are doing and how dare anyone criticise us and our hard working bushfire fighting volunteers!
 How it all started.
..as a small ignition ten days prior. How it all started.
..as a small ignition ten days prior.
.
Further Reading
.
[1] ‘2006 Grose Valley Fire – a cover up‘, article by The Habitat Advocate, 20101217, >https://www.habitatadvocate.com.au/?p=3220
.
[2] ‘2006 Grose Valley Fires – any lessons learnt?‘, article by The Habitat Advocate, 20120118, >https://www.habitatadvocate.com.au/?p=12859
.
[3] ‘Grose Valley Fire Forum Report – FINAL (BMWHI 20070402).pdf‘, >[Read Report] (4.2 mb)
.
[4] Rural Fire Service’s official report of Grose Valley Bushfires, report by Incident Controller Mal Cronstedt, Rural Fire Service, 20070208, >’Lawsons Long Alley Section 44 Report‘
.
[5] ‘Blue Mountains Council Business Paper 20070424 Item 7 Cost of Grose Fire’, Blue Mountains Council, >Blue-Mountains-Council-Business-Paper-20070424-Item-7-Cost-of-Grose-Fire.pdf
.
[6] ‘Blue Mountains World Heritage’, by Alex Colley (text) and Henry Gold (photography), published by The Colong Foundation for Wilderness, 2004, Foreward: “This book celebrates one of the greatest achievements of the Australian conservation movement – the creation of the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area” ~ Bob Carr, Premier of New South Wales, March 2004. ^http://www.colongwilderness.org.au/BMWH_book/BMWH_book.htm, ^http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/917
.
[7] ‘Back from the Brink: Blue Gum Forest and the Grose Wilderness’, book by Andy Macqueen, 1997, ^http://infobluemountains.net.au/review/book/bftb.htm
.
‘The Cradle of Conservation’
‘Everyone has been to the lookouts. Many have been to the Blue Gum Forest, deep in the valley – but few know the remote and hiden recesses of the labyrinth beyond. Here, an hour or two from Sydney, is a very wild place.
The Grose has escaped development. There have been schemes for roads, railways, dams, mines and forestry (Ed: ‘logging’), but the bulldozers have been kept out. Instead, the valley became the ‘Cradle of Conservation’ in New South Wales when it was reserved from sale in 1875 – an event magnificently reinforced in 1931 when a group of bushwalkers were moved to save Blue Gum Forest from the axe.
This is story of the whole Grose Wilderness, and of the Blue Gum Forest in particular. It is the story of people who have visited the wilderness: Aborigines, explorers, engineers, miners, track-builders, bushwalkers, conyoners, climbers…those who have loved it, and those who have threatened it.’
.
[8] ‘Battle for the Bush: The Blue Mountains, the Australian Alps and the origins of the wilderness movement‘, book by Geoff Mosley, 1999, published by Envirobook in conjunction with The Colong Foundation for Wilderness Limited. ^http://themountainjournal.wordpress.com/interviews-profiles/geoff-mosley/
.
Tags: 5R Risk Management Framework, Aerial Attack, Blue Gum Forest, Blue Mountains, Blue Mountains City Council, Blue Mountains District Bush Fire Management Committee, Blue Mountains National Park, Blue Mountains World Heritage Institute, Bob Debus, Bush Fire Coordinating Committee, Climate Change and Risk Mitigation, Fire Detection Technologies, Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area, Grose Fire Group, Grose Valley, Grose Valley Fire, Grose Valley Fire Forum, Grose Valley Fires 2006, Inter-Agency Review, Lawson's Long Alley, Mal Cronstedt, Mt Tomah Forum, Phil Koperberg, Post Fire Recovery, Protection of Natural and Cultural Values, RAFT Capacity, Resourcing and Investment, Review Processes and Public Communication, RFS, RFS Section 44 Report, Risk Management Strategies for Multiple Outcomes, Role of the Media, Rural Fire Service, The Role of Fire as an 'Ecological Process'
Posted in Blue Mountains (AU), Threats from Bushfire | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Tuesday, March 13th, 2012
This article by the Editor was first published as a letter entitled ‘Premises at Risk’ in the Blue Mountains Gazette 20051116.
 Flogging the bush for housing, undefendable in the event of a bushfire
Stuarts Road, Katoomba – a house has since been approved by Council and subsequently built on this site, killing the wildlife habitat in the process. Flogging the bush for housing, undefendable in the event of a bushfire
Stuarts Road, Katoomba – a house has since been approved by Council and subsequently built on this site, killing the wildlife habitat in the process.
(Photo by Editor 20070922, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge)
.
Part and parcel of choosing to live in the Blue Mountains is that, by being on ridgelines surrounded by Eucalypt forests, many properties are inherently exposed to bushfire threat. Whether bushfires be caused by lightning (rarely), accidentally by people, RFS-prescribed, or by arson (usually); bushfire risk management is a community responsibility – not just the lot of Rural Fire Service volunteers.
The arson threat aside,
“residents, land owners and land managers of the Blue Mountains need to accept that they are in a bushfire prone area and their properties may be subject to ember attack when threatened by bushfire.”
[Blue Mountains Conservation Society Bushfire Policy].
.
To dispel a rural myth, not all native habitats recover from bushfire. Certain species exist only in ecosystems that are never burnt. Post-bushfire regrowth often sporns dominant species like Eucalypt and Acacia, whereas original biodiversity may take centuries to recover. Bushfire is often a precursor to infestations of grass and weeds, and if followed by intense
rain, also a catalyst for eroding irreplaceable native soils.
The antique premise ‘hazard reduction’ has become spin for pre-emptive burning that is prone to escaping out of control and so itself a hazard.
Slashing and bulldozing under the premise of ‘Asset Protection Zone’ is also proving ineffective against ember attack and wildfire. But like arson, the Hazard Reduction and APZ theories contribute to the net loss of important habitat.
Proven effective and sustainable is early detection & response to spot fires.
Most artificial fires start on developed land, so this is where control measures should be focused – maintenance of gardens and guttering, retrofitting houses with materials and defences to resist fire, planting fire-retardant hedging around houses and implementing countermeasures recommended by Australian Standard 3959.
The future of sustainable bushfire risk management starts by preventing houses being built where they cannot be safely protected from bushfires.
Effective ‘hazard reduction’ is investigating and catching the arsonists.
Wednesday, January 18th, 2012
On Sunday 13th November 2006 two separate bushfire ignitions were believed to have been started by lightning just west of the Grose Valley of the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area, according to the Rural Fire Service (RFS). One ignition was located outside the small rural village of Hartley Vale in a valley referred to as Lawsons Long Alley, while the other was in rugged bushland at Burra Korain Head about 4 km east of the village of Mount Victoria. Ten days later catastrophe…
 Pyrocumulus cloud as the Grose Valley goes up in smoke on 23rd November 2006 Pyrocumulus cloud as the Grose Valley goes up in smoke on 23rd November 2006
.
‘Two bushfires that were believed to have been started by lightning strikes on Monday are burning in the Blue Mountains National Park. A fire burning 2 km north of Mount Victoria has burnt out about 1100 hectares of private property and parkland and is burning on both sides of the Darling Causeway. The Darling Causeway remains closed to traffic and motorists are advised to use the Great Western Highway and Bells Line of Road as alternate routes.
A second fire burning about 5 km north of Blackheath in the Grose Valley has burnt out about 500 hectares of parkland. Waterbombing aircraft are slowing the progress of the fire as it is burning in difficult and inaccessible terrain.’
[Source: New South Wales Rural Fire Service Blue Mountains website, Fire Name: Lawsons Long Alley, Time Message Issued: 1700, Date Message Issued: 16/11/06, ^http://lists.rfs.org.au/mailman/listinfo/bluemountains-info]
.
At the time the RFS reported that the ‘fire is not threatening any properties or homes at this stage‘, but it was this reassurance that lulled the fire fighting effort into a false sense of security. Over the coming days the fires were not earnestly suppressed but instead allowed to burn out of control as neither were ‘threatening any properties or homes at this stage‘. Famous last words. Worse was that a series of broadscale backburns were started by the RFS at Hartley Vale, Blackheath and along Bells Line of Road – each of which at times got out of control.
.
Comparison with 2003 Canberra Firestorm
.
Three years prior, four ignitions that had been purportedly been sparked by lighting on 8th January 2003 were allowed to burn out of control in remote bushland outside Canberra, Australian Capital Territory (ACT), and starting outside the ACT in NSW. At the time, those fires were deemed not to be threatening any properties or homes at that stage too. Ten days later, the four fires – McIntyre’s Hut Fire, the Bendora Fire, the Stockyard Spur Fire and the Mount Gingera Fire all coalesced into what became known as the 2003 Canberra Firestorm in which four people perished.
 McIntyre’s Hut Fire 20030108 – distant, isolated and remote at this stage.
Ten days later it became the 2003 Canberra Firestorm McIntyre’s Hut Fire 20030108 – distant, isolated and remote at this stage.
Ten days later it became the 2003 Canberra Firestorm
.
Three years hence, the two bushfires west of the Grose Valley after seven days had coalesced into what has become known as the 2006 Grose Valley Fires that ended up incinerating 14,070 hectares of wild bush habitat, including the iconic Blue Gum Forest down in the Grose Valley inside the Greater Blue Mountains World heritage Area .
Both catastrophic bushfires were ultimately the responsibility of the RFS in New South Wales to suppress in order to prevent them becoming uncontrollable firestorms. The RFS failed catastrophically on both occasions with RFS Commissioner Phil Koperberg at the helm. The lessons from the 2003 Canberra Firestorm had not been heeded.
 An aerial view of a fire-devastated Chauvel Circle in the suburb of Chapman on 21st January, 2003 in Canberra,
where 15 of 20 homes in the street were destroyed by fire.
Four people were killed and 419 homes destroyed when the fires being fought on five fronts swept through the nation’s capital.
(Photo by Daniel Berehulak, Getty Images) An aerial view of a fire-devastated Chauvel Circle in the suburb of Chapman on 21st January, 2003 in Canberra,
where 15 of 20 homes in the street were destroyed by fire.
Four people were killed and 419 homes destroyed when the fires being fought on five fronts swept through the nation’s capital.
(Photo by Daniel Berehulak, Getty Images)
.
According to the report of the official enquiry into the 2003 Canberra Firestorm by ACT Coroner Maria Doogan, she states:
‘During the inquiry it was submitted that the severity of the firestorm could not have been foreseen. I do not accept this. Australia has a recorded history of extreme fire events dating back to at least 1851. As discussed in Chapter 7 (of the Coroner’s Report), CSIRO fire expert Phil Cheney predicted several years ago a conflagration of the type experienced in January 2003. He made his prediction on the basis of information in the report of one of the seven inquiries that have been held since 1986 to examine various aspects of the ACT’s emergency services.
‘The point to make here is that experiences in life, be they good or bad, serve no useful purpose if we fail to learn from them. It is hoped, therefore, that the many lessons that can be learnt from this catastrophe in the ACT are in fact learnt and result in positive action, not just supportive words and shallow promises.’
[Source: ‘The Canberra Firestorm: Inquest and Inquiry into Four Deaths and Four Fires between 8 and 18 January 2003’, Vol 1, Ch1, pp.2-3., by ACT Coroner]
.
Blue Mountains Council’s response to the 2006 Grose Valley Fires
.
The 2006 Grose Valley Fires coalesced into a conflagration on Thursday 23rd November 2006 down in the World Heritage Grose Valley. Many in the local Blue Mountains community were outraged that this could have been allowed to have occurred. Public demands for answers finally led Blue Mountains Council two months later on Tuesday 30th January 2007 to agree to support the call of ‘concerned residents’ for the New South Wales Government to undertake a thorough, independent review of the Grose Valley Fires.
It is important to note that at the time there was a Labor Government in New South Wales, which was ultimately held responsible for both the 2003 and 2006 bushfire emergency responses.
The following is a copy of the official meeting minutes of Blue Mountains Council’s Ordinary Meeting of 20070130, two months after the 2003 Grose Valley Fires:
.
‘A Motion was moved by Councillors (Terri) Hamilton (Independent) and (Daniel) Myles (Liberal):
.
1. That the Council gratefully acknowledges the efforts of all the volunteers, professionals and agencies that worked together to control the recent Grose Valley Fire.
.
2. That the Council, in order that improvements in fire management can continue for the Blue Mountains and other parts of NSW, as a matter of urgency, writes to the Premier of New South Wales, the Hon Morris Iemma, stating it supports the call of concerned residents on the New South Wales Government, which appeared on page 13 of the Blue Mountains Gazette of 6 December, 2006, as follows:
“1. Undertake a thorough, independent review of the Grose Valley Fire, involving all stakeholders with particular attention to the following questions:
- Were fire detection and initial suppression timely and adequate?
- Were resources adequate, appropriate and supported?
- Were the adopted strategies the best available under the circumstances?
- Could other strategies of closer containment have offered lower risk to the community, better firefighter safety, higher probabilities of success, lower costs and less impact on the environment?
- Was existing knowledge and planning adequately utilised?
- Is fire management funded to the most effective way?
2. Ensure adequate funding is available for post-fire restoration, including the rehabilitation of environmental damage.
3. Fund more research to improve understanding of fire in the Blue Mountains landscape and methods for fire mitigation and suppression.
4. Improve research and training in strategies for controlling fires in large bushland areas.
5. Improve pre-fire planning to support decision-making during incidents.
6. Improve systems to ensure that local fire planning and expertise is fully utilised during incidents, and that the protection of the natural and cultural values of World Heritage areas and other bushland are fully considered.”
.
3. That the independent review includes addressing the questions raised by Blue Mountains Conservation Society:
a. The Blue Mountains City Council therefore supports the following adopted position of the Blue Mountains Conservation Society and would like the review to address the following questions:
i. In what circumstances are back burning from the “Northern Strategic Line” and the Bells Line of Road appropriate?
ii. What can be improved to ensure that lightning strikes or arson fires are contained as quickly as possible?
iii. What can be done to better manage fire risk in the Grose Valley in terms of preparation and suppression to minimise damage to people, property and biodiversity?
iv. What is needed to allow remote area fire teams to be able to work at night when conditions are more benign?
v. How can funding of bushfire management and suppression be changed to reduce overall costs to the community. (Federal funding of suppression under section 44 means funding for trail maintenance and planning is limited.)
.
b. If practicable, would the review also address the following?
i. The World Heritage Area contains a number of threatened species and ecological communities that, in addition to the direct threats associated with climate change, are particularly vulnerable to increased fire frequency and intensity.
ii. The effects on biodiversity of the fire regimes in the Grose Valley over the last 40 years, where there has been a succession of large intense wild fires without sufficient interval between them.
iii. Climate change predictions suggest a probability of more frequent and more intensive fire events, with significant implications for fire management and integrity of ecosystems.
iv. The Blue Mountains City Council also supports and requests involvement in the forum being organised by the Director of the Central Branch of the National Parks and Wildlife Service, Bob Conroy, on the 17 February 2007.
.
4. That the Council emphasises that the requested review should be of a scientific and technical nature.
.
5. That a copy of this letter be forwarded to the Minister for Emergency Services, the Hon Tony Kelly, the Member for the Blue Mountains, the Hon. Bob Debus, and the New South Wales Opposition Leader, Peter Debnam.
.
Upon being PUT to the Meeting, the MOTION was CARRIED, the voting being:
FOR:
- Fiona Creed (Liberal)
- Terri Hamilton (Independent)
- Pippa McInnes (Greens)
- Daniel Myles (Liberal)
- Kerrin O’Grady (Greens)
- Lyn Trindall (Blue Mountains First
.
AGAINST:
- Mayor Jim Angel (Labor)
- Kevin Frappell (Labor)
- Alison McLaren (Labor)
- Adam Searle (Labor)
- Chris Van der Kley (Liberal) and Chair of Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee
 The Hartley Vale backburn 20061115 escaped up Hartley Vale Road and over the Darling Causeway (above) toward the Grose Valley to the right
(Photo by Editor 20070204, free in pubic domain, click to enlarge) The Hartley Vale backburn 20061115 escaped up Hartley Vale Road and over the Darling Causeway (above) toward the Grose Valley to the right
(Photo by Editor 20070204, free in pubic domain, click to enlarge)
..
Editor’s Note:
Ahead of the Blue Mountains Council voting for the above motion, two Labor Councillors, Clr Chris Van der Kley (also Chair of the Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee) and Clr Kevin Frappell (Labor) moved an alternative motion, however it was lost upon voting. This proposed alternative motion was labelled an ‘amendment’ but it was significantly different in detail. The proposed amendment excluded calls for an independent review (per the first item in the original motion).
This proposed amendment also excluded asking the six key questions put by the concerned residents such as ‘Were fire detection and initial suppression timely and adequate?‘, ‘Is fire management funded to the most effective way?‘, etc.
This proposed amendment also excluded that part of Item 1 which recommended strategic improvements to bushfire management such as ‘Ensure adequate funding is available for post-fire restoration, including the rehabilitation of environmental damage‘ and ‘Fund more research to improve understanding of fire in the Blue Mountains landscape and methods for fire mitigation and suppression‘, etc.
This proposed amendment instead drew upon the view of the leadership of the Blue Mountains Conservation Society at the time that considered an independent enquiry would equate to criticism and assigning blame and so be politicised. This did however include advocating “an interagency and technical review process, to tease out the lessons learned.”
.
The Amendment (although lost in the Council voting) is important for the record and read as follows:
1. That the Blue Mountains City Council gratefully acknowledges the efforts of all the volunteers, professionals and agencies that worked together to control the recent Grose
Valley fire.
.
2. That the Blue Mountains City Council supports the recent position adopted by the Blue Mountains Conservation Society in relation to the Grose Valley fire in November
2006. We note and support the position of the Society when it says,
“The circumstances of the bushfire are complex and it is not in anyone’s interest for criticism or blame to be apportioned. However, there is much to be gained by looking at what was done and how it can be improved. The Society does not therefore support a large public inquiry and its attendant politicisation. Instead, the Society advocates an interagency and technical review process, to tease out the lessons learned.”
.
3. That the Blue Mountains City Council therefore supports the following adopted position of the Blue Mountains Conservation Society and would like the review to
address the following questions:
- In what circumstances are back burning from the “Northern Strategic Line” and the Bells Line of Road appropriate?
- What can be improved to ensure that lightning strikes or arson fires are contained as quickly as possible?
- What can be done to better manage fire risk in the Grose Valley in terms of preparation and suppression to minimise damage to people, property and biodiversity?
- What is needed to allow remote area fire teams to be able to work at night when conditions are more benign?
- How can funding of bushfire management and suppression be changed to reduce overall costs to the community. (Federal funding of suppression under Section 44 means funding for trail maintenance and planning is limited.)
.
If practicable, would the review also address the following?
- The World Heritage Area contains a number of threatened species and ecological communities that, in addition to the direct threats associated with climate change, are particularly vulnerable to increased fire frequency and intensity.
- The effects on biodiversity of the fire regimes in the Grose Valley over the last 40 years, where there has been a succession of large intense wild fires without
sufficient interval between them.
- Climate change predictions suggest a probability of more frequent and more intensive fire events, with significant implications for fire management and
integrity of ecosystems.
- That the Blue Mountains City Council also supports and requests involvement in the forum being organised by the Director of the Central Branch of the National Parks and Wildlife Service, Bob Conroy, on the 17 February 2007.
.
Upon being PUT to the Meeting, the AMENDMENT was LOST, the voting being:
FOR:
- Mayor Jim Angel (Labor)
- Kevin Frappell (Labor)
- Alison McLaren (Labor)
- Adam Searle (Labor)
- Chris Van der Kley (Liberal, and Chair of Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee)
.
AGAINST:
- Creed (Liberal)
- Hamilton (Independent)
- McInnes (Greens)
- Myles (Liberal)
- O’Grady (Greens)
- Trindall (Blue Mountains First)
.
[Source: Blue Mountains Council’s Ordinary Meeting, 20070130, Minute No. 7, File Ref. C01095. Subject: ‘Grose Valley Fire’, pp.15-16]
.
Editor’s Analysis:
.
- Similar failure by the RFS and the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) to muster all available necessary resources to suppress and extinguished both the Lawson’s Long Alley and Burra Korain Head fires, demonstrated that lessons from the 2003 Canberra Firestorm had not been learnt. Critical time was lost in the initial days of the ignitions at both to effectively suppress the fires while they were of a small size and weather conditions relatively favourable to enable suppression.
- The RFS strategy to apply excessive broadscale backburning on multiple fronts at at Hartley Vale, Blackheath and Bells Line of Road exacerbated the complexity and scale of both fires and in the most part contributed to the conflagration of all the fires down in the Grose Valley on 23rd November 2006
- The shortcoming of not mustering all necessary resources to suppress and extinguish bushfires, irrespective of whether a fire is immediately affecting property and homes or not, is flawed, negligent and only heightens the inherent risk of a bushfire escalating out of control. The risk of a bushfire escalation into uncontrollable firestorm is heightened as time allows for the prospect of worsening bushfire weather conditions – increased wind, wind gusts, wind direction, temperatures, and lowering humidity – contributory factors in both the respective Canberra and Grose Valley Fires. There is no indication that this operational culture has changed.
- That a bushfire is situated in inaccessible terrain is not an excuse for bushfire management not to muster all airborne and RAFT resources to suppress and extinguish it as soon as feasibly possible
- After local community realisation that the bushfire had overrun the Grose Valley including burning through the iconic Blue Gum Forest on 23rd November, an informal collection of local ‘concerned residents‘ formed numbering 143 and co-ordinated by Blue Mountains resident Ian Brown. By Wednesday 6th December, within days of the fire finally being suppressed (3rd Dec), this informal group had collectively paid for a full page letter in the Blue Mountains Gazette newspaper costing $2,131.40(page 13). The letter was entitled ‘Burning Issues – fire in the Grose Valley – A statement funded and supported by concerned residents‘. The context was that detailed in Council’s carried motion above.
- Blue Mountains Council’s response was simply a manifestation of the “supportive words and shallow promises” whom ACT Coroner Maria Doogan had cautioned in the Coroner’s Report into the 2003 Canberra Firestorm. No effective Council follow up to its supportive words was undertaken. Sure per Council’s carried motion, Council’s then acting General Manager, Dave Allen, sent off the letter with supportive words to the NSW Premier Morris Iemma, on 20th February 2007, but Council took no other review or enquiry action.
- In the Central Blue Mountains, there are three government agencies responsible for bushfire management – the New South Wales Rural Fires Service, the National Parks and Wildlife Service as part of the NSW Department of Environment (what ever its frequently changing title) and Blue Mountains Council. Collectively these three bodies have co-operated under the Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee, which was/is chaired by Blue Mountains Councillor Chris van der Kley.) and is responsible for planning in relating to bush fire prevention and coordinated bush fire fighting, as well as responsible for advising the Commissioner on bush fire prevention; mitigation and coordinated bush fire suppression. Included on the Committee is also the Commissioner of the RFS, and a nominated representative respectively from the NSW Fire Brigades, Forests NSW, NPWS, the Local Government Association of NSW, the Shires Association of NSW, the NSW Rural Fire Service Association, NSW Police, a nominee of the Minister for the Environment (then Bob Debus), a representative of the Nature Conservation Council of NSW, a person appointed by the Minister on the recommendation of the NSW Farmers Association, a representative of the Department of Community Services and a representative of the Department of Lands. In March 2008, the Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee (BMBFMC) staged a series of community workshops on the Plan’s review process. The Plan was approved on 14th December 2000 with a required review every five years. So by the Grose Valley Fire, the Plan was a year out of date and by March 2008 the Plan was three years out of date.
- It is not surprisingly that the above proposed amendment to the Council letter to the NSW Premier excluded calls for an independent review. Those who proposed the motion and who voted for it were either all Labor Party members or in the case of Liberal Councillor Chris Van Der Kley, Chair of the Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee who was operationally involved. An independent enquiry and the proposed strategic improvements to the bushfire management establishment would have likely revealed operational and government failings and recommended changes to the RFS structure, strategies, and management and importantly to its culture. The amendment was rejected anyway due to Labor having insufficient votes on Council.
- On Sunday 13th November 2006 two separate bushfire ignitions were believed to have been lit by lightning just west of the Grose Valley of the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area by the RFS. Following a back burn/hazard reduction burn that had got out of control up Hartley Vale Road and crossed the Darling Causeway, on Wednesday 15th November the RFS declared a formal escalation to a Section 44 bushfire emergency. This four day delay in detection and suppression is unexplained by the RFS.
- Despite the calls by the concerned residents (with Blue Mountains Council’s supportive words) for the ‘NSW Government to undertake a thorough, independent review of the Grose Valley Fire, involving all stakeholders, so such independent review was done.
- The local Labor member for the NSW Seat of Blue Mountains at the time and NSW Minister for the Environment was Bob Debus MP, who categorically refused requests for either an independent review or a public review into the management of the Grose Valley Fires.
- The Blue Mountains Conservation Society (BMCS) similarly rejected calls for a public enquiry, stating “the circumstances of the bushfire are complex and it is not in anyone’s interest for criticism or blame to be apportioned. However, there is much to be gained by looking at what was done and how it can be improved. The Society does not therefore support a large public inquiry and its attendant politicisation. Instead, the Society advocates an inter-agency and technical review process, to tease out the lessons learned.” It needs to be pointed out that key committee members of the BMCS were/are also active members of the RFS, which raises the issue of and actual or perceived conflict of interest.
- There were two reviews of sorts, none independent and none public.
- On Tuesday 19th December 2006 there was apparently an ‘Inter-Agency Review‘ which took place at Katoomba behind closed doors by members of bushfire management and operating personnel involved in the fire fighting. Despite requests by this Editor, no minutes or reports of that meeting were ever forthcoming. The meeting was internal and secret.
- On Saturday 17th February 2007, there was a ‘Grose Valley Fire Forum‘ held at Mount Tomah organised by Director of the Central Branch of the National Parks and Wildlife Service, Bob Conroy, and the Blue Mountains World Heritage Institute. Only selected participants were permitted to attend – mainly from the bushfire management, fire experts and selected members of the Blue Mountains Conservation Society. A copy of the report of that forum will be publicised on this website shortly.
- Following ongoing community concerns about the lack of transparency, no evidence of any lessons being learned from the Grose Valley Fires and even of a cover up into some of the operational decisions, in January 2007 Bob Debus MP announced a suggestion of there being an Environmental Summit to be staged in the Blue Mountains to provide the first public forum into important environmental issues affecting the Blue Mountains region, notably to discuss the Grose Valley Fire. Well, by the time the summit eventuated it was over a year later and held on the weekend of 23rd and 24th February 2008. By then Bob Debus had moved to federal politics (though still representing the Blue Mountains via the Seat of Macquarie. The summit was chaired by the RFS Commissioner responsible for the 2006 Grose Valley Fires, Philk Koperberg (now local Labor MP) and even the bushfire Incident Controller of the 2006 Grose Valley Fires, RFS Superintendent Mal Cronstedt, was in attendance. However, the summit was now called a conference and the agenda had expanded to many issues including Energy, Social Systems, Natural Systems and Water. Discussion about bushfire was restricted to a two hour workshop and so available time to the Grose Fire to one or two questions which copped only official spiel. It was a classic Labor tactic or stalling on accountability until the community gives up or forgets.
- Since 2006, the Blue Mountains community still doesn’t know whether in the 2006 Grose Valley Fire or currently:
- Fire detection and initial suppression was/is timely and adequate?
- Whether bushfire management resources were/are adequate, appropriate and supported?
- Whether in the Grose Valley Fire the adopted strategies were the best available under the circumstances?
- Whether other strategies of closer containment could have offered lower risk to the community
- Whether currently it has better firefighter safety, higher probabilities of success, lower costs and will cause less impact on the environment?
- Whether existing knowledge and planning is adequately utilised?
- Whether bushfire management is funded to the most effective way?
- Is adequate funding available for post-fire restoration, including the rehabilitation of environmental damage?
.
Another three years hence, in the Blue Mountains we have witnessed from afar the catastrophic Victorian ‘Black Saturday’ Bushfires of 7th February 2009.
.
Another three years hence in 2012, have we learnt anything?
.
Tags: 2003 Canberra Firestorm, Bliue Mountains Conservation Society, Blue Gum Forest, Blue Mountains Bush Fire Management Committee, Blue Mountains City Council, Blue Mountains National Park, broadscale backburning, Burra Korain Fire, Burra Korain Head, funding of bushfire management, Grose Valley Fire Forum, Grose Valley Fires 2006, Labor Government, Lawsons Long Alley Fire, McIntyre's Hut Fire, Northern Strategic Line, NSW Rural Fire Service, RFS, RFS Commissioner Phil Koperberg, RFS Superintendent Mal Cronstedt
Posted in Blue Mountains (AU), Threats from Bushfire | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
Tuesday, December 20th, 2011
 The Blue Gum Forest’s fire-scarred trees of December 2006
some of which have graced the Grose Valley in the Blue Mountains for hundreds of years.
Photo: Nick Moir (Source: Sydney Morning Herald, 20111211, Front Page) The Blue Gum Forest’s fire-scarred trees of December 2006
some of which have graced the Grose Valley in the Blue Mountains for hundreds of years.
Photo: Nick Moir (Source: Sydney Morning Herald, 20111211, Front Page)
.
The following articles are drawn from those by Gregg Borschmann, the first of which hit the front page of the Sydney Morning Herald on Monday 11th December 2006, following the massive bushfire conflagration that coalesced in the Grose Valley on 23rd November 2006.
From the community’s perspective, no noticeable lessons have been since learned by the Rural Fire Service (RFS) responsible. The prevailing bushfire management culture is that unless private property is directly, bushland is not valued and so not defended from bushfire. Indeed the approach is to let a bushfire burn as a defacto hazard reduction, so long as it doesn’t threaten human life or property. The RFS does not consider bushland an asset worth protecting from bushfire no matter what its conservation value, so with such a mindset such an ecological tragedy could well happen again.
.
‘The ghosts of an enchanted forest demand answers’
.
[Source: ^http://www.smh.com.au/news/national/the-ghosts-of-an-enchanted-forest-demand-answers/2006/12/10/1165685553891.html]
.
‘More than seventy years ago this forest inspired the birth of the modern Australian conservation movement. Today Blue Gum Forest stands forlorn in a bed of ash. But was it unnecessarily sacrificed because of aggressive control burning by firefighters focused on protecting people and property? That is the tough question being asked by scientists, fire experts and heritage managers as a result of the blaze in the Grose Valley of the upper Blue Mountains last month.
As the fate of the forest hangs in the balance, the State Government is facing demands for an independent review of the blaze amid claims it was made worse by control burning and inappropriate resources.
This comes against a backdrop of renewed warnings that Australia may be on the brink of a wave of species loss caused by climate change and more frequent and hotter fires. There are also claims that alternative “ecological” approaches to remote-area firefighting are underfunded and not taken seriously.
In an investigation of the Blue Mountains fires the Herald has spoken to experienced fire managers, fire experts and six senior sources in four agencies and uncovered numerous concerns and complaints.
- It was claimed that critical opportunities were lost in the first days to contain or extinguish the two original, separate fires.
- Evidence emerged that escaped backburns and spot fires meant the fires linked up and were made more dangerous to property and heritage assets – including the Blue Gum Forest. One manager said the townships of Hazelbrook, Woodford and Linden were a “bee’s dick” away from being burnt. Another described it as “our scariest moment”. Recognising the risk of the backburn strategy, one fire officer – before the lighting of a large backburn along the Bells Line of Road – publicly described that operation as “a big call”. It later escaped twice, advancing the fire down the Grose Valley.
- Concerns were voiced about the role of the NSW Rural Fire Service Commissioner, Phil Koperberg.
- Members of the upper Blue Mountains Rural Fire Service brigades were unhappy about the backburning strategy.
- There were doubts about the mix and sustainability of resources – several senior managers felt there were “too many trucks” and not enough skilled remote-area firefighters.
- Scientists, heritage managers and the public were angry that the region’s national and international heritage values were being compromised or ignored.
- There was anecdotal evidence that rare and even common species were being affected by the increased frequency and intensity of fires in the region.
- Annoyance was voiced over the environmental damage for hastily, poorly constructed fire trails and containment lines, and there were concerns about the bill for reconstruction of infrastructure, including walking tracks.

The fire manager and ecologist Nic Gellie, who was the fire management officer in the Blue Mountains for the NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service during the 1980s and ’90s, says the two original fires could have been put out with more rapid direct attack.
“Instead, backburning linked up the two fires and hugely enlarged the fire area … what we saw would be more accurately described as headfire burning, creating hot new fire fronts. While it protected the town of Blackheath, the plateau tops burnt intensely – and that created new problems both for management of the fire and the protection of biodiversity.
“When extreme fire weather, hot days and high winds arrived as predicted, the expanded fire zone was still not fully contained – and that was the cause of most of the high drama and danger that followed.”
In that dramatic week, Mr Gellie confronted Mr Koperberg with his concerns that the commissioner was interfering with the management of the fire by pushing hard for large backburns along the northern side of towns in the Blue Mountains from Mount Victoria to Faulconbridge, along what is known in firefighting circles as the “black line”.
The Herald has since confirmed from numerous senior sources that “overt and covert pressure” from head office was applied to the local incident management team responsible for fighting the fire.
There were also tensions relating to Mr Koperberg’s enthusiasm for continuation of the backburning strategy along the black line – even when milder weather, lower fuel levels and close-in containment were holding the fire.
Several sources say the most frightening threat to life and property came as the fire leapt onto the Lawson Ridge on “blow-up Wednesday” (November 22) – and that those spot fires almost certainly came from the collapse of the convection column associated with the intensification of the fire by the extensive backburns.
The Herald has also confirmed that
- The original fire lit by a lightning strike near Burra Korain Head inside the national park on Monday, November 13, could not be found on the first day. The following day, a remote area fire team had partly contained the fire – but was removed to fight the second fire. The original fire was left to burn unattended for the next couple of days;
- An escaped backburn was responsible for the most direct threat to houses during the two-week emergency, at Connaught Road in Blackheath. However, at a public meeting in Blackheath on Saturday night, the Rural Fire Service assistant commissioner Shane Fitzsimmons played down residents’ concerns about their lucky escape. “I don’t want to know about it. It’s incidental in the scheme of things.”
 Blackheath escarpment broadscale backburn – “incidental in the scheme of things“?
(Photo by Editor 20061209, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge) Blackheath escarpment broadscale backburn – “incidental in the scheme of things“?
(Photo by Editor 20061209, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge)
.
Mr Koperberg, who is retiring to stand as a Labor candidate in next year’s state elections, rejected the criticisms of how the fire was fought.
He told the Herald: “The whole of the Grose Valley would have been burnt if we had not intervened in the way we did and property would have been threatened or lost. We are looking at a successful rather than an unsuccessful outcome.
“It’s controversial, but this is world’s best backburning practice – often it’s the only tool available to save some of the country.”
The commissioner rejected any criticism that he had exerted too much influence. “As commissioner, the buck stops with me. I don’t influence outcomes unless there is a strategy that is so ill-considered that I have to intervene.”
Mr Koperberg said it was “indisputable and irrefutable” that the Blue Mountains fire – similar to fires burning now in Victoria – was “unlike any that has been seen since European settlement”, because drought and the weather produced erratic and unpredictable fire behaviour.
.
 Phil Koperberg
NSW Rural Fire Service Commissioner at the time of the Grose Fire Phil Koperberg
NSW Rural Fire Service Commissioner at the time of the Grose Fire
.
The district manager of the Blue Mountains for the Rural Fire Service, Superintendent Mal Cronstedt, was the incident controller for the fire.
Asked if he would do anything differently, Mr Cronstedt answered: “Probably.” But other strategies might have also had unknown or unpredictable consequences, he said.
Jack Tolhurst, the deputy fire control officer (operations) for the Blue Mountains, said: “I am adamant that this fire was managed very well. We didn’t lose any lives or property and only half the Grose Valley was burnt.”
Mr Tolhurst, who has 50 years’ experience in the Blue Mountains, said: “This fire is the most contrary fire we have ever dealt with up here.”
John Merson, the executive director of the Blue Mountains World Heritage Institute, said fire management was being complicated by conditions possibly associated with climate change.
“With increased fire frequency and intensity, we are looking at a fundamental change in Australian ecosystems,” he said. “We will lose species. But we don’t know what will prosper and what will replace those disappearing species. It’s not a happy state. It’s a very tough call for firefighters trying to do what they think is the right thing when the game is no longer the same.
“What we are seeing is a reflex response that may no longer be appropriate and doesn’t take account of all the values we are trying to protect.”
 Grose Valley incinerated 23rd November 2006
(Photo by Editor 20061209, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge) Grose Valley incinerated 23rd November 2006
(Photo by Editor 20061209, free in public domain, click photo to enlarge)
..
‘The burning question’
.
[Source: ^http://www.smh.com.au/news/national/the-burning-question/2006/12/10/1165685553945.html]
.
‘A bushfire scars a precious forest – and sparks debate on how we fight fire in the era of climate change.
.
“Snow and sleet are falling on two bushfires burning in the Blue Mountains west of Sydney.” ~ ABC Radio, November 15 (2006).
The news report was almost flippant, something that could happen only in Dorothea Mackellar’s land of drought and flooding rains. Later that evening, two weeks from summer, Sydney had its coldest night in more than a century.
Over the past month – as an early summer collided with a late winter and a decade-long drought – NSW and Victoria have battled more than 100 bushfires. But of them all, last month’s Blue Mountains blaze reveals tensions and systemic problems that point to a looming crisis as bushfire fighters struggle to protect people, property, biodiversity and heritage values in a world beset by climate change.
The tensions have always been there – different cultures, different ways of imagining and managing the landscape. Perhaps they are illustrated by a joke told by two Rural Fire Service crew in the Blue Mountains. “How does the RFS put out a fire in your kitchen? By backburning your sitting room and library.” The joke barely disguises the clash between the imperative of saving lives and homes, and the desire to look after the land, and the biodiversity that underpins our social and economic lives.
For fire managers, whose first priority will always be saving people and property, the equation has become even more tortured with a series of class actions over fires in NSW and the ACT. As one observer put it: “These guys are in a position where they’re not going to take any chances. No one will ever sue over environmental damage.”

For bushfire management the debate tentatively started a couple of decades ago. The challenge was to do what poets, writers and painters have long grappled with – coming to terms with a country whose distinctiveness and recent evolutionary history have been forged in fire. Drought and climate change now promise to catapult that debate to centre stage.
It is perhaps no accident that such a defining fire has occurred in one of the great amphitheatres of the Australian story, the Grose Valley in the upper Blue Mountains. Charles Darwin passed by on horseback in 1836, and described the valley as “stupendous … magnificent”.
The Grose has long been a microcosm of how Australians see their country. In 1859 some of the first photos in Australia were taken in the valley. Proposals for rail lines and dams were forgotten or shelved. The first great forest conservation battle was fought and won there in 1931-32.
But now the valley is under threat from an old friend and foe – fire.
Ian Brown has worked on dozens of fires in the Blue Mountains. He is a former operations manager for the National Parks and Wildlife Service.
“All fires are complex and difficult, and this sure was a nasty fire … But we need lots of tools in the shed. Those hairy, big backburns on exposed ridges so close to a blow-up day with bad weather surprised me. Frightened me even.”
For Brown, even more worrying is the trend.
“Parts of the Grose have now burnt three times in 13 years and four times in 24 years. Most of those fires started from arson or accident. Many of the species and plant communities can’t survive that sort of hammering.”
Ross Bradstock, a fire ecologist, agrees. Professor Bradstock is the director of the new Centre for the Environmental Risk Management of Bushfires at the University of Wollongong, which is funded by the Department of Environment and Conservation and the Rural Fire Service. He says Australia stands out as one of the countries whose vegetation may be most affected by climate change.
Bradstock says that in south-eastern Australia the potential for shifts in fire frequency and intensity are “very high … If we’re going to have more drought we will have more big fires.”
But the story is complicated and compounded by the interaction between drought and fire. The plants most resistant to fire, most able to bounce back after burning, will be most affected by climate change. And the plants that are going to be advantaged by aridity will be knocked over by increased fire frequency. “In general, the flora is going to get whacked from both ends – it’s going to be hit by increased fire and climate change. It’s not looking good.”
.
Wyn Jones, an ecologist who worked for the wildlife service, says the extremely rare drumstick plant, Isopogon fletcheri, is a good example. There are thought to be no more than 200 specimens, restricted to the upper Grose. Last week, on a walk down into the Blue Gum Forest, Jones found three – all killed by the fire.
.
The NSW Rural Fire Service Commissioner, Phil Koperberg, has been a keen supporter of Bradstock’s centre. Asked if he agreed with the argument that the Grose had seen too much fire, Mr Koperberg replied: “It’s not a comment I disagree with, but had we not intervened in the way we did, the entire Grose Valley would have been burnt again, not half of it.”
The great irony of the fire is that it was better weather, low fuels and close-in containment firefighting that eventually stopped the fire – not big backburns.
Remote area firefighting techniques have been pioneered and perfected over recent decades by the wildlife service. In 2003 a federal select committee on bushfires supported the approach. It recommended fire authorities and public land managers implement principles of fire prevention and “rapid and effective initial attack”.
Nic Gellie, a fire ecologist and former fire manager, has helped the wildlife service pioneer ecological fire management. The models are there – but he says they have not been used often enough or properly.
Doubts have been expressed about the sustainability of the current remote area firefighting model. It is underfunded, and relies on a mix of paid parks service staff and fire service volunteers. Most agree the model is a good one, but not viable during a longer bushfire relying on volunteers.
The Sydney Catchment Authority pays $1 million for Catchment Remote Area Firefighting Teams in the Warragamba water supply area. It has always seemed like a lot of money. But it looks like a bargain stacked against the estimated cost of $10 million for the direct costs and rehabilitation of the Grose fire.
Curiously, one unexpected outcome of the great Grose fire may be that the valley sees more regular, planned fire – something the former wildlife service manager Ian Brown is considering.
“If climate change means that the Grose is going to get blasted every 12 years or less, then we need more than just the backburning strategy. We need to get better at initial attack and maybe also look at more planned burns before these crises. But actually getting those burns done – and done right – that’s the real challenge.”
It may be the only hope for Isopogon fletcheri.
 Fletcher’s Drumstricks (Isopogon fletcheri)
http://www.anbg.gov.au Fletcher’s Drumstricks (Isopogon fletcheri)
http://www.anbg.gov.au
.
. Distribution of Isopogon fletcheri is restricted to a very small area in the Blackheath district of the Blue Mountains.
Given restricted distribution, it is susceptible to local extinction due to environmental and demographic uncertainty and in particular pathogens such as Phytophthora cinnamomi. Distribution of Isopogon fletcheri is restricted to a very small area in the Blackheath district of the Blue Mountains.
Given restricted distribution, it is susceptible to local extinction due to environmental and demographic uncertainty and in particular pathogens such as Phytophthora cinnamomi.
What needs to be done to recover this species? Continued habitat protection.
http://www.threatenedspecies.environment.nsw.gov.au/tsprofile/profile.aspx?id=10440
.
.
What price now?
.
[Source: ^ http://www.smh.com.au/news/national/what-price-now/2006/12/10/1165685553948.html?page=2]
.
The Blue Gum Forest stands tall, straight and surreal in a fire-ground of still smouldering ash. Three weeks ago it was intensely burnt during bushfires in the Grose Valley. The future of the iconic forest – some trees are thought to be 200 to 300 years old – now hangs in the balance.
Last week the massive white-trunked blue gums were dropping their scorched leaves to reveal a stark and unrecognisable forest of tall trunks, bare limbs and fallen logs.
The director of the Colong Foundation for Wilderness, Keith Muir, did not speak out during the fires, but now he wants answers.
.
-
“Could the Blue Gum have been saved using other firefighting strategies that also protected life and property?
-
Was the fire that burnt this very special forest made more intense, unpredictable and extensive by massive backburning operations?
-
Was the Blue Gum sacrificed for the sake of a de facto fuel reduction exercise that didn’t consider heritage values?
-
We need answers. We need an independent inquiry. This is too important to happen again.”
.
In the early 1930s the Herald supported a campaign by bushwalkers to save the Blue Gum from grazing and agricultural development. It was the first successful Australian conservation campaign to protect an almost pure stand of tall mountain blue gum ( Eucalyptus deanei) on about 40 hectares of river flats in the rugged Grose Valley of the upper Blue Mountains. The bushwalkers raised £130 to buy the lease covering the forest and create the Blue Gum Forest Reserve.
The Herald visited the Blue Gum Forest again last week with a forest ecologist, Wyn Jones, and Ian Brown, former National Parks and Wildlife Service operations manager with overall responsibility for fire management. In 1994 Jones, then an ecologist with the service, helped to describe scientifically the rare and newly discovered Wollemi pine. He first saw the Blue Gum Forest more than 40 years ago. He has been involved with it professionally and as a bushwalker ever since.
He said the forest would re-shoot and regrow, but it remains to be seen when and how. He predicted its immediate future would be decided over the next six months. That would depend largely on the vagaries of climate. Severe wind storms, a hot dry summer or even persistent rain, fungal growth and insect attack could all compromise the forest’s ability to bounce back quickly.
More uncertain and potentially bleak is the long-term prognosis. Jones said changing fire regimes caused by humans could be further complicated by climate change, a recipe for more frequent and hotter fires.
The Blue Gum Forest has been burnt four or five times in less than 50 years: by wildfire in 1957, possibly 1968, and in 1982, 1994 and 2006.
“Without human interference , this forest may have been burnt once or perhaps twice in 50 years, not five times,” Jones said.
Jones is convinced cracks in majestic gums were caused by the fire. If they are deep enough to effectively ringbark the surviving trees, then the demise of the forest promises to be a slow and painful affair.
“The old Blue Gum Forest is gone,” he said. “We don’t know what the Blue Gum of the future will look like. We could be heading for strange and very different days.”
===========
‘Friends of the giants’
.
In 1931 the Herald’s conservation reporter, J.G. Lockley, writing under the name Redgum, led a campaign to save the Blue Gum Forest.

“To destroy the trees would be unforgivable vandalism .. if they are permitted to stay, they will stand straight and true for many generations … Every acre on which those grey gums are growing should be reserved for the distant days, when the nation will know the true worth of the giant trees, which are not understood.”
.
‘Blue Gum Lessons’
.
(Editor’s letter in the Blue Mountains Gazette, 20061220)
.
‘One of our most precious natural heritage assets, the Blue Gum Forest, has been allowed to be scorched by bushfire. This demands an independent enquiry into current fire fighting practices to ensure such a tragedy is not repeated.
Not a witch hunt, but what is needed is a constructive revision into improving bushfire fighting methods incorporating current research into the issue. The intensity and frequency of bushfires have become more prevalent due to disturbances by man, including climate change.
An enquiry should consider the assets worth saving; not just lives, homes and property but natural assets of the World Heritage Area. Fire fighting methods should seek to protect all these values. It seems back-burning, however well-intentioned, burnt out the Blue Gum. This is unacceptable. What went wrong? The future survival of our forests depends on how we manage fire.’
.

A Grose Valley Fire Forum was held at Mount Tomah on Saturday 17th February 2007, but the public were denied entry.
An independent enquiry was never conducted. A public enquiry was never conducted.
.
Tags: backburns, Blackheath, Blue Gum Forest, Blue Mountains, Blue Mountains World Heritage Area, broadscale backburning, ecological values, forest values, Grose Valley, Grose Valley Fires 2006, Isopogon fletcheri, Mal Cronstedt, old growth, Phil Koperberg, RFS, Rural Fire Service
Posted in Blue Mountains (AU), Threats from Bushfire | No Comments »
Add this post to Del.icio.us - Digg
|
|
 Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Click image to enlarge
Inscribed on the asset register of World Heritage sites in 1994…but how much has been wiped out by October’s bushfires?
[Photo Source: New South Wales Government,
^http://www.nationalparks.nsw.gov.au/oxley-wild-rivers-national-park/travel-info]
Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Click image to enlarge
Inscribed on the asset register of World Heritage sites in 1994…but how much has been wiped out by October’s bushfires?
[Photo Source: New South Wales Government,
^http://www.nationalparks.nsw.gov.au/oxley-wild-rivers-national-park/travel-info]
 Location of Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Click image to enlarge – note the patchy dark green of remnant forests
Location of Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Click image to enlarge – note the patchy dark green of remnant forests Macleay River Bushfire October 2012
– left to burn for a week from 12th Oct 2012 because not a threat to private property
..then the wind picked up…unbelievable!
Macleay River Bushfire October 2012
– left to burn for a week from 12th Oct 2012 because not a threat to private property
..then the wind picked up…unbelievable!
 Putting this 60,000ha bushfire into a Sydney urban perspective
Professional urban fire fighting would not allow 60,000 hectares of private property and human lives to burn
– such would historically dwarf the Great Fire of London.
Putting this 60,000ha bushfire into a Sydney urban perspective
Professional urban fire fighting would not allow 60,000 hectares of private property and human lives to burn
– such would historically dwarf the Great Fire of London.
 Satellite infrared image of the fire called Georges Junction inside the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Having already burnt out a massive 14,000 hectares and is likely to join up with the Freds Creek fire.
The active edge of the fire shows up bright yellow; the red areas are the burnt areas.
(Photo by New England RFS)
Satellite infrared image of the fire called Georges Junction inside the Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Having already burnt out a massive 14,000 hectares and is likely to join up with the Freds Creek fire.
The active edge of the fire shows up bright yellow; the red areas are the burnt areas.
(Photo by New England RFS)
 Properties between Georges Junction and Five Day Creek were at threat from fire yesterday
(Photo: The Armidale Express)
Properties between Georges Junction and Five Day Creek were at threat from fire yesterday
(Photo: The Armidale Express)

 Macleay River Bushfire
(Photo by Sean Bremmer)
Macleay River Bushfire
(Photo by Sean Bremmer)
 World Heritage Listing because local people thought it was so important to save before it was gone
World Heritage Listing because local people thought it was so important to save before it was gone Trying to save the surviving remnant patches of Gondwana Rainforest ecosystems
(Ed: These few green shades are emblematic of Australian ransacking)
Read: >Large Map
[Source: ^http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/gondwana/pubs/gondwana-map.pdf]
Trying to save the surviving remnant patches of Gondwana Rainforest ecosystems
(Ed: These few green shades are emblematic of Australian ransacking)
Read: >Large Map
[Source: ^http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/gondwana/pubs/gondwana-map.pdf]
 Enormous Antarctic Beech (Nothofagus moorei)
At Cobark Park, Barrington Tops, 50 metres tall
Enormous Antarctic Beech (Nothofagus moorei)
At Cobark Park, Barrington Tops, 50 metres tall
 Hoop Pine
(Araucaria cunninghamii)
Found naturally in the dry rainforests of New South Wales and Queensland and in Papua New Guinea.
The trees can live up to 450 years and grow to a height of 60 m.
Hoop Pine
(Araucaria cunninghamii)
Found naturally in the dry rainforests of New South Wales and Queensland and in Papua New Guinea.
The trees can live up to 450 years and grow to a height of 60 m.
 Parma Wallaby (Macropus parma)
Endemic to rainforests and sclerophyll forests in New South Wales from the Watagan Mountains in the South to the Gibraltar Range in the North.
Parma wallabies were thought to have become extinct a century ago until being discovered again in the 1970s.
Parma Wallaby (Macropus parma)
Endemic to rainforests and sclerophyll forests in New South Wales from the Watagan Mountains in the South to the Gibraltar Range in the North.
Parma wallabies were thought to have become extinct a century ago until being discovered again in the 1970s.
 OxleyWild Rivers National Park – location map
[Source: Google Maps]
.
OxleyWild Rivers National Park – location map
[Source: Google Maps]
.
 Aspley Falls in flood
Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
Aspley Falls in flood
Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
 Australian Red Cedar Forest
Tamborine National Park, Gold Coast Hinterland, Queensland
(such trees have long been logged through the Oxley Rivers region)
Australian Red Cedar Forest
Tamborine National Park, Gold Coast Hinterland, Queensland
(such trees have long been logged through the Oxley Rivers region)
 Brush-tailed Rock Wallaby (Petrogale penicillata) in Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
This species is listed in New South Wales as ‘Vulnerable to extinction’, but that was by the NSW Scientific Committee in 2003, nine years ago
There have been two major bushfires through since then – one in 2009 and now in 2012
How many viable individuals have been lost to the Macleay River Bushfire – does the NSW NPWS know or care?
Brush-tailed Rock Wallaby (Petrogale penicillata) in Oxley Wild Rivers National Park
This species is listed in New South Wales as ‘Vulnerable to extinction’, but that was by the NSW Scientific Committee in 2003, nine years ago
There have been two major bushfires through since then – one in 2009 and now in 2012
How many viable individuals have been lost to the Macleay River Bushfire – does the NSW NPWS know or care?
 Brush-tailed Phascogale
[Source: Animal Hospital, ^http://www.chidlowmarsupialhospital.org.au/page-17-1-identification.html]
Brush-tailed Phascogale
[Source: Animal Hospital, ^http://www.chidlowmarsupialhospital.org.au/page-17-1-identification.html]